Chemistry periodic table/ trends review for quiz I donno when
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
for study :) made on 12/20/2025
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
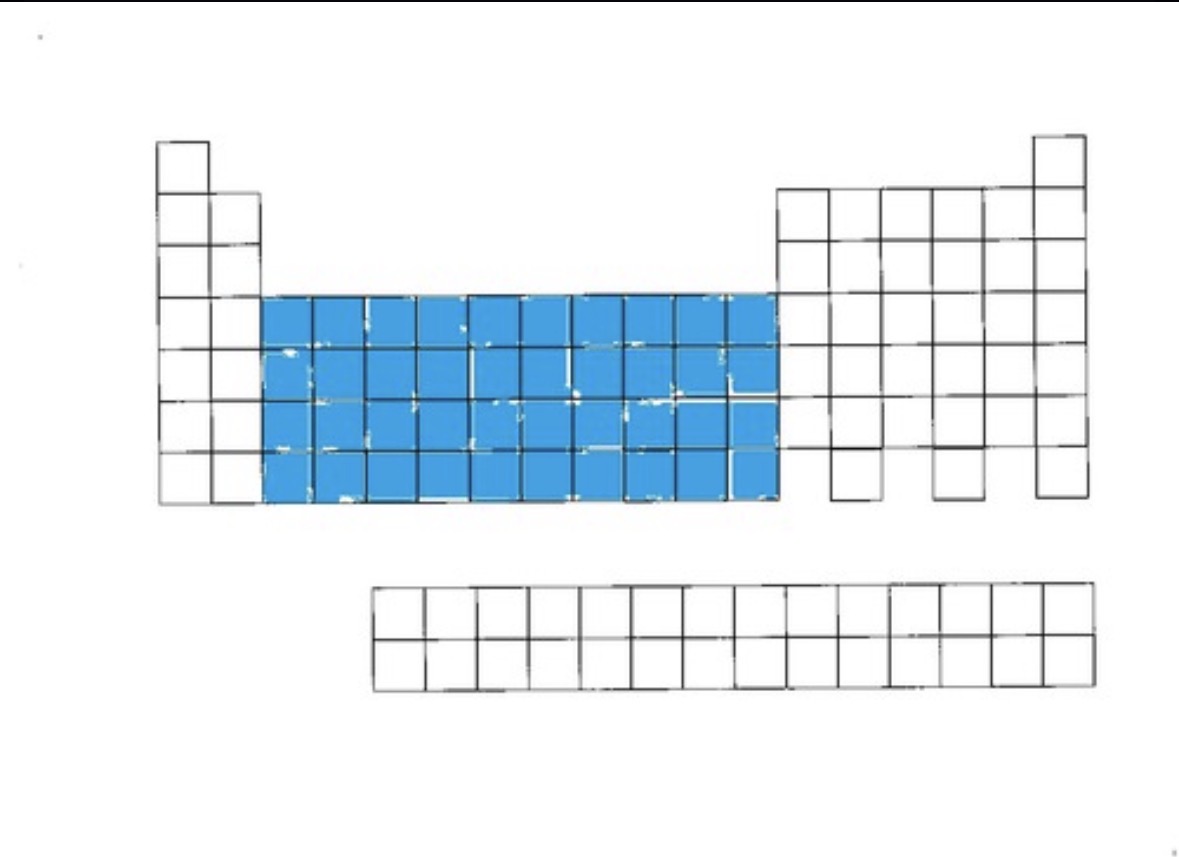
Transition metals
Nonmetals
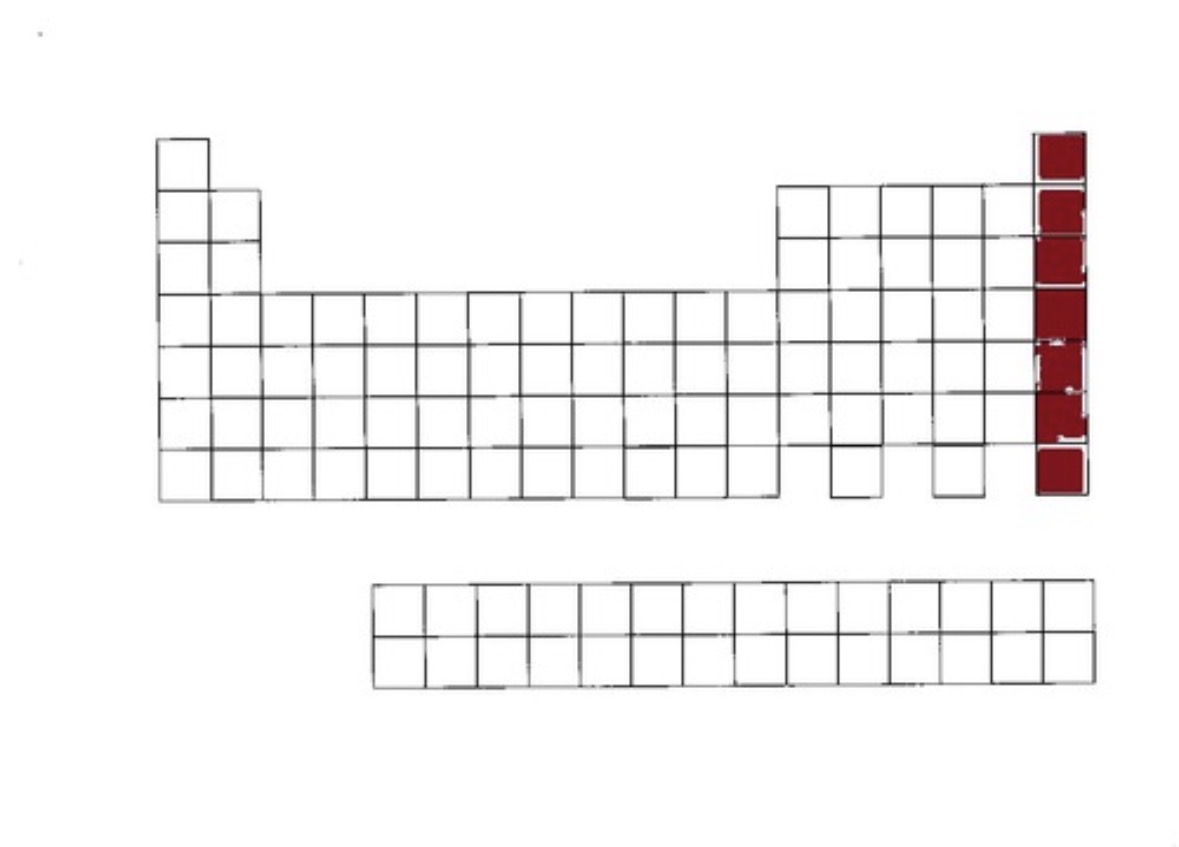
Noble Gases

Metals
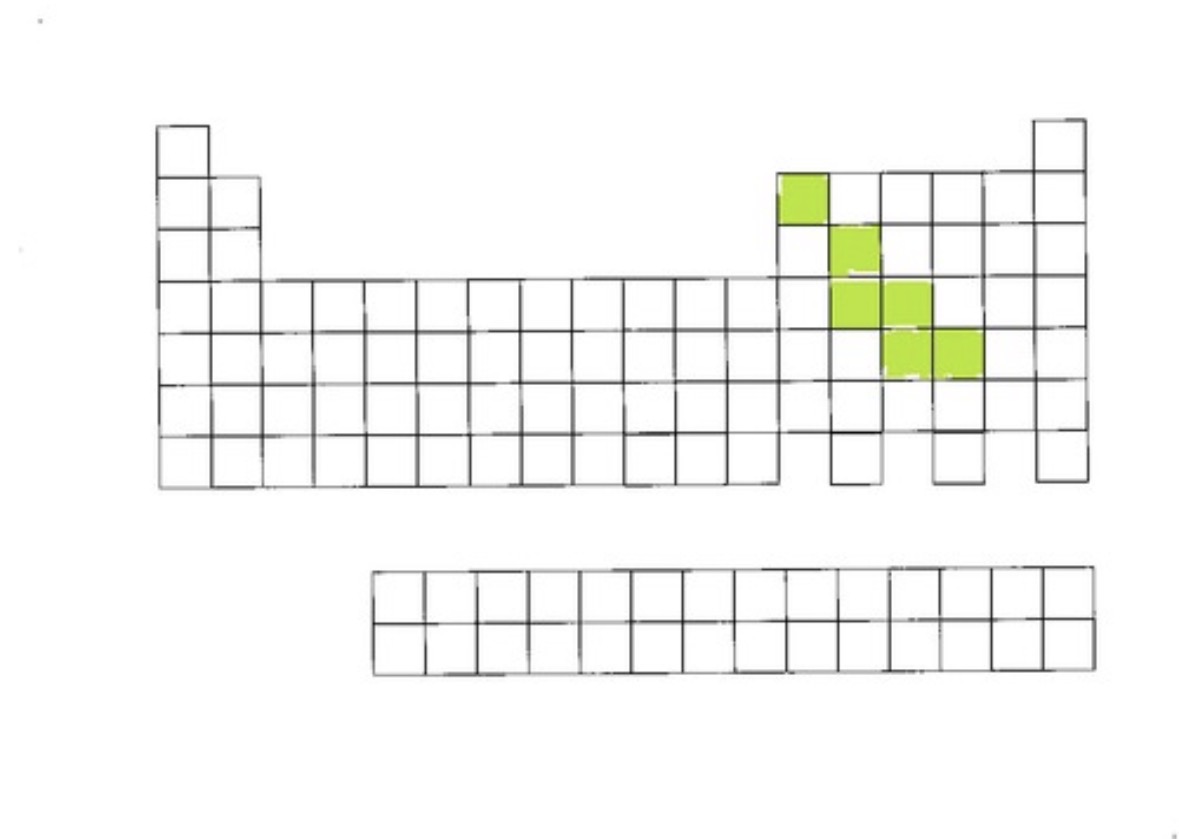
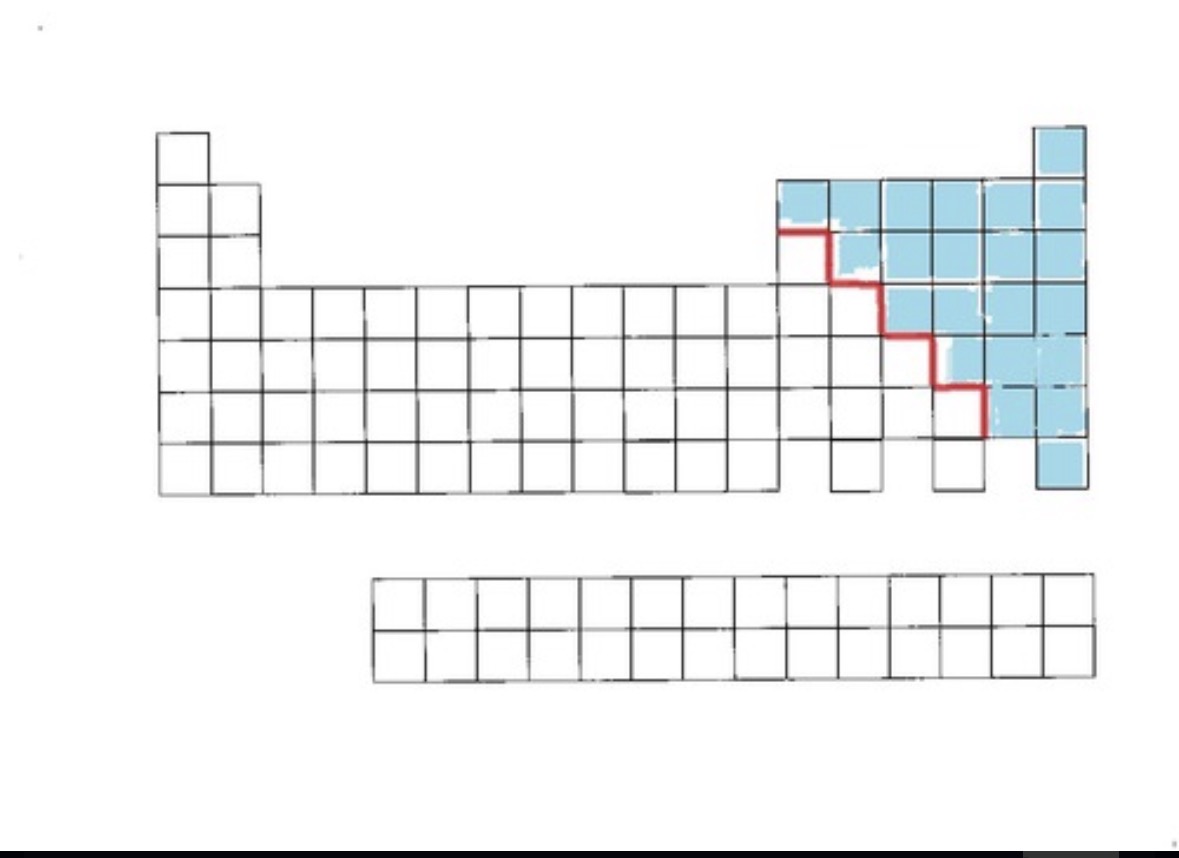
Metalloids
