Lecture 4 - Orbit
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
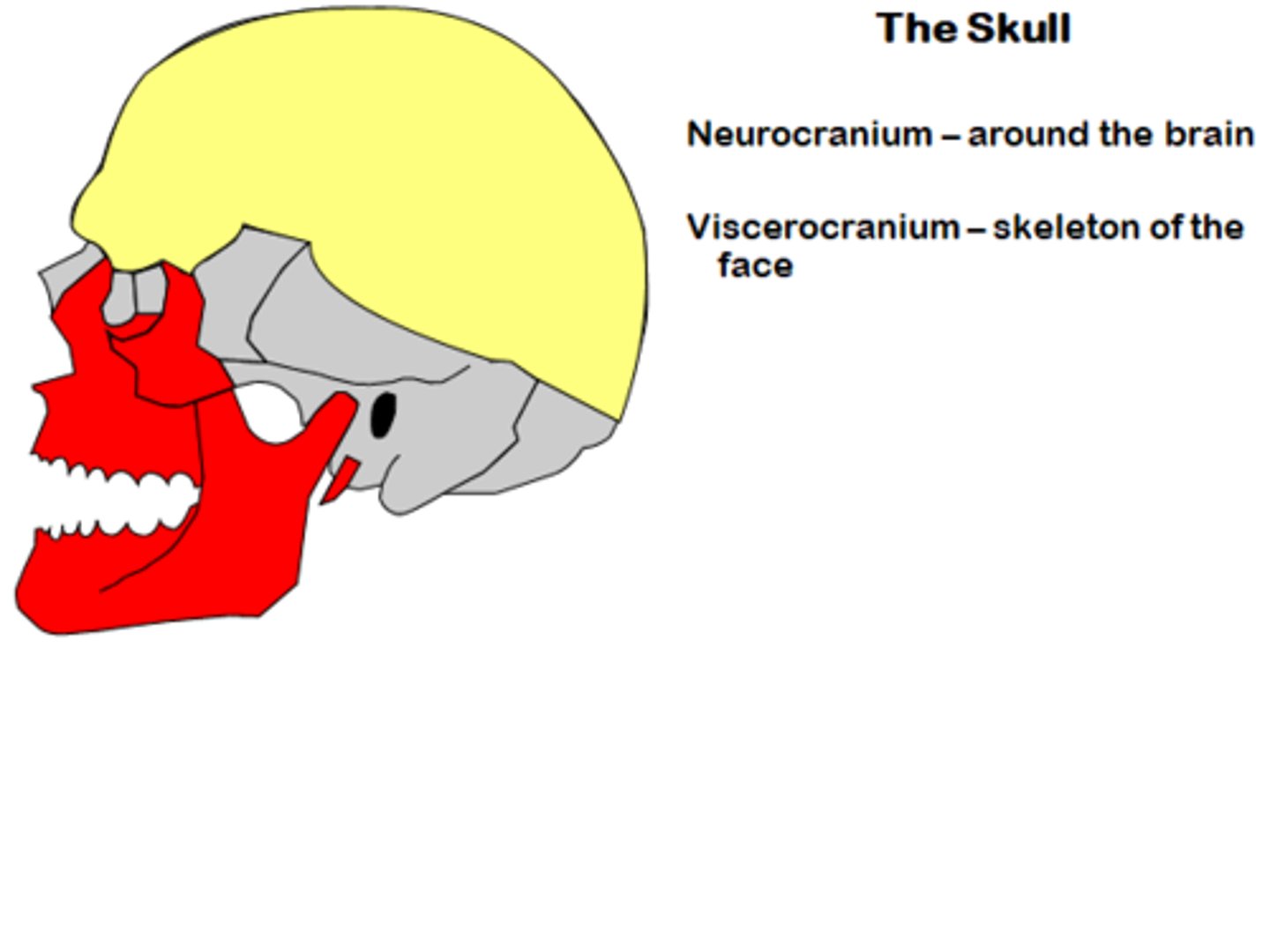
What are the two parts of the skull?
Cranium and Face.
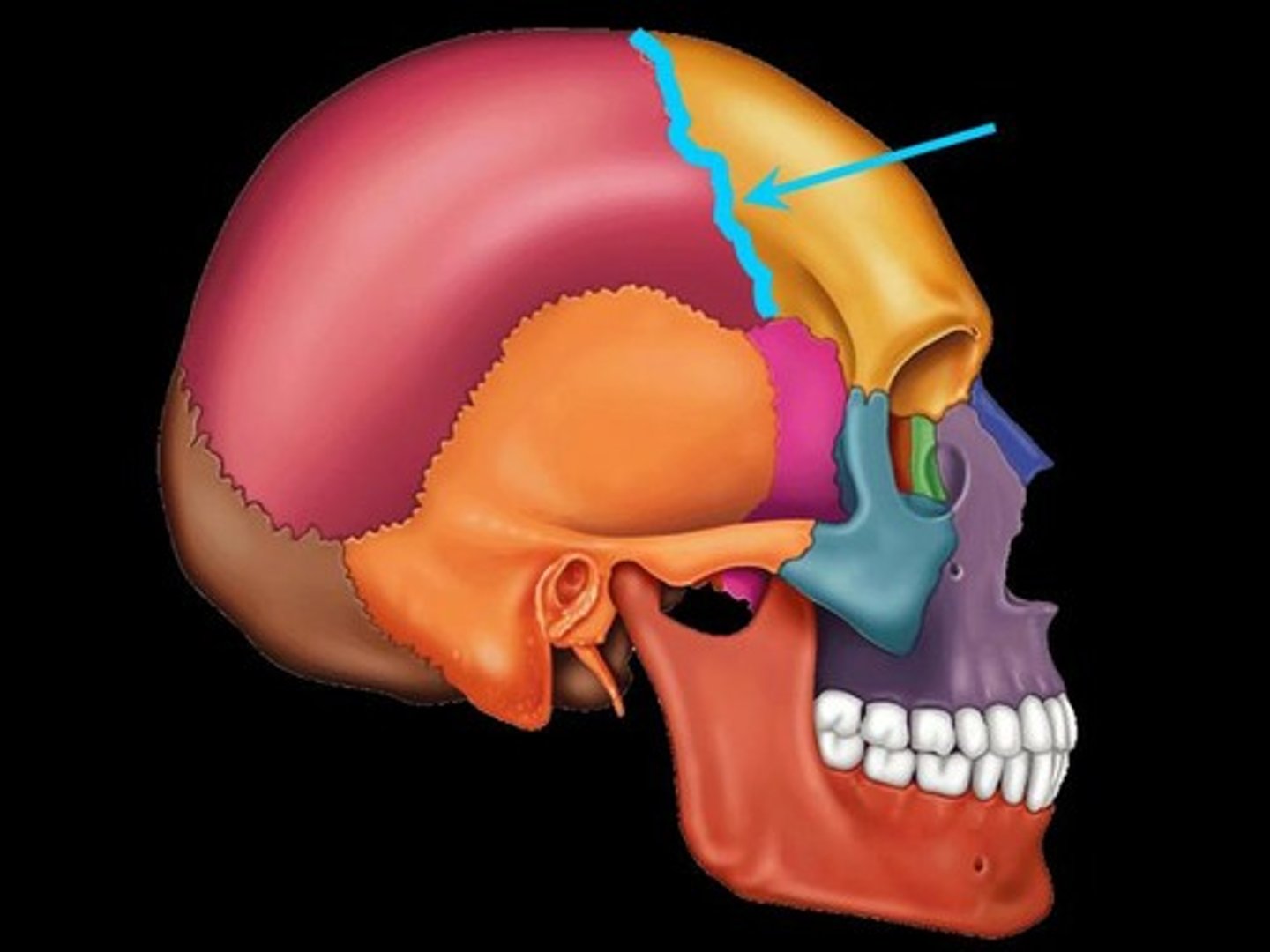
How do most skull bones unite?
At sutures that form immovable joints.
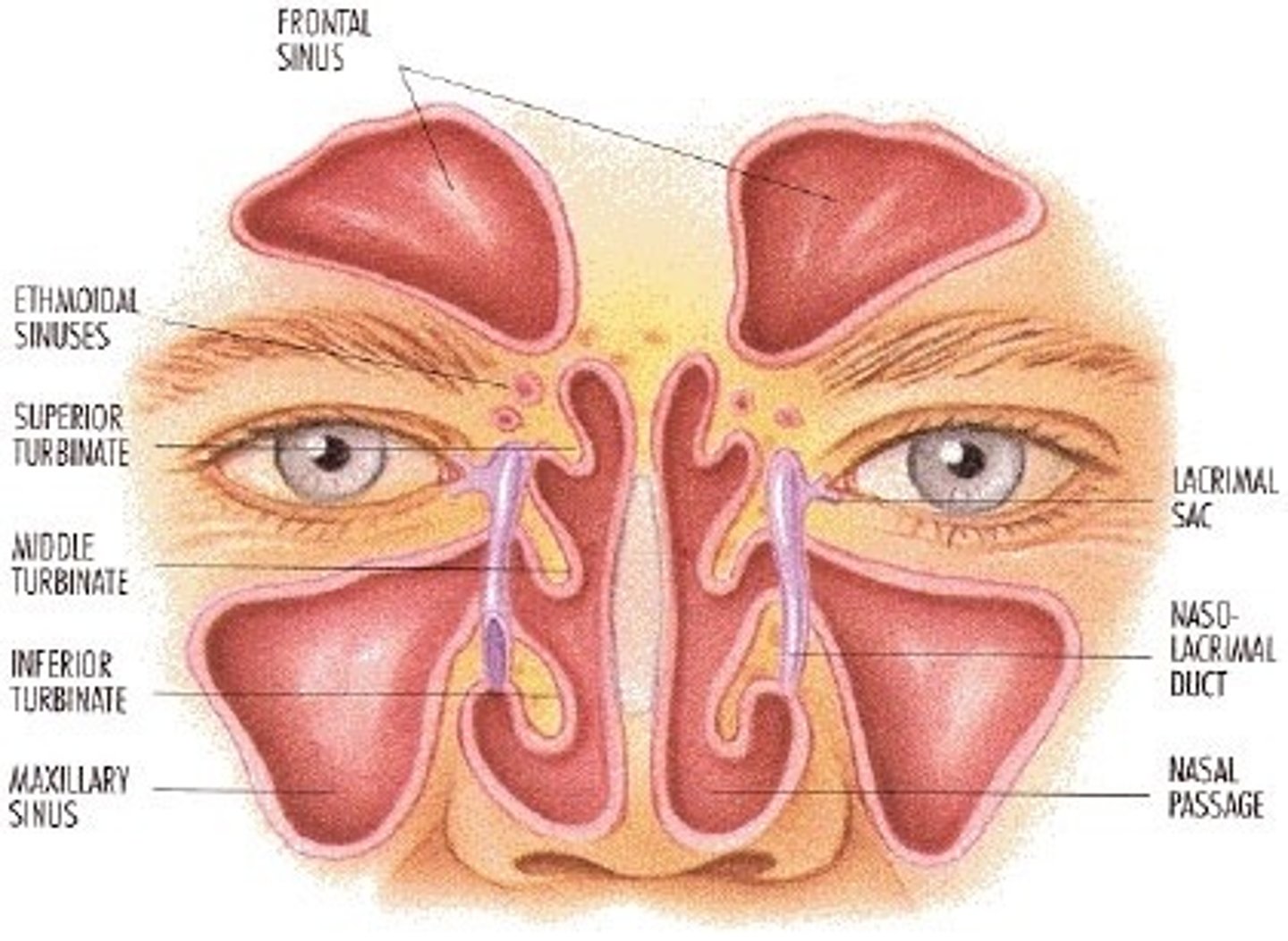
What are sinuses?
Air-filled cavities within several bones.
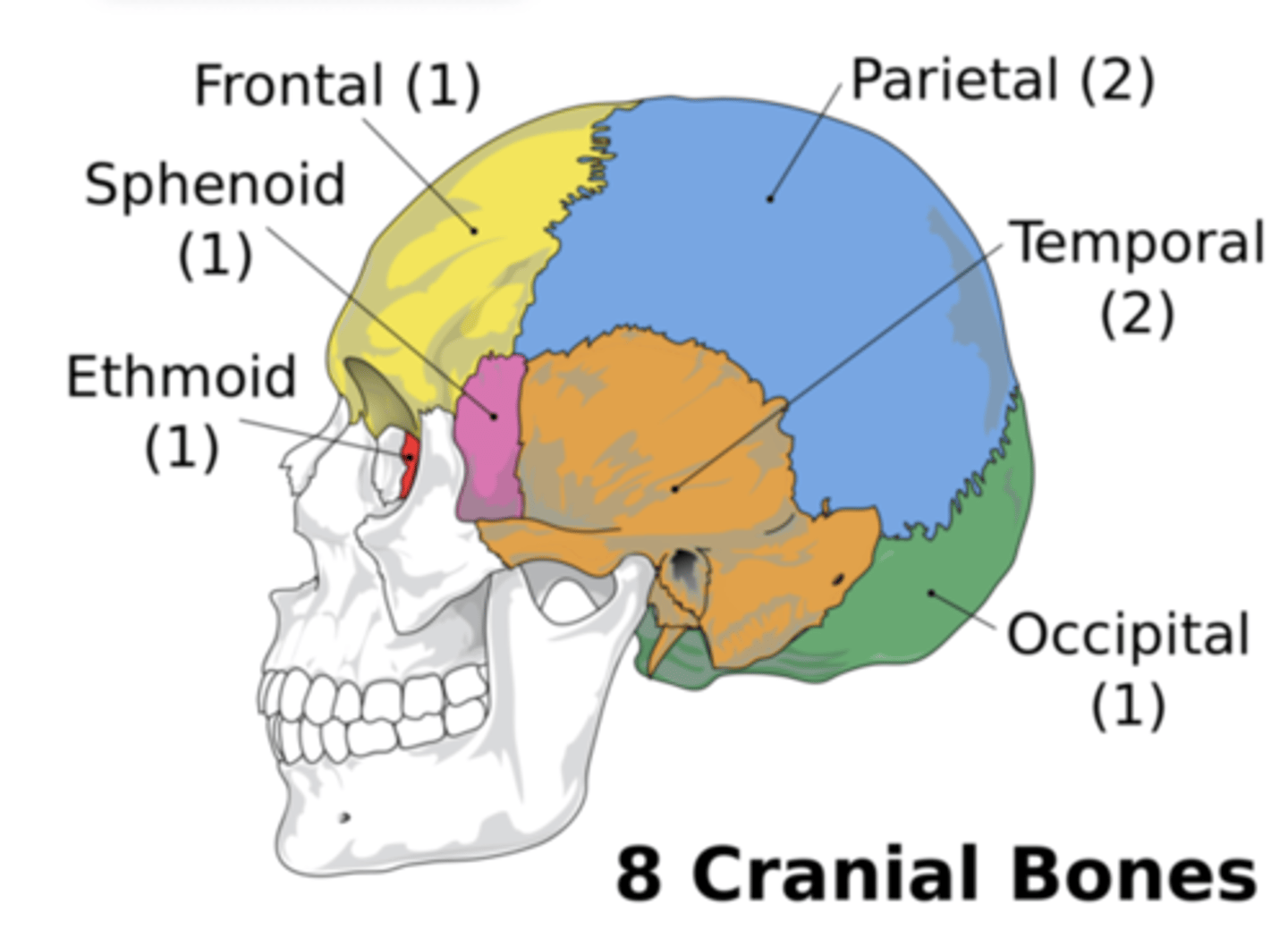
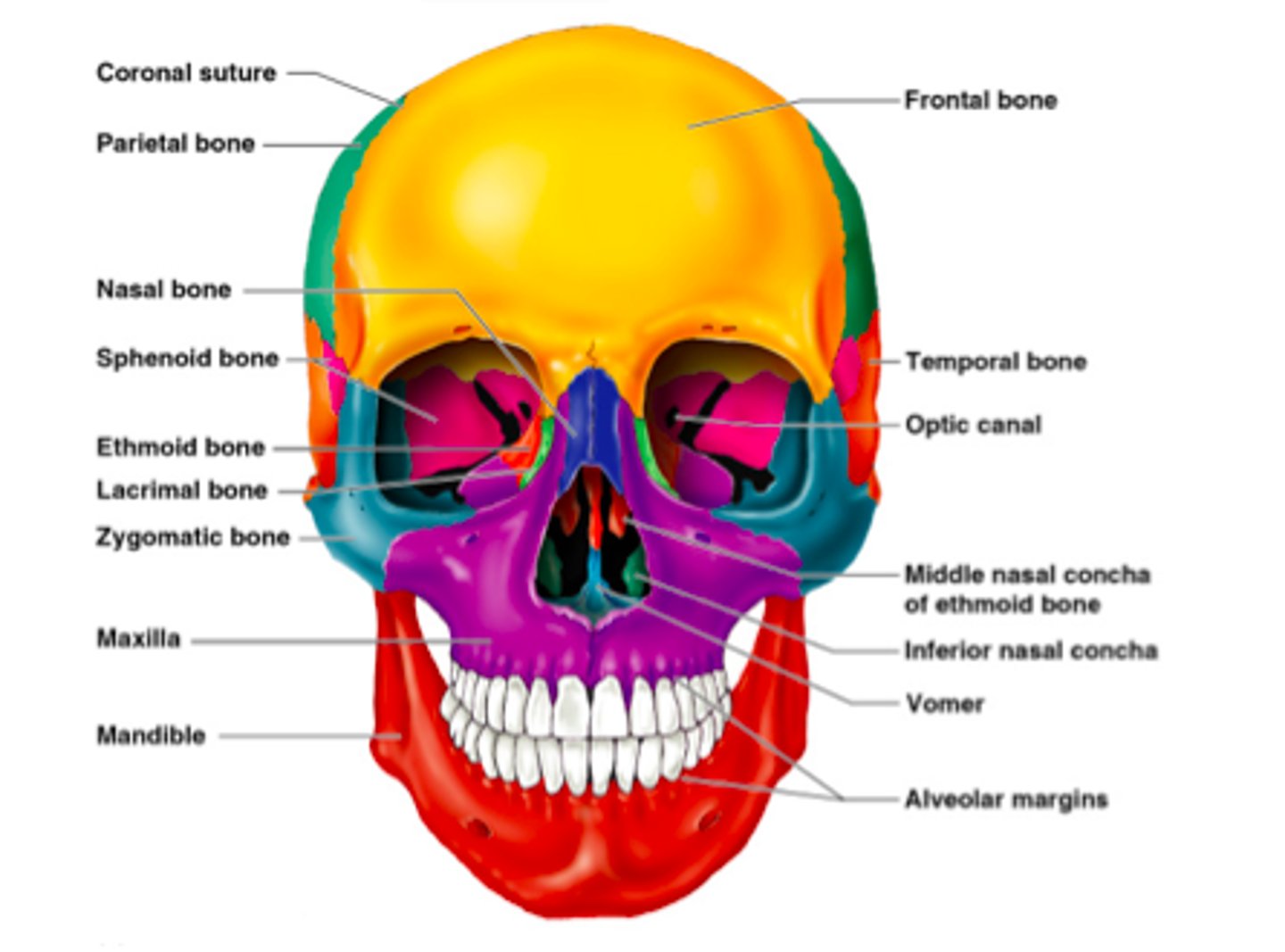
What bones make up the cranium?
Parietal (2), Occipital, Temporal (2), Sphenoid, Ethmoid.
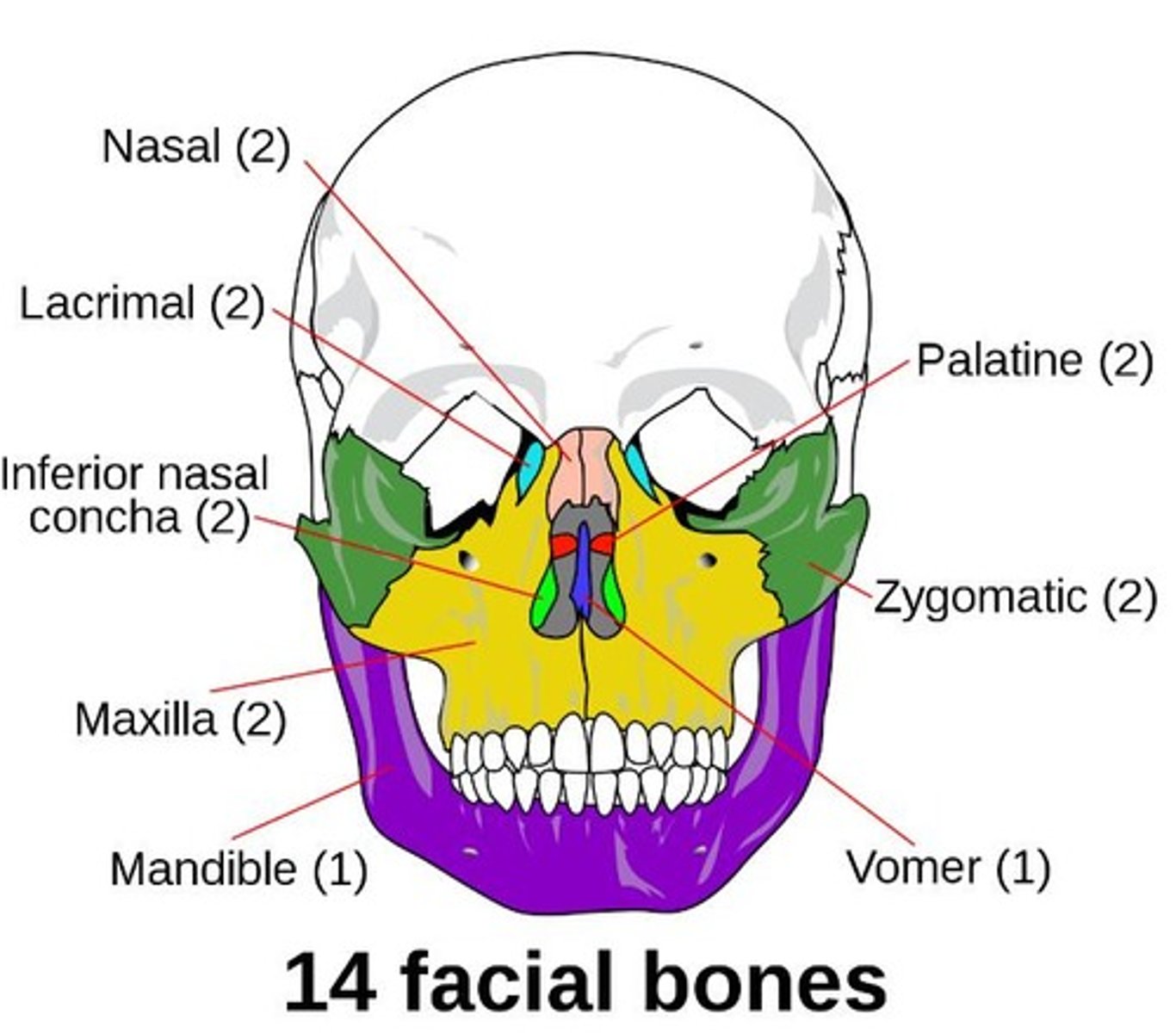
What bones make up the face?
Frontal, Maxilla (2), Nasal (2), Vomer, Inferior conchae, Lacrimal (2), Palatine (2), Zygomatic (2), Mandible.
