Ch. 22: The Immune System
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/205
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 7:01 PM on 3/19/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
206 Terms
1
New cards
The lymphatic system consists of: (8 things)
1. Lymph
2. Lymphatic vessels
3. Lymphatic tissue
4. Lymphatic nodules
5. Lymph nodes
6. Tonsils
7. Spleen
8. Thymus
2
New cards
T or F: The only function of the lymph system is immunity.
False
3
New cards
DO: Describe the functions of the lymphatic system.
4
New cards
3 functions of the lymphatic system
1. Fluid balance
2. Lipid absorption
3. Defense
5
New cards
What volume of lymph is drained by lymph vessels (out of all the fluid that passes from capillaries into the interstitial fluid on a daily basis?
3 liters out of 30 total liters
6
New cards
What are lymphatic vessels in the small intestine called?
lacteals
7
New cards
Chyle
Lymph passing through the lymphatic vessels and on to venous circulation
8
New cards
How does the lymphatic system function in defense?
Filters microorganisms/foreign substances out of lymph in lymph nodes and out of blood in spleen
9
New cards
What 3 things does lymph consist of?
1. Water
2. Solutes from plasma (ions, nutrients, gases, some proteins)
3. Cells (hormones, enzymes, waste products)
10
New cards
How does lymph return to circulation?
via veins
11
New cards
DO:
* List the parts of the lymphatic system.
* Describe the structure of lymphatic vessels.
* Explain how lymph is formed and transported through lymphatic vessels.
* Distinguish between lymphatic tissue and a lymphatic organ.
* Describe the structure and function of tonsils, lymph nodes, the spleen, and the thymus.
