Earth Science: Energy Resources
5.0(1)Studied by 51 people
Card Sorting
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:21 PM on 10/23/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
1
New cards
Fossil Fuels
- fuels such as coal, oil and natural gas that form from the remains of plants and other organisms that were buried and altered over the years
2
New cards
Coal
- combustable black or brownish-black SEDIMENTARY ROCK usually occurring in rock strata in layers or veins called coal beds/coal seams
3
New cards
Coalification
• Diagnenesis
• Diagnenesis
- the formation of coal from plant material by the process of diagenesis & metamorphosis
• sedimentation of organic material
• sedimentation of organic material
4
New cards
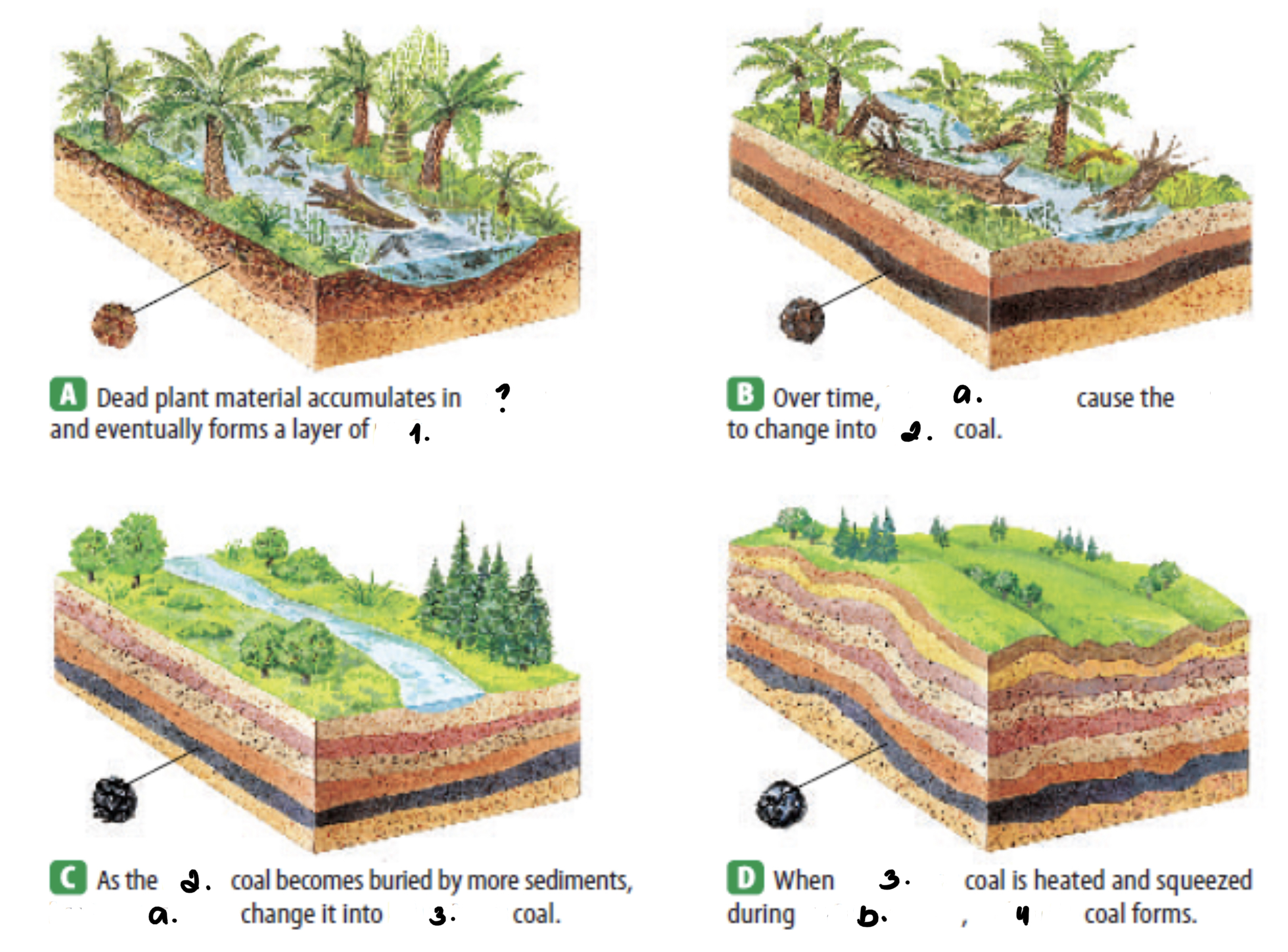
? Swamp
1. Peat
a. heat & pressure
2. lignite coal
3. bituminous coal
b. metamorphism
4. anthracite
1. Peat
a. heat & pressure
2. lignite coal