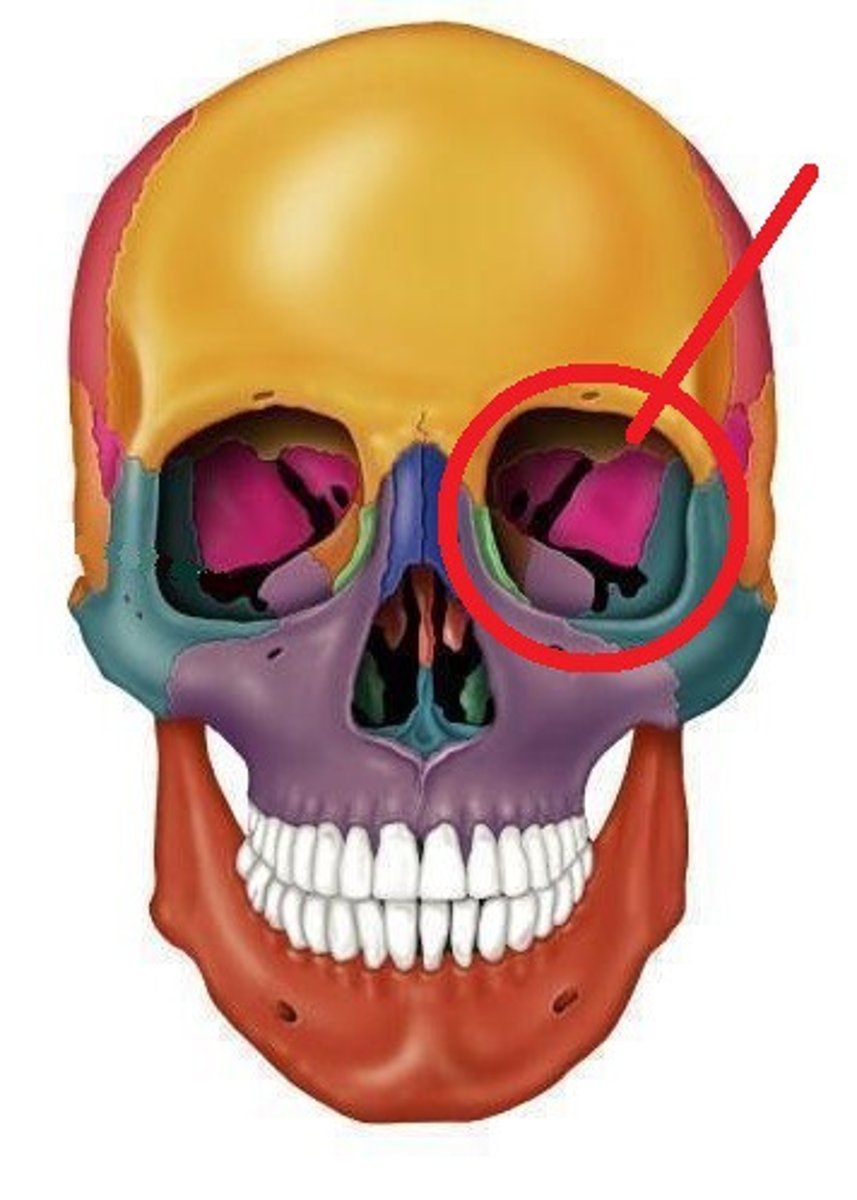
What is the orbit?
Bony cavities in the skull that protect the eyes and adnexa.
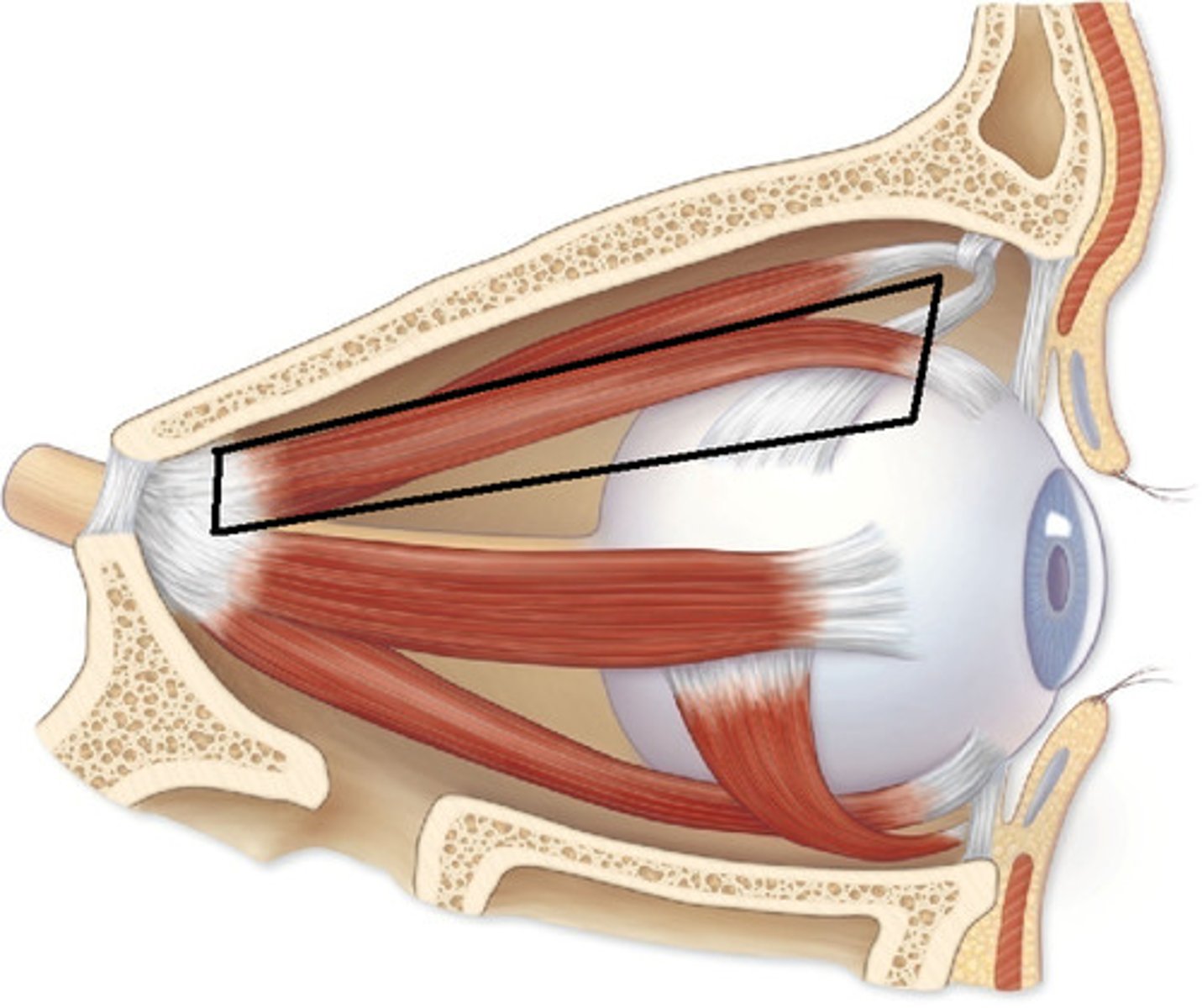
What structures are contained in the orbit?
Globes, extra ocular muscles, orbital nerves, blood vessels, connective tissue, adipose tissue.
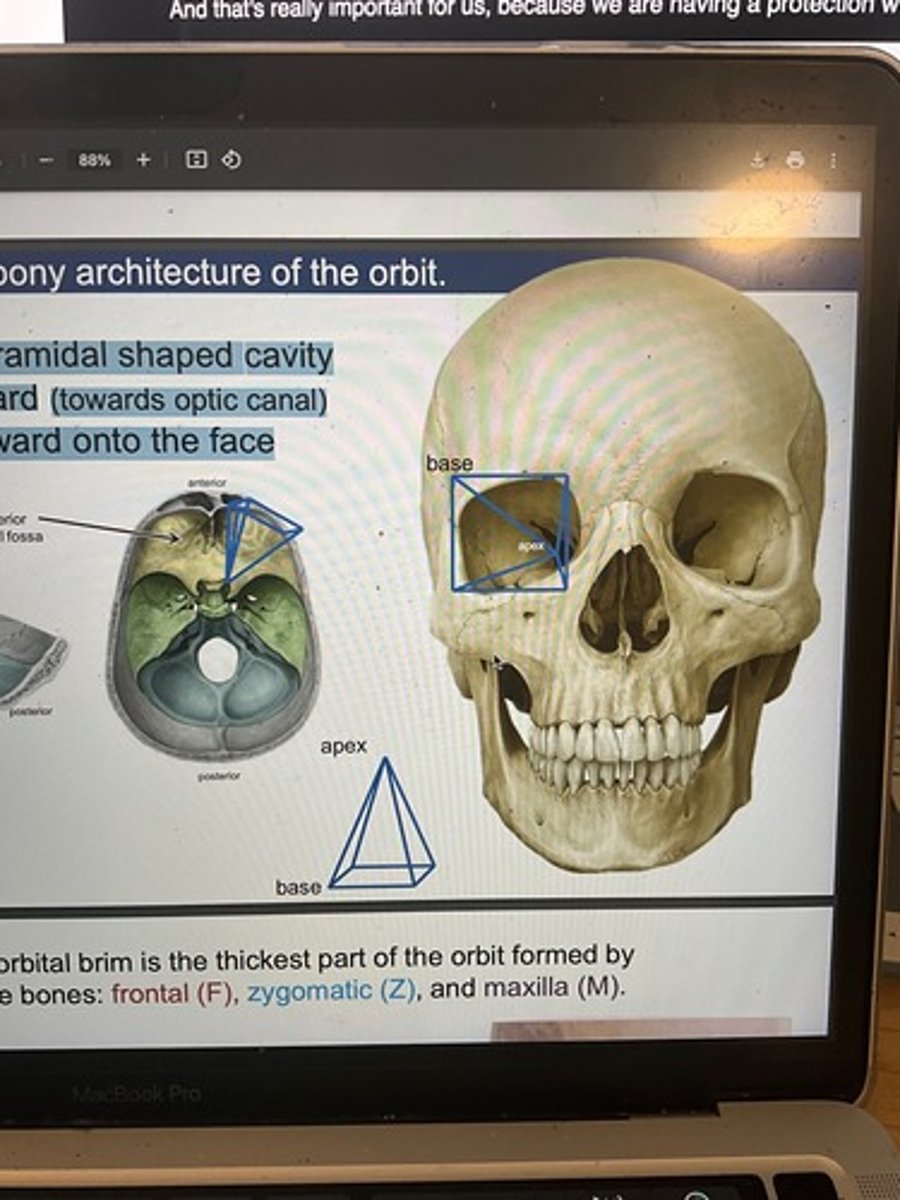
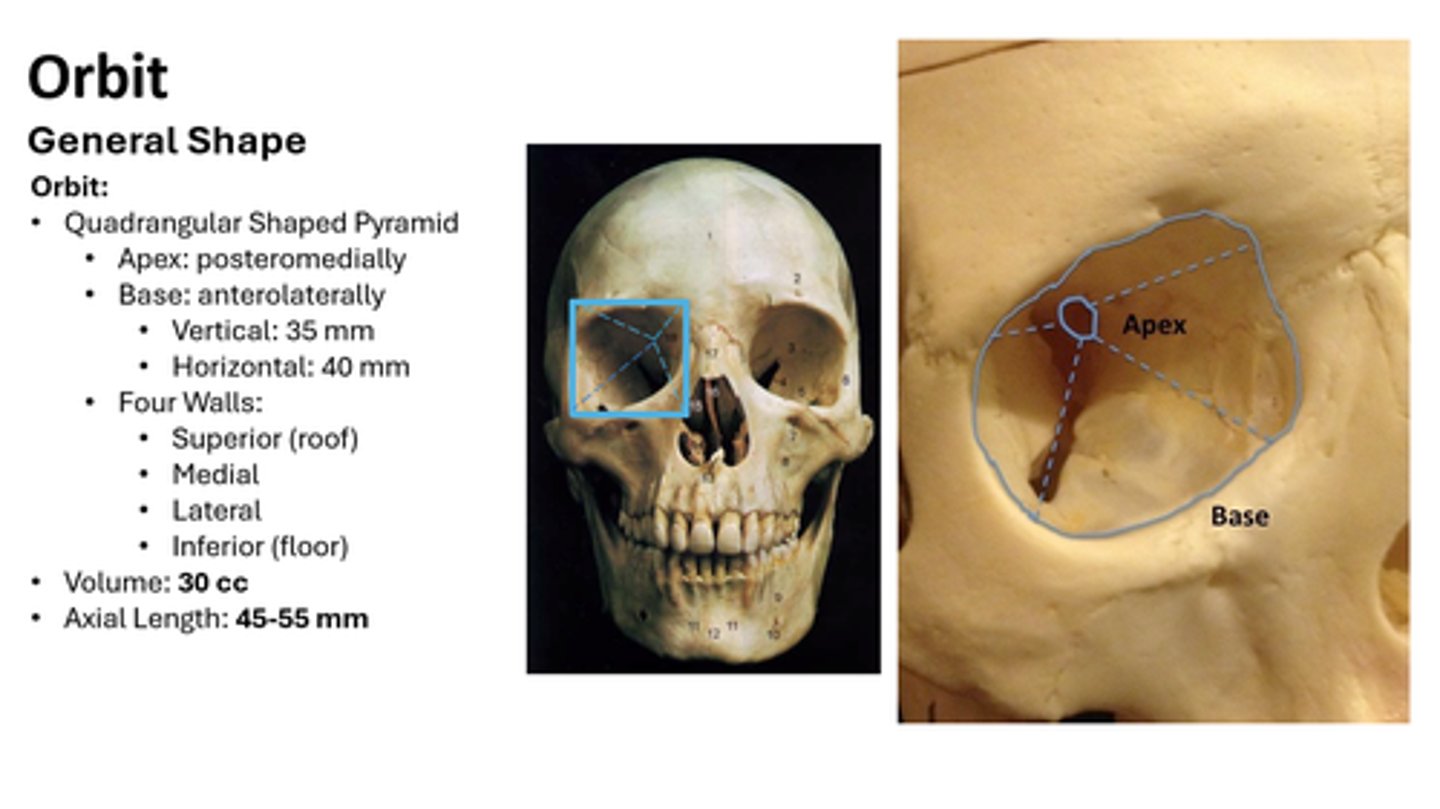
What is the shape of the orbit?
Four-sided pyramid with base at anterior margin, apex posterior.
What are the orbital dimensions?
Height = 35-40 mm, Width = 40-45 mm, Depth = 40-50 mm.
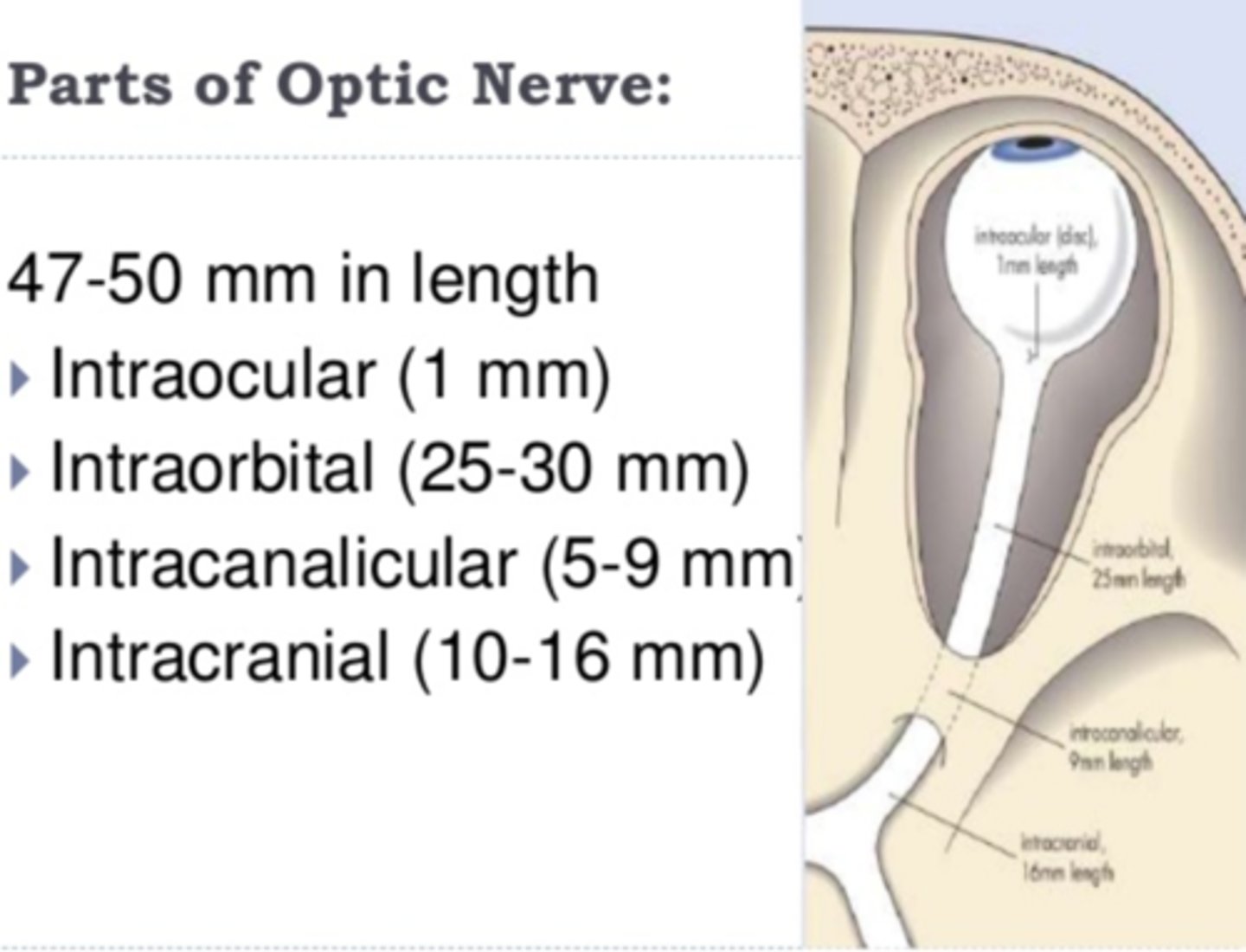
What is the intraorbital optic nerve length and why is it curved?
25-30 mm, curved to allow eye movement without stretching the nerve.
Distance from posterior globe to optic foramen?
18-20 mm.
Volume of orbit vs. eye?
Orbit = 30 ml, Eye = 6.5-7.5 ml.
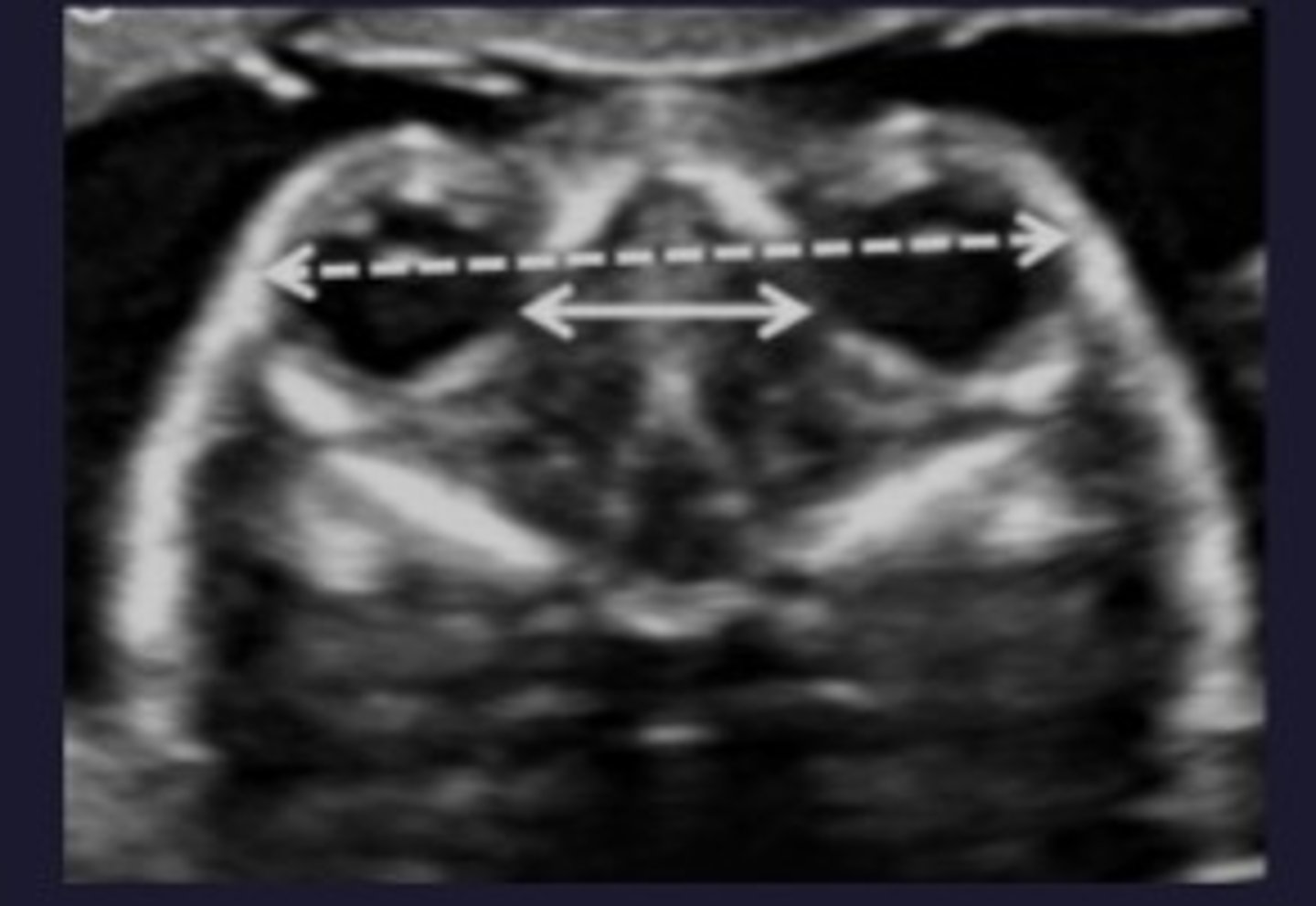
Interorbital distance?
25-35 mm (between medial orbital walls).
