Medical Abbreviations, Laboratory Values, and Disease Terminology
1/126
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
127 Terms
Cardiology
heart and blood vessels
Pulomonology
lungs and respiratory system
Nephrology/ Renal
kidneys
Urology
urinary tract, male reproductive system
Gastroenterology
digestive tract
Neurology
brain and nervous sytem
Psychiatry
mental health
Ophthalmology
eyes and vision
Otolaryngology (ENT)
ear, nose, throat, head, neck
Hematology
blood
Dermatology
Skin
Endocrinology
Hormones
Anesthesiology
Pain relief and anesthesia
Infectious disease
infections
Rheumatolofy
joints, muscles, connective tissue, autoimmune conditions
Orthopedics
bones, joints, ligaments, tendons, muscles
Oncology
cancer/ neoplasm
Obstetrics and gynecology (OBGYN)
female reproductive system, pregnancy and childbirth
Radiology
Imaging for diagnosis/ treatment
Pathology
Diagnosis by lab/ tissue biopsy
Family medicine
Patient of all ages
Internal medicine
Adult care
Pediatrics
Health of infants, children, adolescents
Neonatolofy
Pre-term or babies within 28 days of birth
Geriatics
Elderly patients
Inflammation of skin
dermatitis
Inflammation of kidney
nephritis, glomerulonephritis, pyelonephritis (infection)
Inflammation of liver
hepatitis
Inflammation of stomach
stomitis
Inflammation of pancreas
pancreatitis
Inflammation of colon
colitis
Inflammation of lungs
bronchitis (airway)
pneumonitis (lung tissue)
Inflammation of sinus
sinusitis
Inflammation of heart
myocarditis (muscle)
endocarditis (valves)
Inflammation of brain
encephalitis
PO
By mouth
IV
Intravenous
IM
Intramuscular
SC
Subcutaneous
SL
Sublingual
PR
Per rectum
TOP
Topical
INDH
Inhalation
ID
Intradermal
Qday
Every day
BID
Twice a day
TID
Three times a day
QID
Four times a day
PRN
As needed (WHAT IS IT FOR)
HS
At bedtime
AC
Before meals
PC
After meals
Q4C
Every 4 hours
Q6H
Every 6 hours
Q8H
Every 8 hours
Q12H
Every 12 hours
AAA
Apply to affected area (skin)
OU
Oculus uterque (BOTH eyes)
OS
Oculus sinister (LEFT eye)
OD
Oculus dexter (RIGHT eye)
AU
Auris uterque (BOTH ears)
AS
Auris sinister (LEFT ear)
AD
Auris dexter (RIGHT ear)
Prescription directions
drug name - dose - route - frequency - PRN indication
Etiology
The cause of the disease
Idiopathic
A disease of unknown cause
Iatrogenic
A disease caused by medical treatment
Nosocomical
A disease that is acquired in a hospital or healthcare facility
Risk Factor
Conditions of behaviors that increase the likelihood of developing a disease (BUT NOT CAUSE)
Pathogenesis
The biological mechanism/ process on HOW the disease developed
Pathophysiology
The changes in the body's physiology during or after the disease has developed
Signs
Abnormal features that the patient and/other people can notice (vomiting)
Symptoms
Abnormal features that commonly only the patient can notice (nausea, pain)
Clinical presentations
Signs and symptoms, laboratory, imaging, biopsy findings of a disease together
Complications
Other medical conditions that often (but not always) develop
Comorbidities
Other medical conditions that often co-exist with the first disease
Diagnosis
Identification of a disease based on clinical presentations and testing
Disease Course
The stags and profession of a disease
Prognosis
The likely course and outcome of a disease
Epidemiology
The study of how much and how often a disease is present in a population
Incidence
The number of new cases of a disease in a population
Prevalence
The total number of new AND existing cases of a disease in a population
Mortality
The rate of death of a population caused by disease
Morbidity
The rate of being ill/ have the disease of a population
Onset of a disease
How quickly does a disease occur or be detected
Duration of a disease
How long does the disease process last
Insidious onset
Disease onset that is gradual, subtle and often unnoticed
Acute disease
Disease with short duration, often with quick onset
Chronic disease
Disease with LONG duration, often with slow onset
Hyponatremia
low Na+
Hypernatremia
high Na+
Hypokalemia
low K+
Hyperkalemia
high K+
Hypochloremia
low Cl-
Hyperchloremia
high Cl-
Plasma
liquid, cell-free part of the blood that has been treated with anti-coagulants
Serum
the liquid part of blood AFTER coagulation, therefore devoid of clotting factors as fibrinogen
Agranulocytosis
lack of granulocytes, group of white blood cells
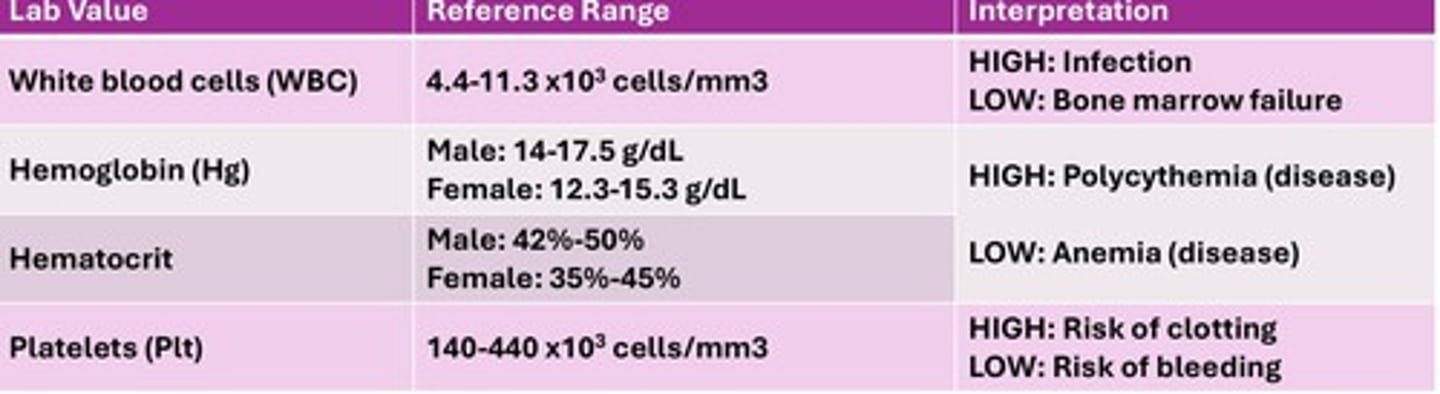
-emia
In blood
-oma
An abnormal mass, usually cancer (not always)