* List the parts of the lymphatic system.
* Describe the structure of lymphatic vessels.
* Explain how lymph is formed and transported through lymphatic vessels.
* Distinguish between lymphatic tissue and a lymphatic organ.
* Describe the structure and function of tonsils, lymph nodes, the spleen, and the thymus.
12
New cards
What are lymphatic vessels formed from?
joined capillaries
13
New cards
What are lymphatic essential for?
fluid balance
14
New cards
What do lymphatic vessels carry lymph away from?
tissues
15
New cards
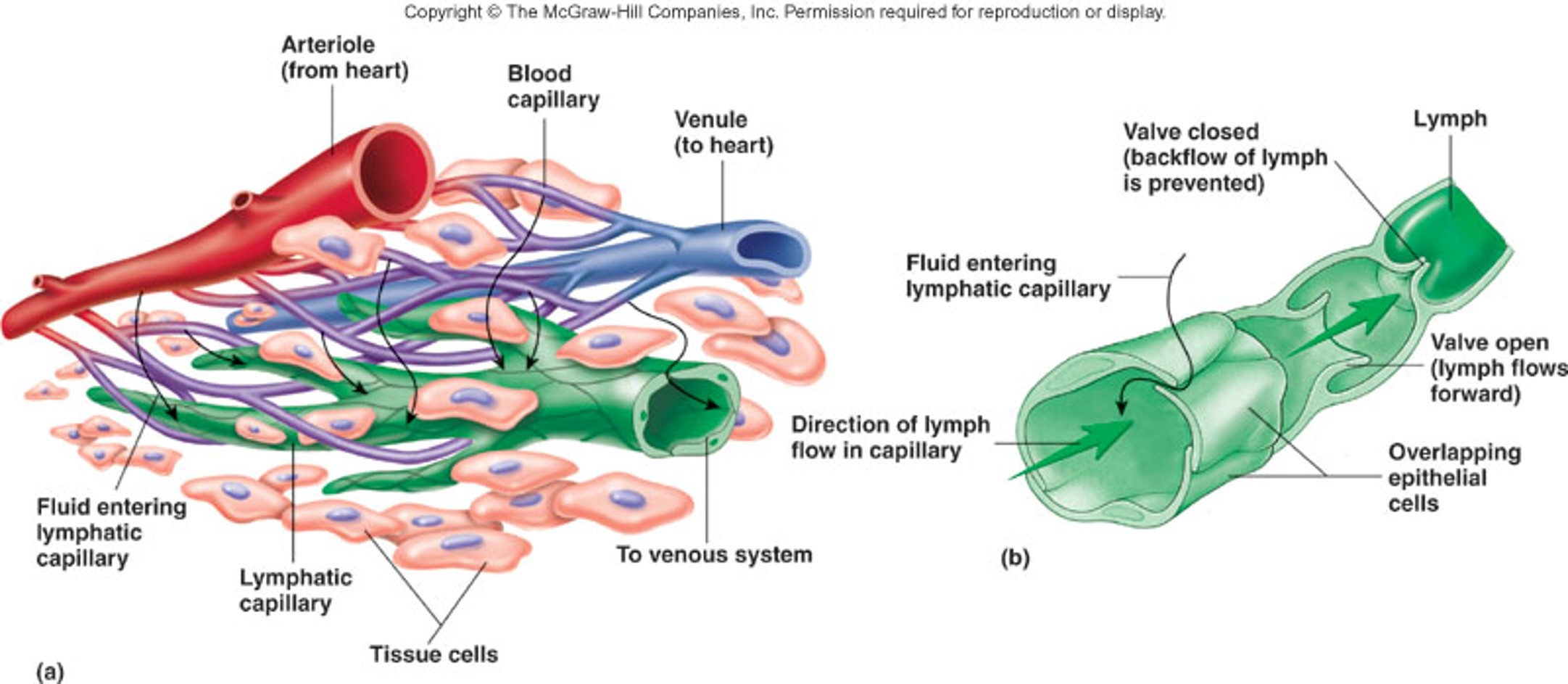
What is unique about lymphatic capillaries? (2 things)
they are dead end tubes, and they only accept fluid in, not out (“one-way valves”)
16
New cards
Lymphatic capillaries are more permeable than what?
blood capillaries (anything can enter lymphatic capillaries)
17
New cards
Lymphatic capillaries drain all parts of the body, except: (3 things)
1. CNS
2. Bone marrow
3. Tissues without blood vessels (cartilage, epidermis, cornea)
18
New cards
Lymph nodes
structures along lymphatic vessels that filter lymph
19
New cards
Lymphatic trunks
structures that drain a major portion of the body are connect to large veins directly or lymphatic ducts
20
New cards
Lymphatic ducts
structures that drain tissues and move lymph into major veins
21
New cards
3 examples of lymphatic trunks and what do they all collectively drain?
1. Jugular trunk
2. Subclavian trunk
3. Bronchomediastinal trunk
They typically join a right thoracic vein separately and drain lymph from the right side of the head, right-upper limb, and right thorax.
22
New cards