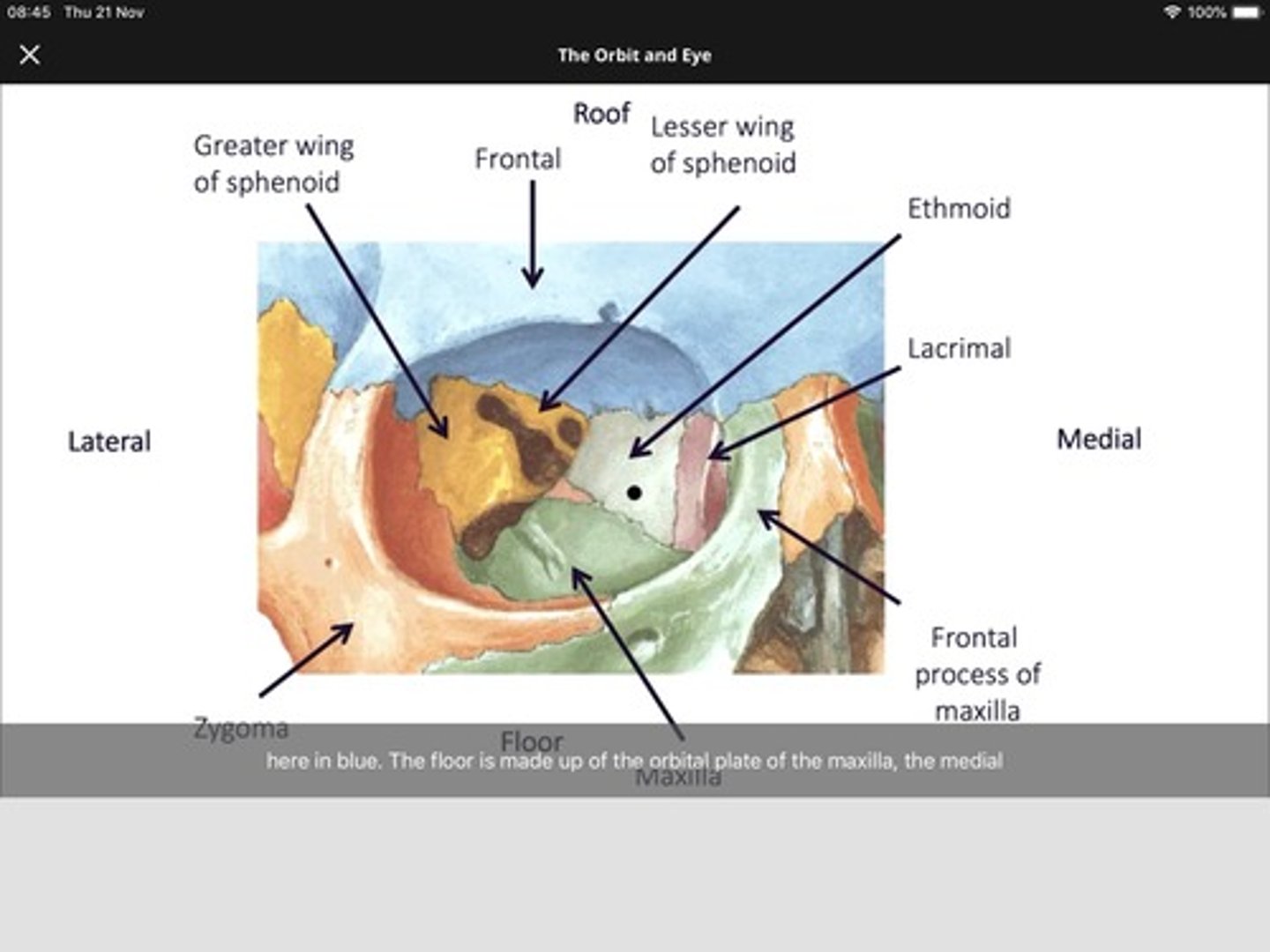
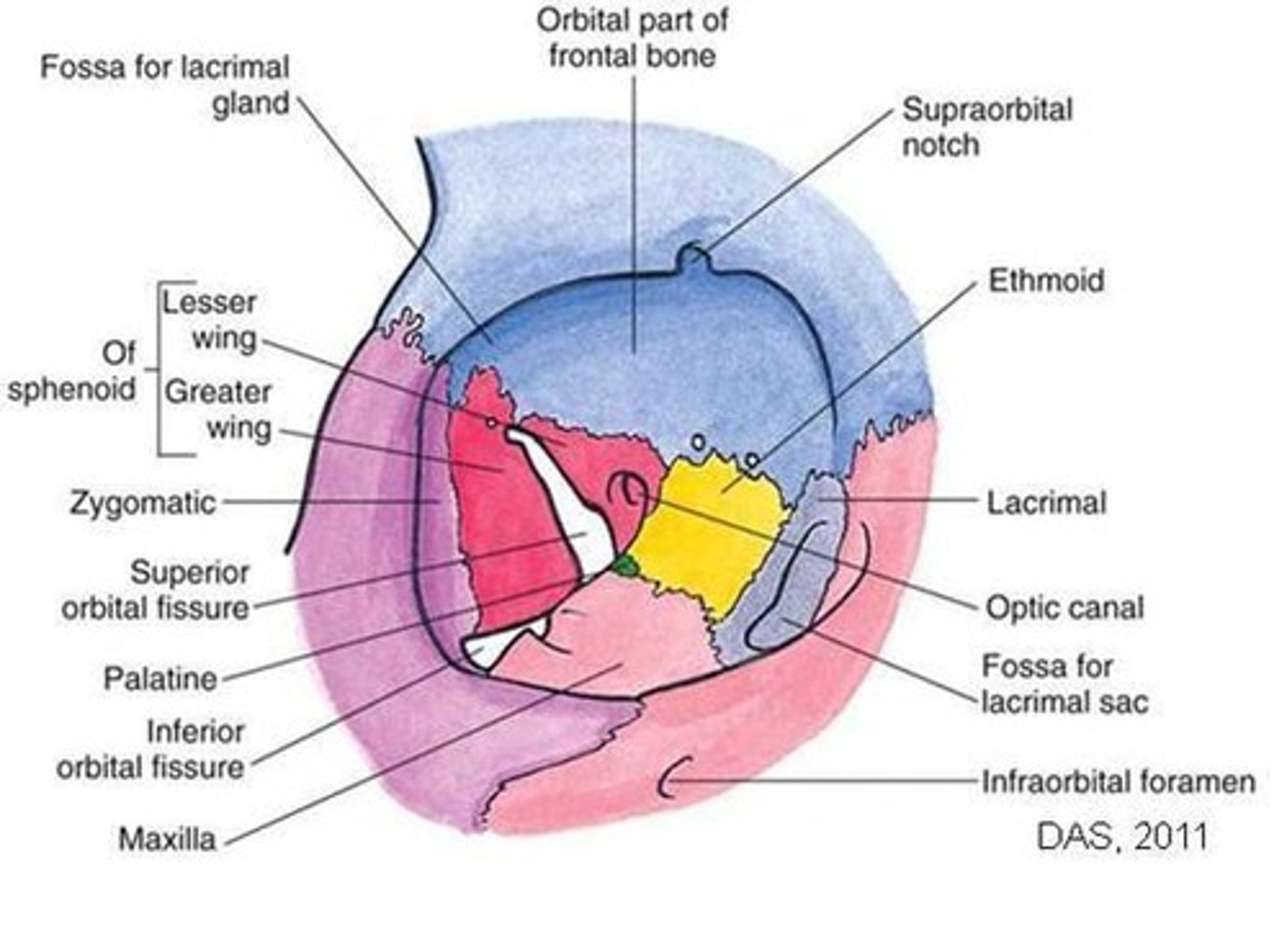
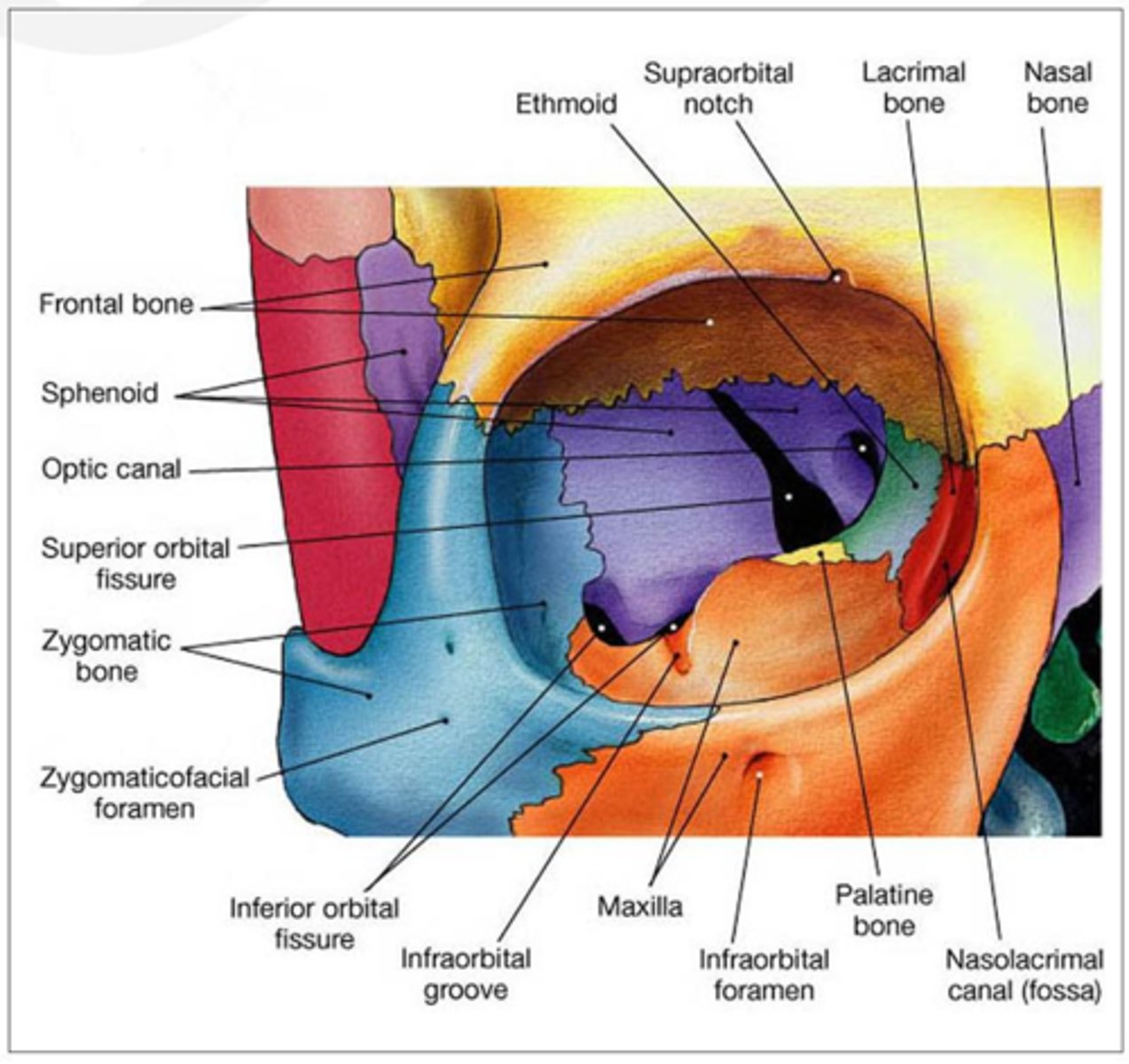
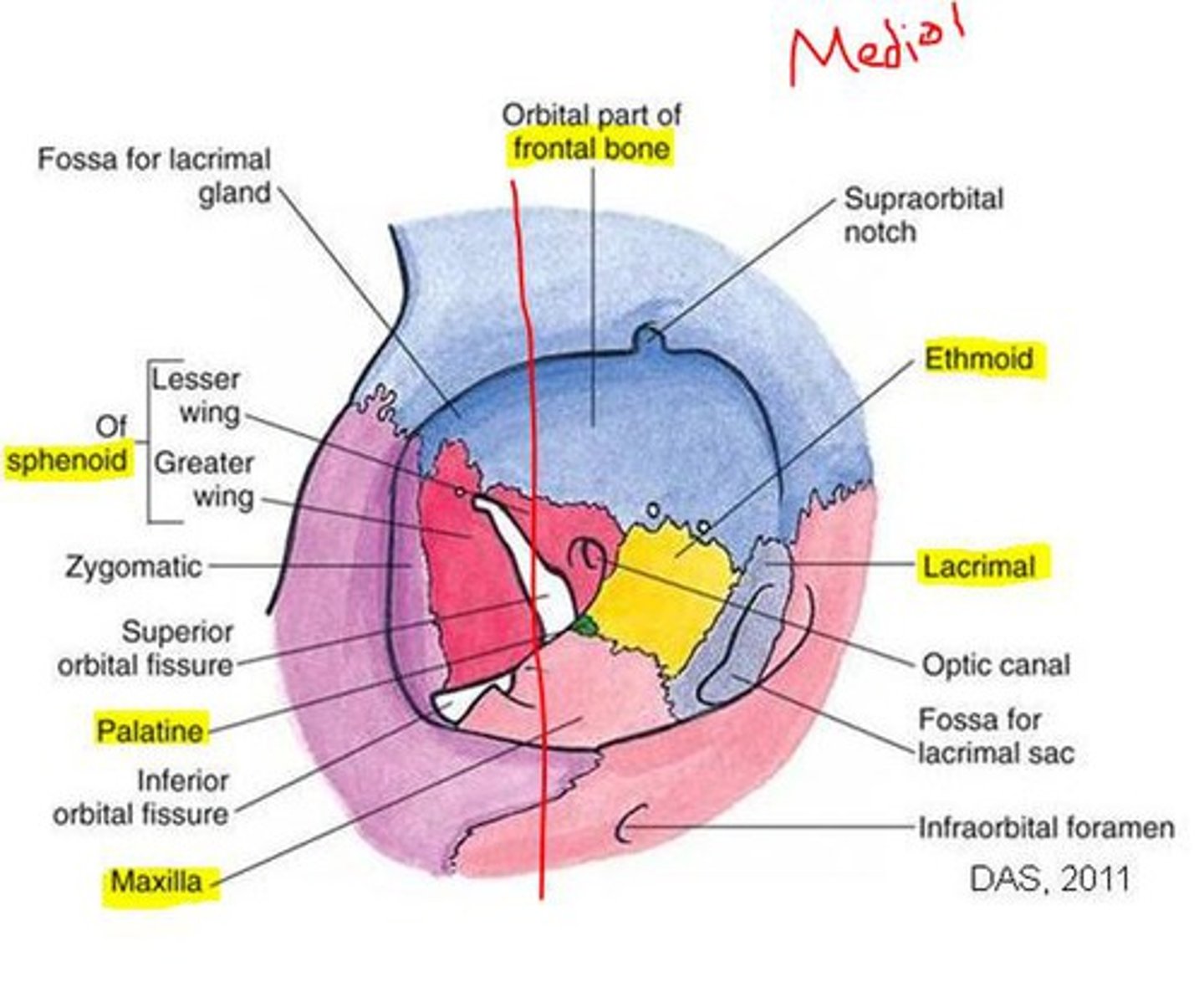
What are the four orbital walls?
Roof, Floor, Medial, Lateral.
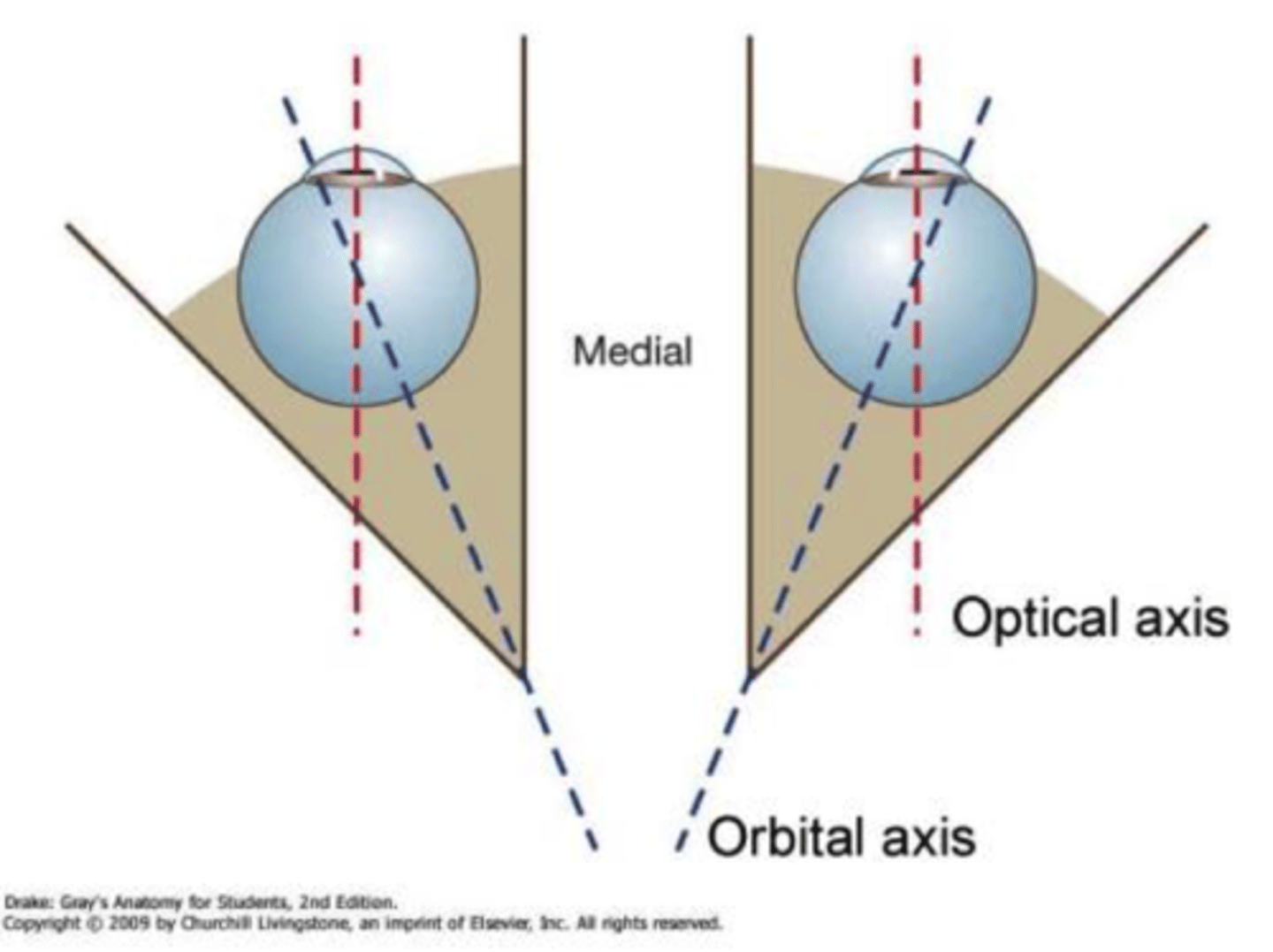
Orientation of medial and lateral walls?
Medial walls parallel to sagittal plane; lateral walls ~90° angle.
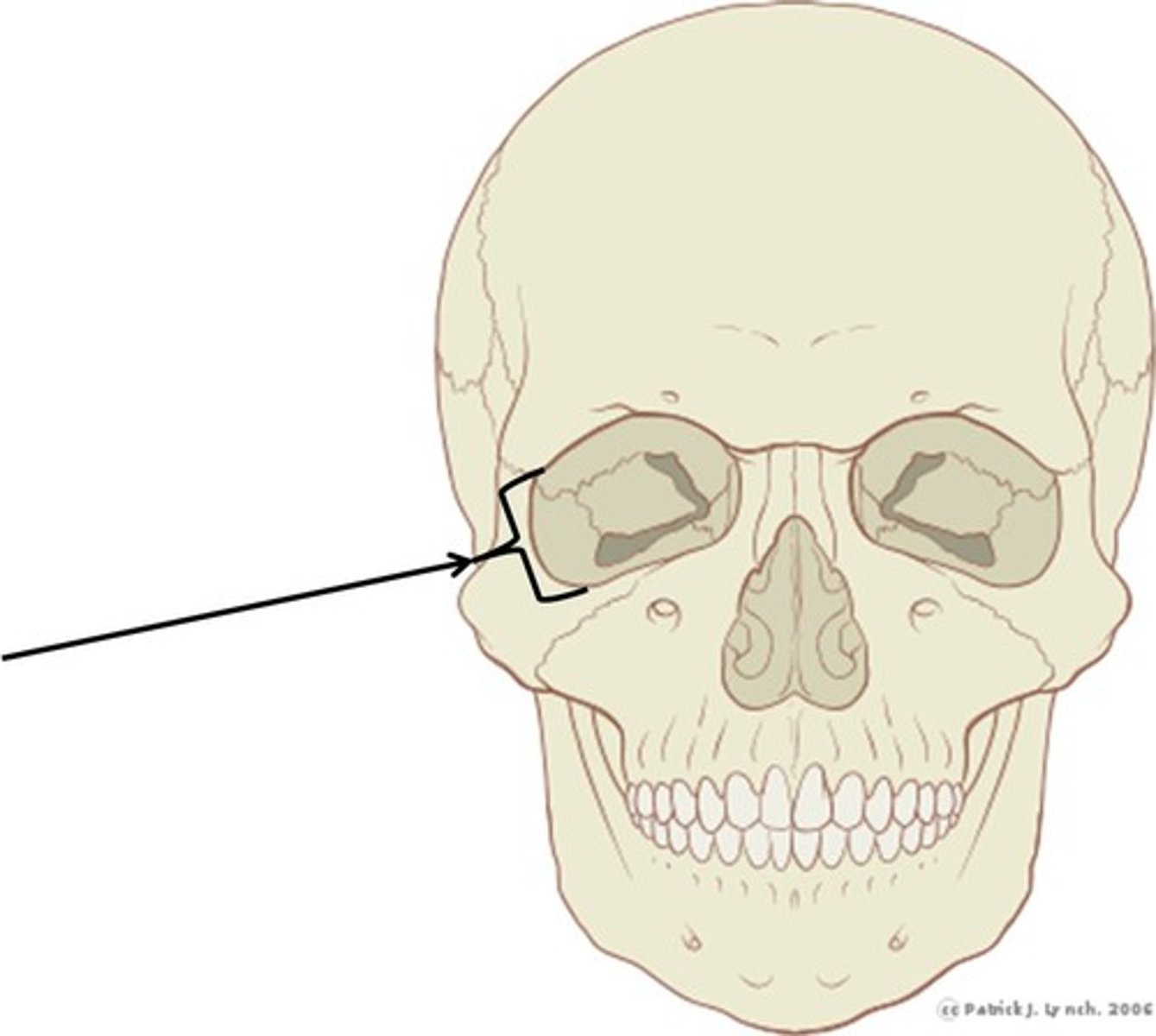
Orbital rims
Thicker than orbital walls; 40-60% of facial fractures involve them.
How many bones make up each orbit?
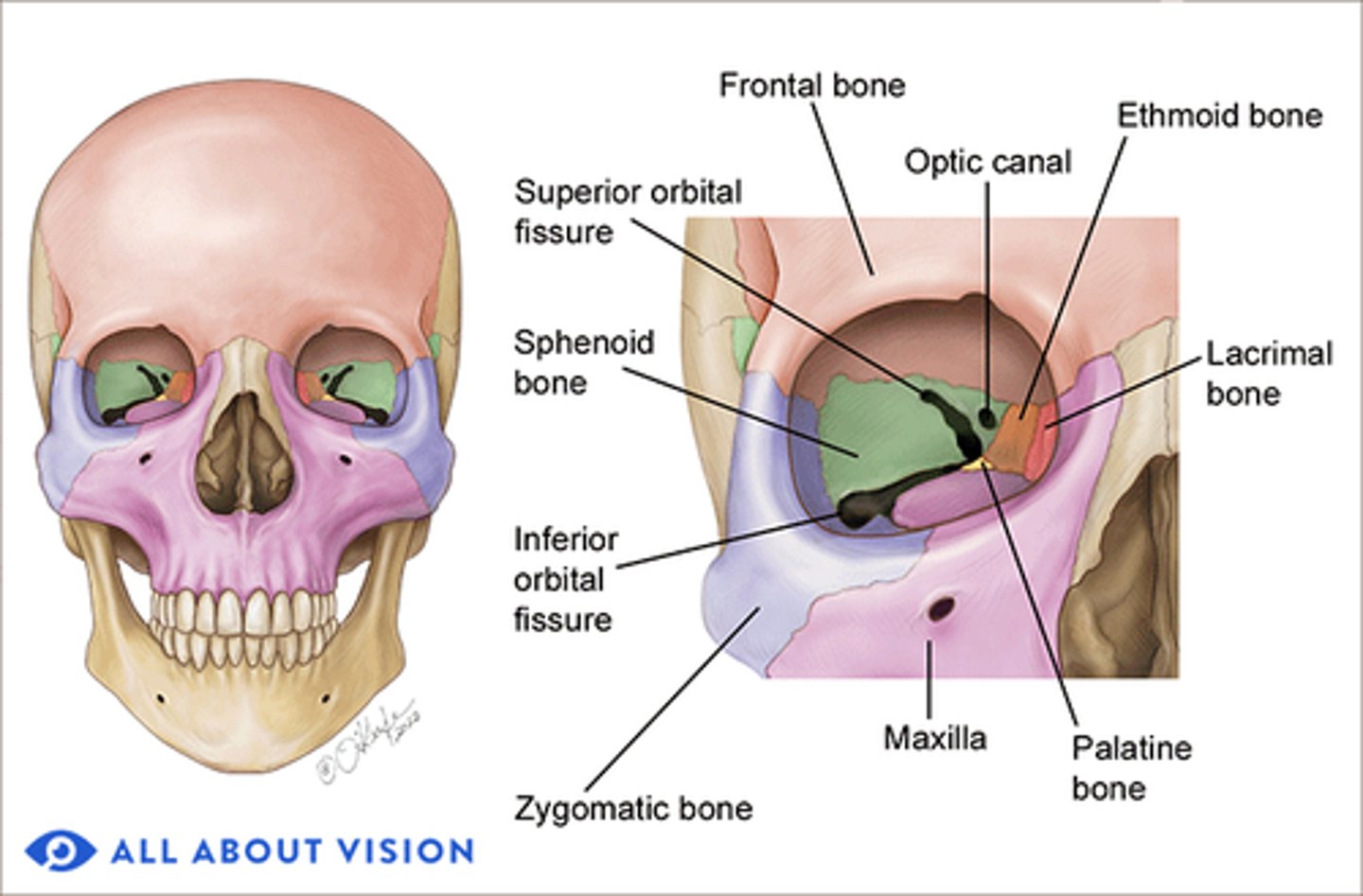
7 bones: Frontal, Maxilla, Zygomatic, Sphenoid, Ethmoid, Palatine, Lacrimal.
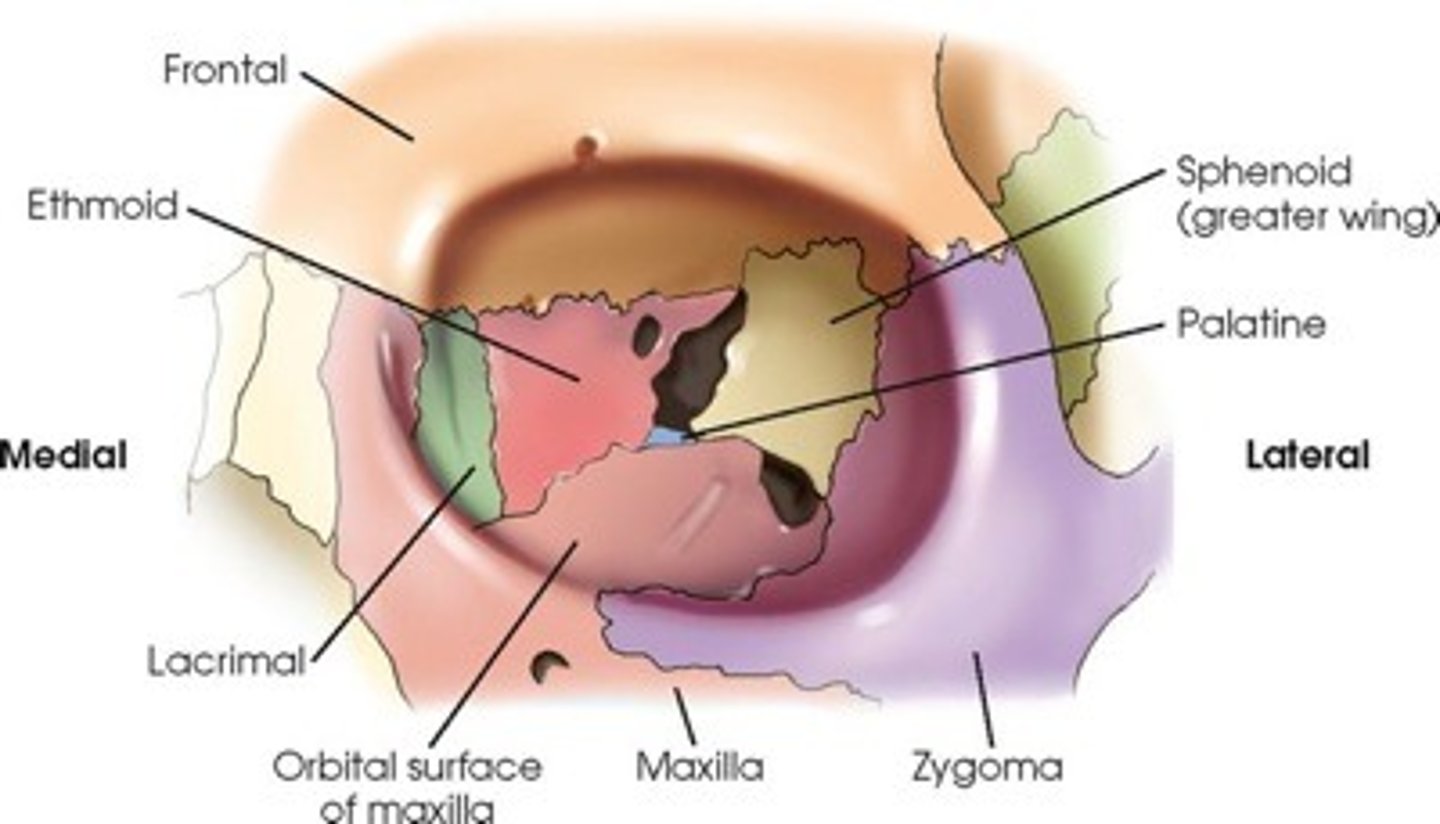
Which bones contribute to both orbits?
