Progress check #3: Unit 4
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
Chemical Equation for cellular respiration
C6H12O6 + 6O2→6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP + HEAT
1 glucose and 6 oxygen react to produce 6 carbon dioxide and 6 water and ATP and heat.
Which reactant is oxidized, which is reduced?
Glucose is oxidized and Oxygen is reduced.
Why is cellular respiration an exergonic process?
It releases energy as a product, which comes from the breakdown of glucose releasing stored energy.
What happens to the energy stored in glucose that is not converted into ATP?
It is released as heat.
Structure of the mitochondria
Has a double membrane, that is smooth. Inner membrane is folded into cristae, which is important because it increases surface area. The presence of the inner membrane creates two different compartments, inter membrane space and matrix.
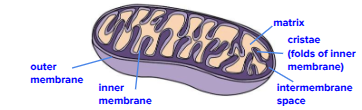
How do the folds of the inner membrane and the resulting membrane-bound spaces facilitate cellular respiration?
The fold increases the surface area of the inner membrane significantly. All three areas contribute to the four stages of cellular respiration, especially with the Electron Transport Chain.
What are the four stages of cellular respiration? Add diagram
Glycolysis, [Pyruvate Oxidation into Acetyl CoA and the Citric Acid (Krebs) Cycle], Oxidative Phosphorylation (Electron transport and chemiosmosis).
![<p>Glycolysis, [Pyruvate Oxidation into Acetyl CoA and the Citric Acid (Krebs) Cycle], Oxidative Phosphorylation (Electron transport and chemiosmosis).</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/b746b104-d27f-49d5-86a5-d95322765a26.png)
Glycolysis (inputs, outputs, where)
Oxidation of glucose
Glucose and NAD+
Pyruvate and NADH and ATP
Cytososl/Cytoplasm
Pyruvate Oxidation
Mitochondria (Matrix)
Pyruvate and NAD+
Acetyl coA, CO2 and NADH NO ATP
The citric acid (Krebs) cycle (inputs, outputs, where)
Mitochondria (Matrix)
Acetyl coA, NAD+ and FAD
CO2, NADH and FADH2 and 2 ATP
Oxidative phosphorylation (inputs, outputs, where)
Inner membrane of the mitochondria, but also the Matrix.
NADH, FADH2 and O2
NAD+, FAD, and H2O and 28-32 ATP
Role of NADH in aerobic cellular respiration
NAD+ is an electron accepter, and turns into NADH, an electron carrier. It brings electrons from the first two cycles to the electron transport chain, where they then reduce oxygen (oxidizing NADH and FADH2) to form water.
Role of FADH2 in aerobic cellular respiration
FAD is an electron accepter, and turns into FADH2, an electron carrier. It brings electrons from the first two cycles to the electron transport chain, where they then reduce oxygen (oxidizing NADH and FADH2) to form water.
Role of oxygen in aerobic cellular respiration
It is the final electron accepter in the electron transport chain, pulling electrons through the chain, driving ATP production.
Why is oxygen the driving force behind aerobic cellular respiration.
Because it pulls the electrons through the transport chain, which causes them to lose energy, where that energy powers protein pumps pumping hydrogen into the intermembrane space, allowing it to interact with ATP synthase, power ATP production. Without oxygen the process would not be able to occur.
Compare and contrast the conditions and efficiency of aerobic cellular respiration with fermentation
Conditions:
ACR requires oxygen, fermentation does not (uses enzymes bacteria and yeast)
ACR is much more efficient producing 28-32 ATP, while fermentation produces only 2 ATP.