3. bituminous coal
b. metamorphism
4. anthracite
• Formation of Coal
5
New cards
Anthracite
• classification of coal depending on the amount of carbon
- 86% to 98% pure carbon and 8% to 3% volatile matter
- 86% to 98% pure carbon and 8% to 3% volatile matter
6
New cards
Bituminous coal
• classification of coal depending on the amount of carbon
- contains 70% to 86% carbon and 46% to 31% volatile matter
- contains 70% to 86% carbon and 46% to 31% volatile matter
7
New cards
Sub-bituminous coal
• classification of coal depending on the amount of carbon
- 70 to 76% carbon and 53 to 42% volatile matter
- 70 to 76% carbon and 53 to 42% volatile matter
8
New cards
Lignite coal
• classification of coal depending on the amount of carbon
- 65% to 70% carbon and 63% to 53% volatile matter
- 65% to 70% carbon and 63% to 53% volatile matter
9
New cards
Peat
• classification of coal depending on the amount of carbon
- consists of partially decomposed vegetation
- has carbon content of less than 60% and is composed entirely of volatile matter
- consists of partially decomposed vegetation
- has carbon content of less than 60% and is composed entirely of volatile matter
10
New cards
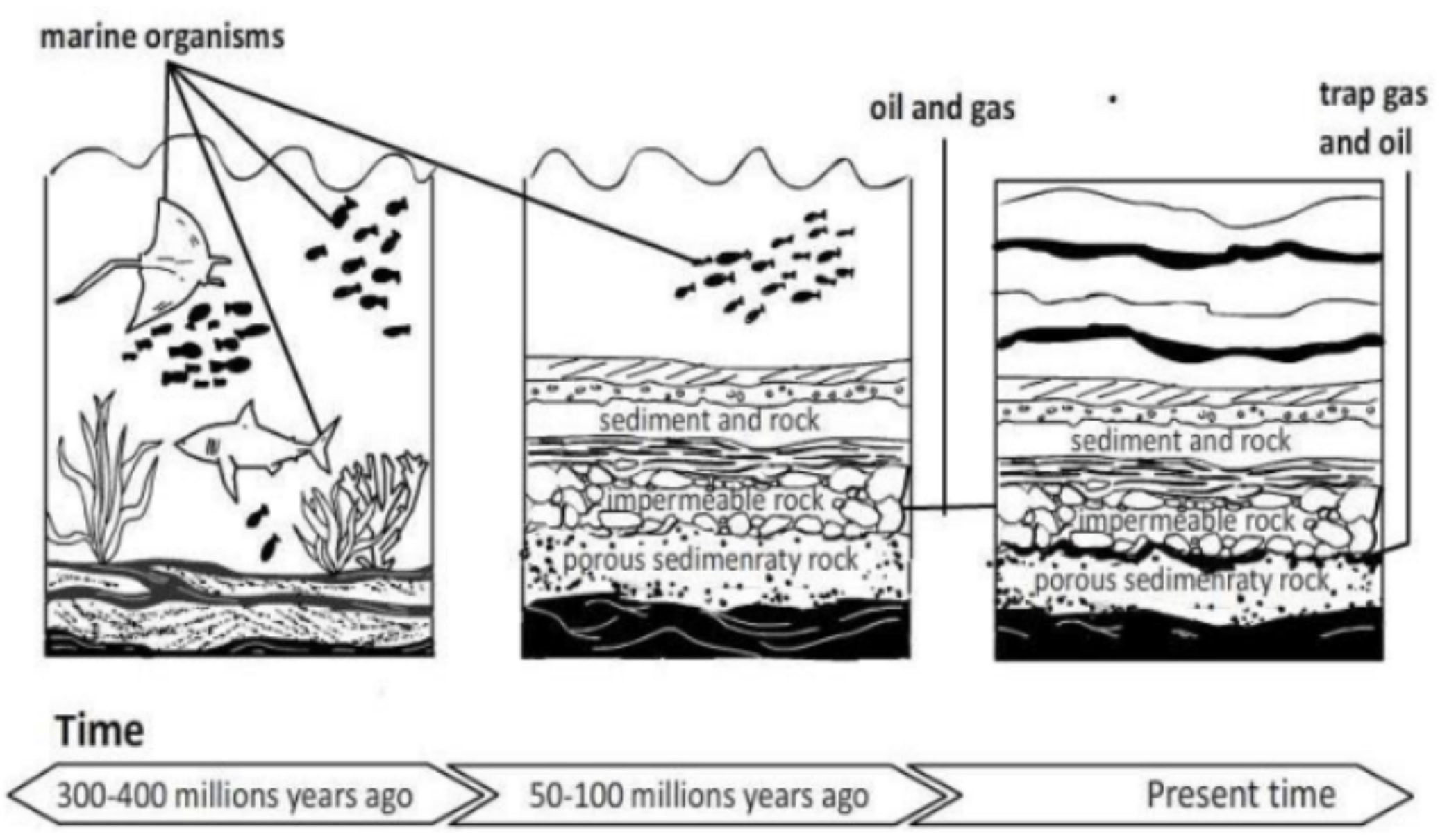
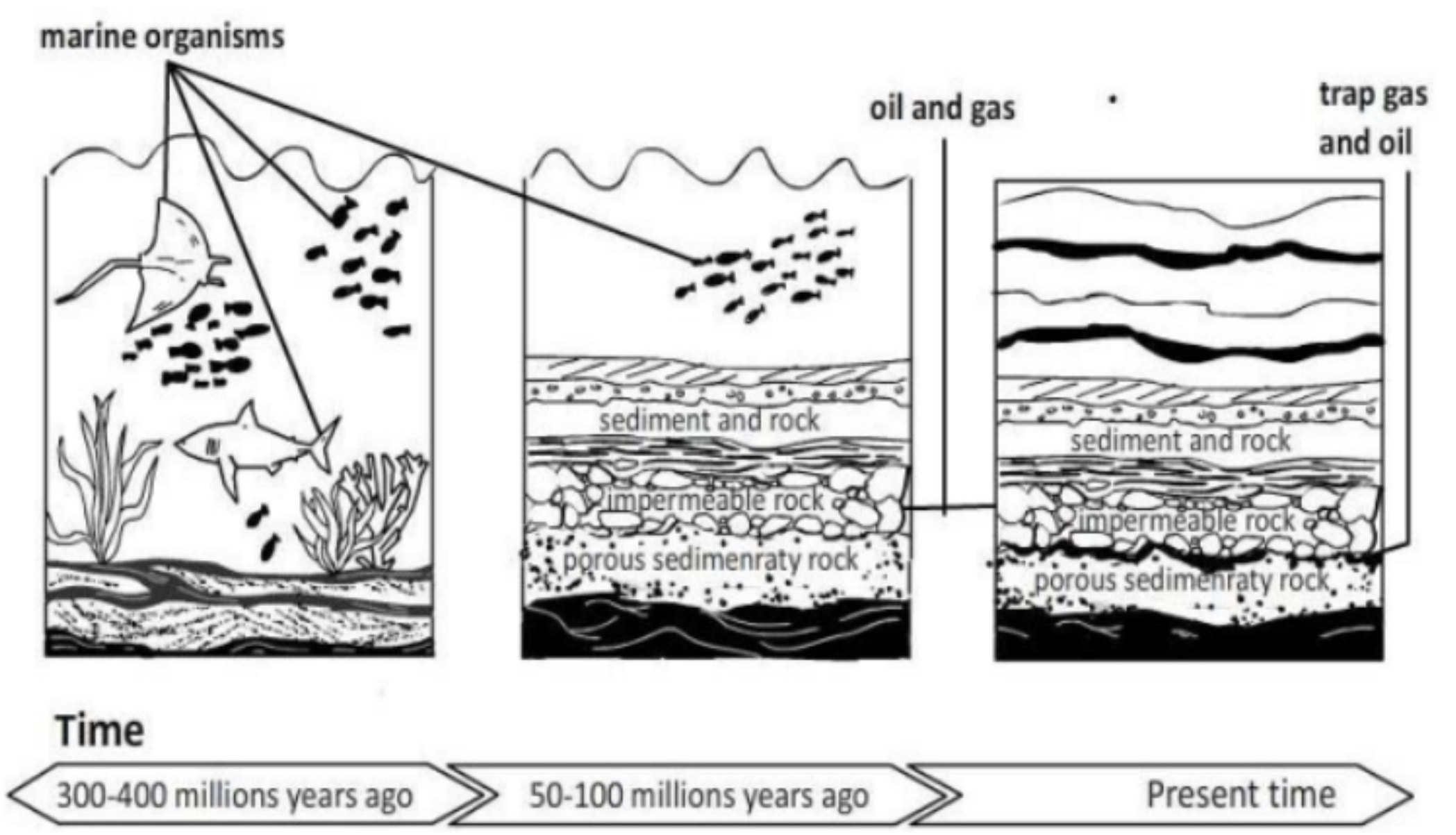
Oil
- an organic material, mostly algae, which was buried in mud at the bottom of the sea and lakes
- subjected to intense heat and pressure in a low oxygen environment
- extracted through a horsehead pump
- subjected to intense heat and pressure in a low oxygen environment
- extracted through a horsehead pump
11
New cards
Natural Gas
- a naturally occurring hydrocarbon gas with the mixture of methane
- odorless and colorless in its natural state
- subjected to intense heat and pressure in a low oxygen environment
- extracted through a horsehead pump
