MGT 8803 - Finance
1/243
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
244 Terms
What metrics make a company successful in the long run?
taking care of customers who want to buy your products and services on a repeated basis
financial manager decisions
investment decisions
how to access capital from the financial markets in terms of debt and equity?
debt holders
investors who give capital to company and get principal and interest payment in return
equity holders or shareholders
owners of corporation, get leftover money after debt holders paid (residual claimants)
value creation
corporation is run with the objective of creating value for the shareholders
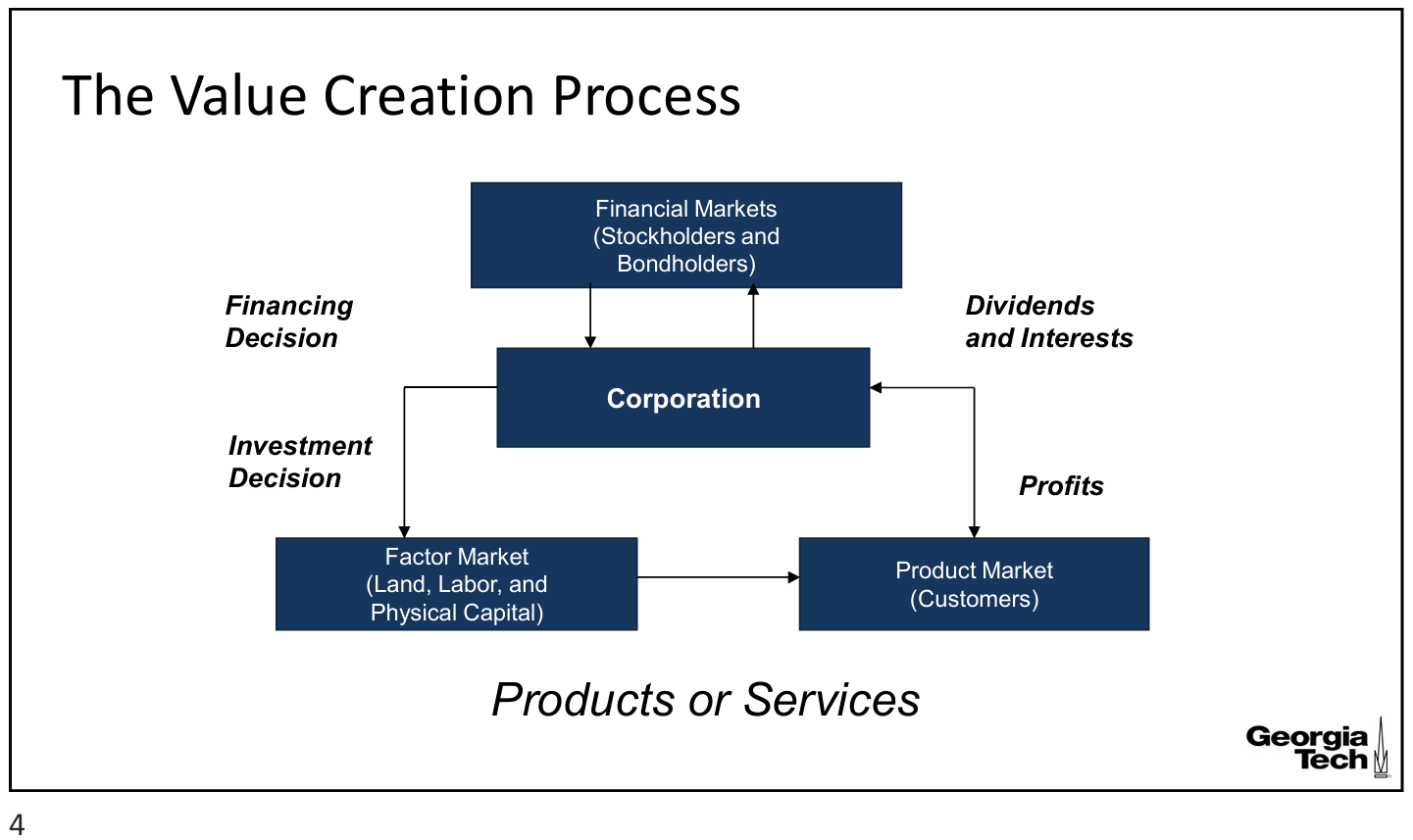
value creation process
role of finance in corporate strategy
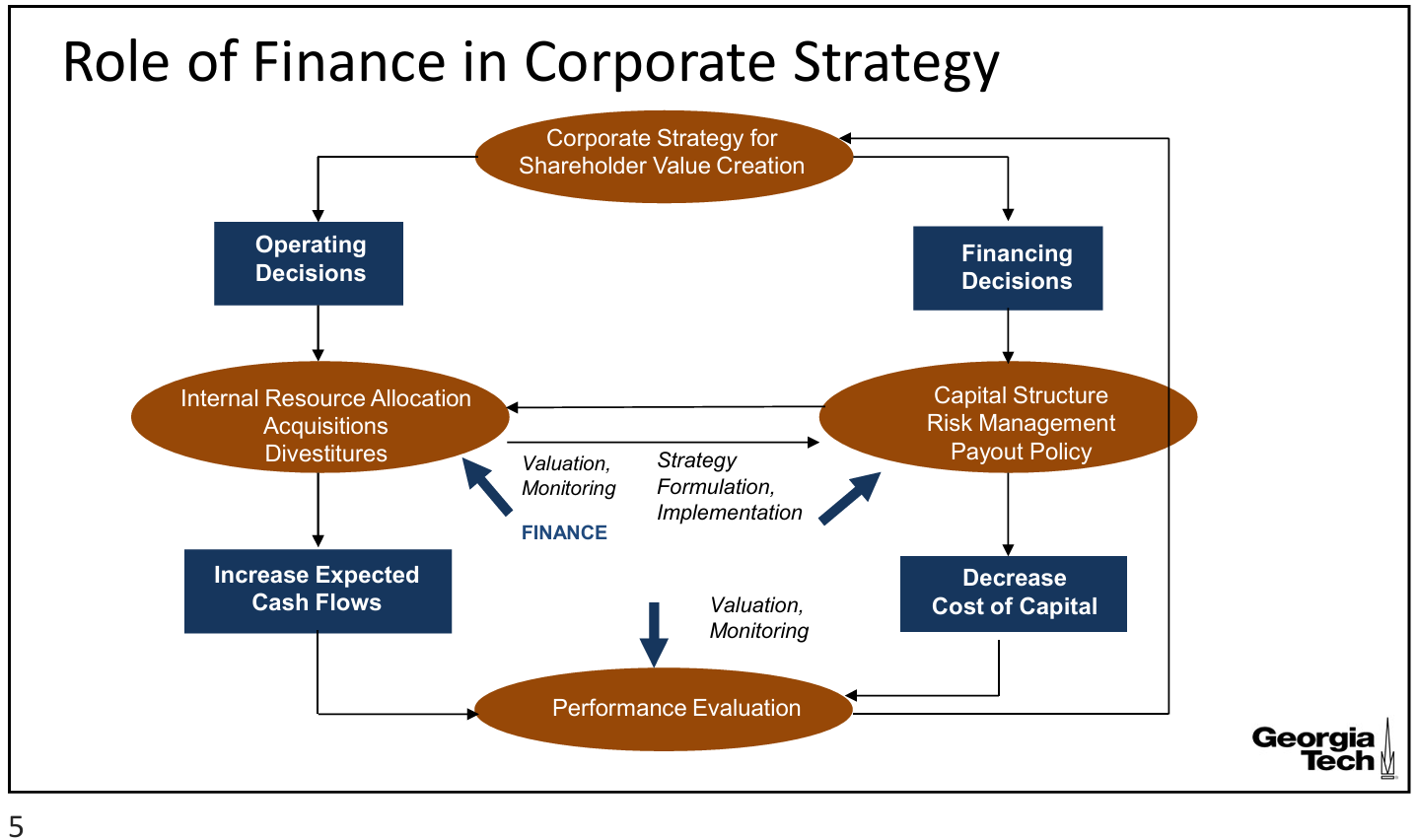
operating and financing
2 types of decisions in corporate strategy for shareholder value creation
operating decisions
internal resource allocation (how to allocate internal capital for future growth?)
acquisitions
divestures (firms or business units that aren’t doing well)
Finance: valuation and monitoring
increase expected cash flows
goal of operating/investment decisions
financing decisions
capital structure (how much debt? how much equity?)