In what percentage of people do the three trunks (the jugular, subclavian, & bronchomediastinal trunks) join to form the right lymphatic duct, which then joins a right thoracic vein?
about 20%
23
New cards
What does the thoracic duct drain?
the remainder of the body (that the jugular, subclavian, and bronchomediastinal trunks don’t)
24
New cards
Lymph Drainage Into Veins (figure)
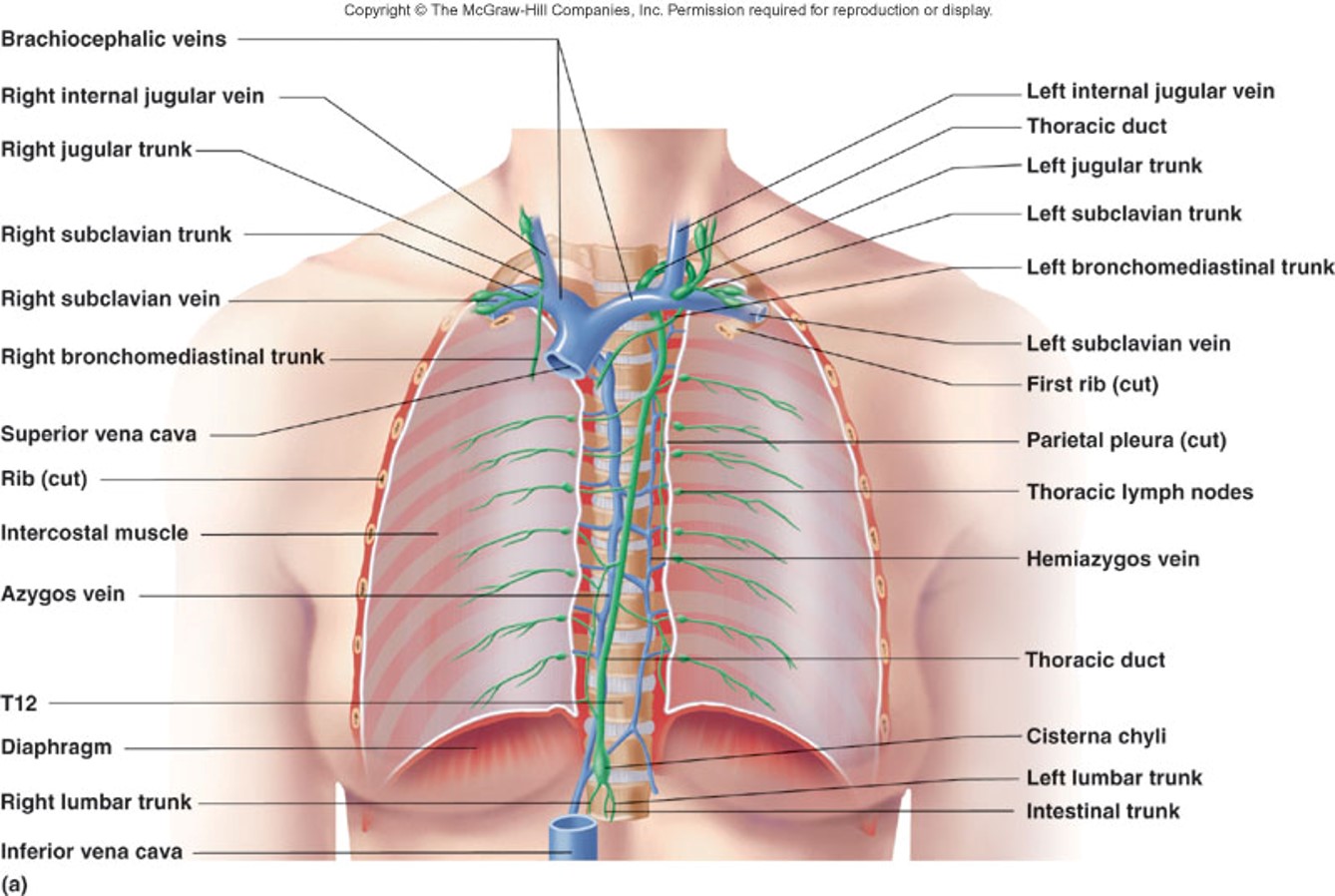
25
New cards
3 mechanisms of lymph movement
1. Contraction of lymphatic vessels (where primitive heart pumps with pacemaker cells)
2. Contraction of skeletal muscles (where the surrounding muscle cells contract, compressing lymph vessels)
3. Thoracic pressure changes (where vessels expand and fill upon inhalation and vessels compress and push lymph upon exhalation)
26
New cards
Lymphedema
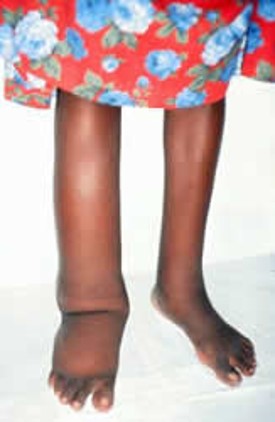
27
New cards
Lymphatic organs contain: (4 things)
1. lymphatic tissue (lymphocytes primarily)
2. macrophages
3. dendritic cells
4. reticular cells
28
New cards
Where do lymphocytes come from?
bone marrow, but they may mature elsewhere
29
New cards
What do reticular fibers do?
filter & trap microorganisms
30
New cards
Which structures of the lymphatic system are encapsulated? (3 things)
1. lymph node
2. spleen
3. thymus
31
New cards
Which structures of the lymphatic system are unencapsulated? (4 things)
1. digestive, respiratory, urinary, and reproductive tracts
2. lymphatic tissue
3. lymphatic nodules
4. tonsils
32
New cards
What specific tissue makes up unencapsulated lymphatic system structures?
MALT - mucosa associated lymphoid tissue that is in and beneath the mucous membranes of the structures we covered
33
New cards
What 2 cells mainly make up diffuse lymphatic tissue?