Frontal, Sphenoid, Ethmoid.
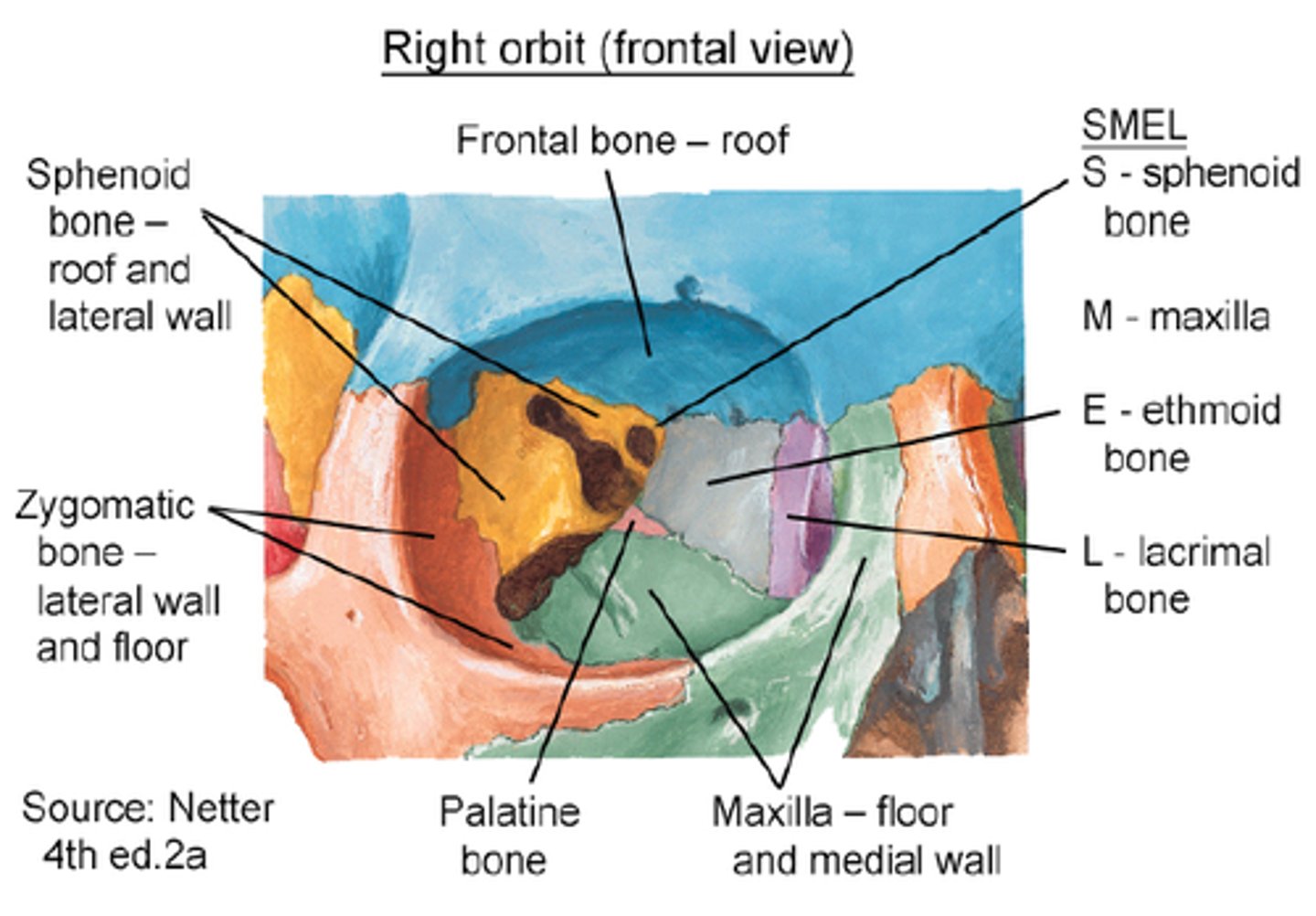
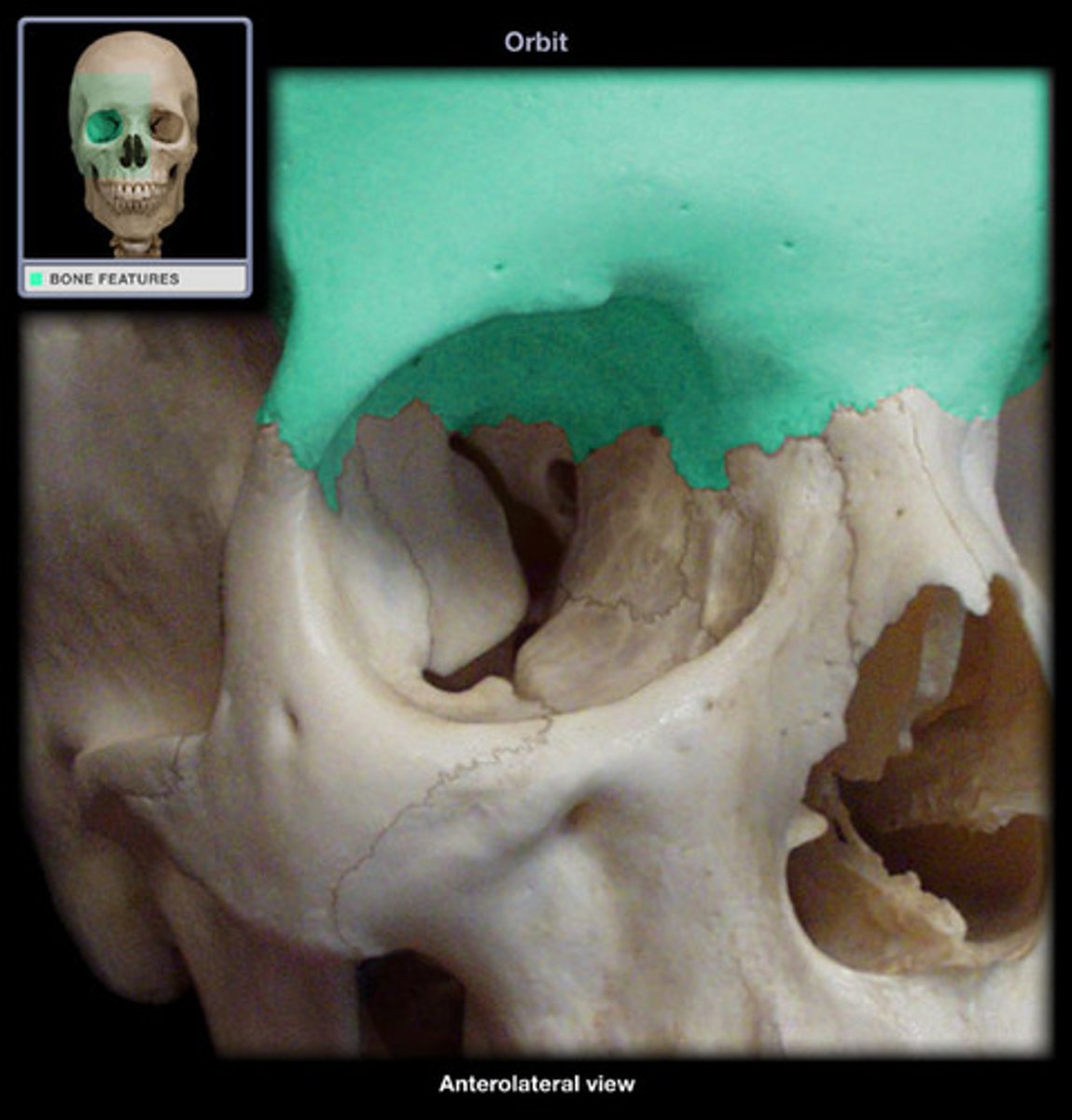
What bones make up the orbital roof?
Orbital plate of frontal bone (anterior), Lesser wing of sphenoid (posterior).
- orbital roof is triangular
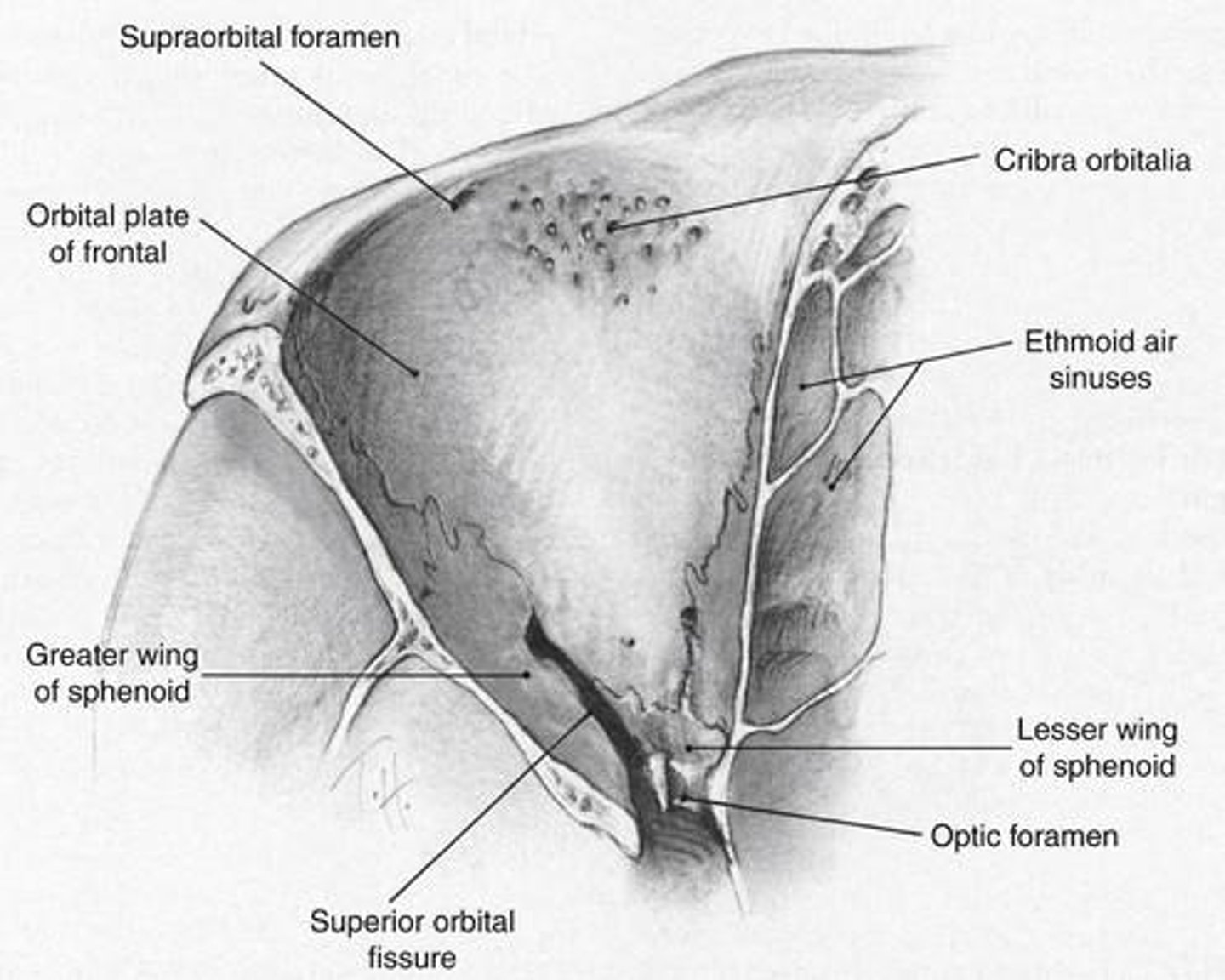
What structures are associated with the orbital roof?
Frontal bone: Lacrimal gland fossa, trochlea attachment
Lesser wing of sphenoid: optic canal.
What does the orbital roof separate?
Separates the orbit from the frontal sinus and the anterior cranial fossa (protects against spread of infection).
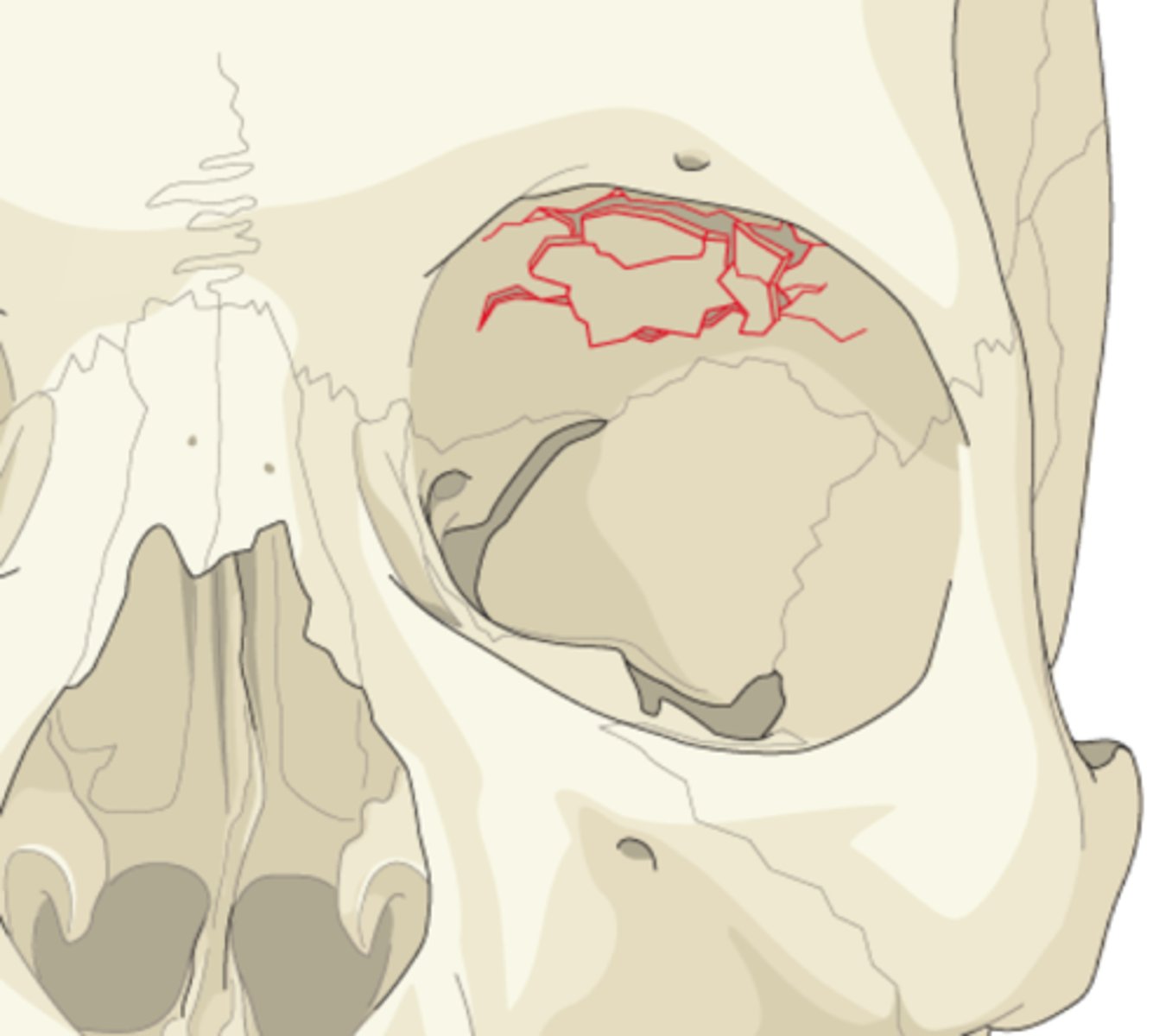
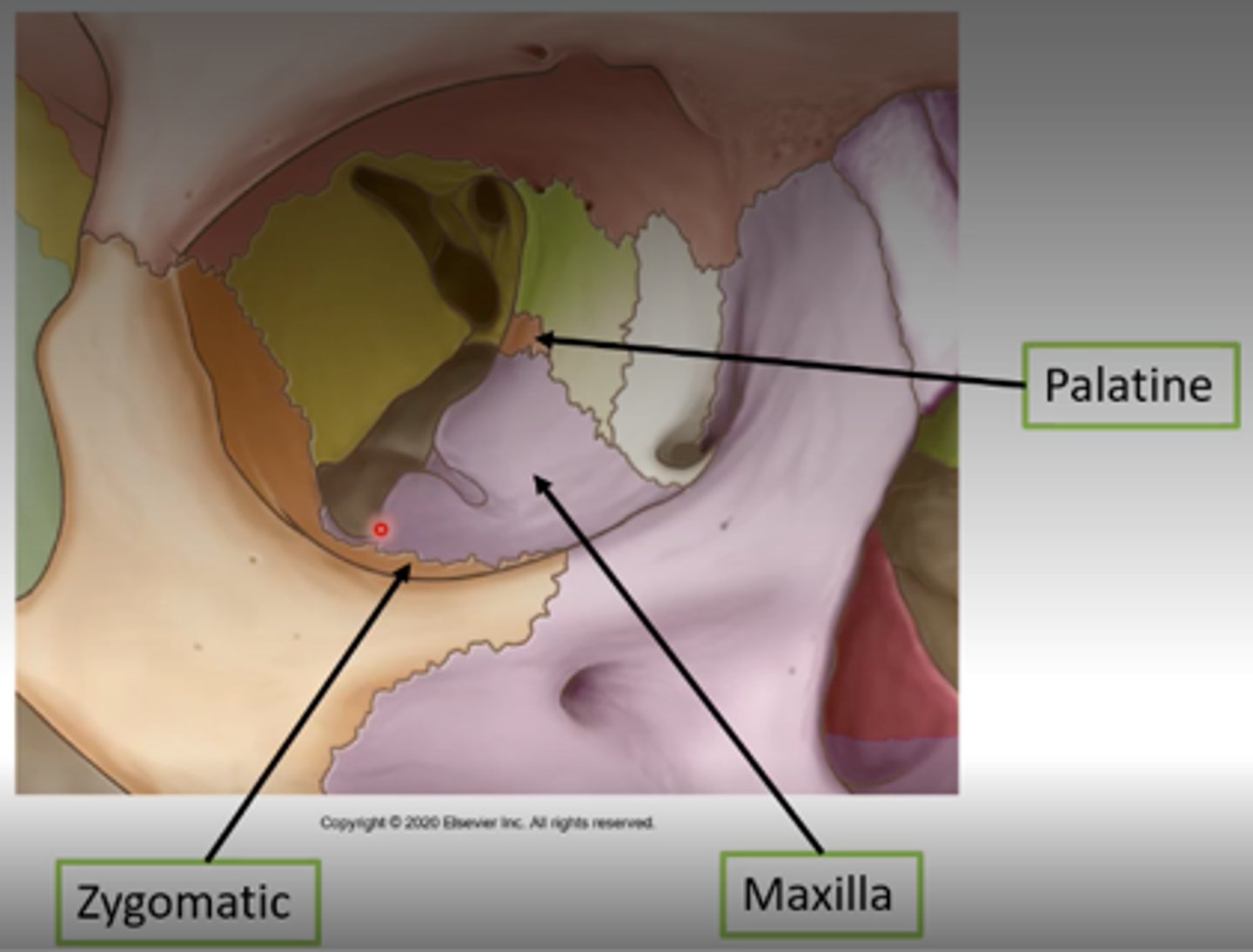
What bones make up the orbital floor?
Maxillary (largest), Zygomatic, Palatine.
Clinical importance of orbital floor?
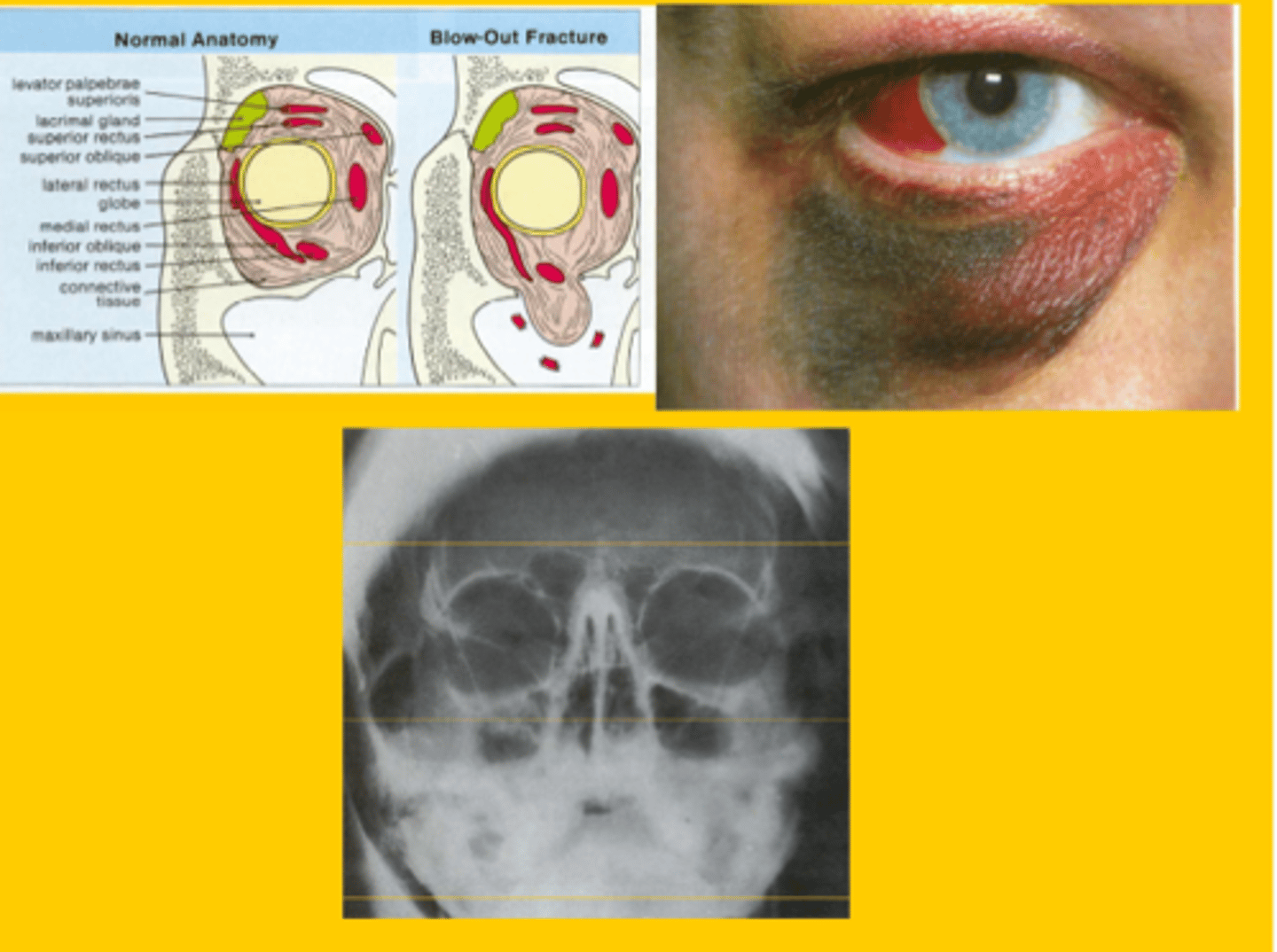
Weakest area → common site of "blow-out" fractures at infraorbital canal.