- odorless and colorless in its natural state
- subjected to intense heat and pressure in a low oxygen environment
- extracted through a horsehead pump
12
New cards
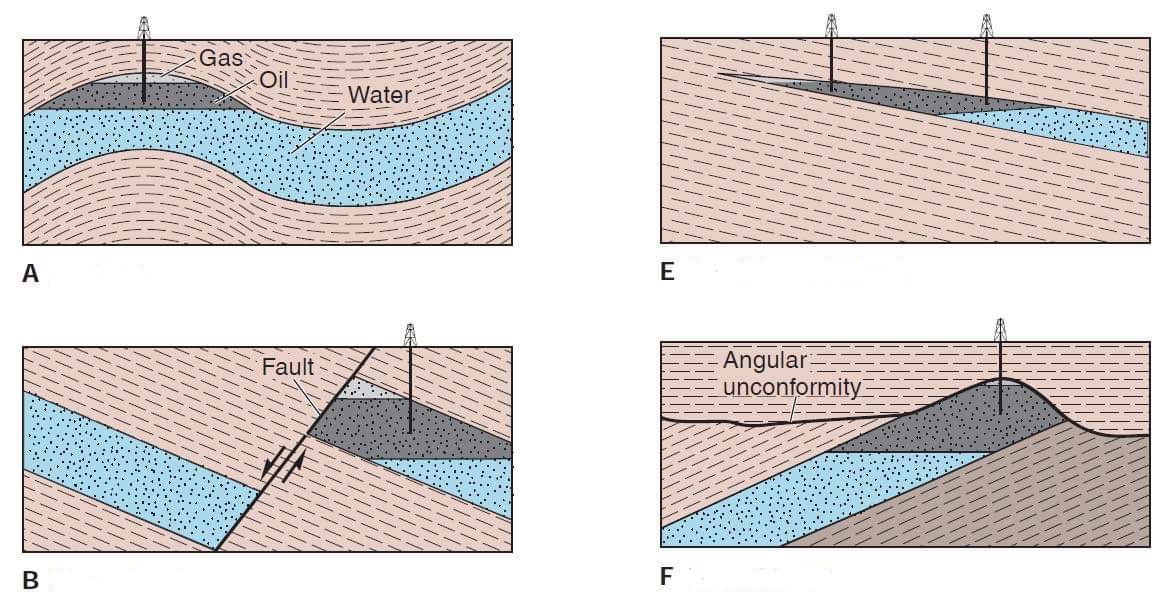
A. Anticline
B. Normal Fault
E. Sandstone pinchout
F. Unconformity
B. Normal Fault
E. Sandstone pinchout
F. Unconformity
• Identify the Areas of Traps
13
New cards
C. Thrust Fault
D. Sandstone lenses
G. Reef(a small “patch” reef)
H. Salt Dome
D. Sandstone lenses
G. Reef(a small “patch” reef)
H. Salt Dome
• Identify the Areas of Traps
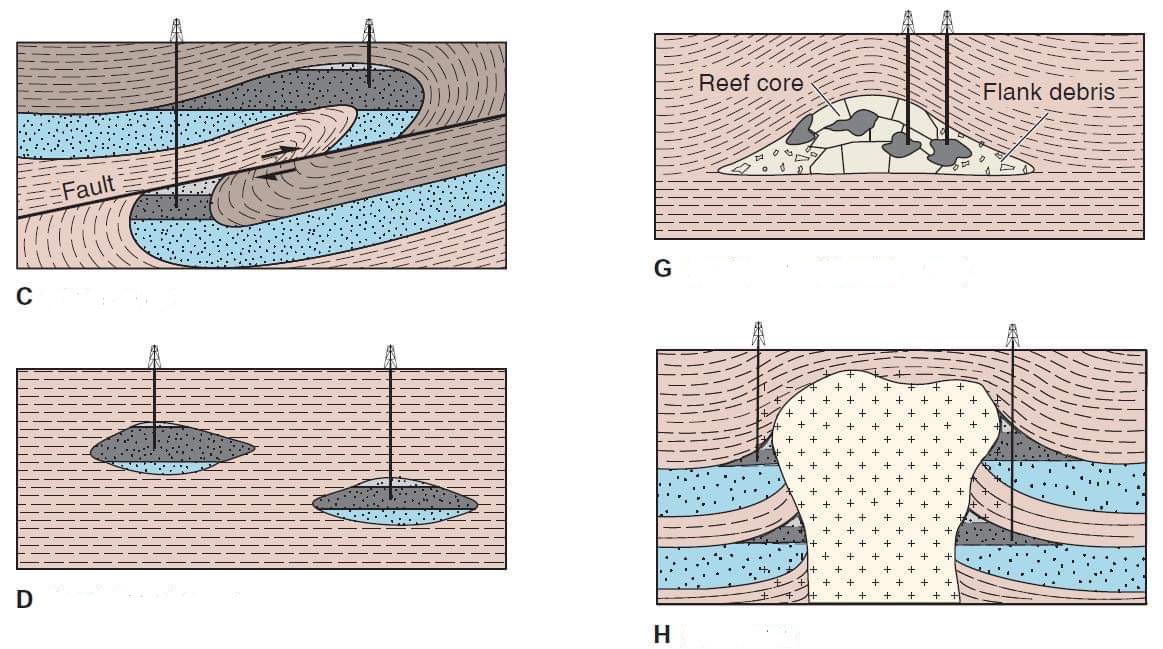
14
New cards
Solar, Wind, Hydroelectric, Biomass & Geothermal
• Renewable energy resources
15
New cards
Geothermal
- the heat from the Earth
- resources range from the shallow ground to hot water and ho9t rock found a few miles beneath the Earths surface and down deeper to the extremely high temperature of molten rock called magma