1. lymphocytes
2. macrophages
34
New cards
Where is diffuse lymphatic tissue located? (3 things)
1. deep to mucous membranes
2. around lymphatic nodules
3. in lymph nodes & spleen
35
New cards
Lymphatic nodules
denser arrangements of lymphatic tissue
36
New cards
Lymphatic nodules are numerous in:
the loose connective tissue of the digestive, respiratory, urinary, & reproductive systems
37
New cards
Peyer’s patches
aggregations of lymphatic nodules in small intestine & appendix
38
New cards
Lymphatic follicles
Lymphatic nodules found in the lymph nodes and spleen
39
New cards
How many lymph nodes are there dispersed primarily on or near blood vessels?
Approximately 450 superficial & deep
40
New cards
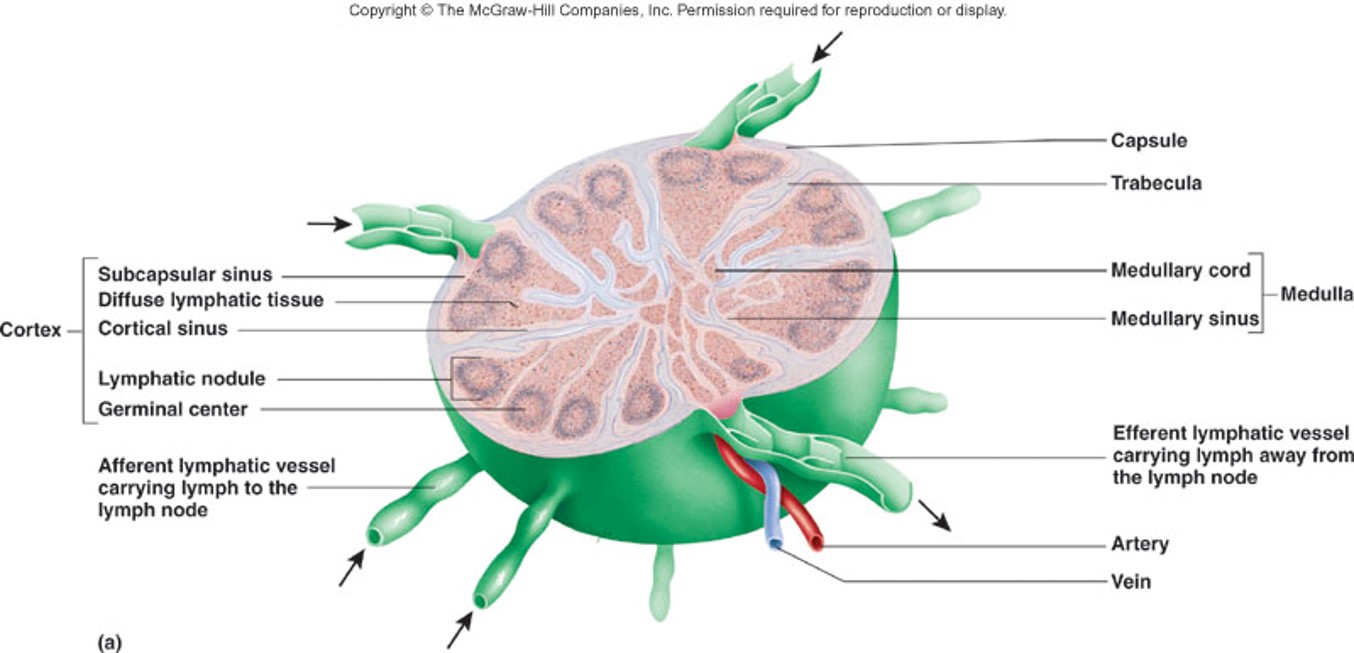
Parts of a lymph node
capsule, cortex, and medulla (trabeculae extend from the cortex to within)
41
New cards
What fibers form the supporting network of lymph nodes?
reticular fibers
42
New cards
Macrophages line lymphatic sinuses and do what?
remove things like bacteria
43
New cards
Lymphocytes proliferate in ____ when stimulated by bacteria, then end up in ____, ____, and ____.
germinal centers & blood, lymph, and lymph tissue
44
New cards
How do cancer cells often spread to circulation?
by migrating to lymph nodes
45
New cards
p. 777 activity:
* Why does removing axillary lymph nodes result in lymphedema?
* Explain why exercise can help reduce lymphedema.
* Explain why a compression bandage or garment can help reduce lymphedema.
* Why does removing axillary lymph nodes result in lymphedema?
