Exam 2 Reactions (Chapters 14 & 15)
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
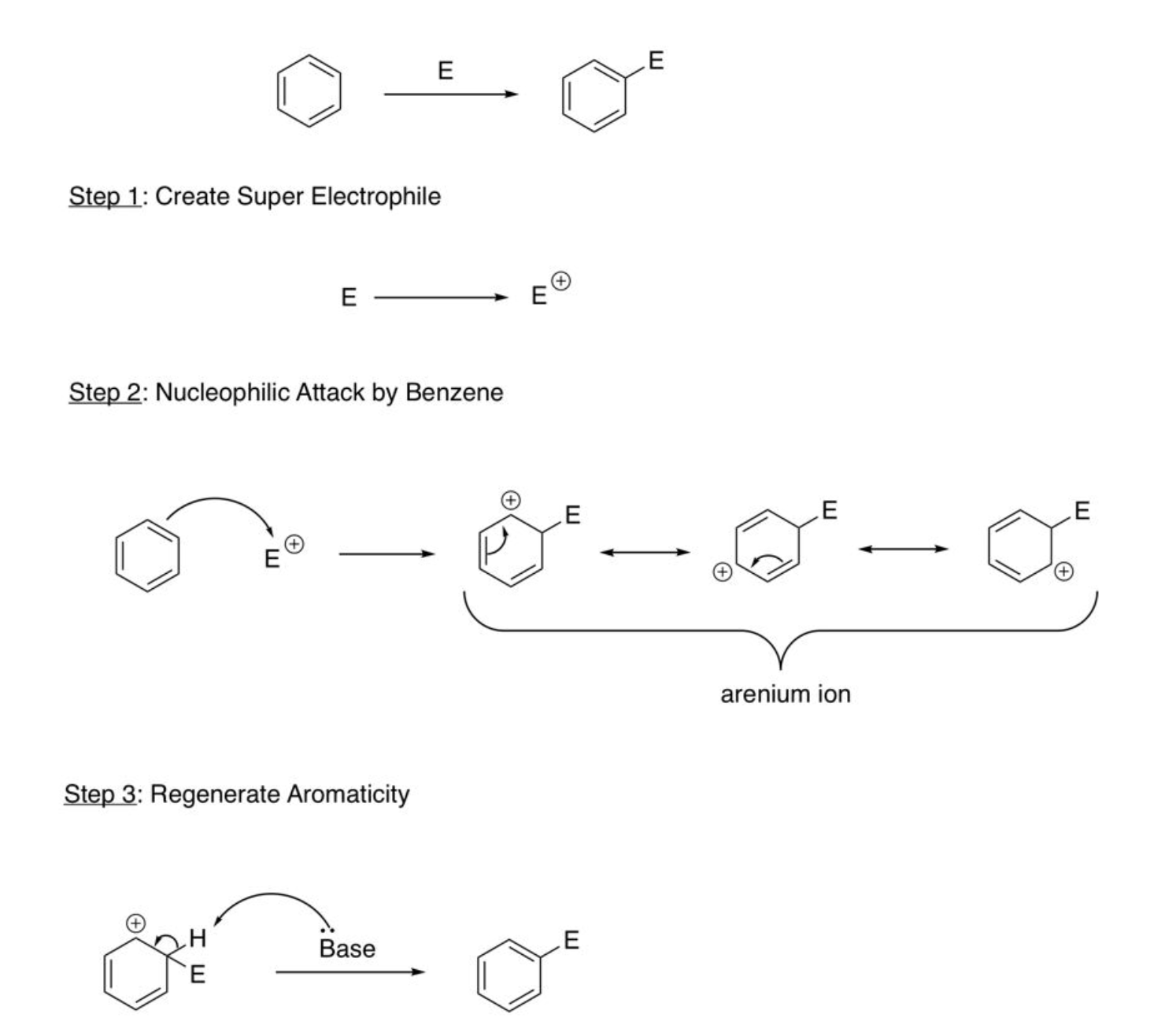
Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution
Create super electrophile, nucleophilic attack by benzene, regenerate aromaticity
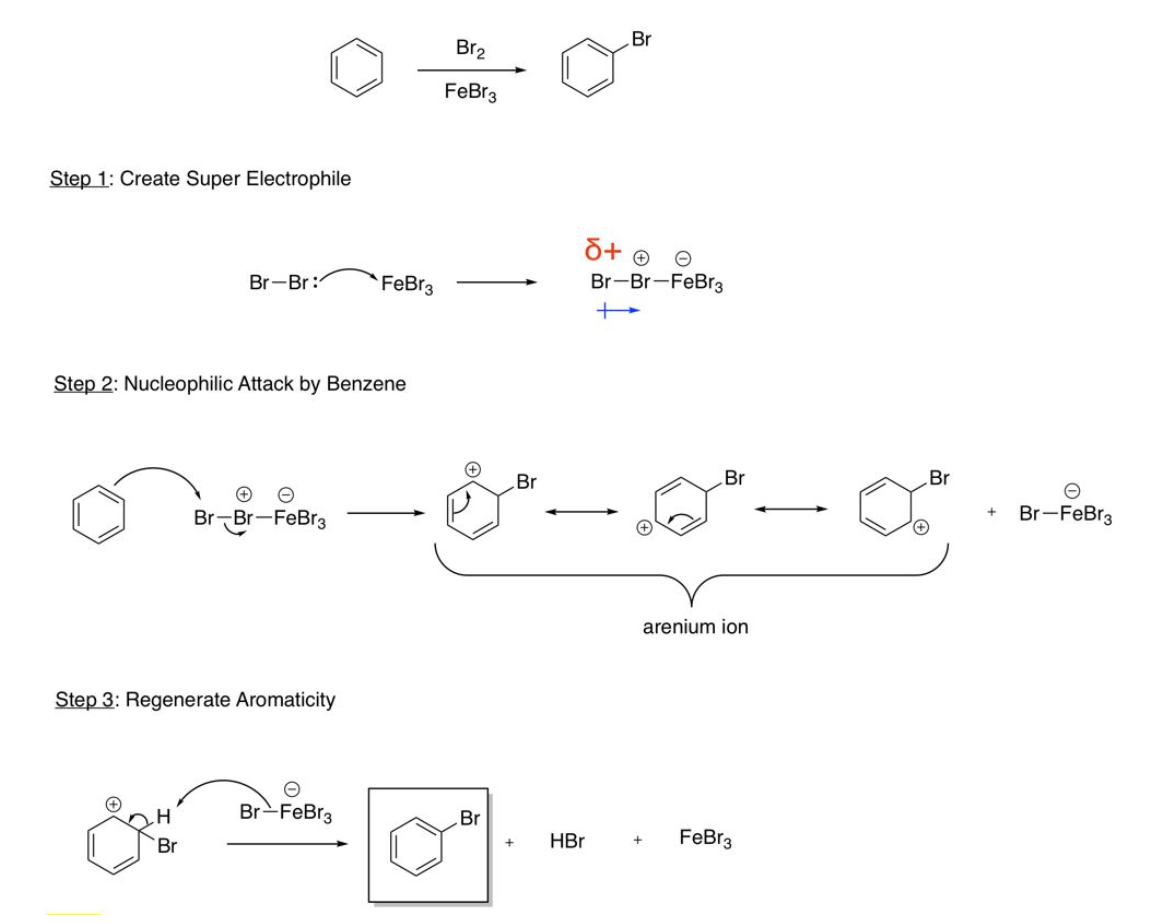
EAS Halogenation
Create super electrophile (Br2 bonds to FeBr3 or Cl2 bonds to AlCl3), nucleophilic attack by benzene (DB bonds to Br or Cl), regenerate aromaticity (BrFeBr3 or ClAlCl3 bonds to H and bond breaks to regenerate aromaticity)
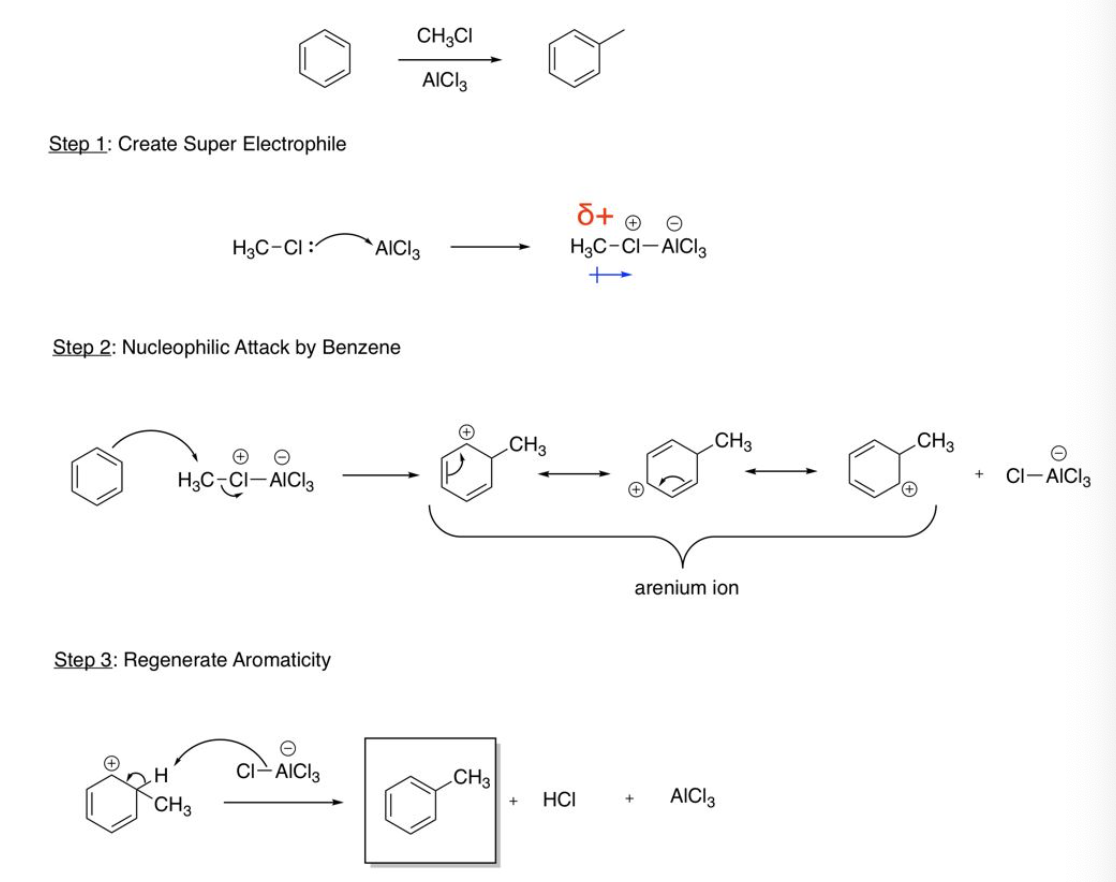
