HCS081 access theory
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
MS access 2016
well known ex of DB applic for Windows
(allows user to create custom DBs that store info in organised structure)
DB management system (DBMS)
database
collection of info that's organized so it can be easily accessed, retrieved, updated, & managed
complete database aka
FILE
→ file is made up of ind records
exs of databases
• Telephone Directory
• Student Enrollment
• Payroll Database
• AhLiki Wholesale System
how to start MS access & its interface
open access > blank database
enter file name> file location
click create
4 database components
tables, forms,queries, reports
2 types of database
flat file database & relational database
flat file database
Contains only single table to hold records
(No relos req)
relational database
Contains >1 table that must be related
(Relos req to connect tables)
4 rules of database theory
1) Reduce redundancy & inconsistency (eliminate entering data multiple times)
2) Facilitate maintenance (need to accurately change data, ideally once)
3) Maintain accuracy (relos help reduce potential for errors)
4) Simplify info retrieval (extracting info shld be easy & quick)
designing & planning database
• Consider 4 DB Rules when in design process
• Store 1 value per field
• Assign PK for each table
primary key

1/more fields that uniquely identifies each record in table
(each table must have PK)
exs of PK
StudentiD of Student Table
EmployeeCode of Employee table
Receipt# of Payment Table
foreign key
'primary key' of another table
(Essential in drawing relos betw tables)
relationship

Enforcing referential integrity to avoid inconsistence of data entry
3 types of relos
one to one (1-1) = record in 1 table relates to only 1 record in another table
one to many (1-∞) = record in 1 table relates to more than 1 record in another table
many to many (∞-∞) = many records in 1 table relate to many records in another table
referential integrity
relational concept that dets outcome of actions on related tables
2 rules of referential integrity will be reinforced if: (3)
*Both fields have same data type
*Both tables stored in same database
*Relo type is identified
(2 rules of referential integrity)
1. can't add record to related table unless there's alr matching record in primary table
2. can't delete record from primary table while matching records still exist in related table
table (database object)
Allows you to enter & edit records in spreadsheet-line environment
usually 1st component to be created in DB
Consist of Fields & Records
2 table views
design & datasheet view

table design view
Allows you to modify & edit structure of table
can:
enter field names & data types for each field
change field properties for each field
field name
descr contents of data stored in columns
1st step in creating table (field name)
assign suitable field names
Max 64 characters
Max 255 fields per table
naming rules (field name) (3)
descr content of data
fields must have diff names
Keep names short
data type depends on
type of data field will hold (content entered)
7 data types
1. Short Text
2. Long Text
3. Number
4. Date/Time
5. Currency
6. Autonumber (Counter)
7. Yes/No
short text (data type)
Default. For text content
long text (data type)
For large amounts of text content
number (data type)
Only use when you expect to do calcs (Byte, integer, long integer, double, single)
date/time (data type)
stores date & time data
currency (data type)
Special type of no field
autonumber (data type)
Value's automatically assigned starting from 1
yes/no (data type)
Approp when field can have only 1 of 2 diff values
field properties
Det how field data is inputted & displayed
11 field properties
field size, format, decimal places, input musk, caption, default value, validation rule, validation text, required, allow zero length, indexed
field size (field property)
used to control max no of characters in field
format (field property)
Dets how Access displays & prints data
decimal places (field property)
Dets no of dps displayed & printed in no. & Currency fields
input musk (field property)
Specifies pattern for all data to be entered in this field
caption (field property)
Supplies label for Access to use in forms & reports
default value (field property)
Assigns value that Access inserts into field in new records added to table
validation rule (field property)
Check data entered in field against set of criteria
validation text (field property)
Defines error msg that appears when you enter value prohibited by validation rule
required (field property)
Indicates that some data must be entered in field before record can be saved
allow zero length (field property)
Dets whether 0 length strings aren't valid entries
indexed (field property)
Creates index on field to speed up searches
datasheet view
where you enter, edit & modify records
5 alterations you can make in datasheet view
1. Change appearance of columns (hide, freeze, change font/adjust width, etc.)
2. Edit, delete, sort, filter records
3. Undo mistakes
4. Freeze fields
5. Save filtered records as query
first record button

Directly points user to 1st record of table
prev record button

Moves cursor to prev record
current record
Displays no of currently active record out of total no of records in table
next record button

Moves cursor to next record
last record button

Directly points user to last record
new record button

Adds new record to table
database terms
Entity = object that makes up part of data (ex. person, song, book)
Attribute = descrs entity; distinguishing entities of same type
(ex. person's name, author, movie title)
Table = collection of entities/things
Column = vertical collection of attributes/fields
Row = horizontal collection of related info/entities (aka database record)
2 rules to follow when forming relos betw tables in DB
1. data type of PKs & Foreign Keys must be same
2. field properties of PKs & Foreign Keys must be same
sorting data
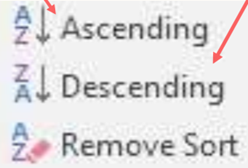
feature that enables users to arrange & display records in datasheet (either in Ascending/Descending order)
filtering records

To extract specific info from 1 specific table
Fastest way to view group of related records when working on 1 table
Save Filter as Query
3 filtering options
filter by selection

advanced filter/sort

filter by form

queries
way to Q DB/extract specific info from 1/more tables
result = "dynaset"

steps in query design view
Identify key fields & criteria listed in Q
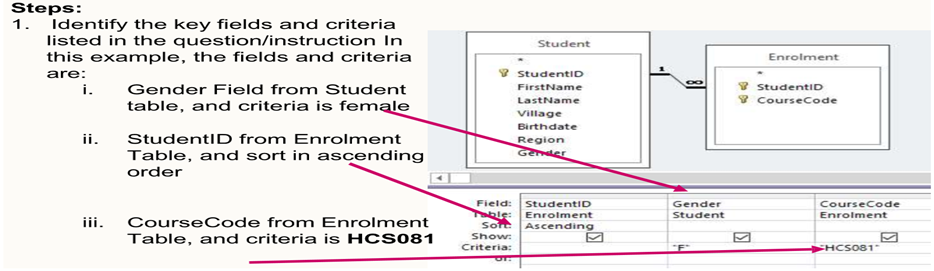
3 types of queries
1. Select Query = extract data from tables based on criteria
2. Action Query = perform action on records that meet criteria
3. Union Query = combines fields from 2/more tables
forms
feature used to enter, modify & view records
data entry & maintenance easier than using tables
4 types of forms

5 form advantages
- Displays 1 record at time
- Can contain graphs / images
- Rearrange fields
- Can contain fields from >1 table
- special field display functions
report
Present data from tables & queries in easy to read format
report wizard + pre-designed report options
Best option to create simple report
Offers pre-designed report options:
1. Single Column
2. Groups/total
3. Mailing Label
4. Summary
5. Tabular
altg, database should have: (4)
1. Tables
a. Relationships
2. Queries
3. Forms
4. Reports
form design
you have options to choose which field(s) to be incl in object
columnar
layout option for 1 of DB objects (report)
which is not a DB object: report wizard, table, form, query
= report wizard
attribute that best descr diff betw relational & flat line DB
= PK