- resources range from the shallow ground to hot water and ho9t rock found a few miles beneath the Earths surface and down deeper to the extremely high temperature of molten rock called magma
16
New cards
? Geothermal Water
• Low Temperature
• Medium Temperature
• High Temperature
• Low Temperature
• Medium Temperature
• High Temperature
• Geothermal energy involves heated water used in generating electricity
Type of Geothermal Energy
- from 20 to 90 degrees Celsius
- from 90 to 160 degrees Celsius
- 160 degrees Celsius and above; found near volcanoes
Type of Geothermal Energy
- from 20 to 90 degrees Celsius
- from 90 to 160 degrees Celsius
- 160 degrees Celsius and above; found near volcanoes
17
New cards
Dry Steam Power Plant
• types of geothermal power plant
- hot steam from underground is piped directly into turbines, which powers the generator
- hot steam from underground is piped directly into turbines, which powers the generator
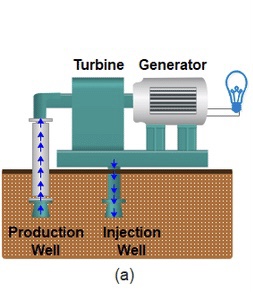
18
New cards
Flash Steam Power Plant
• types of geothermal power plant
- hot water from underground is pumped into a cooler temperature flash tank
- the sudden change in temperature creates steam which powers the generator
- hot water from underground is pumped into a cooler temperature flash tank
- the sudden change in temperature creates steam which powers the generator
19
New cards
Binary Cycle Power Plant
• types of geothermal power plant
- hot water from underground is pumped through a heat exchangers which heats a second liquid that transforms into steam
- hot water from underground is pumped through a heat exchangers which heats a second liquid that transforms into steam
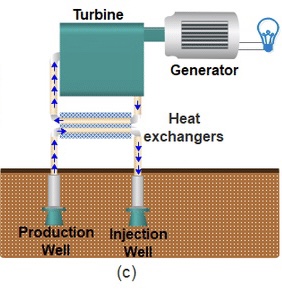
20
New cards
Open Loop System
• kind of geothermal heat pump
- water is taken directly from a source and into the heat pump
- it is then recycled back out into the same source