What separates the floor from the lateral wall?
Inferior orbital fissure.
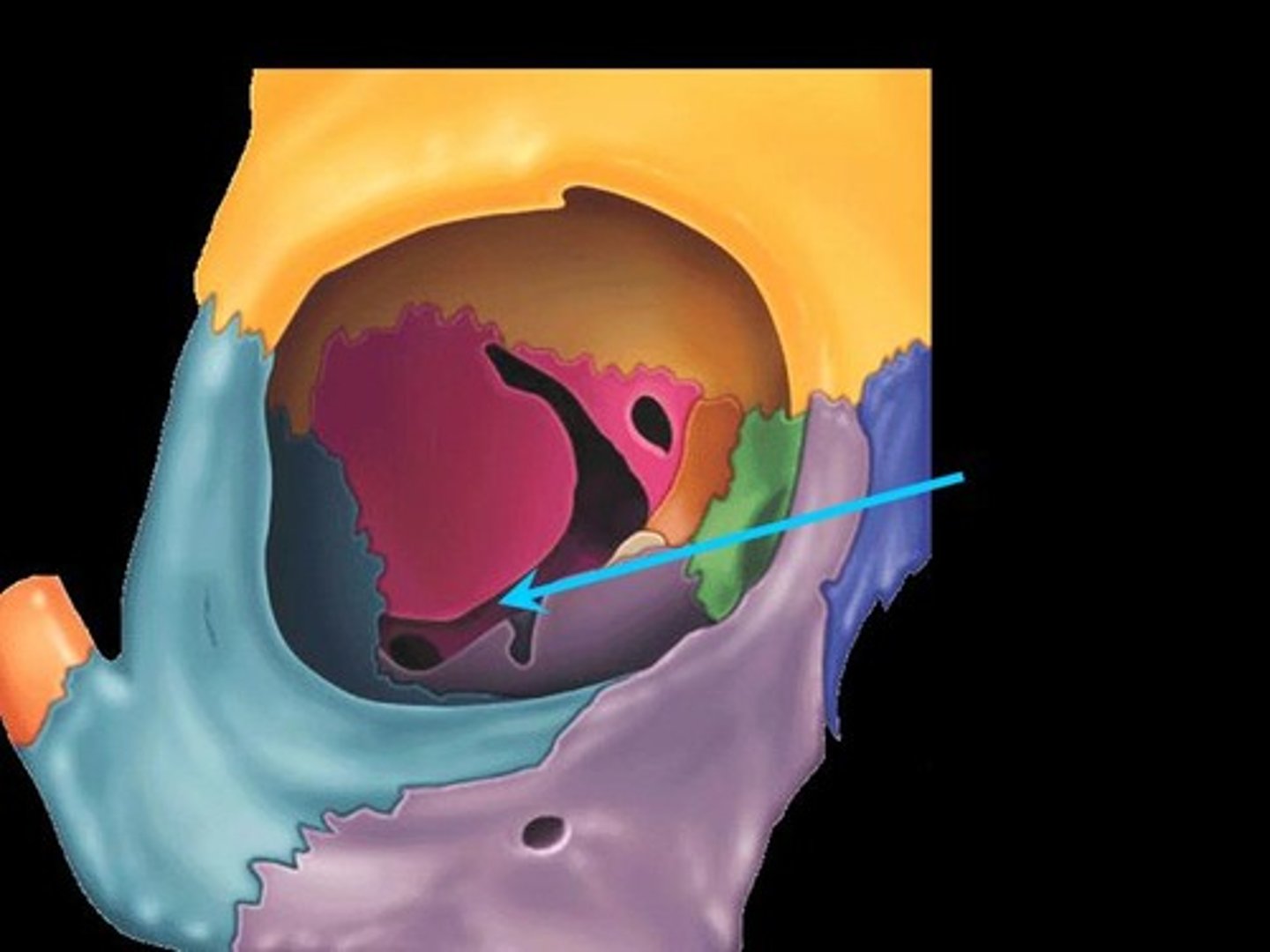
What structures are related to the infraorbital foramen?
Infraorbital nerve, artery, and vein.
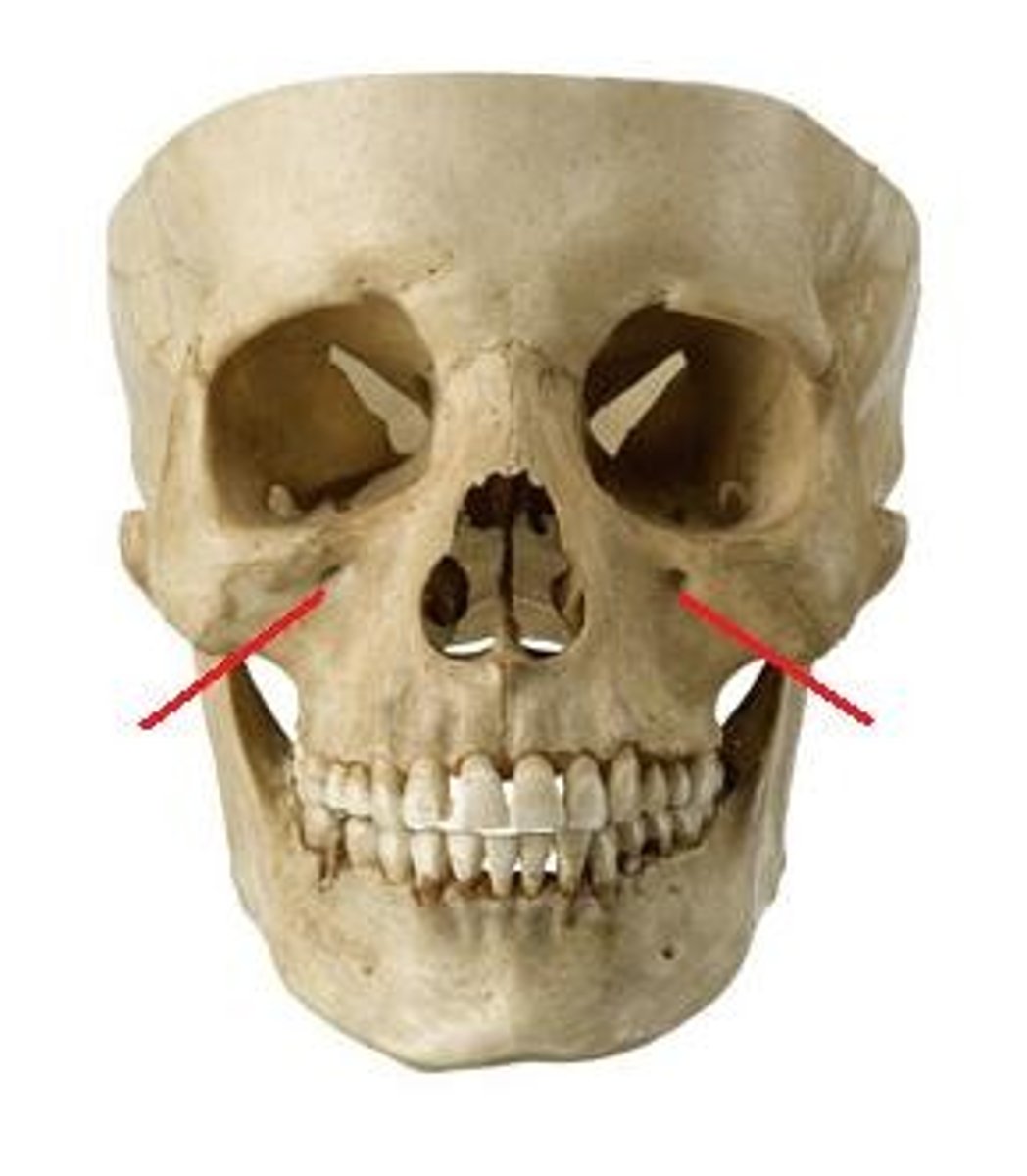
Most common fracture site of the orbit?
Floor (along infraorbital canal).
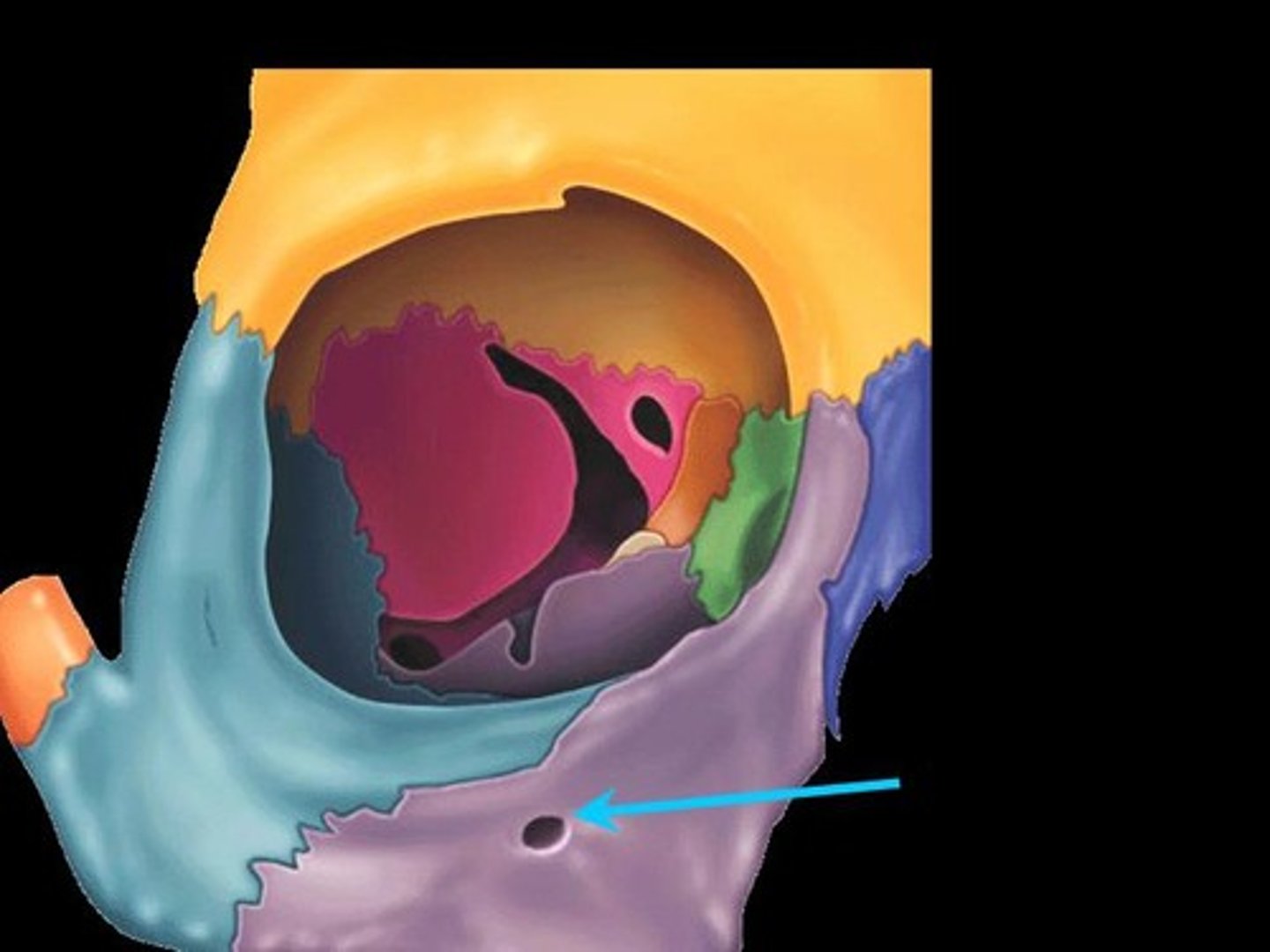
Signs of orbital blow-out fracture?
Orbital swelling, ecchymosis, numbness of the lower eyelid (infraorbital nerve damage), diplopia (inferior rectus muscle is trapped)
What bones make up the medial wall?
Frontal process of maxilla, Lacrimal bone, Orbital plate of ethmoid (lamina papyracea), Lesser wing of sphenoid.
papyracea = "paper thin"
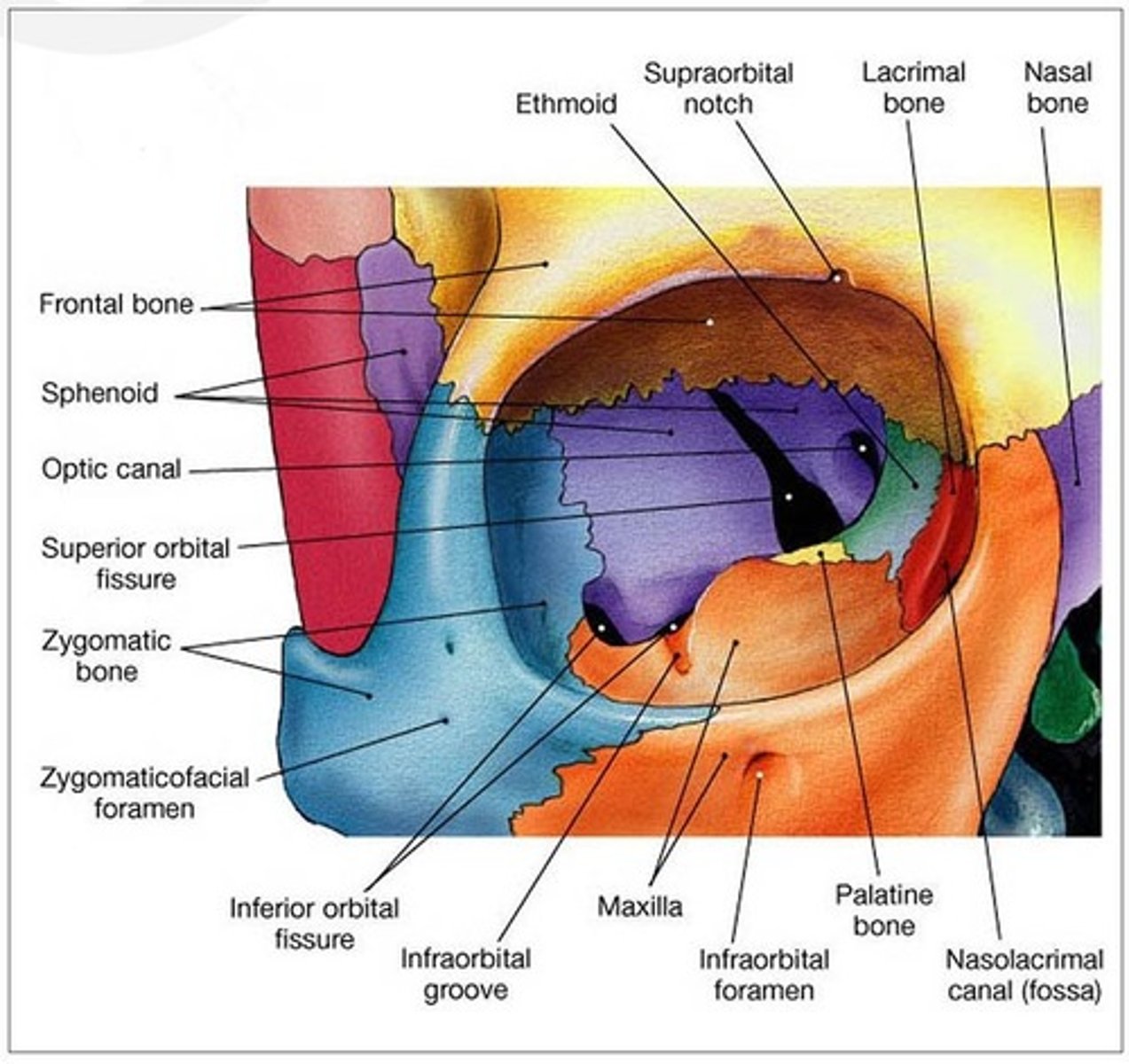
Why is the medial wall important?
Thinnest orbital wall, vulnerable to fracture; separates orbit from ethmoid sinus.
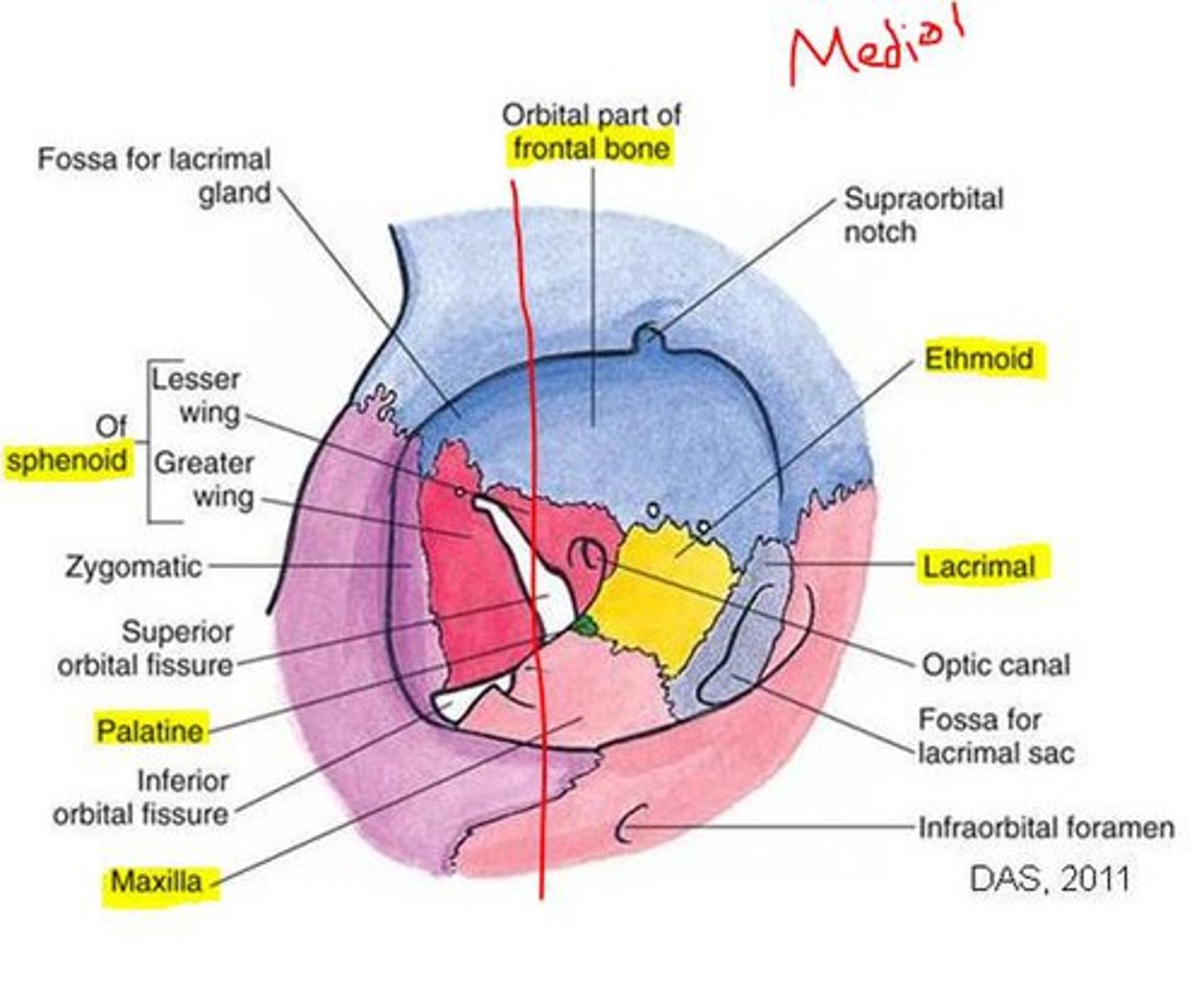
Bones of the lateral wall?
Zygomatic (anterior), Greater wing of sphenoid (posterior).
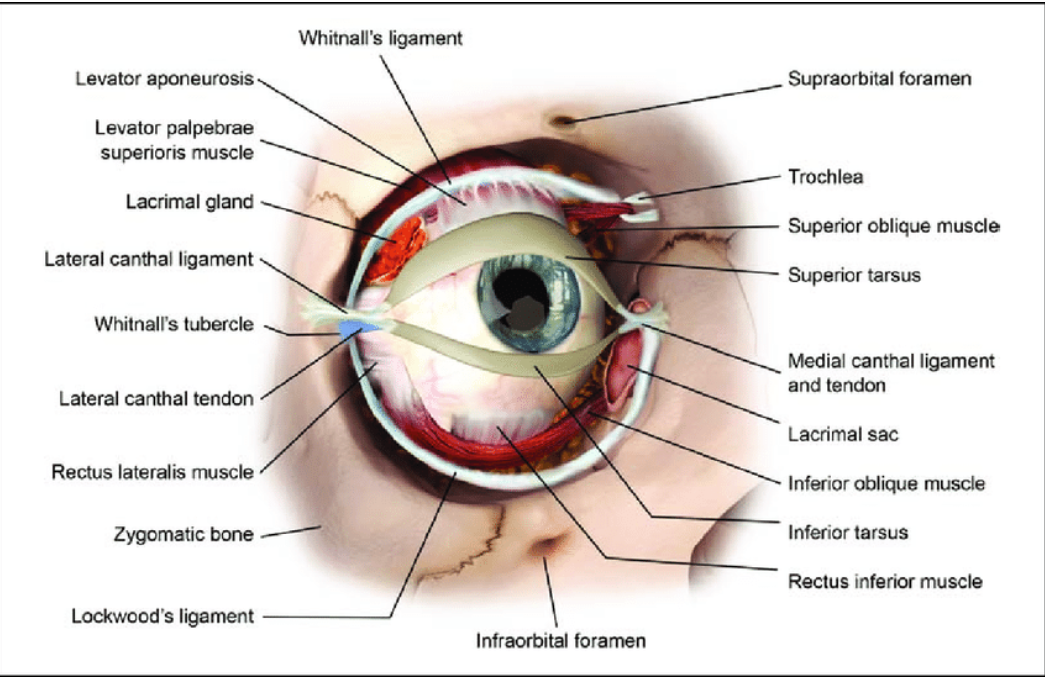
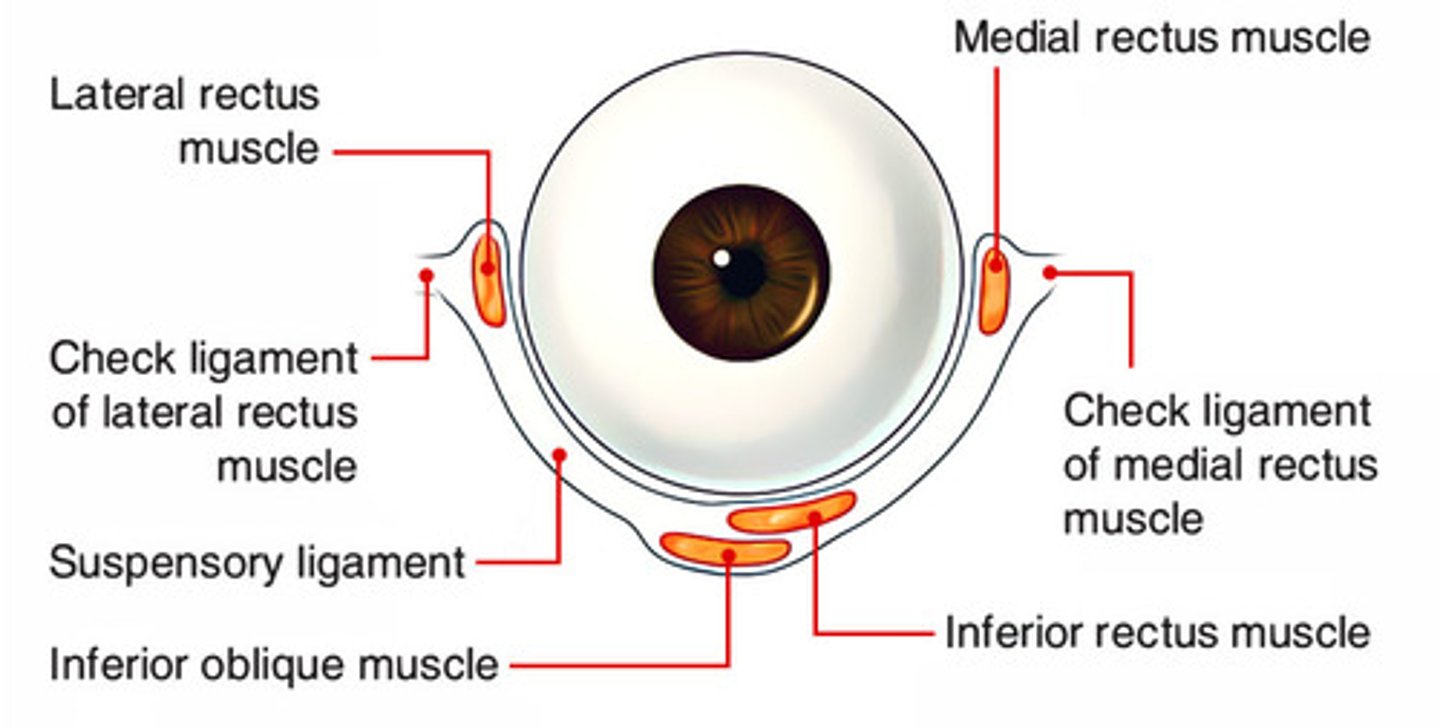
What attaches at the Whitnall tubercle (lateral orbital tubercle)?