Friedel-Crafts Alkylation (methyl and ethyl)
Create super electrophile (methyl/ethyl halide bonds to AlCl3 or FeBr3), nucleophilic attack by benzene (DB bonds to methyl or ethyl), regenerate aromaticity (BrFeBr3 or ClAlCl3 bonds to H and bond breaks to regenerate aromaticity)
Friedel-Crafts Alkylation (secondary and tertiary)
Create super electrophile (halide bonds to AlCl3 or FeBr3 then carbon group leaves to create carbocation), nucleophilic attack by benzene (DB bonds to carbocation), regenerate aromaticity (BrFeBr3 or ClAlCl3 bonds to H and bond breaks to regenerate aromaticity)
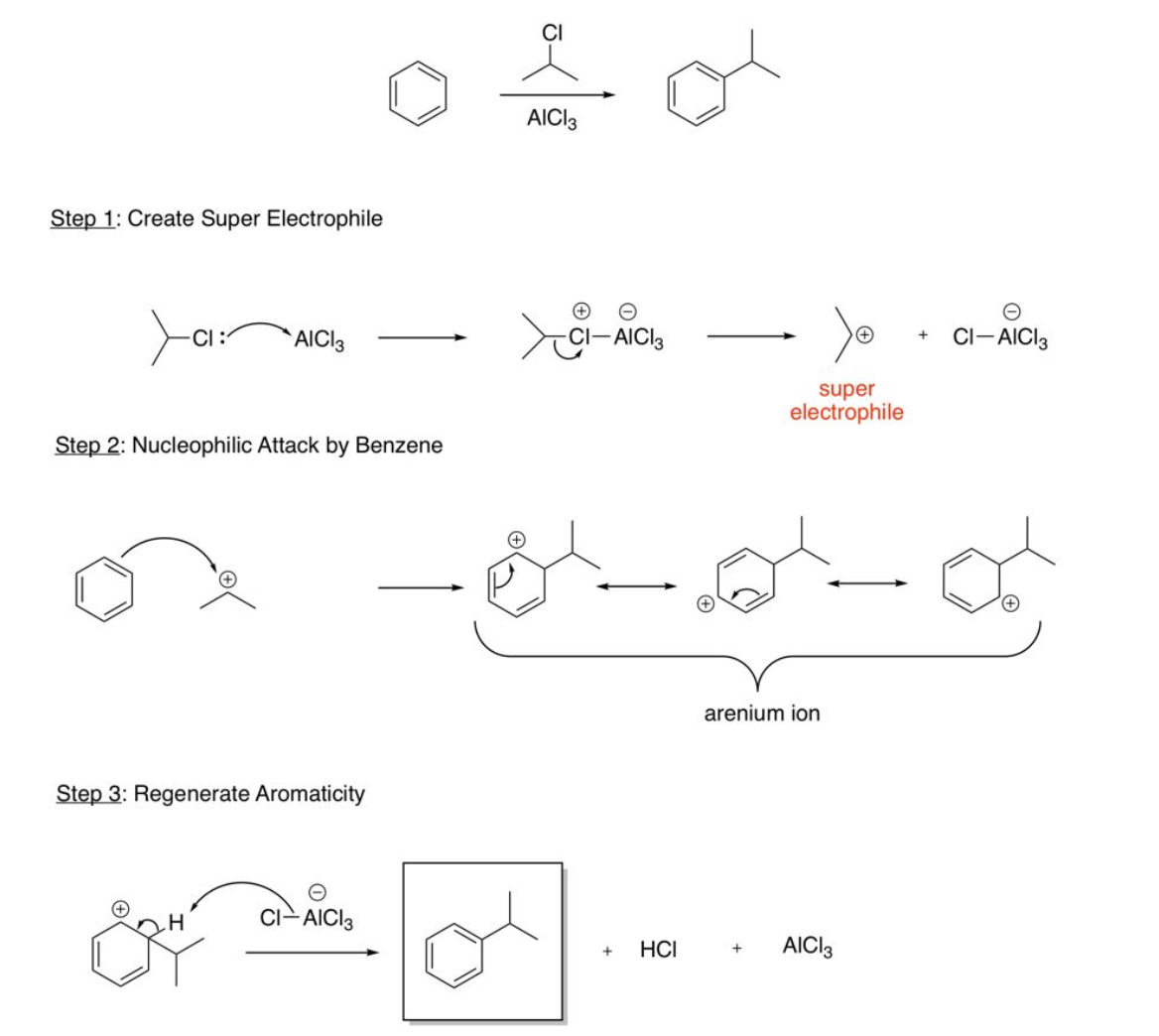
Friedel-Crafts Alkylation (primary other than ethyl)
Create super electrophile ( halide bonds to AlCl3 or FeBr3 then carbon leaves to form carbocation and rearrangement for stability occurs), nucleophilic attack by benzene (DB bonds to methyl or ethyl, regenerate aromaticity (BrFeBr3 or ClAlCl3 bonds to H and bond breaks to regenerate aromaticity)
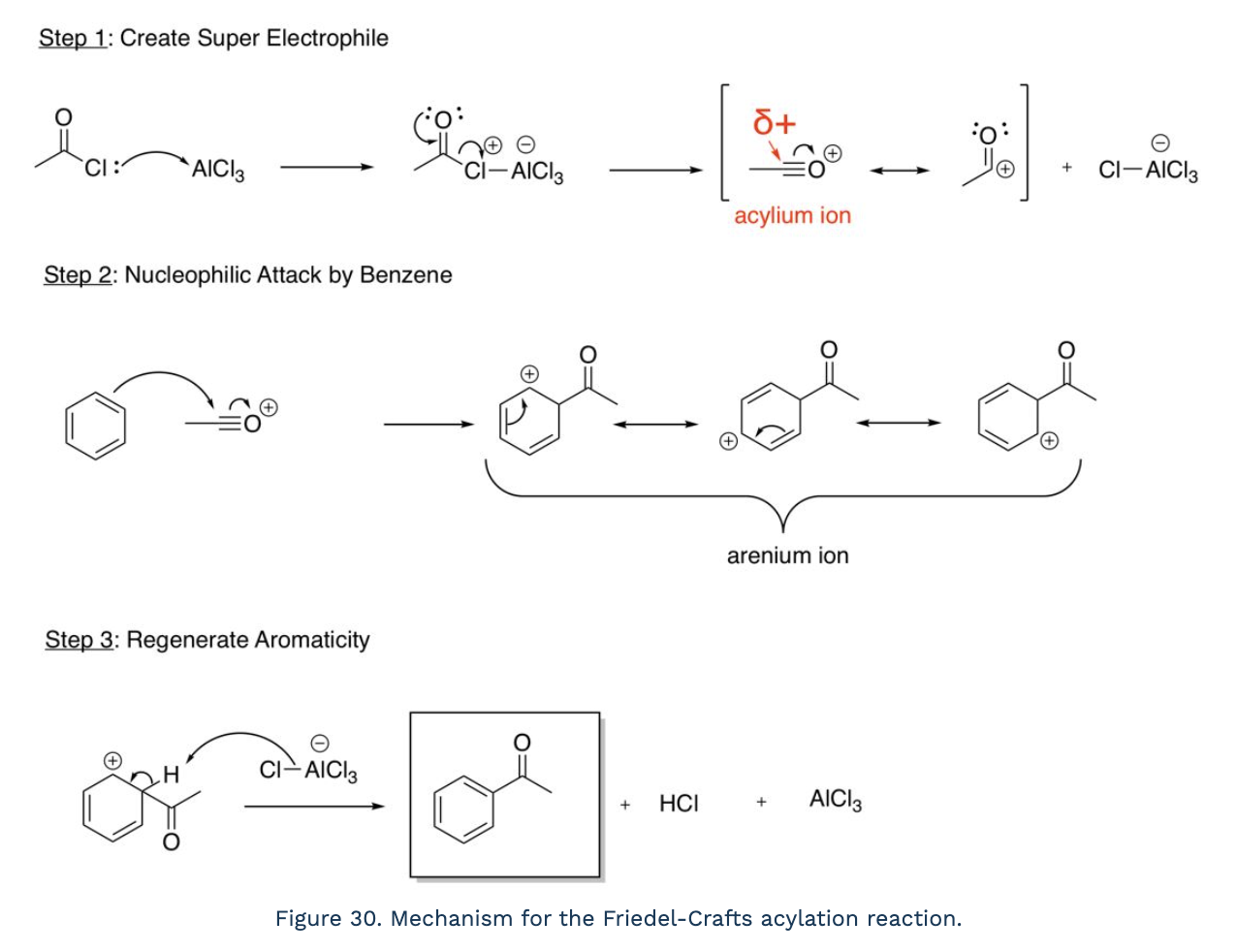
Friedel-Crafts Acylation
create super electrophile (halogen bonds to compound, lone pairs move down and halogen leaves to create acylium ion), nucleophilic attack by benzene (stabilizes charge on oxygen), regenerate aromaticity
