[organising animals] breathing and gas exchange
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
[ AQA GCSE Biology Student Book, page 60-61 ] [ BBC Bitesize 'Organisation ⇢ Animal Organisation - Gaseous Exchange Systems' page 3-5 ]
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
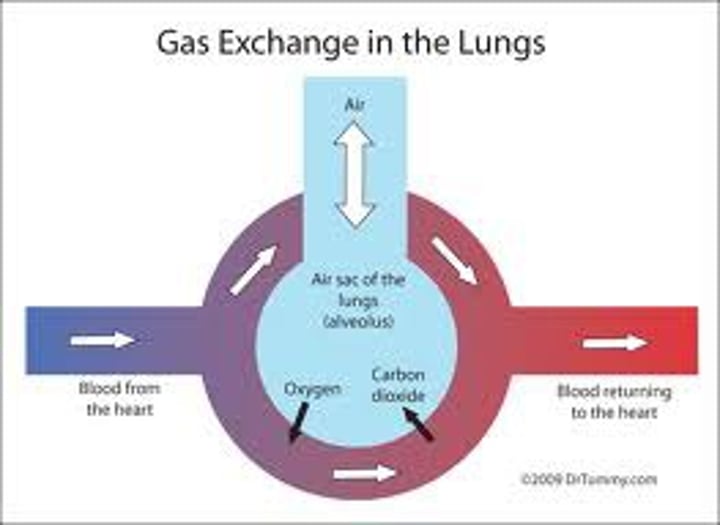
Gas Exchange
The process by which oxygen and carbon dioxide move between the bloodstream and the lungs.
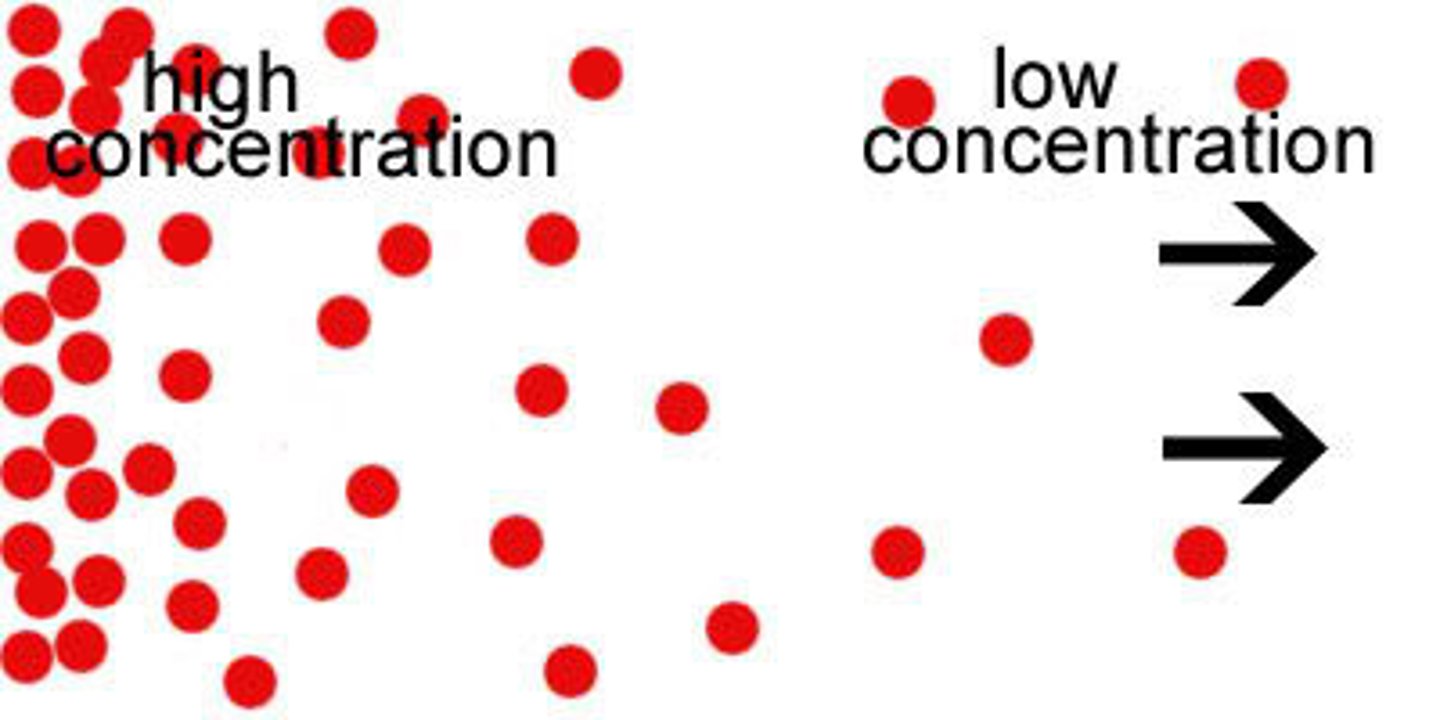
Diffusion
The movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
Breathing
Movement of air into and out of the lungs
Respiratory System
Organ system which replaces oxygen and removes carbon dioxide from the blood
Lungs are made up of...
