6 MAGNETISM AND ELECTROMAGNETISM
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
define “magnetic field line”
can show the size and direction of magnetic fields.
they always point from north to south
what is a magnetic field
a magnetic field is a region where magnetic materials experience a force
how can magnetism be induced
when magnetic materials are brought into a magnets magnetic field that material acts as a magnet
the magnetism has been induced by the original magnet
the closer the magnet and the magnetic material are, the stronger the induced magnetism will be
what is a soft magnetic material
a soft magnetic material loses its induced magnetism quickly, for example iron
what is a hard magnetic material
a hard magnetic material keeps its induced magnetism permanently, for example steel
how to increase the strength of a magnetic field around a coil of wire
add a magnetically soft iron core through the middle of the coil to increase the strength of the magnetic field
what do magnets do
magnets attract and repel other magnets. they also attract magnetic substances
practical: investigate the magnetic field pattern for a permanent bar magnet using compasses
compasses align themselves with magnetic fields
use a compass and move it around to find the magnetic field
practical: investigate the magnetic field pattern for a permanent bar magnet using iron fillings
iron fillings align themselves with magnetic fields
place the magnet under a piece of paper and scatter the iron fillings on top
tap the paper until the fillings form a clear pat
how to create a uniform field between two magnets
place the north and south poles of two permanent bar magnets near each other. a uniform field will form.
what happens when current flows through a conducting wire