* Explain why exercise can help reduce lymphedema.
* Explain why a compression bandage or garment can help reduce lymphedema.
46
New cards
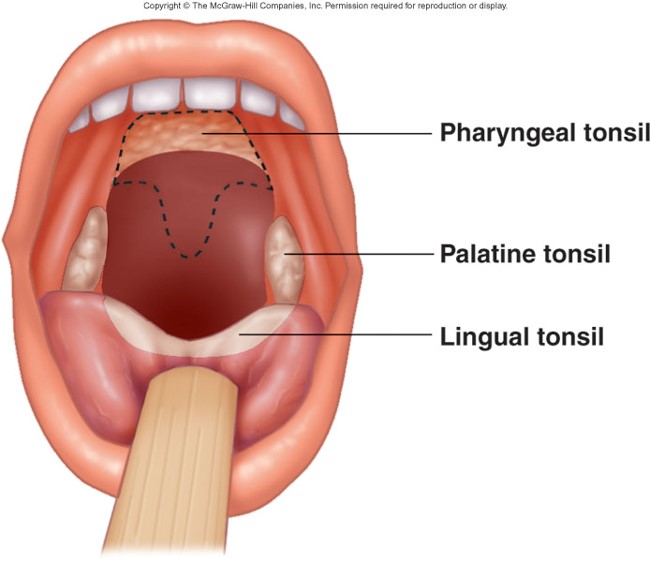
Tonsils
Large groups of lymphatic nodules & dense lymphatic tissue located in the mucous membranes in the pharynx
47
New cards
What is the function of the tonsils?
protection from bacteria and other harmful substances entering the pharynx from the nasal or oral cavity
48
New cards
3 tonsil groups
1. Pharyngeal (the “adenoids”)
2. Palatine (the “tonsils”)
3. Lingual
49
New cards
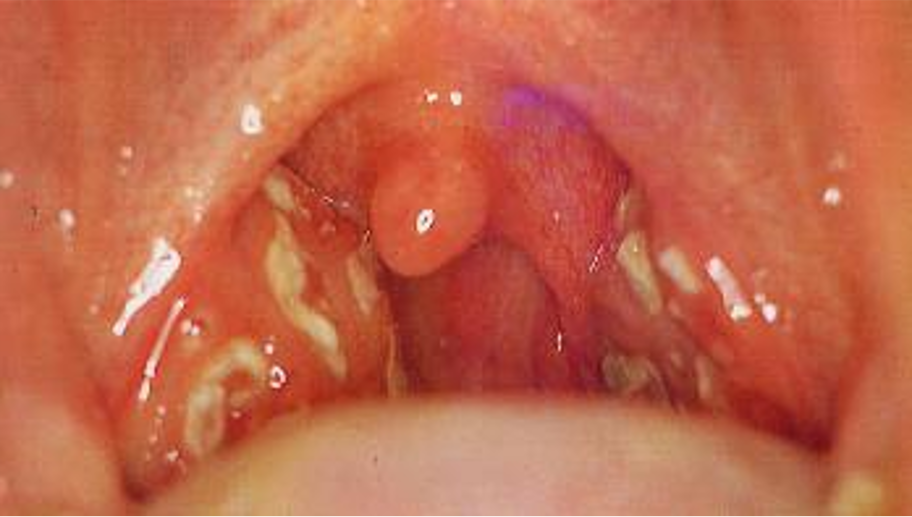
Tonsillitis (picture)
50
New cards
The tonsils that are referred to as "the tonsils" are the
A. lingual tonsils.
B. palatine tonsils.
C. pharyngeal tonsils.
D. splenic tonsils.
A. lingual tonsils.
B. palatine tonsils.
C. pharyngeal tonsils.
D. splenic tonsils.
B. palatine tonsils.
51
New cards
Where is the spleen located? What does it do?