- Superior levator aponeurosis
- lateral canthal tendon
- lateral check ligament
- suspensory ligament of Lockwood.
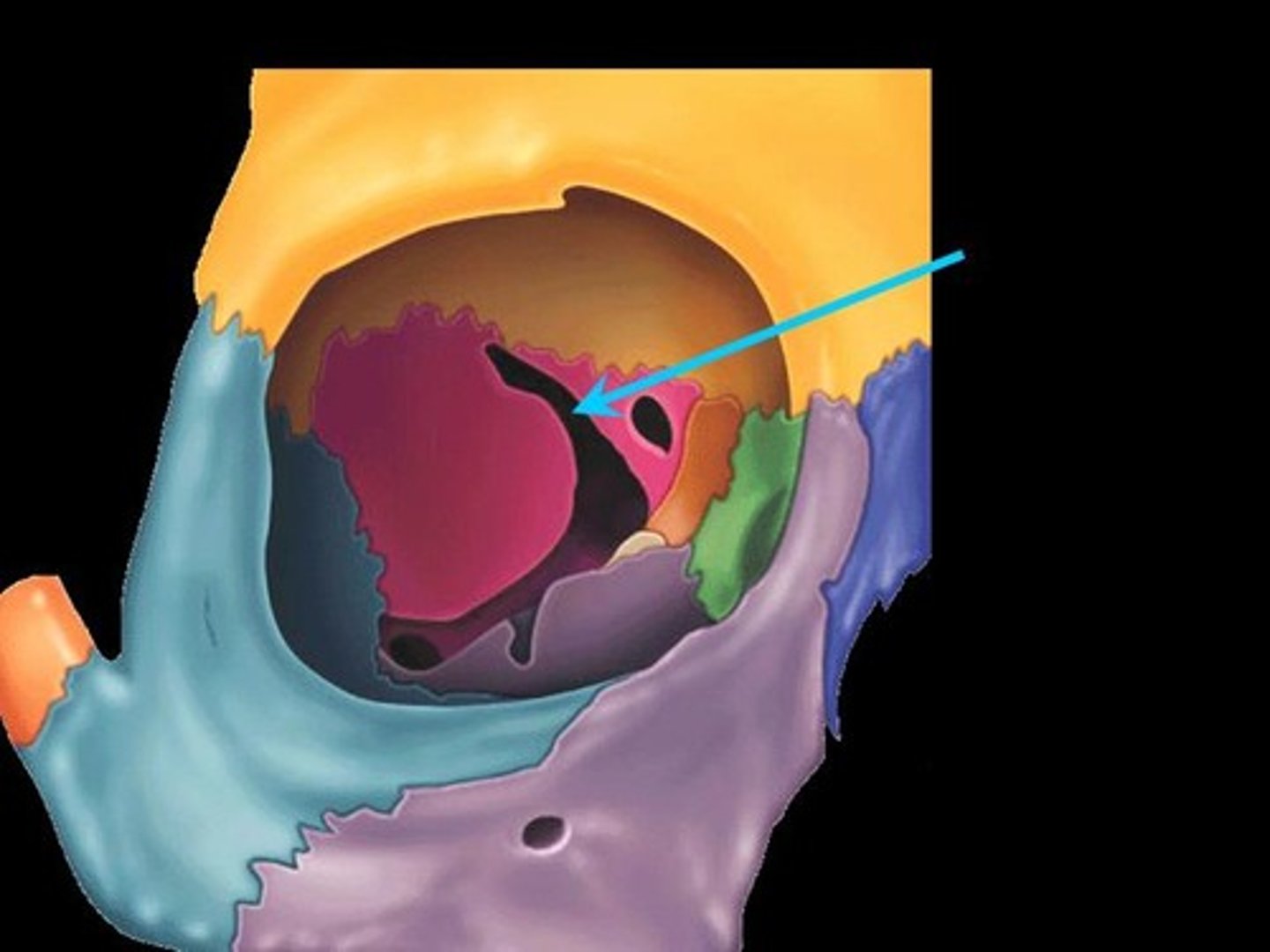
What fissures are associated with the lateral wall?
Superior orbital fissure - separates lateral wall from roof
Inferior orbital fissure - separates lateral wall from floor
What bones form the orbital margins?
Frontal (superior), Zygomatic (lateral), Maxillary (inferior).
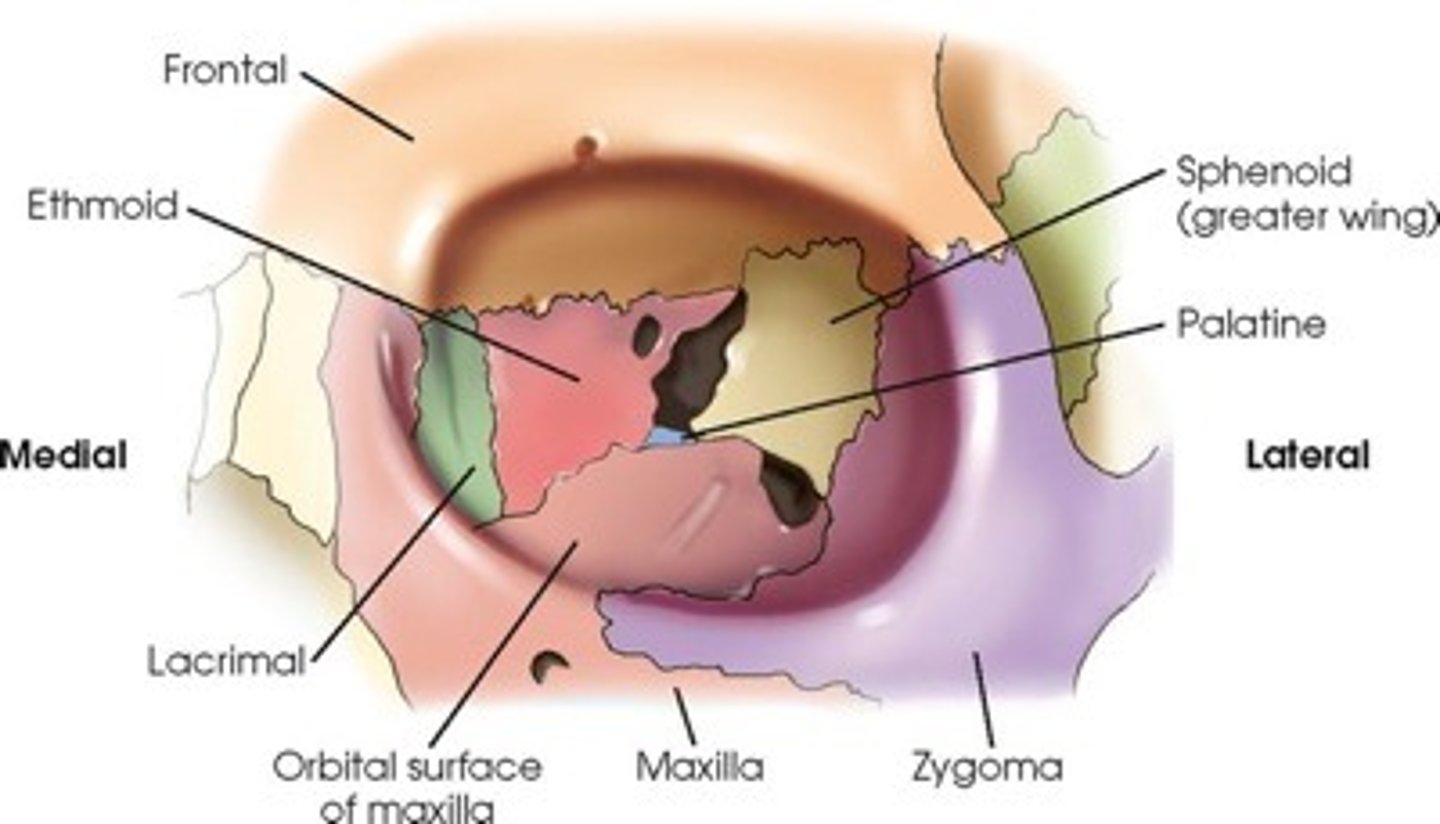
Which orbital margin is strongest?
Lateral margin.
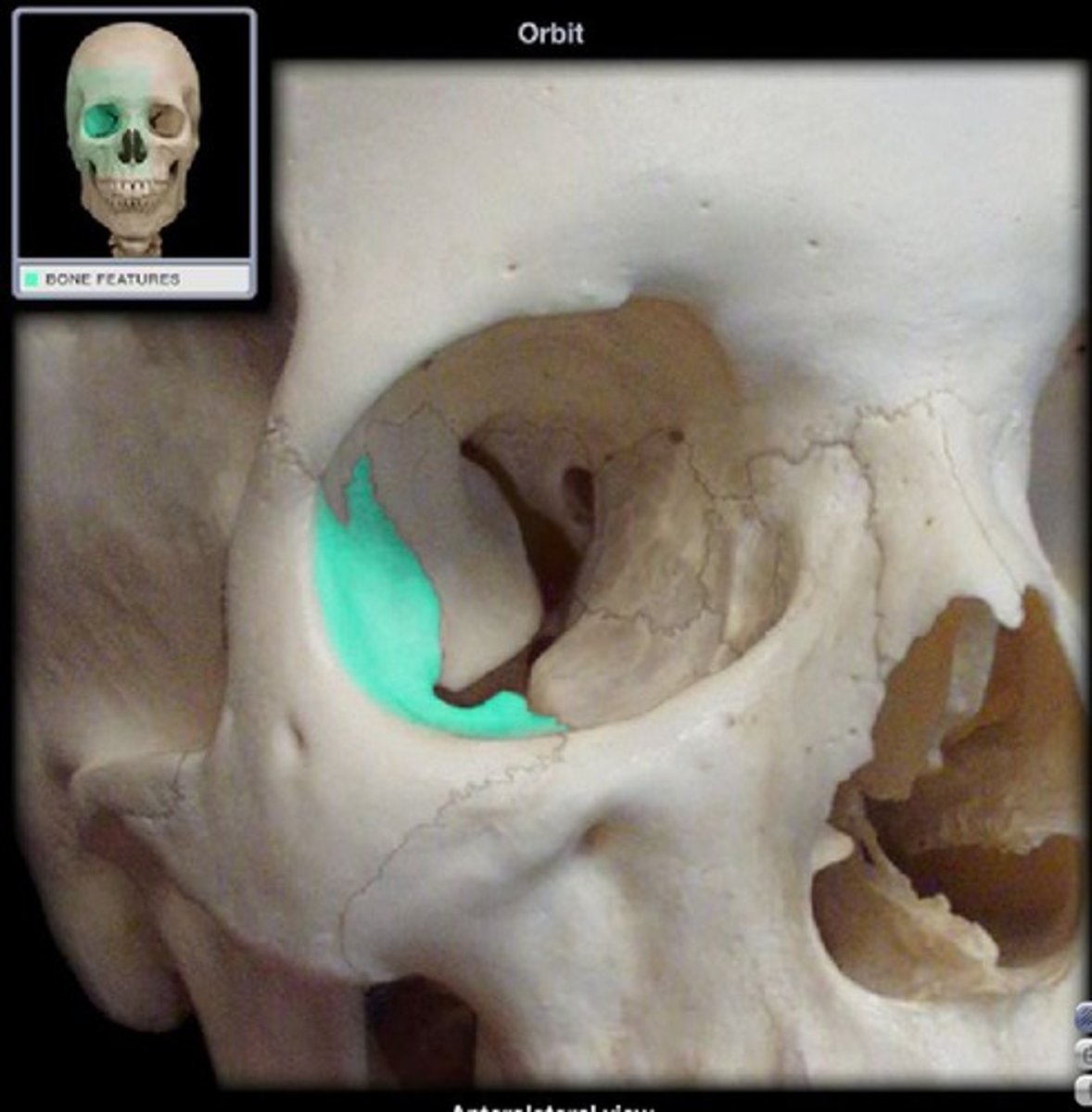
What is the shape of the medial margin?
It is not continuous—it forms a spiral (posterior lacrimal crest superiorly, anterior lacrimal crest inferiorly).
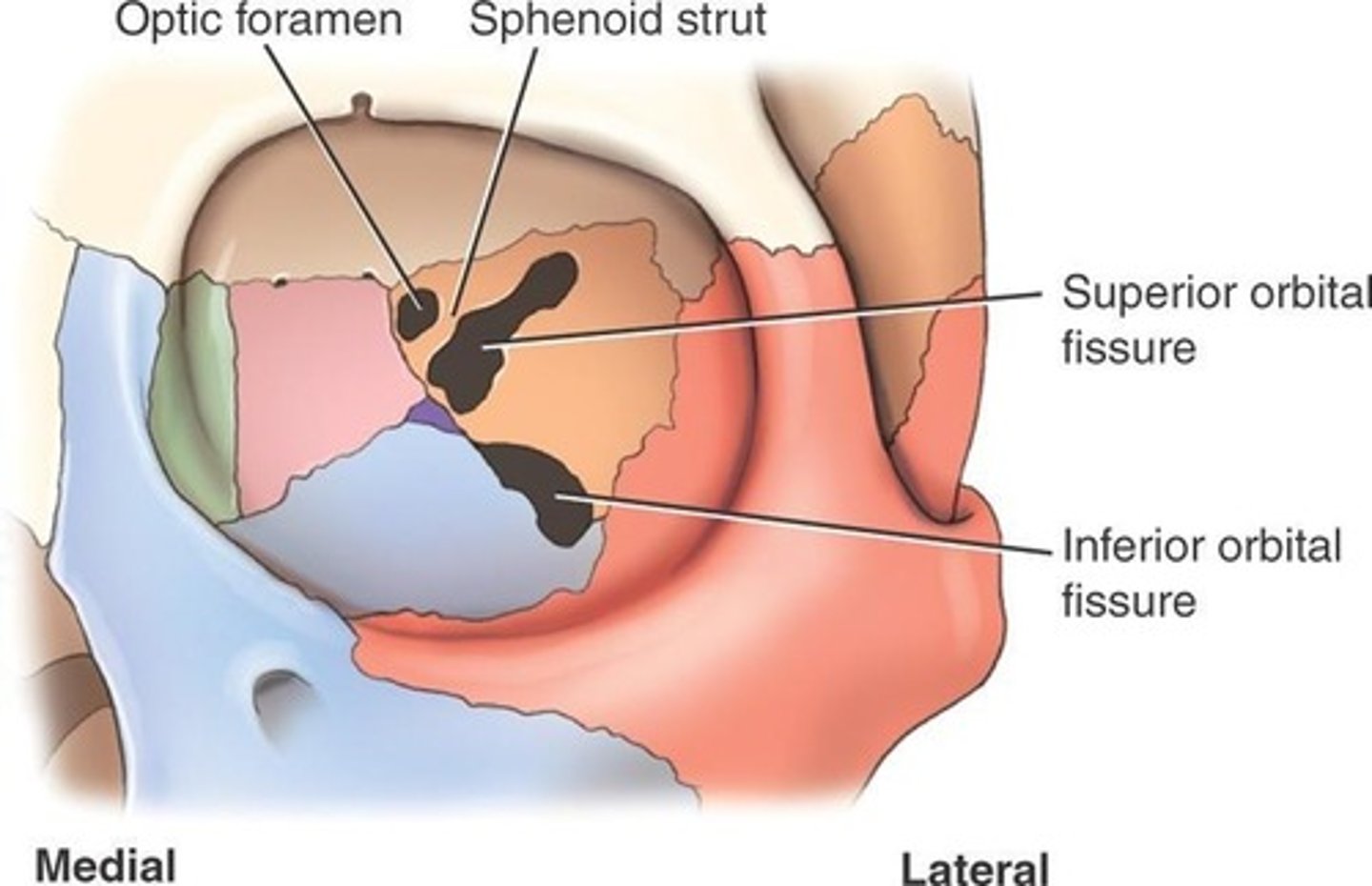
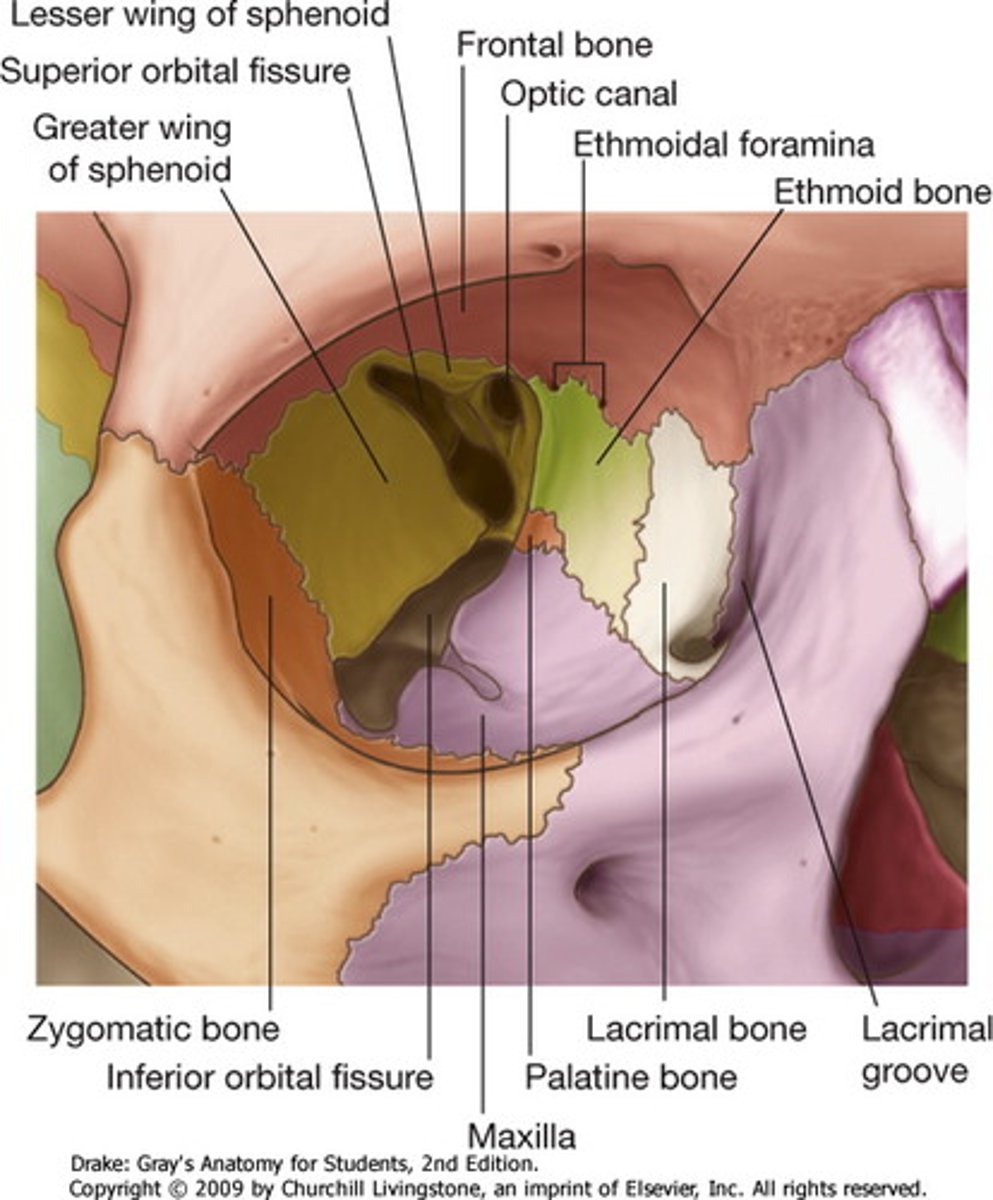
What passes through the optic foramen?
Optic nerve (CN II) exits the orbit here, Ophthalmic artery enters the orbit here.
- aka optic canal
- communication between orbital cavity and middle cranial fossa
What passes through the infraorbital foramen?
Infraorbital nerve, artery, vein.
- 2-4 mm below inferior orbital margin
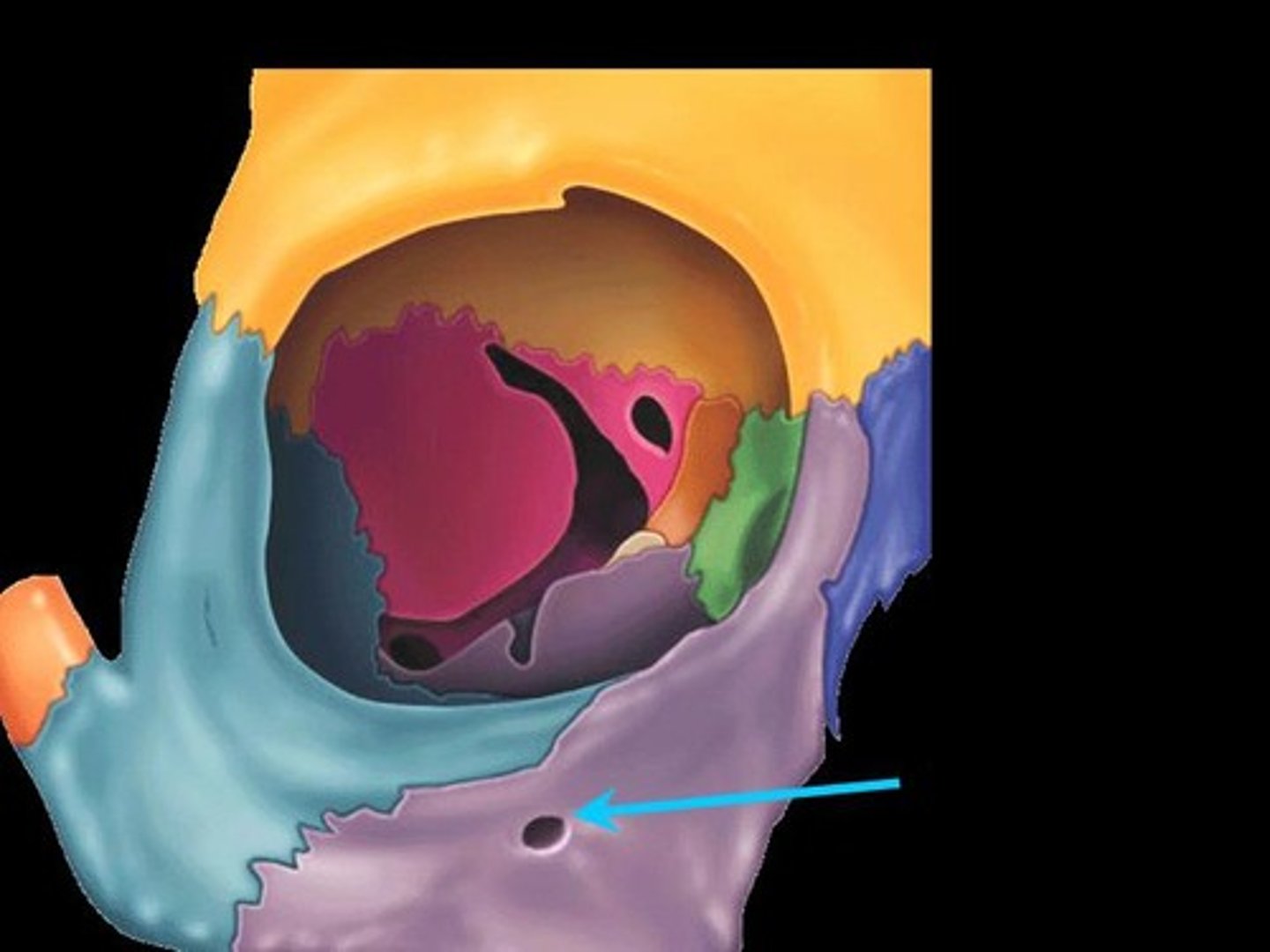
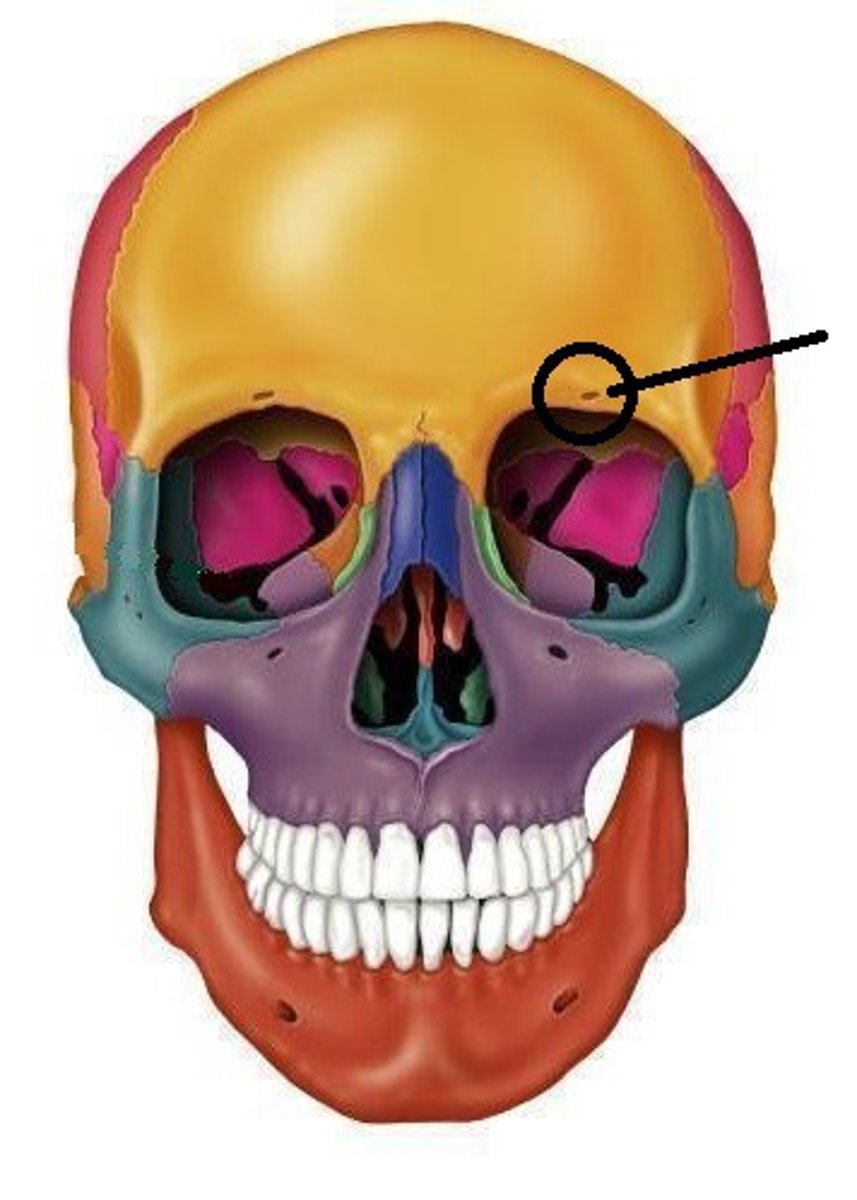
What passes through the supraorbital notch?