…elastic tissue so tissue so that they can expand when you breathe in
1st Stage of Gas Exchange
Air enters your body through your mouth and nose.
2nd Stage of Gas Exchange
Air moves down the trachea
3rd Stage of Gas Exchange
Air moves down each bronchus and moves through each bronchiole
4th Stage of Gas Exchange
Air moves into the alveoli where it diffuses through a cell wall, into the bloodstream
Composition of (inhaled) Air
Nitrogen 78%
Oxygen 21%
Other Gases 1%
Composition of (exhaled) air
Nitrogen 78%
Oxygen 16%
Carbon Dioxide 5.04%
Other 0.96%
The amount of oxygen your body needs determines…
…how fast you need to breathe
Diaphragm
Strong sheet of muscle at the bottom of the chest cavity that helps with breathing.
Ribs
Bones which surround the lungs to form the ribcage and protect the lungs
Pleural Membranes
Thin, moist membranes surrounding the lungs that make an airtight seal.
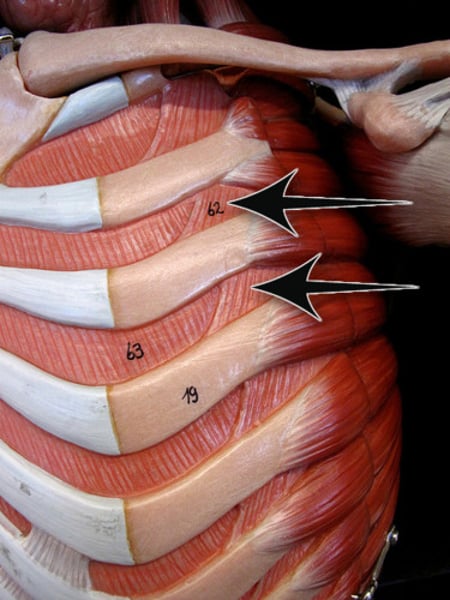
Intercostal Muscles
Sets of muscles between the ribs which raise and lower the rib cage.
Thorax
The ribs and upper backbone, and the organs found in the chest, also known as the pleural or chest cavity.
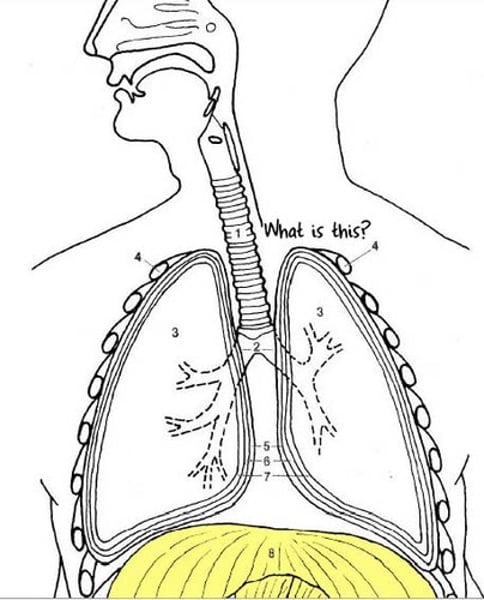
Trachea
The tube that leads from the mouth towards the lungs.