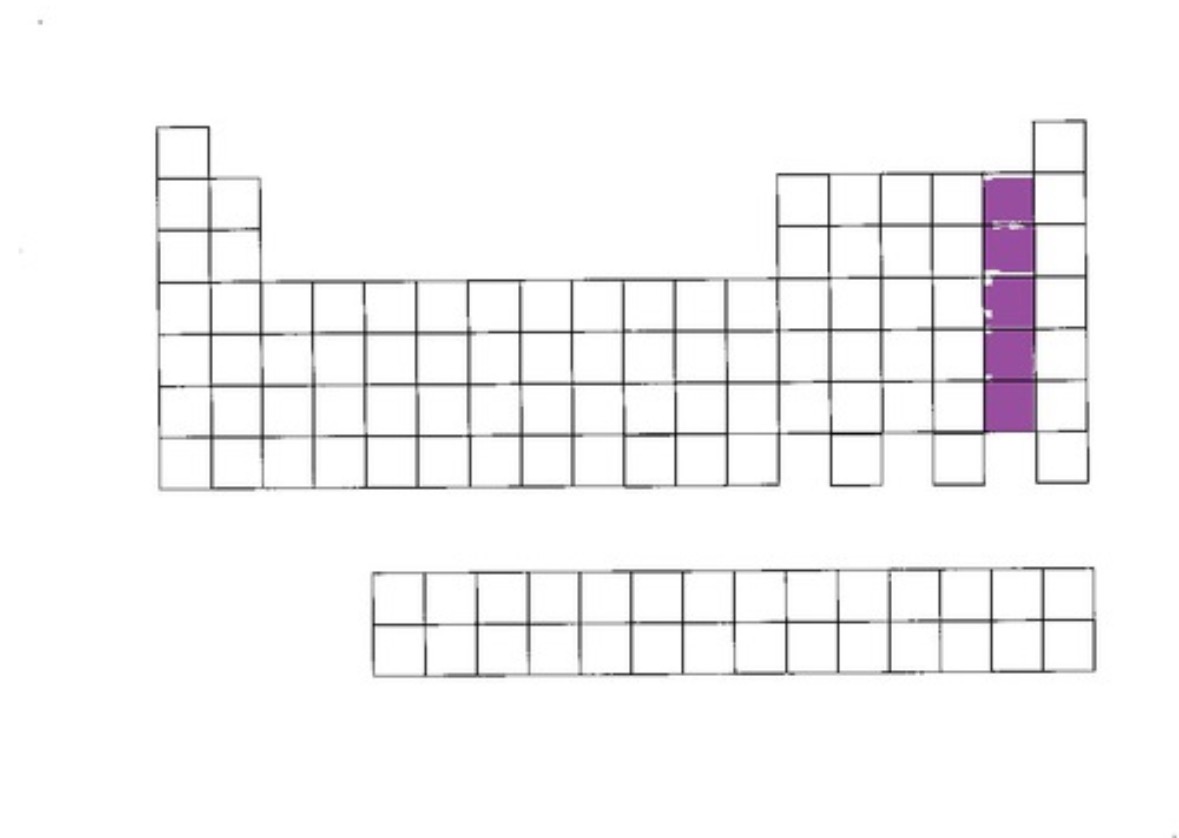
Halogens
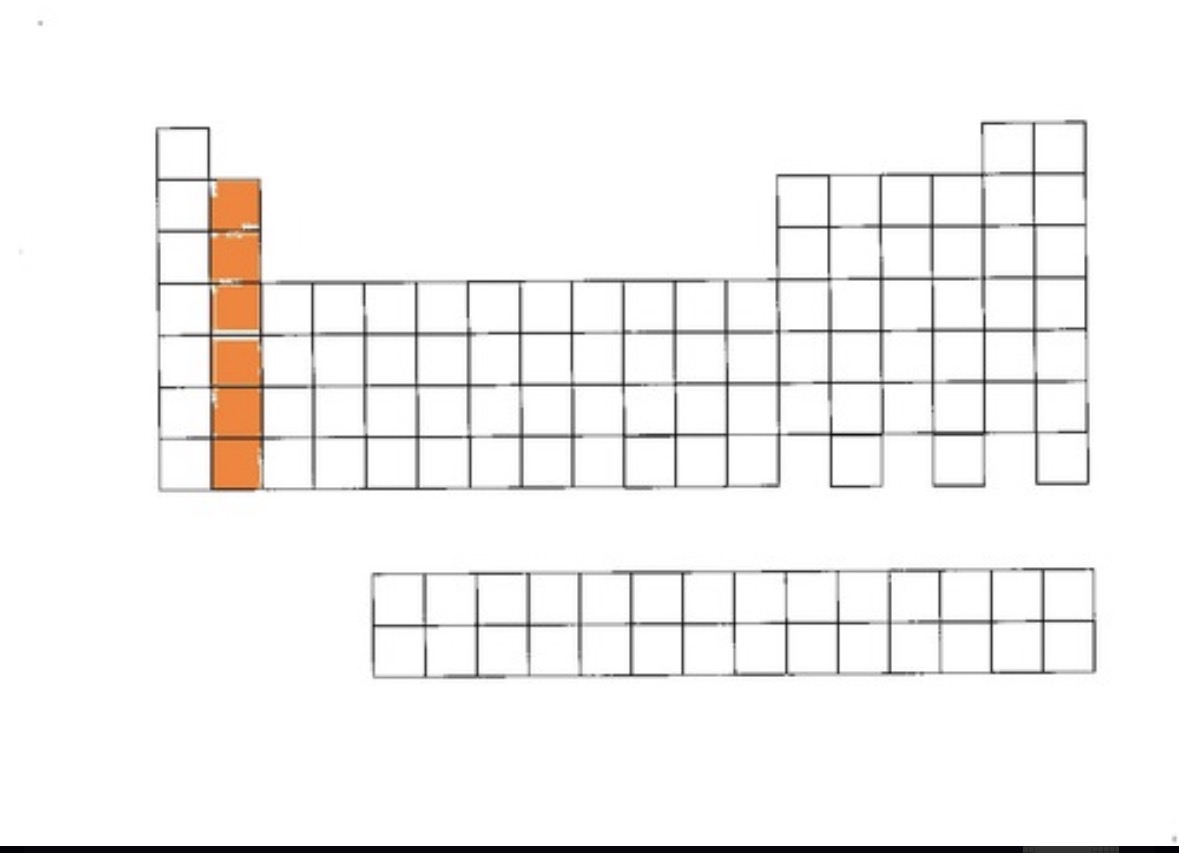
Alkaline earth metals
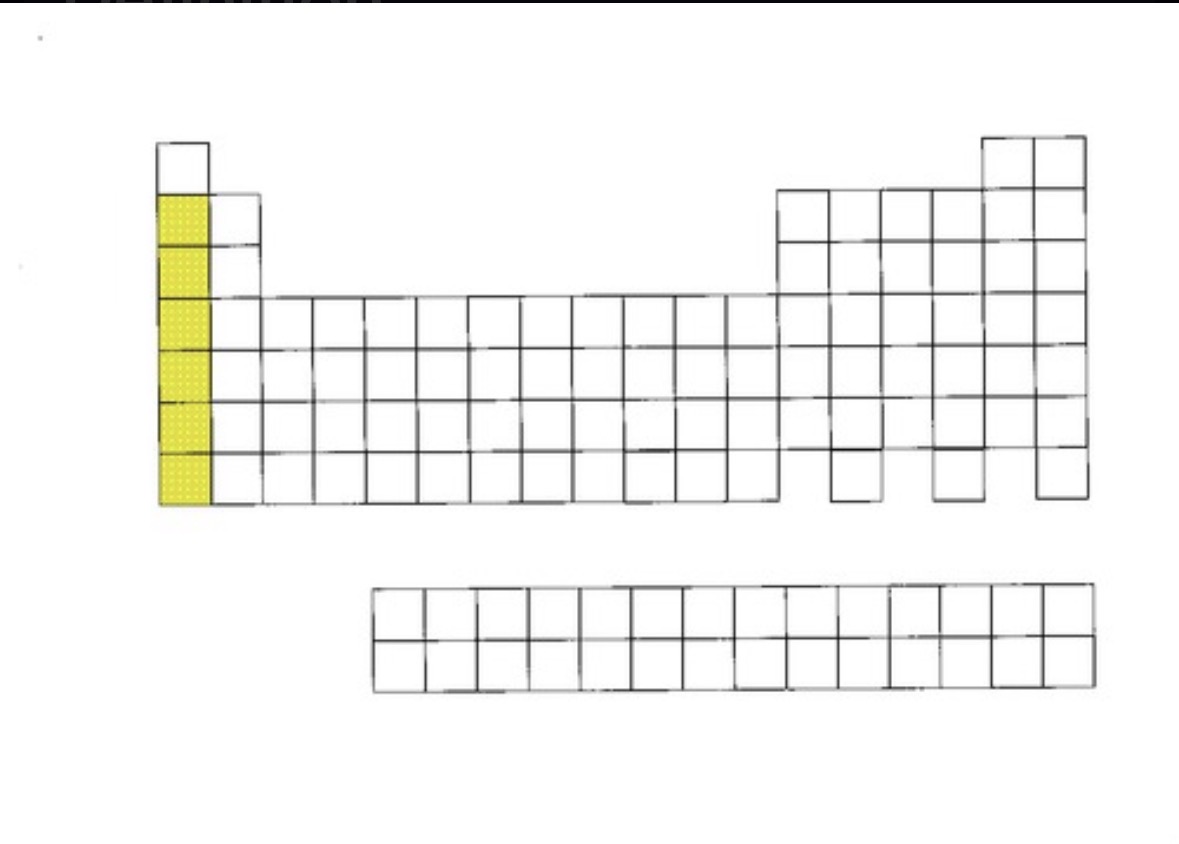
Alkali metals
Location of S
left side
Location of P
Right side
Location of d
Middle
Location of F
Bottom separated part
Groups
Top row numbered 1-18
Periods
the side numbered 1-7
Alkali metals location
Group 1
Halogens location
Group 17
Noble gases location
group 18
Alkaline earth metals location
group 2