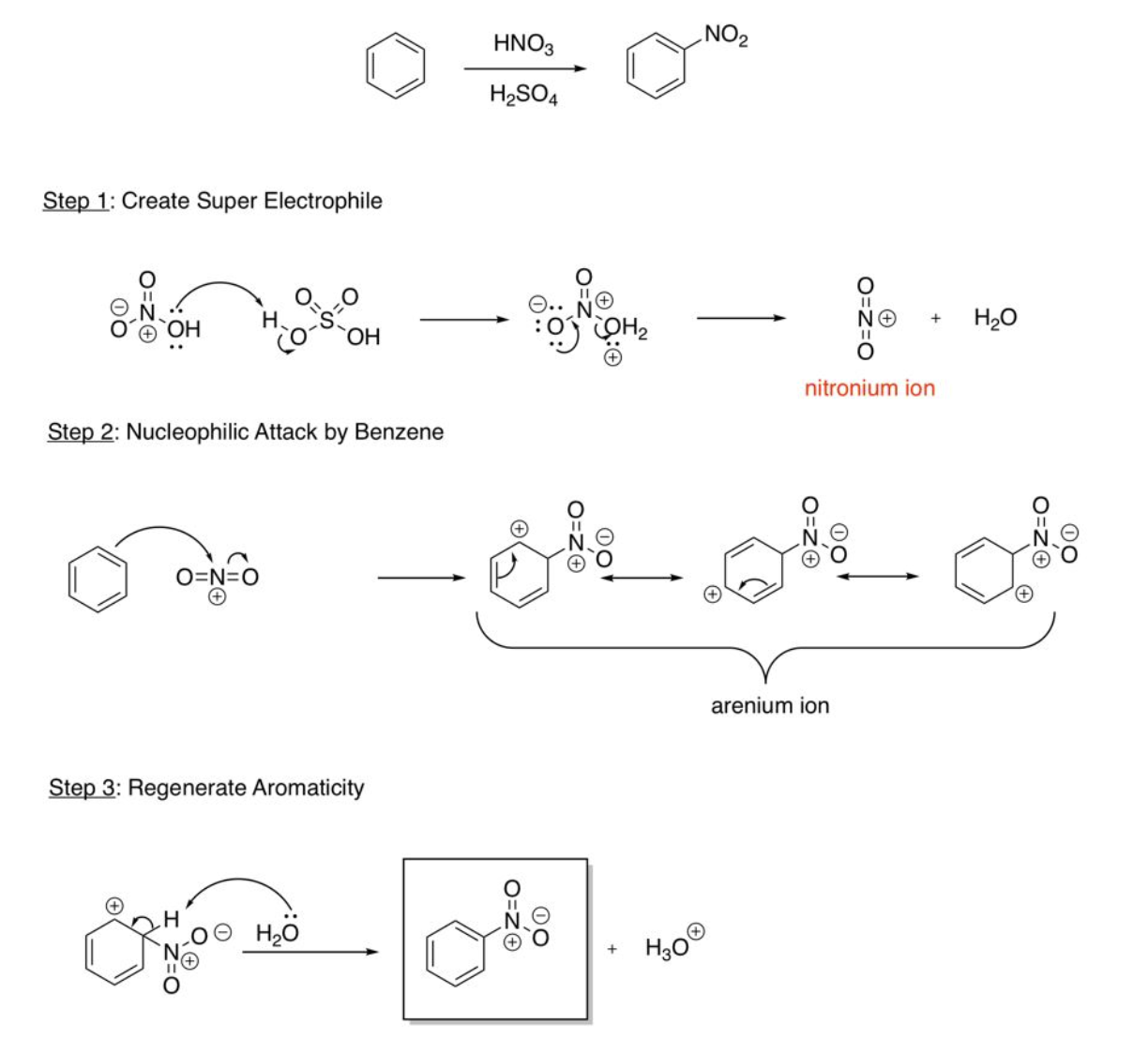
EAS Nitration
create super electrophile (OH of HNO3 steals H from H2SO4, OH2 group then leaves and nitronium ion is created), nucleophilic attack by benzene (bonds to nitrogen, kicking one DB electrons onto oxygen), regenerate aromaticity
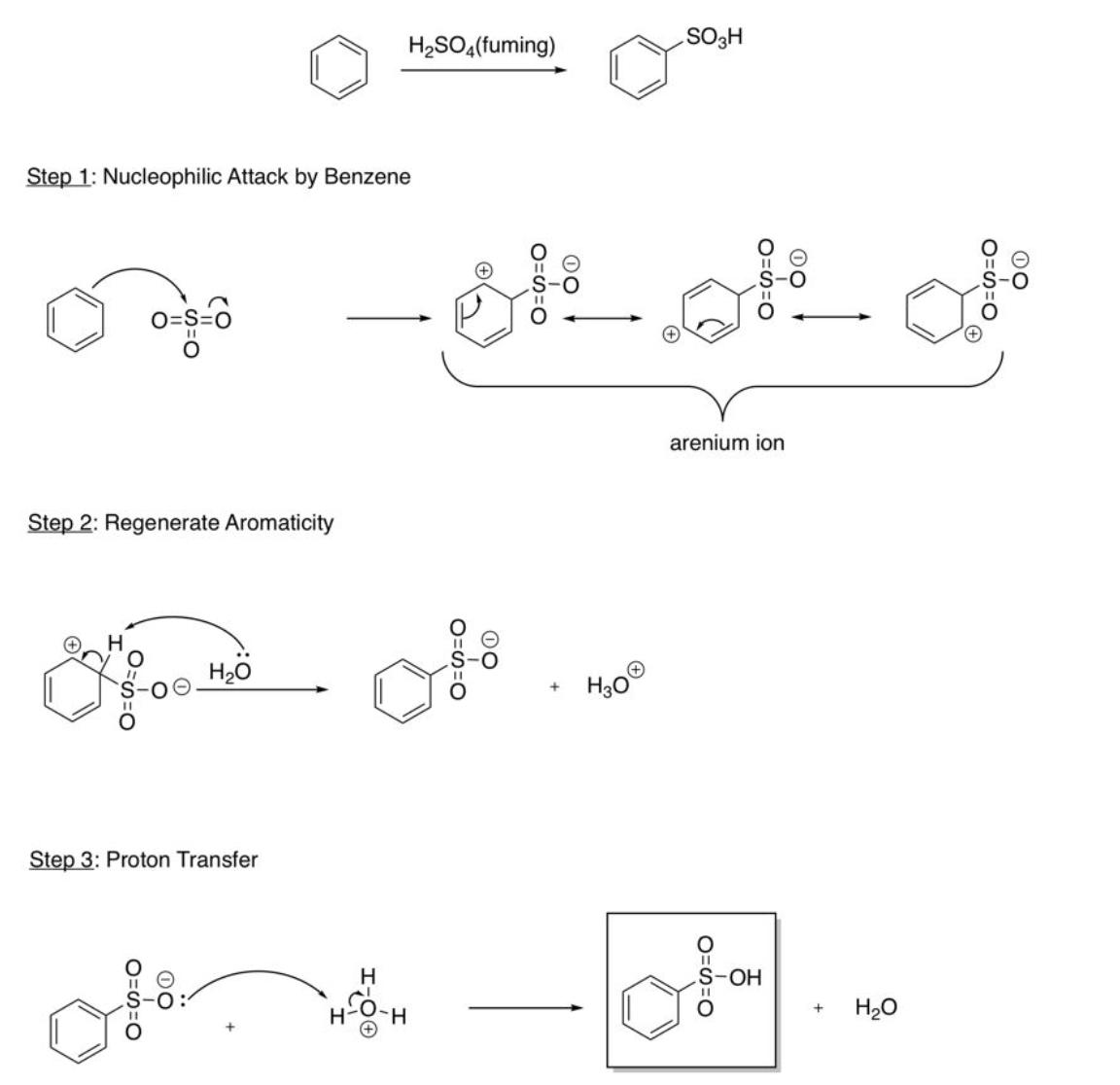
EAS Sulfonation
H2SO4 fuming contains super electrophile SO3 gas, nucleophilic attack by benzene (onto sulfur, electrons go onto oxygen), regenerate aromaticity (H2O takes H), proton transfer (add H to negatively charged O from H3O)