risk management
payout policy
Finance: strategy, formulation, implementation
goal of financing decisions
decrease cost of capital
financing decision in the value creation process
financial markets (stockholders and bondholders) → corporation
operating/investment decision in the value creation process
corporation → factor market (land, labor, and physical capital)
ultimate goal of financial management
maximizing shareholder wealth
the firm and financial markets
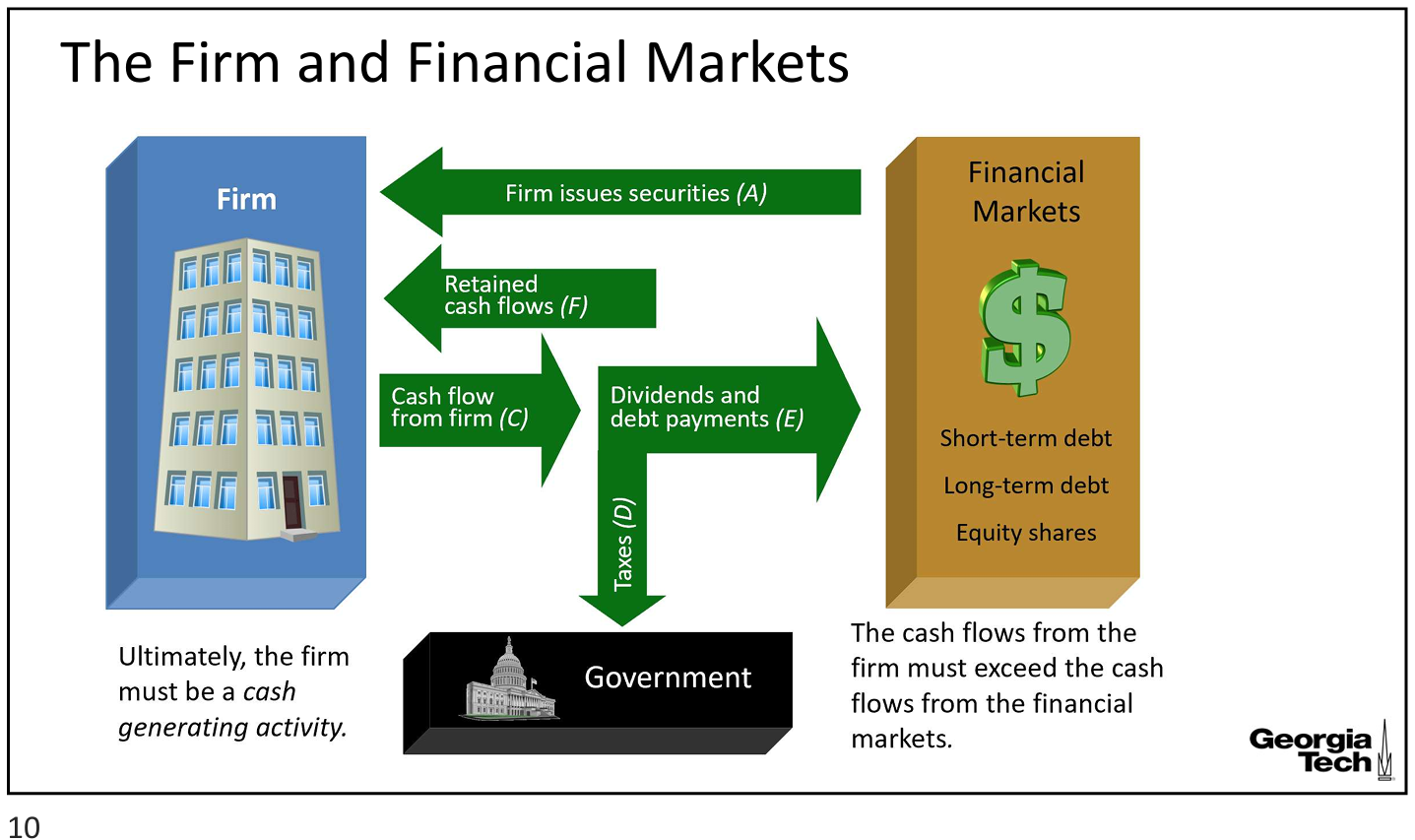
cash generating activity
ultimately, firm must be a
exceed
the cash flows from the firm must _____ the cash flows from the financial markets
financial markets → firm
firm issues securities (A)
retained cash flows (F)
firm → financial markets
cash flow from firm (C)
→ dividends and debt payments (E)
→ taxes (D) to gov
capital budgeting or capital expenditure/investment decision
process of determining exactly which assets to invest in and how much to invest for future growth
capital budgeting steps
Identification
Evaluation
Selection
Implementation
identification
find out opportunities and generate investment proposals
types of investment
required
replacement
expansion
diversification
evaluation
costs, benefits; estimating the project’s relevant cash flows and appropriate discount rate
expected cash flow stream (benefits)
discount rate (cost of capital)
selection
choosing a decision making rule (accept/reject criterion)
decision rules:
net present value (NPV)
profitability index (PI)
internal rate of return (IRR)
payback period (PP)
implementation
establishing an audit and follow-up procedure (revisit whether you got the expected benefits or fell short)
monitor magnitude and timing of cash flows
check if project still meets selection criterion
decide on a continuation or abandonment
review previous steps if failure rate is high
what to look at on statement of cash flows
cash flows from investing activities (capital expenditures)
long
most investments are ____ term
time value of money
a dollar today is worth more than a dollar in the future (but how much more and what does it depend on?)