when current flows through a conducting wire a magnetic field is produced around the wire
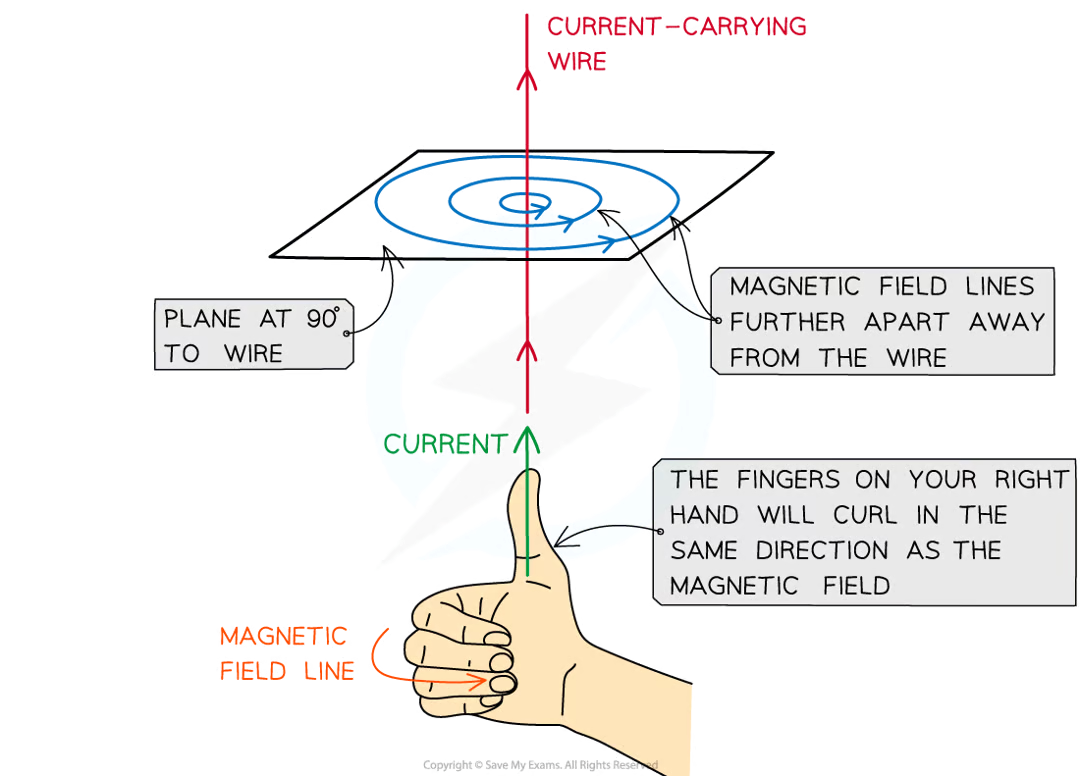
how does the right hand thumb rule work
the thumb points along the direction of current
the other fingers give the direction of the magnetic field
how to draw magnetic field diagrams
a circle with a dot in the centre shows that current is flowing out of the plane
a circle with a cross in the centre shows that current is flowing into the plane
as the distance from the wire increases, the circles get further apart as the magnetic field is the strongest near the wire
what factors affect magnetic field strength
a larger current will produce a larger magnetic field
the greater the distance from the conductor, the weaker the magnetic field is
when does the motor effect occur
when a wire with current flowing through it is placed in a magnetic field and experiences a force
why does the motor effect happen
because of the two interacting magnetic fields
one magnetic field is produced around the wire due to the current flowing through it
the other magnetic field is the one in which the wire is placed in (e.g. between two magnets)
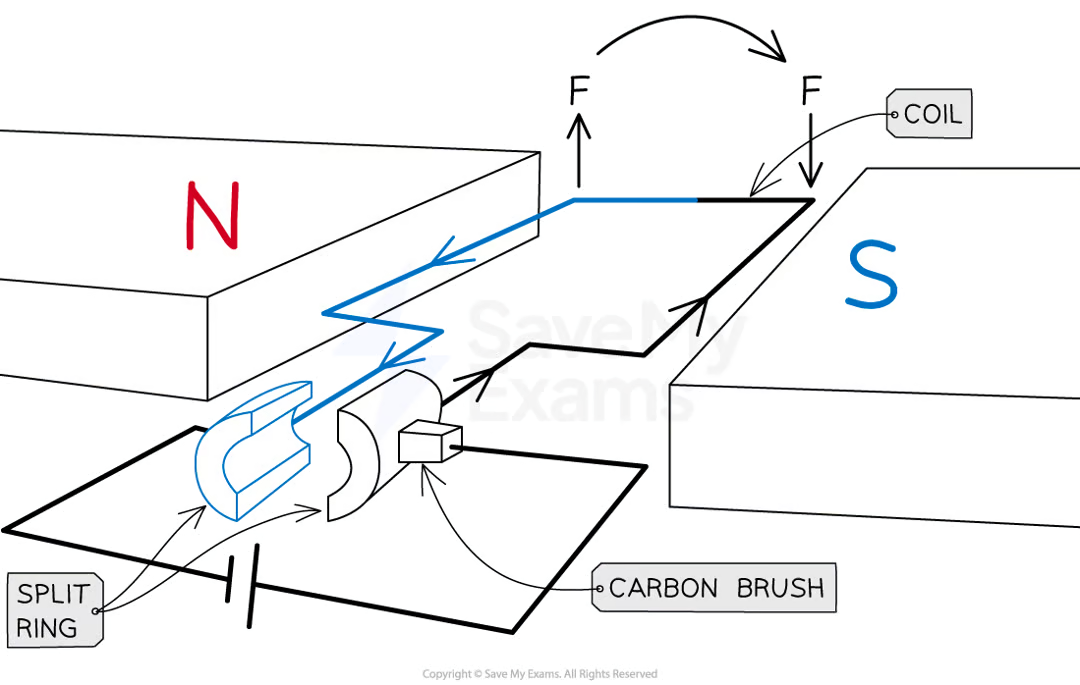
how can you create a simple d.c. electric motor
a coil of wire which is free to rotate is positioned in a uniform magnetic field
the coil is attached to a split ring commutator, which is connected in a circuit with the cell via contact with conducting carbon brushes.
the coil of wire, when horizontal, forms a complete circuit with a cell
what are the forces on the coil when horizontal in a d.c. motor
current flowing through the coil produces a magnetic field which interacts with the uniform external field, so a force is exerted on the wire
the forces act in opposite direction on each side of the coil, causing it to rotate.