Reverse EAS Sulfonation (Desulfonation)
proton transfer (H2O takes H from OH), destroy aromaticity (DB takes H), regenerate aromaticity (DB between S and O reforms, bond breaks to create DB on ring)
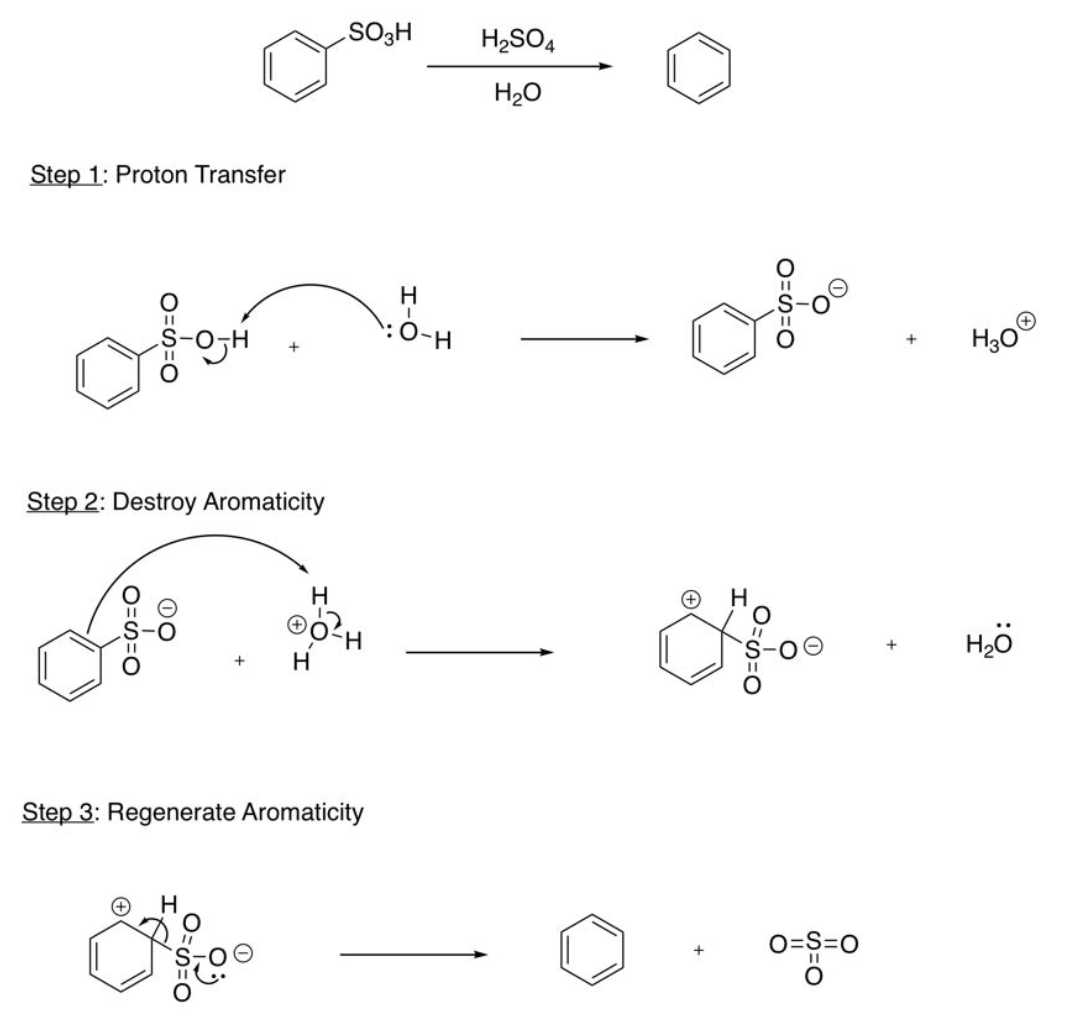
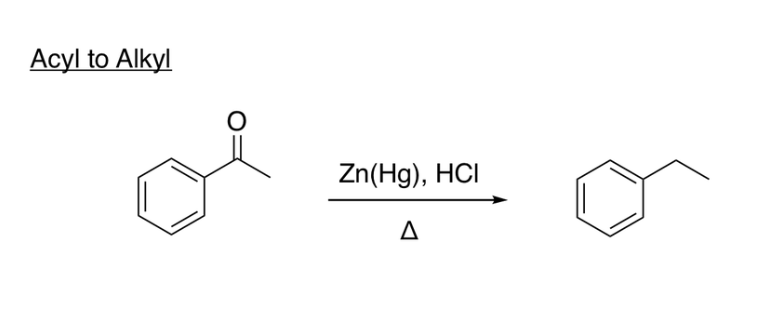
Clemmensen Reduction
(Acyl to Alkyl reagents) Zn(Hg), HCl, heat
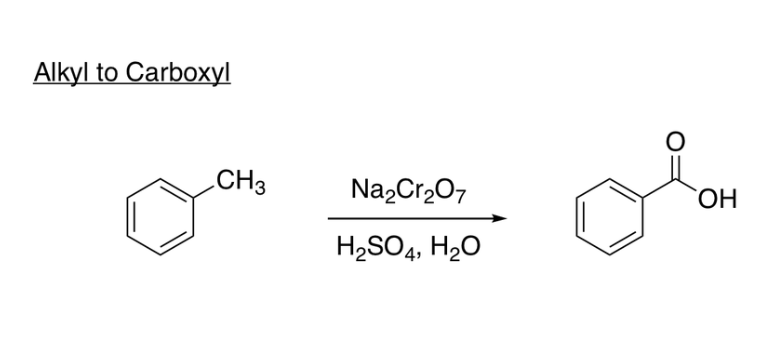
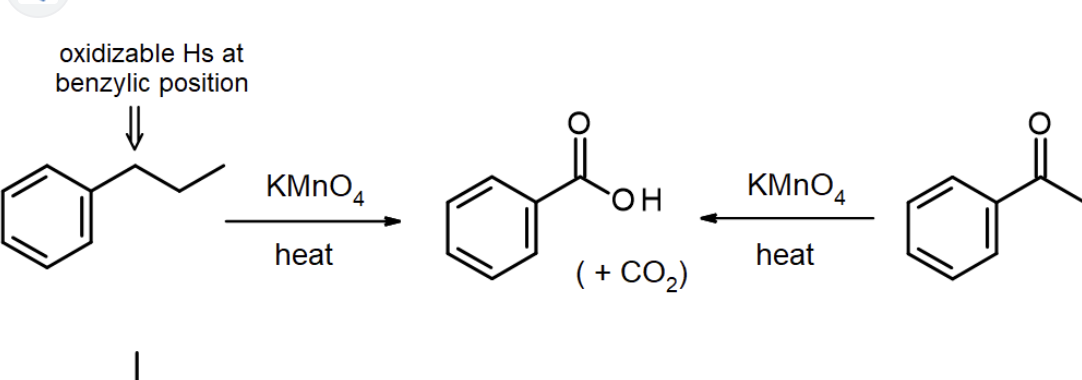
Side-Chain Oxidation Book method
(Alkyl to Carboxyl reagents) Na2Cr2O7, H2SO4, H2O
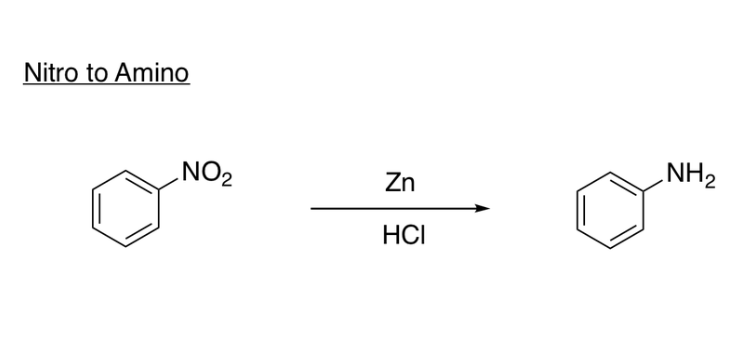