- water is taken directly from a source and into the heat pump
- it is then recycled back out into the same source
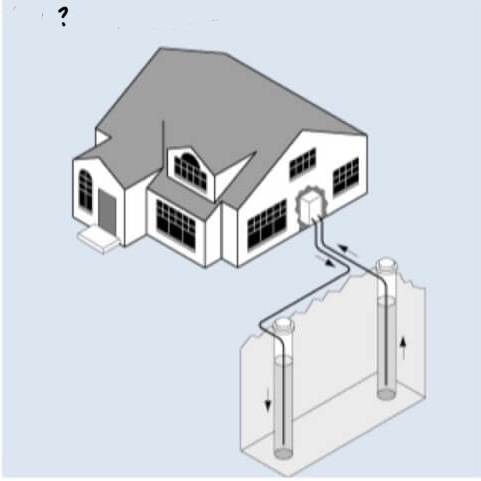
21
New cards
Closed Loop System
a. Horizontal
b. Vertical
c. Pond/Lake
a. Horizontal
b. Vertical
c. Pond/Lake
• kind of geothermal heat pump
- underground pipers circulate liquid that is heated or cooled by the earth
- the liquid is then transferred via an exchanger to heat or cool the structure
- underground pipers circulate liquid that is heated or cooled by the earth
- the liquid is then transferred via an exchanger to heat or cool the structure
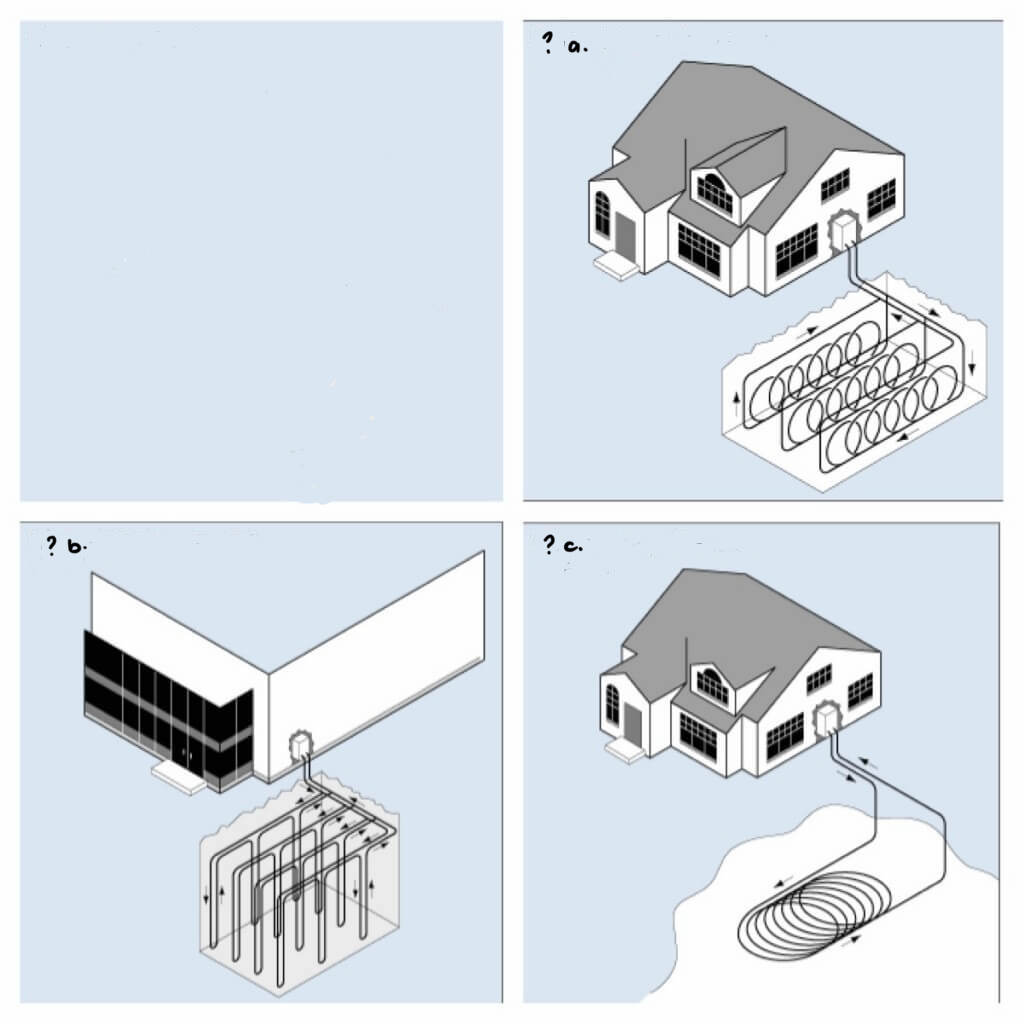
22
New cards
Dam
• main components of hydroelectric power plant
- creates a large waterfall and stores enough water to always supply the plant.
- helps regulate flooding
- creates a large waterfall and stores enough water to always supply the plant.