once the coil has rotated 90 degrees, the split ring is no longer in contact with the brushes, so no current flows through it and no forces act on it
what are the forces on the coil in the vertical position in a d.c. motor
the momentum of the coil causes the coil to continue to rotate slightly
the split ring reconnects with the carbon brushes and current flows through the coil again
even though the coil has flipped, current still flows towards the cell on the left, so the coil continues to rotate in the same direction, making the coil continuously spin
what factors affect the d.c. motor
the speed at which the coil rotates can be increased by increasing the current or the strength of the magnetic field
the direction of rotation can be changed by reversing the current direction or reversing the poles of the magnet (reversing the direction of the magnetic field)
the force supplied by the motor can be increased by increasing the current, the strength of the magnetic field or adding more turns to the coil
how does the motor effect in loudspeakers work
the loudspeaker consists of a coil of wire which is wrapped around one pole of a permanent magent
an alternating current passes through the coil of the loudspeaker, creating a changing magnetic field around the coil
the magnetic field produced around the coil interacts with the field from the permannet magnet
the interacting magnetic fields will exert a force on the coil
as the magnetic field is constantly changing direction, the force exerted on the coil will constantly change direction, making the coil oscillate
the oscillation of the coil causes the speaker cone to oscillate, which makes the air oscillate, creating sound waves
what factors affect magnetic force
stronger magnetic fields produce stronger forces
increasing the amount of current flowing through the wire to increase the magnetic field
using stronger magnets will increase the magnetic field
placing the wire at 90 degrees to the direction of magnetic field lines will mean maximum interaction between the two magnetic fields
what happens if the two interacting magnetic fields are parallel
there will be no interaction between the two magnetic fields and therefore no force produced
how does fleming’s left hand rule work
the thumb is the thrust (direction of force)
the first finger is the magnetic field
the second finger is the current
how are electromagnets made
wind a wire with current flowing through it into a coil to strengthen the magnetic field by concentrating the field lines
if this wire is wound around a soft magnets, then an electromagnet is made
what determines the strength of a electromagnet
increasing the current in the coil will increase the strength of a magnetic field
increasing the number of turns to the coil will increase the strength of a magnetic field
what is the magnetic field in a straight wire
concentric circles which gradually get further apart from eachother
what is the magnetic field in a flat circular coil
the magnetic field lines circle around each part of the coil, passing through the centre of it

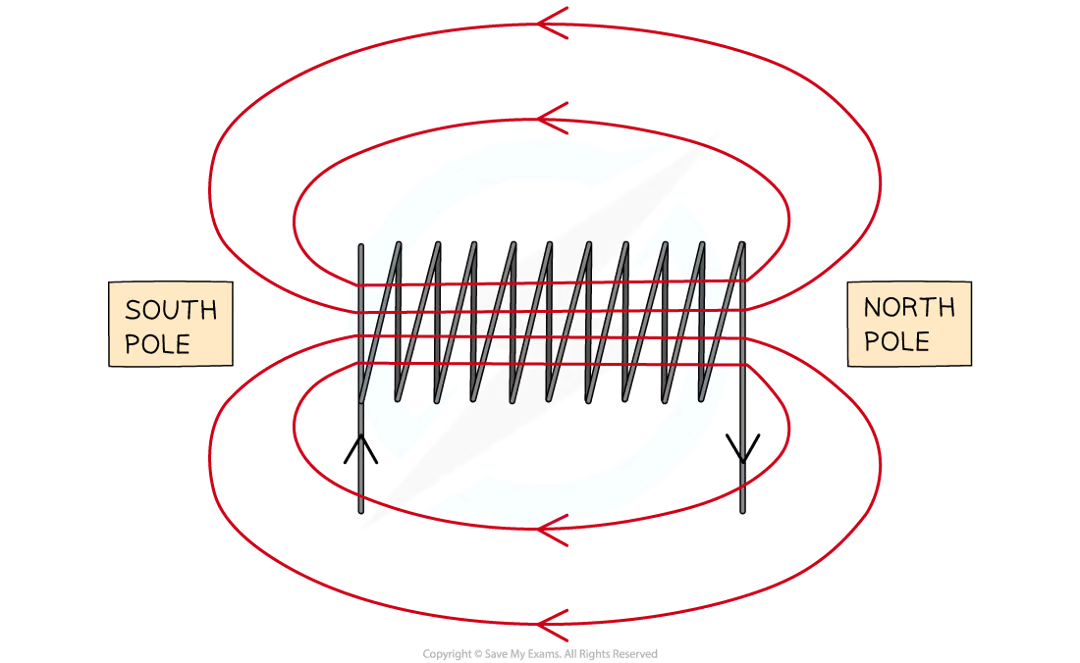
what is the magnetic field in a solenoid
it is strong and uniform
the ends of the solenoid behave like the north/south poles of a magnet
if the current is travelling around in a clockwise direction, then it is the south pole
if the current is travelling around in an anti clockwise direction then it is the north pole
what factors affect the magnetic field strength of a solenoid
increasing the size of the current will increase magnetic field strength
increasing the number of turns in the coil in a given length will increase magnetic field strength
adding an iron core through the centre of the coils will become an induced magnet, making it a stronger magnet overall
define electromagnetic induction
when a voltage is induced in a conductor or a coil when it moves through a magnetic field or when a magnetic field changes through it
how is a voltage induced
a voltage will be induced in the conductor if there is relative movement between the conductor and the magnetic field
when a conductor is moved through a magnetic field, the wire cuts through the field lines, inducing a voltage in the wire.