future value = FVt =
PV * (1+r)t
FV Excel
=FV(r, t,, -PV)
present value
amount of money you need to invest today in order to duplicate some future dollar amount
present value = PV =
FVt / (1 + r)t
PV Excel
=PV(r, t,, -FV)
unknown interest rate Excel
=RATE(t,, PV, -FV)
unknown # periods Excel
=NPER(r,, PV, -FV)
present value of an annuity (PMT) =
(r * PV) / ( 1 - (1 + r)-t )
present value of an annuity Excel
=PMT(r, t, -PV)
net present value
measures value created for shareholders by the investment project
NPV =
C0 + C1/(1+r) + C2/(1+r)2 + … + CT/(1+r)T
NPV > 0
accept
project increases shareholder value
NPV < 0
reject
project destroys shareholder value
NPV = 0
depends
have to look at all past cash flow projections
negative
early cash flows (like C) are typically ____ for most investment projects because of large upfront investments
highest
choose project with _____ NPV
independent project
acceptance or rejection is independent of the acceptance or rejection of other projects
mutually exclusive project
can accept A or can accept B or reject both but cannot accept both
payback period
number of periods (usually years) required for the sum of the project’s expected cash flows to equal its initial cash outlay
the time it takes for a firm to recover its initial investment
payback period limitations
who decides cutoff?
penalizes long-term projects
completely ignores cash flows beyond cutoff
lowest
choose project with _____ payback period
internal rate of return
discount rate that makes the NPV = 0
>
accept project if IRR __ cost of capital
profitability index
the present value of an investment’s future cash flows divided by its initial cost
AKA cost/benefit ratio
PI =
(CF0 + NPV) / CF0
PI > 1.0
accept
highest
choose project with _____ PI
problems with IRR
multiple IRRs can exist for same project (- to + CF and + to - CF)
scale problem
timing problem
crossover rate
calculate IRR of A-B or B-A
NPV vs. IRR
will generally give same decision
exceptions:
non-conventional cash flows (signs change more than once)
mutually exclusive projects (initial investments, timing of cash flows substantially different)
cash flows, cost of capital (k)
NPV calculation inputs
NPV
NPV decision inputs
NPV > 0
NPV decision rule - accept
NPV < 0
NPV decision rule - reject
Y
does NPV adjust cash flows for time?
Y
does NPV adjust cash flows for risk?
Is NPV consistent with maximization of firm’s equity value?
Y
cash flows, cost of capital (k)
PI calculation inputs
PI
PI decision inputs
PI > 1
PI decision rule - accept
PI < 1
PI decision rule - reject
Y
does PI adjust cash flows for time?
Y
does PI adjust cash flows for risk?
Is PI consistent with maximization of firm’s equity value?
Y
but may fail to select project with highest NPV when ME
cash flows
IRR calculation inputs
IRR, cost of capital
IRR decision inputs
IRR > cost of capital
IRR decision rule - accept
IRR < cost of capital
IRR decision rule - reject
Y
does IRR adjust cash flows for time?
Y
does IRR adjust cash flows for risk?
Is IRR consistent with maximization of firm’s equity value?
Y
but may fail when projects ME, non-conventional cash flows
cash flows
PP calculation inputs
PP, cutoff period
PP decision inputs
PP < cutoff period
PP decision rule - accept
PP > cutoff period
PP decision rule - reject
N
does PP adjust cash flows for time?
N
does PP adjust cash flows for risk?
Is PP consistent with maximization of firm’s equity value?
N
rule of thumb for how long it takes money to double
interest rate * time = 72
cash flow statement, cash flow investments
if you want to determine the amount of capital expenditures a company made during the previous year, you should find the company’s most current ______ and look under the caption _________
independent, consistent
if capital projects with conventional cash flows are _____, the NPV and IRR methods should result in _____ “accept” or “reject” decisions
preferred method for evaluating and selecting projects for long-term investments
NPV
principles for relevant cash flows
record cash flows when the money actually moves (NOT accrual)
with-without: Imagine 2 worlds, one in which the investment is made and one in which it is rejected. All cash flows that are different in these 2 worlds are relevant, and those that are the same are irrelevant.
sunk costs
not relevant for present decision
test marketing costs
marketing research expenses expended
erosion costs
cash flow transferred to a new project from sales and customers of other products of the firm
opportunity costs
lost revenues from alternative uses of the asset
depreciation
non-cash expense; add back to income after tax to calculate the investment’s after-tax cash flow (ATCF)
ATCF =
(Revenue - Costs - Depreciation) (1 - Tax) + Depreciation
= (R - C) (1 - Tax) + D(Tax)
working capital
changes that are a result of an investment decision are relevant to the decision; have to lock up some amount of current assets in the project
at beginning of project life, treat as cash outflows
at end, treat as cash inflows
price, volume factors to consider when making cash flow estimates
competition from existing products
competition from technological advances
values to customer