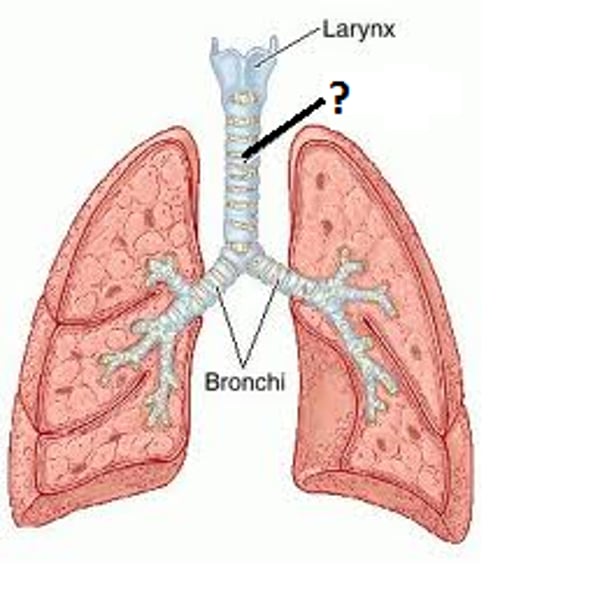
Bronchi
The plural of 'bronchus'. The bronchi are the two major air tubes in the lungs.
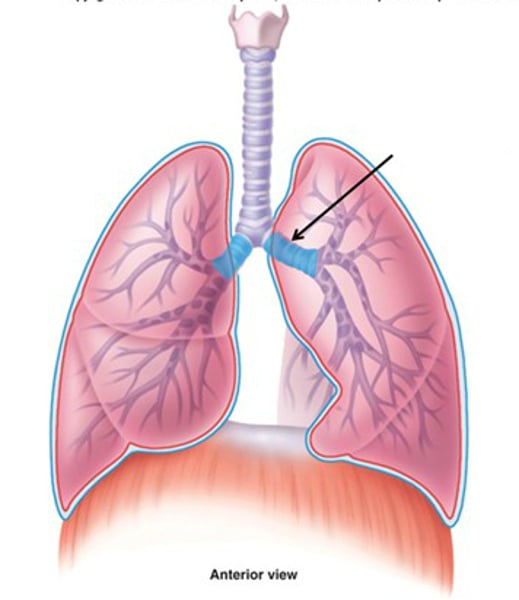
Bronchioles
The many small, branching tubes into which the bronchi subdivide.
Alveoli
Tiny air sacs in the lungs, where gas is exchanged during breathing.
Stage 1 of Breathing in
The intercostal muscles contract, causing the ribs to move upwards and outwards. The diaphragm contracts, pulling downwards. (increased volume of thorax)
Stage 2 of Breathing in
Volume of thorax increases so pressure inside the lungs decreases leading to air being drawn into the lungs.
Stage 1 of Breathing out
The intercostal muscles relax, causing the ribs to move downwards and outwards. The diaphragm relaxes and moves up (decreased volume of thorax)
Stage 2 of Breathing out
Volume of thorax decreases so pressure inside the lungs increases and air leaves the lungs.