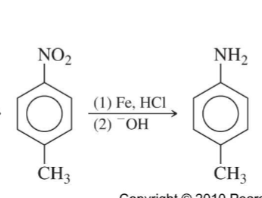
Reduction of Nitro Group
Zn or Sn or Fe, HCl
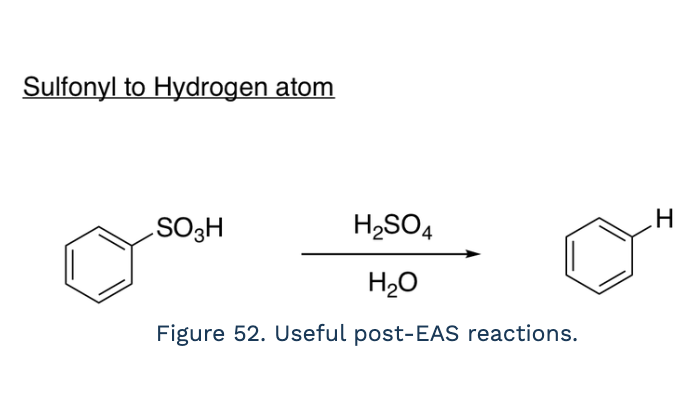
Sulfonyl to Hydrogen atom (reagents, desulfonation)
H2SO4, H2O
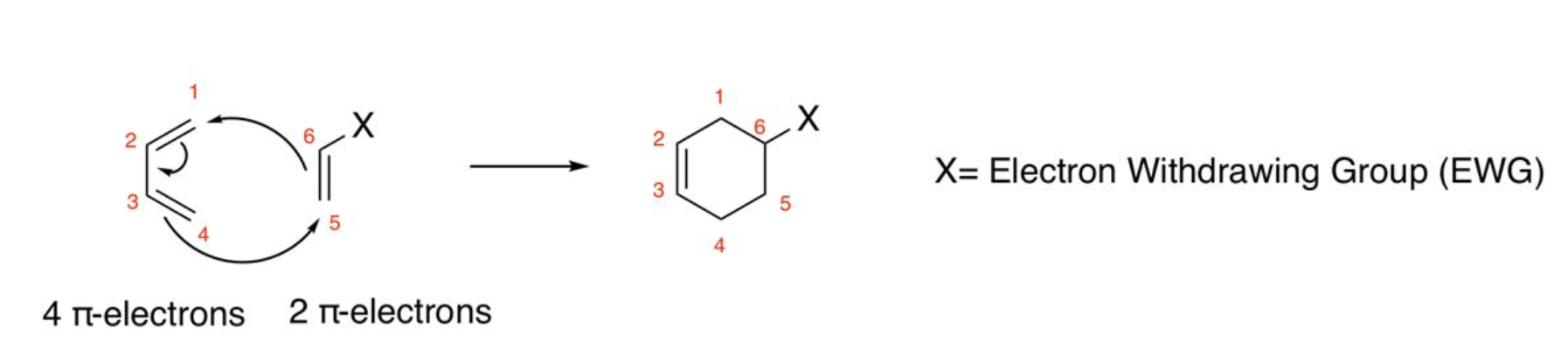
Diels-Alder
electron rich diene + dienophile, must contain a cis diene and EWG, cis dienophile makes syn product, trans dienophile makes anti product, 4+2 pi electrons; do NOT make 1,3 product for two asymmetrical starting materials
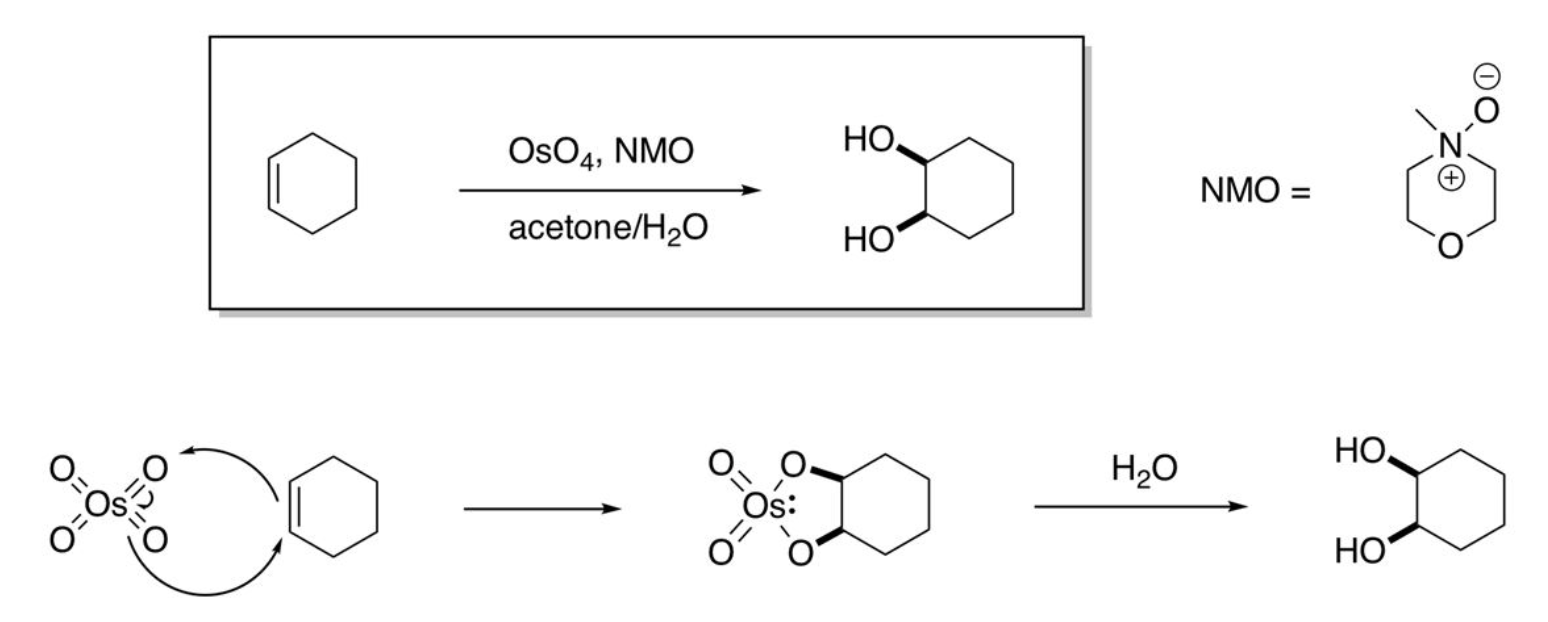
syn-dihydroxylation
using Osmium Tetroxide, 4+2 pi electrons