Supraorbital nerve (CN V1 branch), supraorbital artery, supraorbital vein.
- can be a notch or a foramen
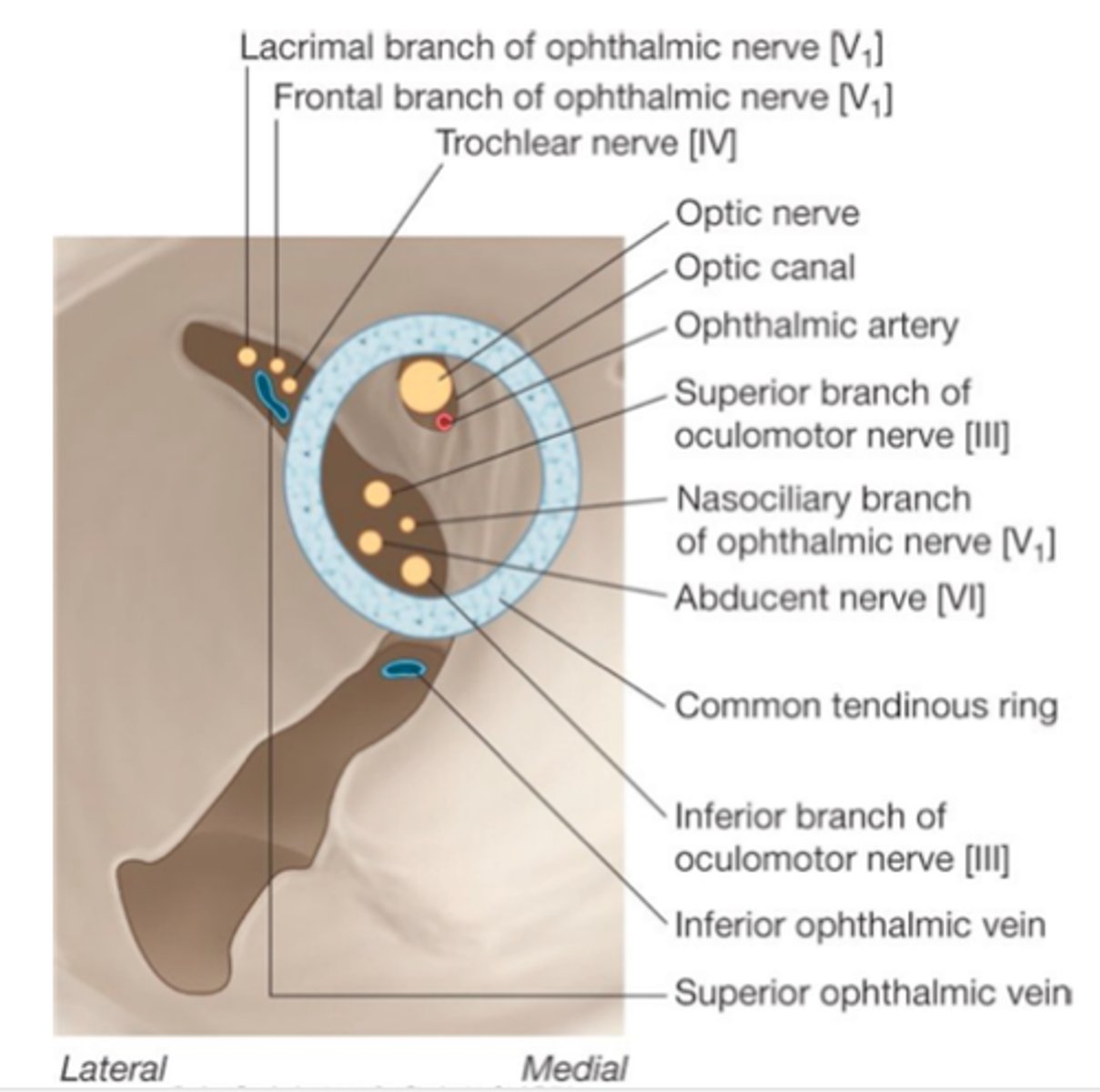
What passes through the superior orbital fissure?
The common tendinous ring (annulus of Zinn)
Inside the annulus/common tendinous ring:
CN III (sup/inf divisions), nasociliary nerve V1, CN VI, nasociliary nerve, optic nerve, ophthalmic artery.
Outside annulus/common tendinous ring: Lacrimal nerve (V1), Frontal nerve (V1), Trochlear nerve (CN IV), Superior ophthalmic vein.
What passes through the inferior orbital fissure?
Zygomatic nerve (V2), Infraorbital nerve (V2), Infraorbital artery & vein, Inferior ophthalmic vein.
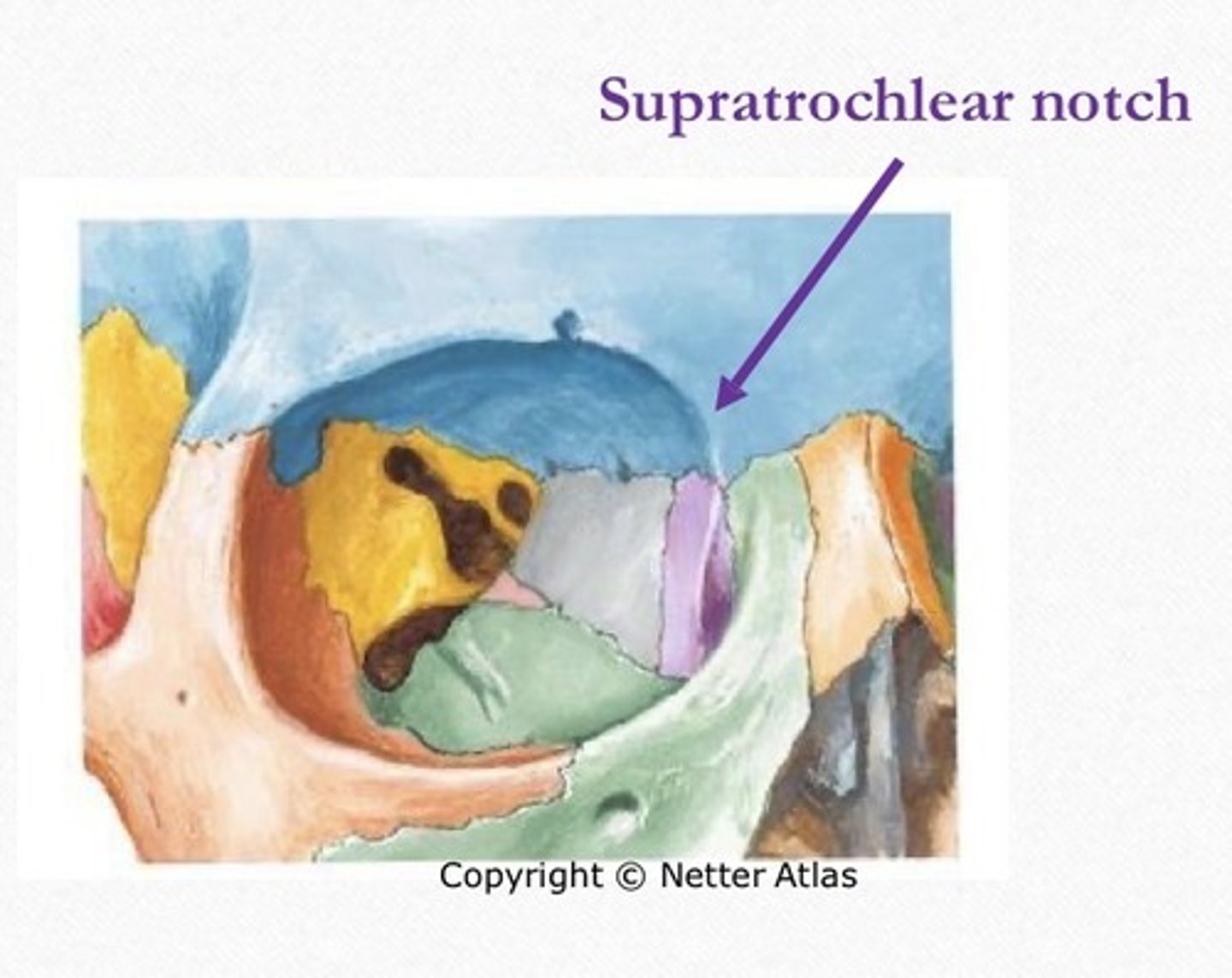
What passes through the supratrochlear notch?
Supratrochlear nerve, artery, and vein
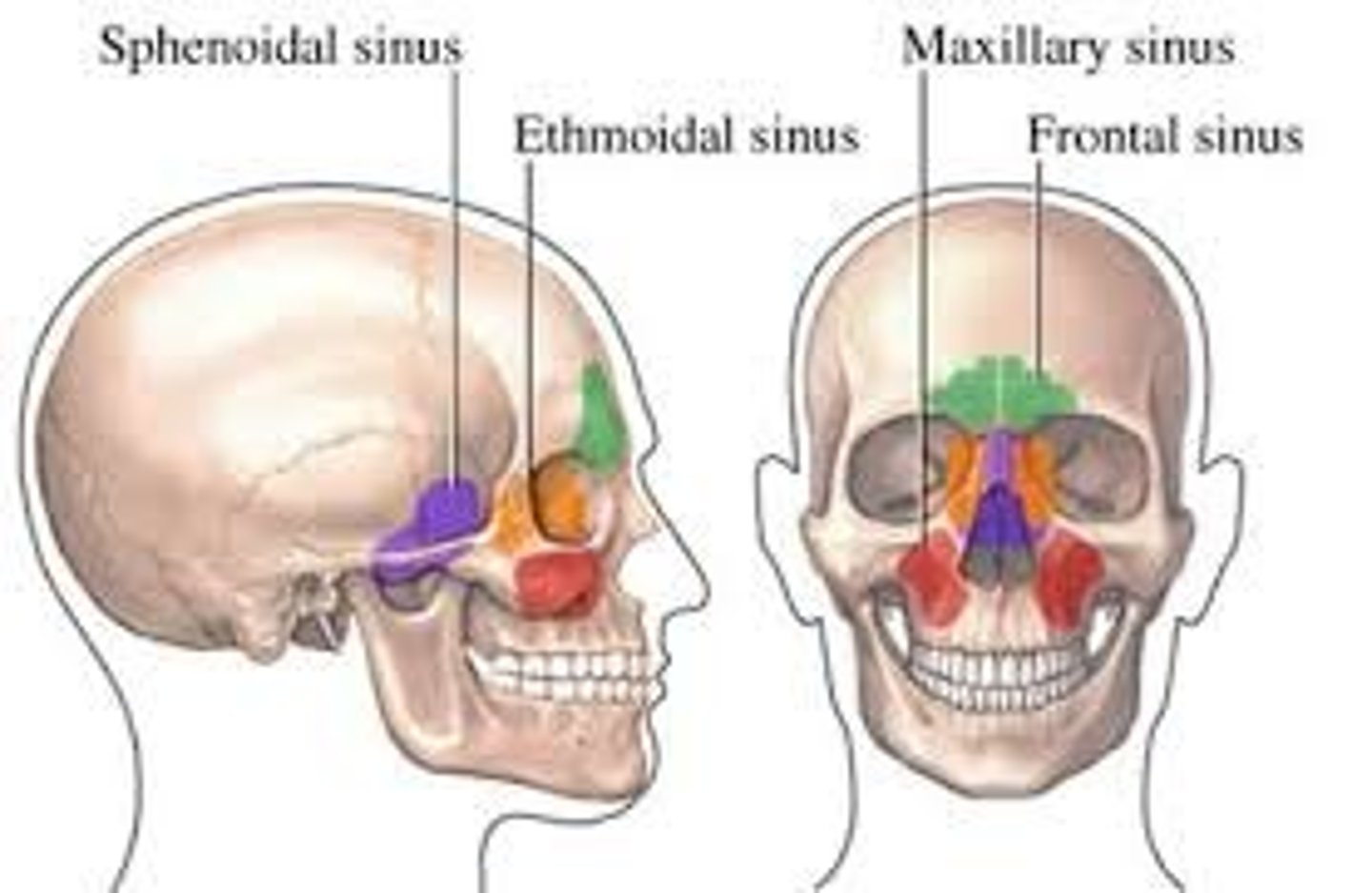
Which bones contain sinuses?
Frontal, Ethmoid, Sphenoid, Maxillary (largest).
What functions do paranasal sinuses serve?
Decrease skull weight, add resonance to voice, communicate with nasal cavity.
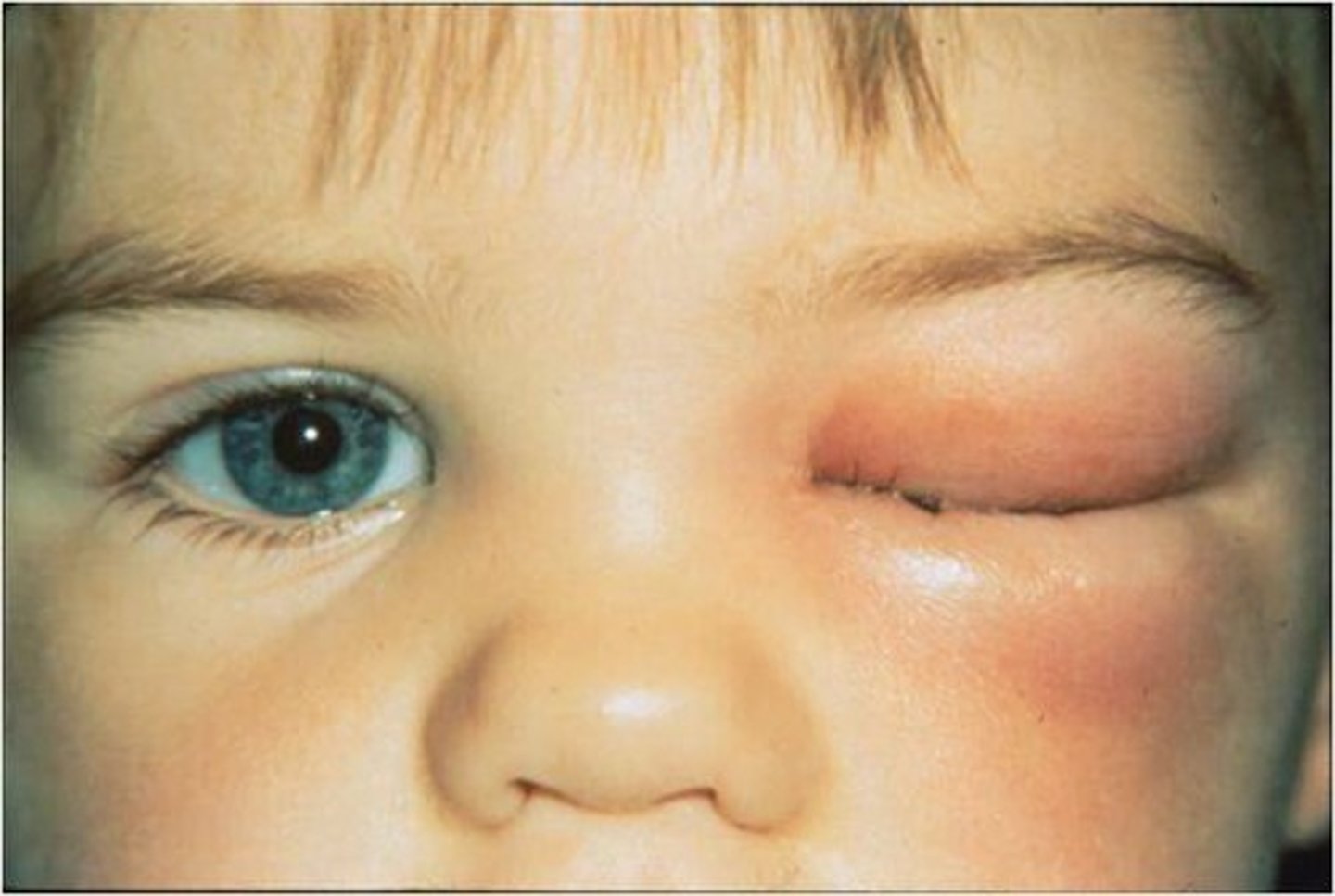
What is orbital cellulitis?
Spread of infection from sinuses to the orbit/brain → could lead to vision loss, brain infection, possibly fatal.
- Often occurs due to sinusitis due to the thin walls of sinus cavities
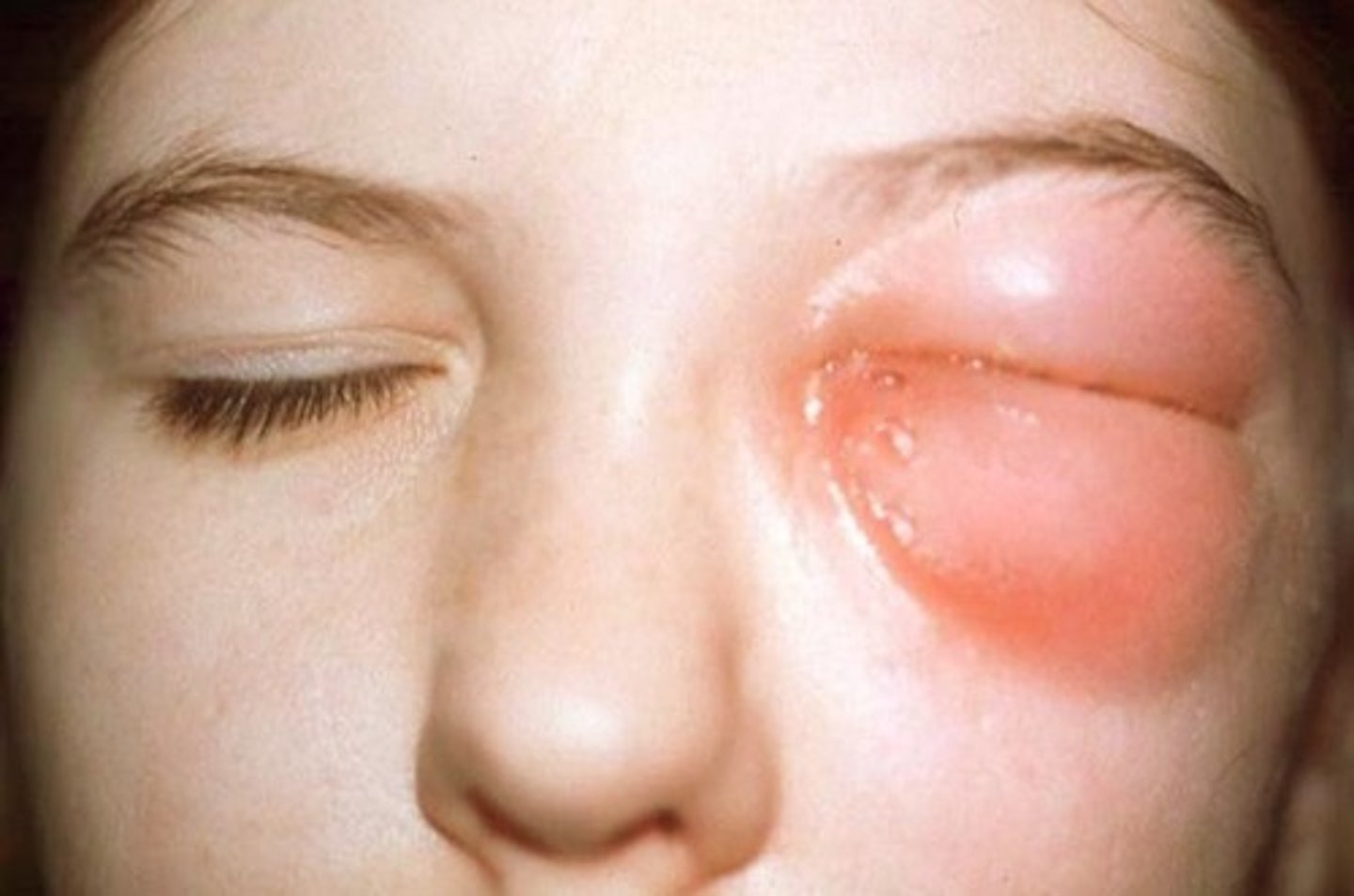
What are the clinical signs and symptoms of orbital cellulitis?