when a magnet is moved through a coil, the field lines cut through the turns on the coil, inducing a voltage in the coil
what factors will increase the size of induced voltage
increasing the speed at which the wire, coil or magnet is moved
increasing the number of turns on the coils in the wire
increasing the size of the coils
increasing the strength of the magnetic field
what factors will affect the direction of the induced voltage
by changing the orientation of the poles of the magnet, it will reverse the direction in which the wire, coil or magnet is moved.
describe the structure of a transformer
a primaru coil
a secondary coil
an iron core, as iron is easily magnetised
what does a transformer do
an alternating current is supplied to the primary coil
the current is continually changing direction, so a changing magnetic field is produced around the primary coil
the iron core is easily magnetised, so the changing magnetic field passes through it
there is now a changing magnetic field inside the secondary coil
the changing magnetic field in the iron core cuts through the secondary coil and induces a voltage
as the magnetic field is continually changing, the induced voltage is alternating
the alternating voltage has the same frequency as the current supplied to the primary coil
if the secondary coil is part of a complete circuit, it will cause an alternating current to flow
relationship between primary and secondary voltages
input voltage/output voltage = primary turns/secondary turns
what is the equation for 100% efficiency
input power (VpIp) = output power (VsIs)
what does a step-up transformer do
increases the voltage of a power source
has more turns on the secondary coil than the primary coil
when are step up transformers used
when electricity is transmitted over large distances, the current in the wire heats them, resulting in energy loss
the electrical energy is transferred at high voltages from power stations
it is then transferred at lower voltages in each locality for domestic uses
the voltage must be stepped up by a stepped up transformer, placed after the power stations
what does a step down transformer do
decreases the voltage of a power source
has fewer turns on the secondary coil than on the primary coil
when is a step down transformer used
for the domestic use of electricity, the voltage must be much lower
this is done by stepping down by the voltage using a step-down transformer, which is placed before buildings
what are alternators
a type of generator that converts mechanical energy to electrical energy in the form of an alternating current
a rectangular coil is forced to spin in a uniform magnetic field
it is connected to a centre-reading meter by metal brushes that press on two metal slip rings
when the coil turns in one direction:
the pointer deflects first one way, the the opposite way, the back
because the coil cuts through the magnetic field lines and an alternating voltage is induced in the coil
an alternating current may be produced when a magnet rotates within a stationary coil
the induced voltage and current alternate because they continuously change direction
what is a dynamo
a dynamo in physics is the name for a direct current generator
a simple dynamo is the same as an alternator except that the dynamo has a split=ring commutator instead of two separate slip rings
as the coil rotates, it cuts through the field lines
this induces a voltage between the end of the coil
the split ring commutator changes the connections between the coil and the brushes every half turn in order to keep the current leaving the dynamo in the same direction (when the coil is perpendicular to the magnetic field lines)
the induced voltage does not reverse its direction as it does in the alternator
instead, it varies from zero to a maximum value twice each cycle of rotation and never changes polarity - current is always positive or always negative.