Transition metals location
the middle groups 3-12
Atomic radius trends
decreases to the right, Increases down
Ionization energy trends
Increases to the right, decreases down
Electronegativity trends
Increases to the right, decreases down
Ionic radius trends
Cations are smaller than neutral atoms, while Anions are bigger than neutral atoms
Valence electrons on periodic table
Groups 1-2 and 13-18. Increases from 1 to 8
Ionic charges on periodic table
Groups 1-2 and 13-18. Goes from +1, +2, +3, 0, -3, -2, -1, 0
Metals definition and location
Conducts heat and electricity. Mainly on the left and center
Nonmetals definition and location
Lacks Metal traits. Mainly on the right side
metalloids definition and location
Shares properties with metals and nonmetals. Found on the stair step line, starting at group 13, 1 2 2 2 1 on right
Periodic law
When elements are listed with increasing atomic number, their properties repeat
isoelectronic
same number of electrons
Calcium ion
Ca +2
A positive, negative and neutral ionic charge is most likely to
positive: lose electrons, Negative: gain electrons, Neutral: Neither Gain or lose electrons
How to determine reactivity
The more down and left you are.
How adding electrons work
Do the opposite that the sign says.
metals or nonmetals will form cations or Anions
Metals form cations, nonmetals form Anions
How is the periodic table arranged?
By increasing atomic number
Elements with the highest and lowest electronegativity
The highest is Flourine, the lowest is Francium
Elements with the highest and lowest atomic radius
The highest is Francium, the lowest is Helium
Elements with the highest and lowest ionization energy
The highest is Helium, the lowest is Francium
elements with zero electronegativity
Noble gases