Sociocultural Approach
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
individual/group - SIT
we don’t have 1 personal self, but several social selves corresponding to group memberships
each identity comes with associated concepts that guide our thoughts/feelings/behaviours
sense of self depends on which of p+s identities is salient (depends on context)
SIT predicts that when 1 s identity becomes salient it influences behaviour
mechanisms of forming SIT: social categorization → organising people into groups based on similar characteristics (+ ourselves) (creates ingroups vs. outgroups)
social identification → adoption of group identity
social comparison → comparing ingroup to outgroup to determine value of membership
+ tendency for people to use group memberships as source of self-esteem
maintain/enhance it by outgroup discrimination or in-group favouritism
rogers & frantz
[A] investigate whether white European immigrants in Zimbabwe adopt prejudiced attitudes toward local African population over time
[P] stratified sample of Ps that had lived in Zimbabwe for varying lengths of time (5-40+ yrs) responded to a survey with examples of laws/customs in which Europeans/Africans were treated diff. Likert scale choices ranging from it being important to maintain current segregation or discontinue it
[F] majority of Ps favoured retaining segregation. longer residence (5-9 years) was associated with stronger support for maintaining segregation
[C] new immigrants inc. adopt local norms/prejudices of general European population the longer they live in the society, suggesting social conformity to group norms plays a role in the formation of stereotypes.
stereotypes ab African population were integrated into identities of newcomers as they began to identify w/ new group + accept ‘social role’
individual/group - SCT
we learn/imitate behaviour thru observational learning (models who provide e.g. of behaviour) based on a behaviour’s consequences
vicarious reinforcement - more likely to imitate behaviour w/ + consequences
learn based on the consequences of someone else’s behaviour
model stands out in contrast to others, behaviour must be consistent and reinforced, liked by observer/observer identifies w/ model
mediating processes to determine whether to acquire new behaviour
Attention: need to pay attention to behaviour/consequences
Retention: individual must remember behaviour. takes time
Reproduction: must be able to perform behaviour that model demonstrates
Motivation: must be motivated to perform behaviour (reward/punishment)
bandura
[A] investigate whether children learn aggression from observation + imitation as supported by the SCT
[P] children placed in a room with a bobodoll under ⅓ conditions: one with an aggressive model (adult models acted aggressively towards doll), a non-aggressive model (adult model played w/ blocks, ignored doll), control group.
then moved to another room to arouse aggression by saying …, then to 3rd w/ bobodoll to observe aggression
[F] children in aggressive condition demo. more aggressive behaviours than those in other conditions. boys more physical, girls more verbally aggressive. children more likely to imitate same-sex adult models
[C] behaviour can be learned through obs./imitation w/o direct reinforcement, demonstrating the role of models in shaping behaviour
individual/group - formation/effect of stereotypes
Formation
SIT categorises groups → need for positive distinctiveness → we attach neg. stereotypes to outgroup
SCT explains formation as learned behaviour
learn from models (enculturation), imitate models bc want to adhere to group norms
grain of truth hypothesis
gatekeepers (media, models) help create schemas ab person based on group membership
form stereotype by personal experience w/ 1 individual from 1 group → generalisation to whole group
Effect
stereotype threat → individual worries that own behaviour is confirming - stereotype about own group → leads to spotlight anxiety + underperformance/distress
steele & aronson
[A] investigate how stereotype threat affects test performance of AfAm
[P] sample consisted of white + AfAm students. Ps given standardised test under ½ conditions: told test of intellectual ability (stereotype threat condition) or problem-solving skills (non-threat condition)
[F] AfAm performed sig. worse than white Ps in first condition, no sig. diff. between Ps in 2nd condition. white Ps performance unaffected by test framing.