anti-dihydroxylation
using CH3CO3H & H2SO4, H2O
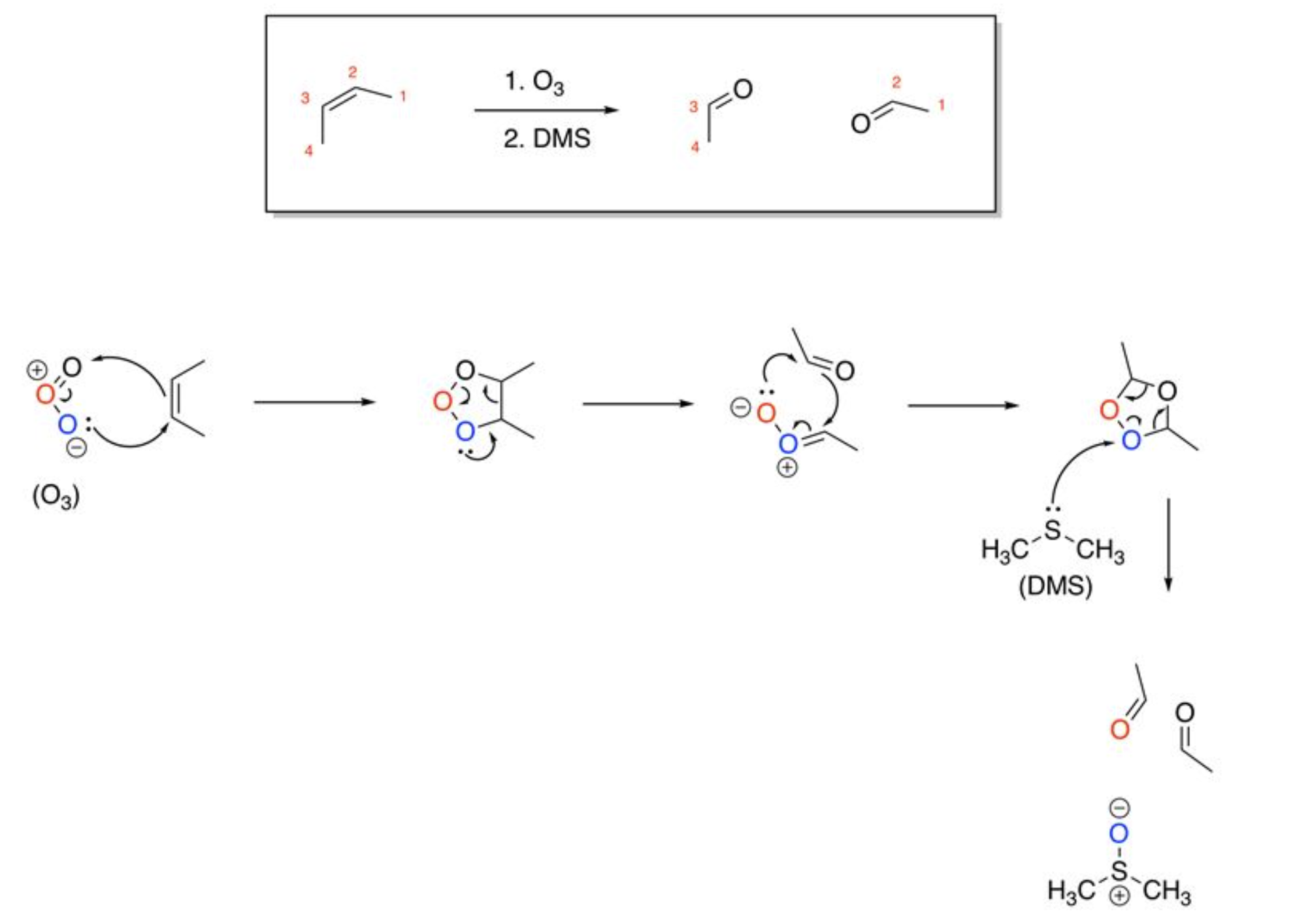
Ozonolysis
4+2 pi electrons
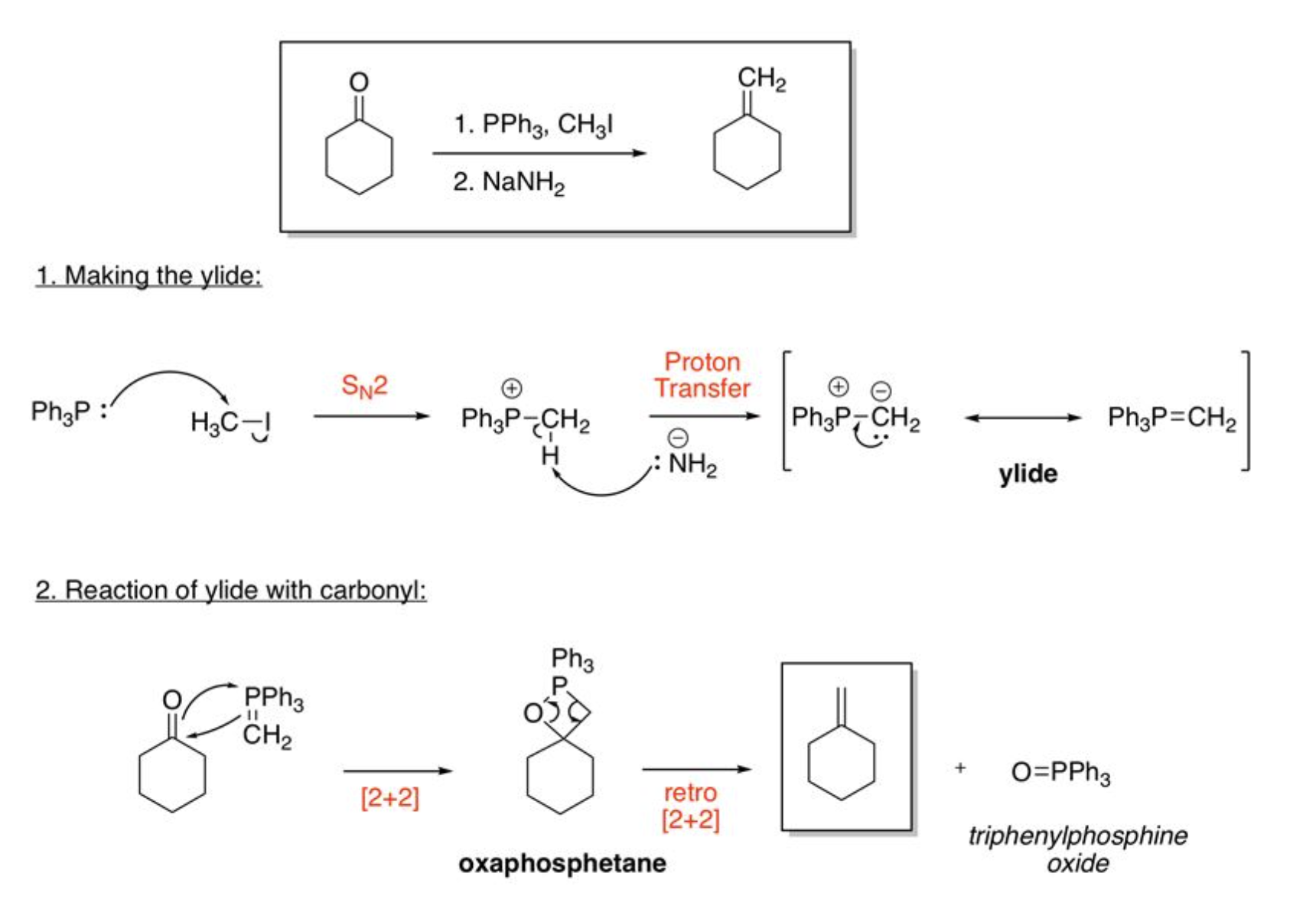
Wittig Reaction
2+2 pi electrons, E alkene when EWG next to negative charge, no EWG gives Z alkene
Sn and HCl
replace NO2 with NH2
NaNO2 and HCl (Arenediazonium)
replace NH2 with N2
CuCN
replaces N2 with CN (benzonitrile)
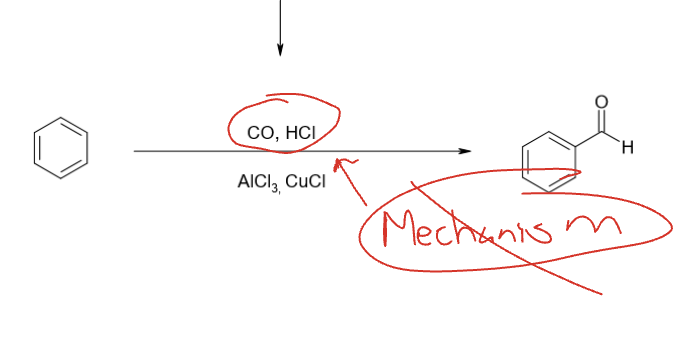
Gatterman-Koch Formylation (don’t need to know mechanism)
CO, HCl
AlCl3, CuCl
Side-Chain Oxidation Ron method
KMnO4, NaOH
H2O, heat
Reduction of Nitro Group