- helps regulate flooding
23
New cards
Penstock
• main components of hydroelectric power plant
- channels water from its natural environment(river or lake) to supply the dam reservoir
- may be an open channel, tunnel or pipeline
- channels water from its natural environment(river or lake) to supply the dam reservoir
- may be an open channel, tunnel or pipeline
24
New cards
Powerhouse
• main components of hydroelectric power plant
- houses the turbines driven by the waterfall and the generator driven by the turbines
- houses the turbines driven by the waterfall and the generator driven by the turbines
25
New cards
Diversion(Run-to-Run)
• type of hydropower power plant
- channels portion of river through penstock; generates power to meet daily need
- channels portion of river through penstock; generates power to meet daily need
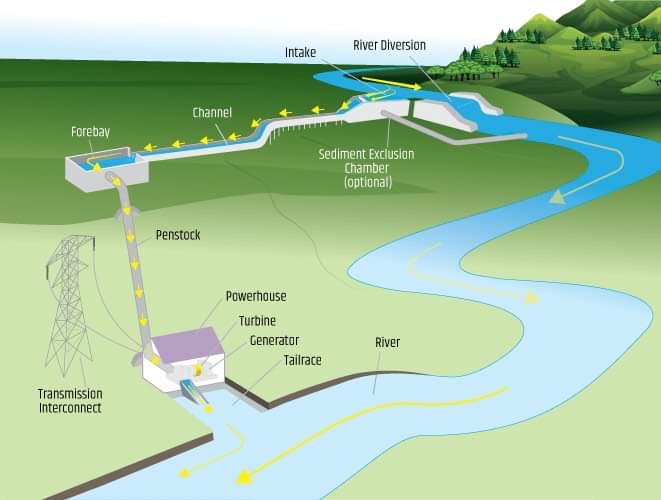
26
New cards
Impoundment
• type of hydropower power plant
- common type which streams reservoir from dam to penstock; used to meet changing demand in electricity
- common type which streams reservoir from dam to penstock; used to meet changing demand in electricity
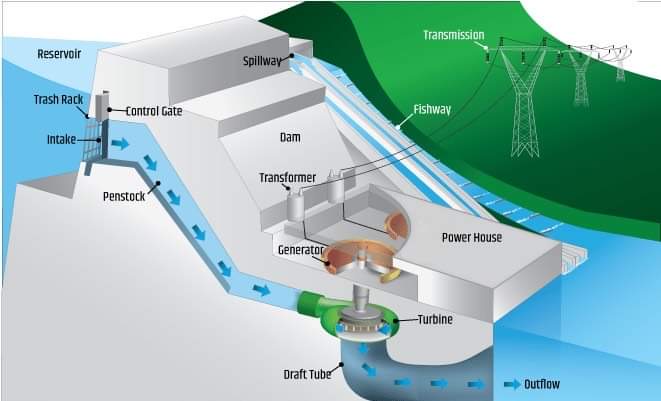
27
New cards
Pumped Storage
• type of hydropower power plant
- has 2 reservoirs of different elevation where it pumps up water from lower to higher reservoir when demand is low using other renewable energy, and releases water from higher to lower reservoir when there’s a peak in electricity demand
- has 2 reservoirs of different elevation where it pumps up water from lower to higher reservoir when demand is low using other renewable energy, and releases water from higher to lower reservoir when there’s a peak in electricity demand
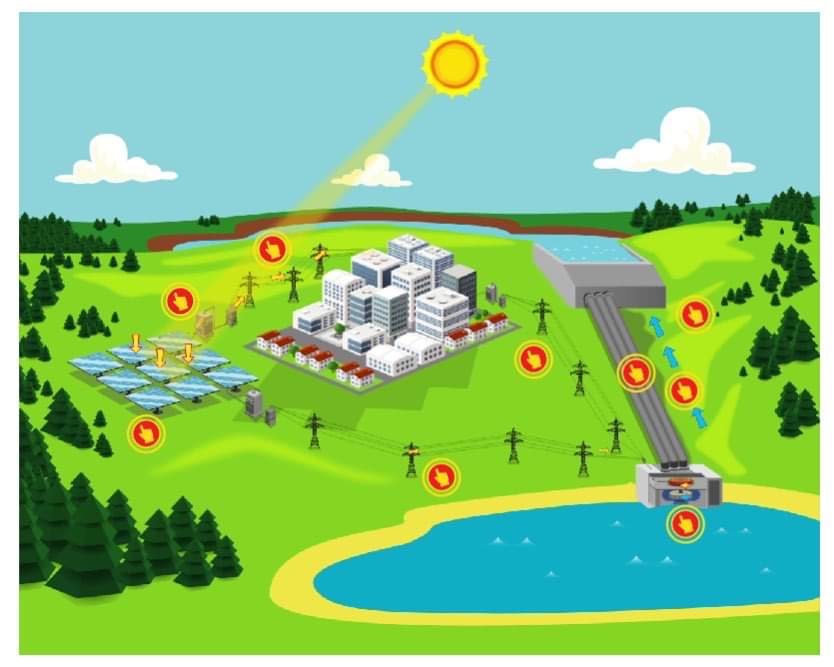
28
New cards
They have Fast flowing rivers and are mountainous
• why are some countries the biggest hydropower producers