[C] AfAm performed worse bc awareness of negative stereotypes surrounding intellectual ability created stereotype threat + impaired performance
cultural origins of behaviour - cultural dimensions (individualism/collectivism)
= pattern of values in a culture that affects behaviour/cognition
concept introduced by hofstede as a way to compare and discuss cultures
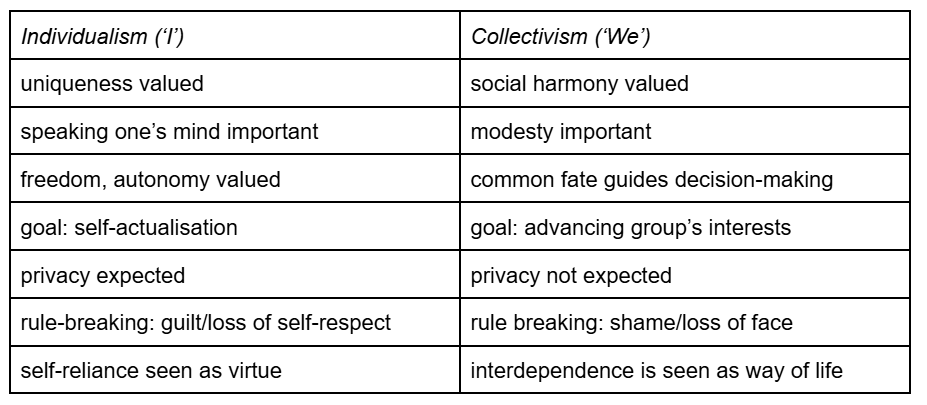
individualism → uniqueness and autonomy valued, self-reliance is seen as a virtue. individual defines personality in terms of own characteristics, and speaking one’s mind important
collectivism → social harmony, group cohesion, modesty valued. interdependence is seen as the way of life, and the ‘goal’ is to advance group interests instead of being self-sufficient.
berry
[A] investigate how culture influences conformity by comparing two different types of cultures to support role of dimensions on behaviour
[P] 3 diff. cultures: temne of sierra leone (collectivist), inuit of baffin island (individualist) + scots (control group) completed variation of Asch’s conformity task, where they were shown series of lines + asked to match 1 to ref. line. on certain trials, Ps given suggestions by researcher (people from ur culture chose this) to see if they conformed. one suggestion was right, but others were wrong
[F] temne showed highest lvls of conformity, inuit lowest, scots between. not much variation within cultures
[C] collectivist culture (temne) had higher conformity → emphasised group harmony/cohesion while individualist culture (inuit) had lower conformity → valued independence. supports hofstede’s theory that dimensions influence behaviour, as the type of culture directly affected the lvl of conformity
[research done before Hofstede’s theory]
cultural influences on behaviour - enculturation
lifelong process by which individuals learn own culture (from parents, school, friends, media, religion) in order to function within culture successfully
via observation, formal instruction, direct experience through + reinforcement
this + social cognition enable cultural transmission (theory of learning according to which individuals acquire sig. amt. of info by just interacting w/ culture)
enculturating gender stereotypes → form of schemas (shaped by caregivers via enculturation but when circle widens, so does influence, so schemas can be broken thru accommodation)
studied thru case studies (obs. + interviews) bc it allows Ps to determine what is most relevant in their lives and bc it’s difficult to operationalise
wood et al.
[A] to investigate gender role enculturation as a result of parenting + toy selection, supporting role of enculturation in shaping gender identity
[P] 2-6 y.o. given selection of gendered toys + adult played with them: half the girls w/ mother, other mother, non-mother, other half w/ fathers. same for boys
researchers analysed which toys children chose + adult’s response
[F] adults reinforced gender-consistent toys. fathers more likely to discourage cross-gender play, mothers more subtle but still did
[C] gender roles socially constructed + reinforced through parenting – hence, enculturation plays key role in shaping gender identity from young age
cultural influences on behaviour - acculturation
process of psych (individual) + cultural (social) changes as result of interaction w/ new culture
in terms of majority (dom.) / minority (non-dom.) culture
2 dimensions:
desire for cultural maintenance (CM) → wish to preserve distinctive aspects of cultural identity
desire for intergroup contact (DC) → wish to have contact w/ other culture
acculturative stress → difficulties in process, stemming from differences between individuals and host culture
discrimination can heighten A.S. bc process seen as too demanding/impacts individual’s self-concept, coping
less desire for DC + isolation
lueck & wilson
[A] investigate factors that predict A.S. in asian immigrants + asian-americans
[P] semi-structured interviews (face-to-face or online) measured level of A.S. and examined factors such as the impact of lang. proficiency/pref., discrimination, social networks, family cohesion, socioecon. status.
[F] 70% of Ps reported A.S. lower stress levels linked to bilingualism, strong social support, integration. higher linked to only using 1 language, discrimination, economic struggles
[C] lvl of A.S. influenced by language proficiency, discrimination, social support, and bicultural identity+integration can help reduce it, supporting importance of acculturation in mental wellbeing