Fe (or Sn or Zn), HCl
OH-
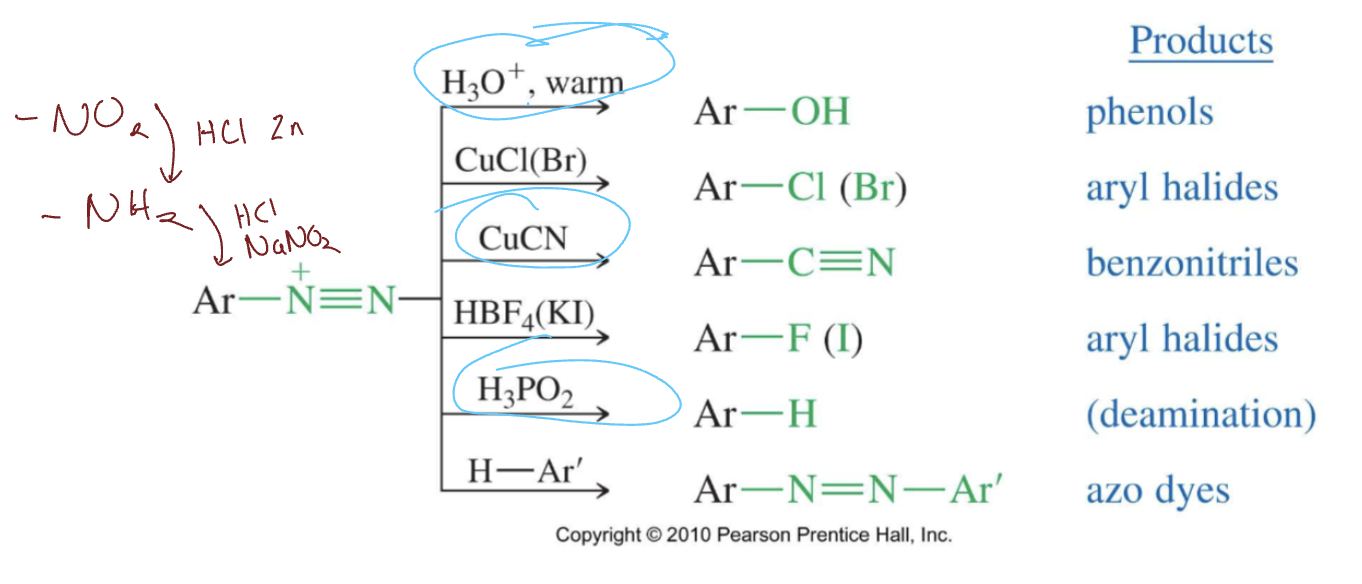
Reactions of Arenediazonium Salts
H3O+ and heat makes phenol (Ar-OH), CuCl(Br) makes aryl halide (Ar-Cl(Br)), CuCN makes benzonitrile (CuCN), HBF4(KI) makes aryl halide (Ar-F(I)), H3PO2 makes deamination (Ar-H), H-Ar’ makes azo dyes (Ar-N=N-Ar’)
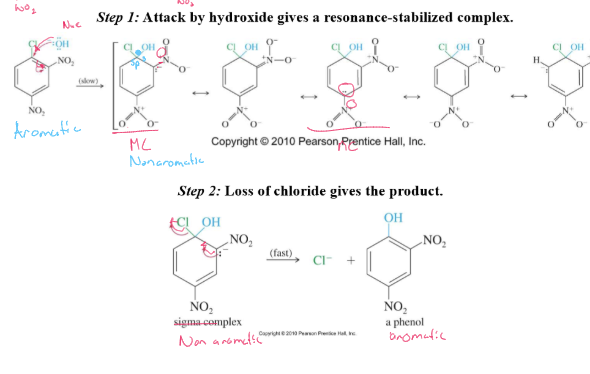
Nucleophilic Aromatic Substitution (NAS)
EWGs (nitro groups) ortho and para to halogen stabilize intermediate leading to nucleophilic substitution
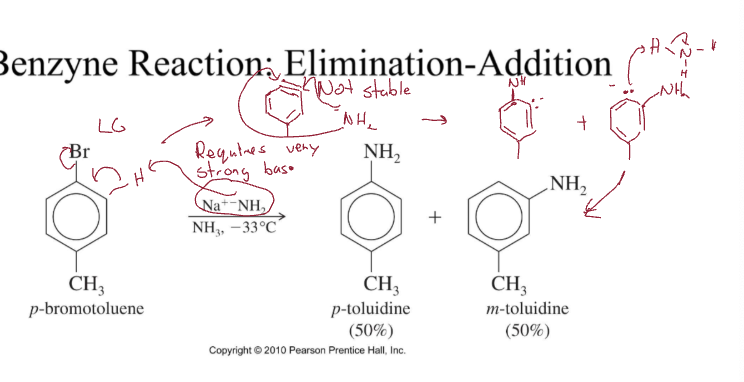
Benzene Elimination-Addition
Requires VERY strong base