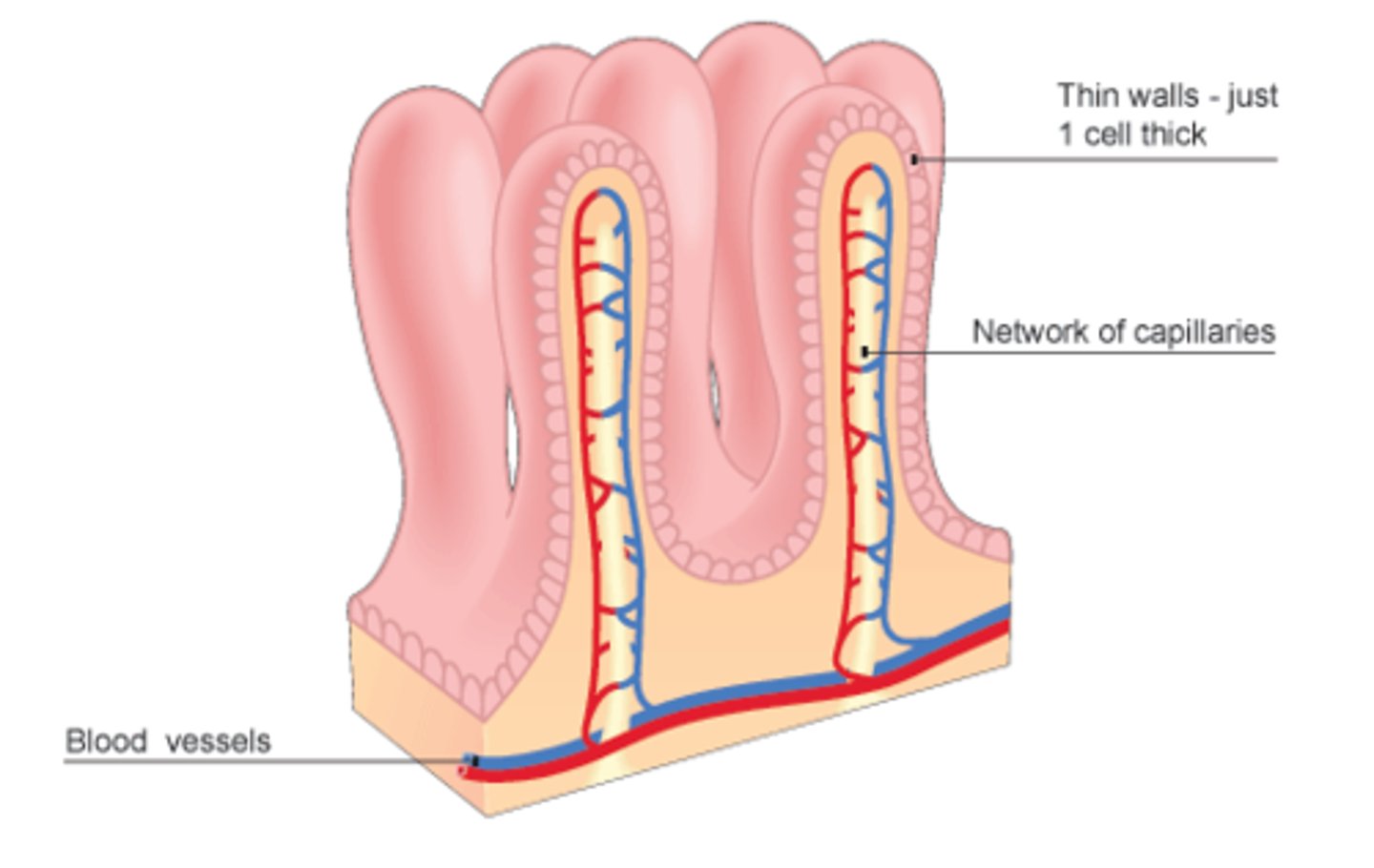
Villi
Finger-like projections in the small intestine that provide a large surface area for the absorption of food.
Concentration Gradient
The difference in the concentration of a chemical across a membrane. The moving blood and ventilated surfaces mean that a steep concentration gradient can be maintained. This increases effective exchange.
As multicellular organisms increase in size, they face two problems:
- their surface area does not increase as fast as the volume -> Insufficient surface area to meet their needs; body systems that add additional absorbing area to exchange surfaces
- their volume increases -> Diffusion is not quick enough to move substances to where they're needed in the organism's body; A transport system
Exchange of gases in fish is very efficient because of:
- the large surface area of the gills
- the large surface area of the blood capillaries in each gill filament
- the short distance required for diffusion - the outer layer of the gill filaments and the capillary walls are just one cell thick
- the efficient ventilation of the gills with water - there is a counter current flow of water and blood
The ventilation of the lungs and the blood flow through the surrounding capillaries mean...
...gases are being removed continually, and steep concentration gradients are set up and maintained for gases to diffuse.