- Sudden onset of pain
- Swelling
- Proptosis
- Decreased ocular mobility
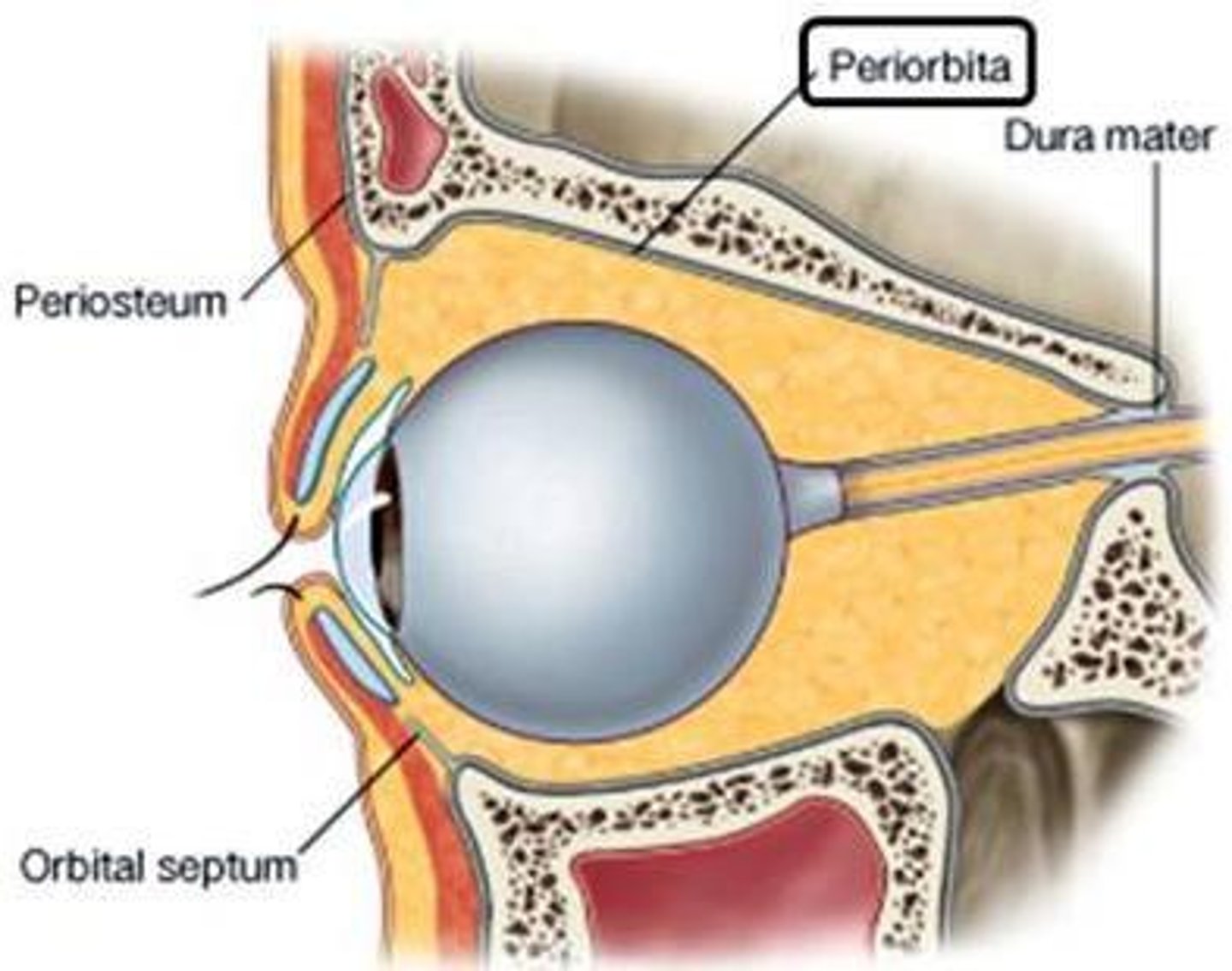
What is the periorbita?
Orbital periosteum; covers orbital bones, attachment for muscles/ligaments, continuous with dura mater.
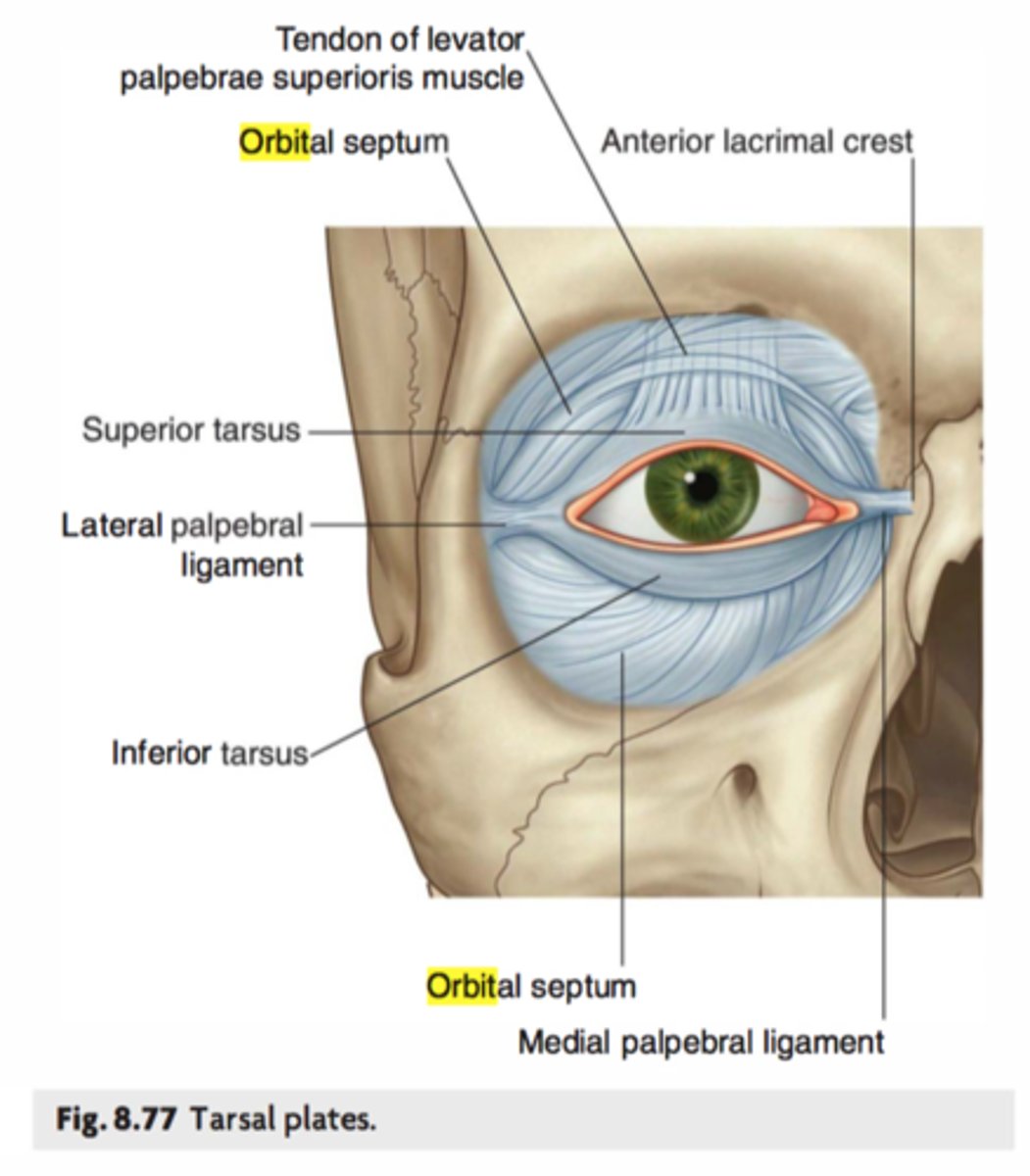
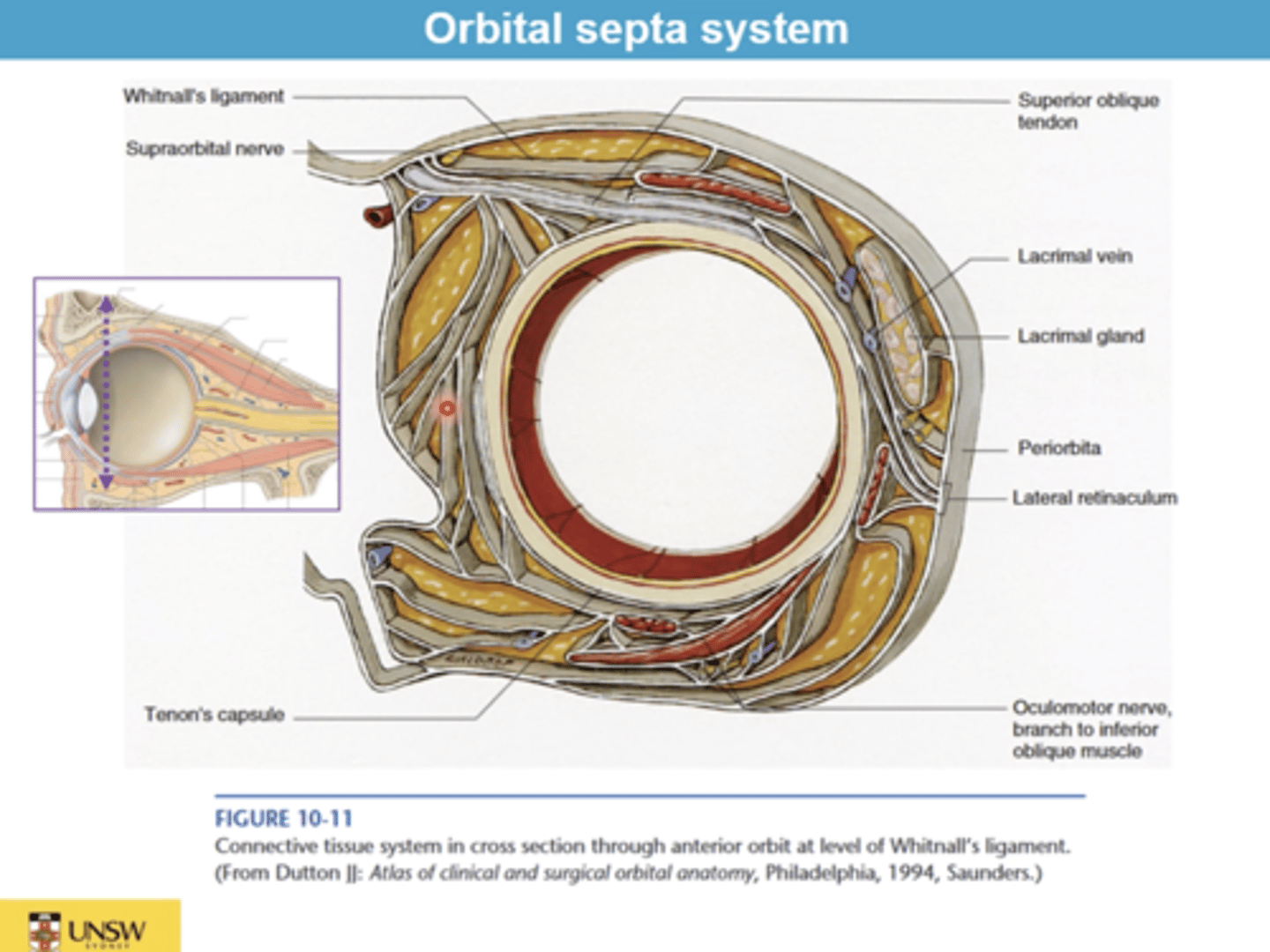
What is the orbital septum?
Connective tissue barrier separating eyelids from orbit, prevents facial infections spreading inward, holds orbital fat in place.
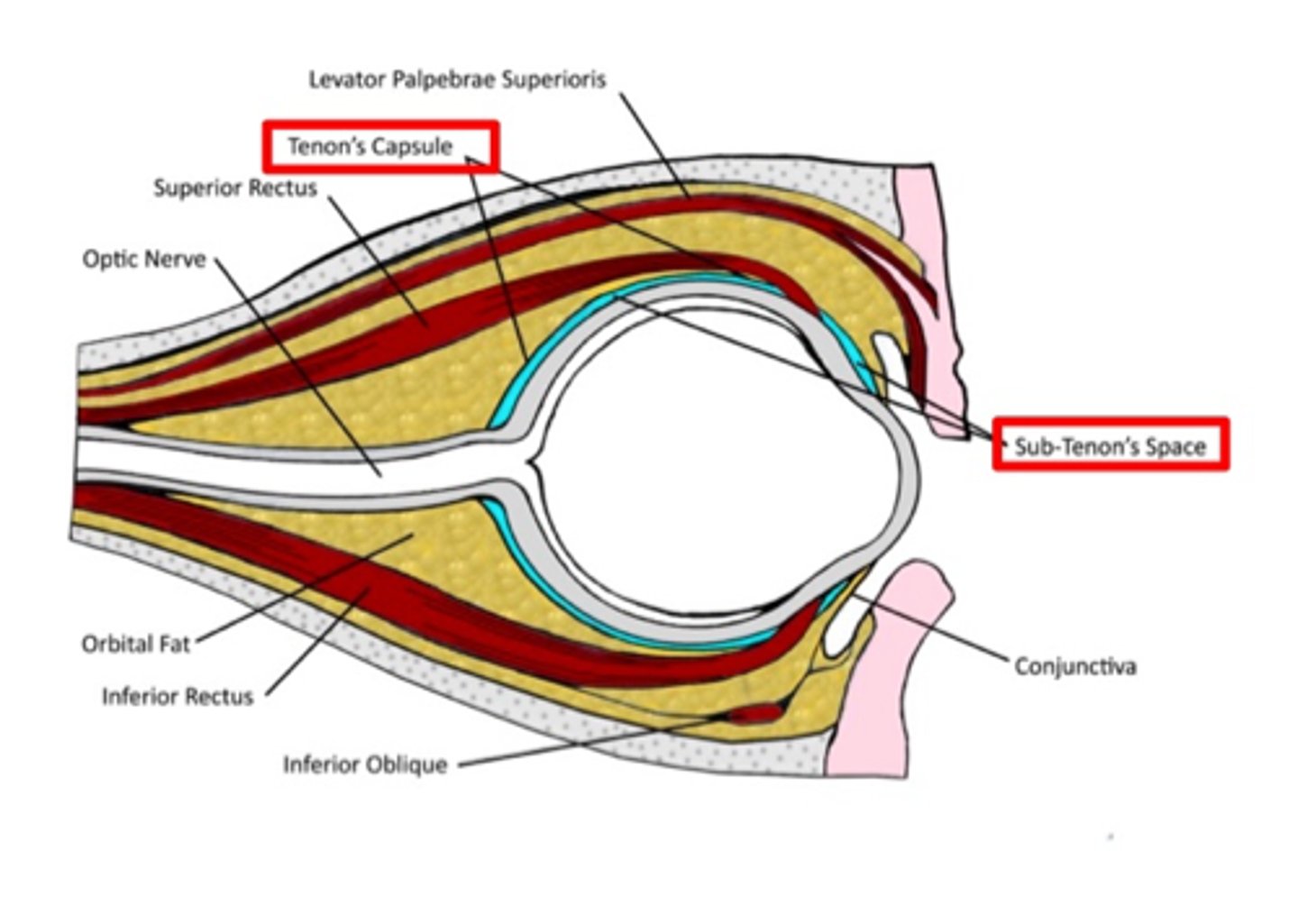
What is Tenon's capsule?
Bulbar fascia encasing globe, continuous with optic nerve dura, allows smooth eye movement, site for anesthetic injections, barrier to infection.
What is the suspensory ligament of Lockwood?
Hammock-like ligament supporting globe, attaching from lacrimal (medial) to zygomatic (lateral).
What is the orbital septal system?
Network of connective tissue slings supporting EOMs & vessels, organizing orbital space into compartments.
What role does orbital fat play?
Cushions globe, aids smooth eye movements, maintains orbital shape.
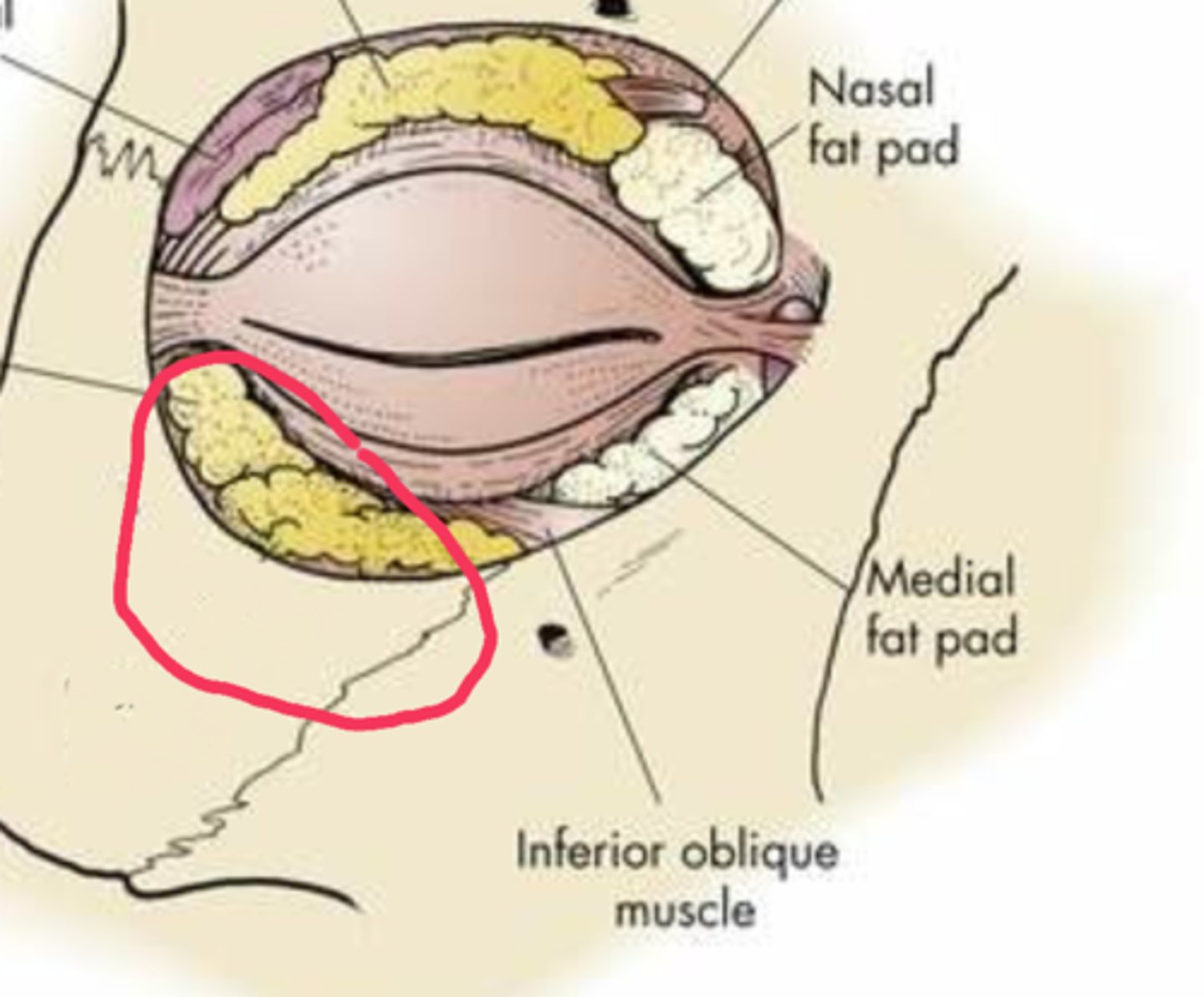
What happens to spaces in the orbit not occupied by ocular structures, connective tissue, nerves, or vessels?
They become filled with fat
What is the intraconal area?
The area inside the muscle cone formed by the four rectus muscles around the optic nerve
Contains the optic nerve, opthalmic artery, and fat
Tumors in the intraconal area would cause the eye to bulge outward (pushes eye out)
What is the extraconal area?
The area outside the muscle cone but still in the orbit.
Contains fat, nerves (ex: infraorbital nerve), and other soft tissues.
Tumors in the extraconal area cause the eye to be pushed to the side or up/down
How many bones make up the orbital roof?
2
How many bones make up the orbital floor?
3
How many bones make up the medial wall?
4
How many bones make up the lateral wall?
2
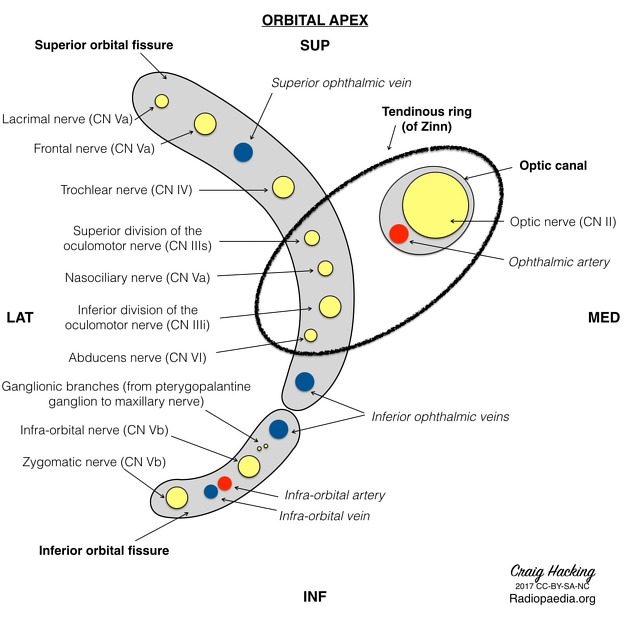
What passes through the superior orbital fissure and the common tendinous ring?
NOA
Nasociliary nerve
Oculomotor nerve
Abducens nerve
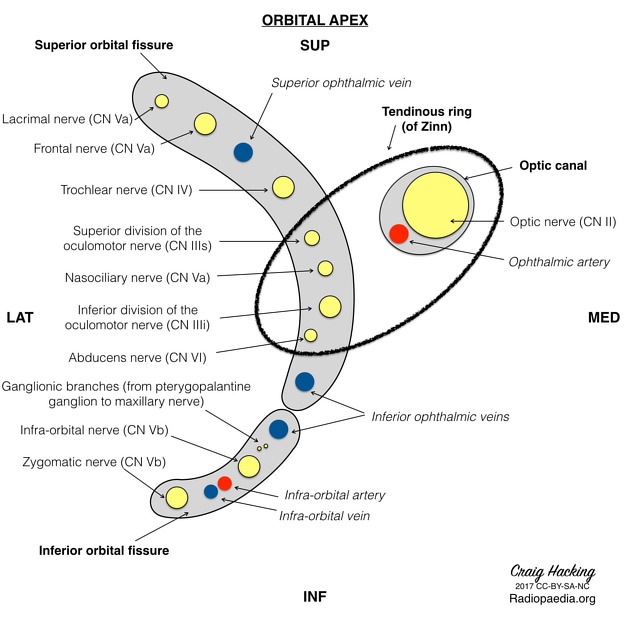
What passes through the superior orbital fissure above the common tendinous ring?
LOFT
Lacrimal nerve
superior Opthalmic vein
Frontal nerve
Trochlear nerve
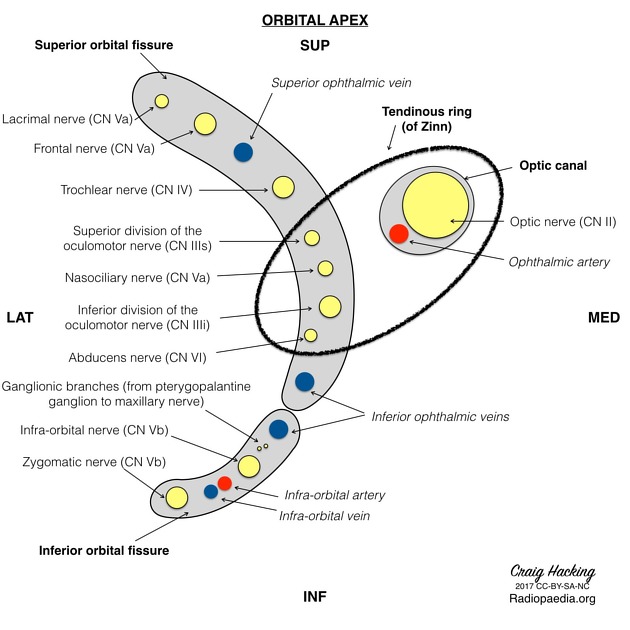
What passes through the inferior orbital fissure (outside the CTR)?
inferior opthalmic vein
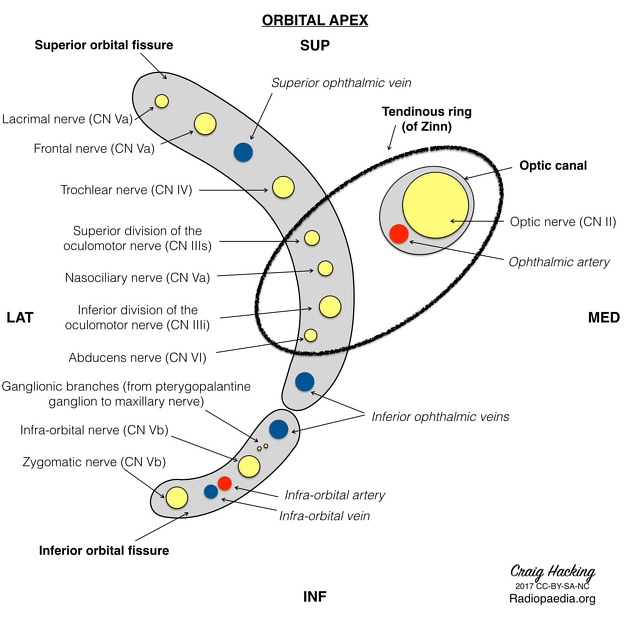
What passes through the optic canal (AND the common tendinous ring)?
Optic nerve (CN III)
Opthalmic artery
Acronym for remembering the bones of the orbital roof?
FRONT LESS
Frontal bone
Lesser wing of sphenoid
Acronym for remembering the bones of the medial wall?
SMEL
Sphenoid (body/lesser wing)
Maxillary (frontal process)
Ethmoid (orbital plate)
Lacrimal
Acronym for remembering the bones of the lateral wall?
GREAT Z
Greater wing of sphenoid
Zygomatic bone
Acronym for remembering the bones of the orbital floor?
My PAL gets his Zs on the floor
Maxillary (orbital plate)
Palatine (orbital process)
Zygomatic (orbital plate)