Left superior abdomen, filters blood
52
New cards
What does rupture of the spleen result in?
bleeding, shock, death
53
New cards
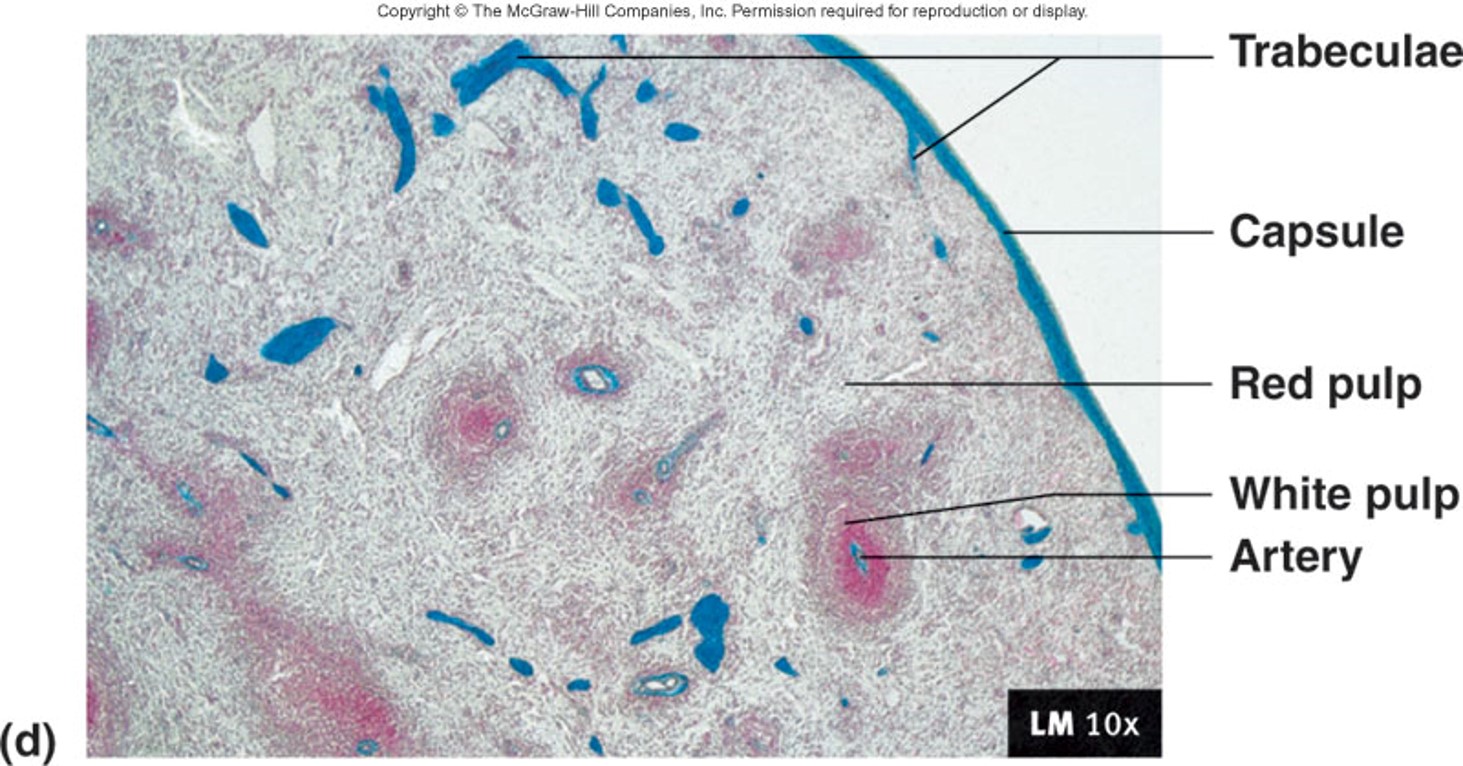
What is 1/4 of the volume of the spleen?
white pulp surrounding arteries
54
New cards
What does white pulp consist of?
the periarterial lymphatic sheath that extends into lymphatic nodules (lymphocytes)
55
New cards
What is 3/4 of the volume of the spleen?
red pulp associated with veins (the venous sinus and splenic cord)
56
New cards
What are venous sinuses?
enlarged capillaries between splenic cords that join with trabecular veins to form the splenic vein
57
New cards
What do splenic cords (reticular cells) produce?
reticular fibers with splenic macrophages in between the spaces
58
New cards
Spleen micrograph, labelled
59
New cards
T or F: Most blood flows through the spleen rapidly.
true
60
New cards
When does slower blood flow through the spleen occur?
when blood percolates through splenic cords
61
New cards
3 functions of the spleen
1. Destroys defective RBCs
2. Detects & responds to foreign substances
3. Limited reservoir for blood
62
New cards
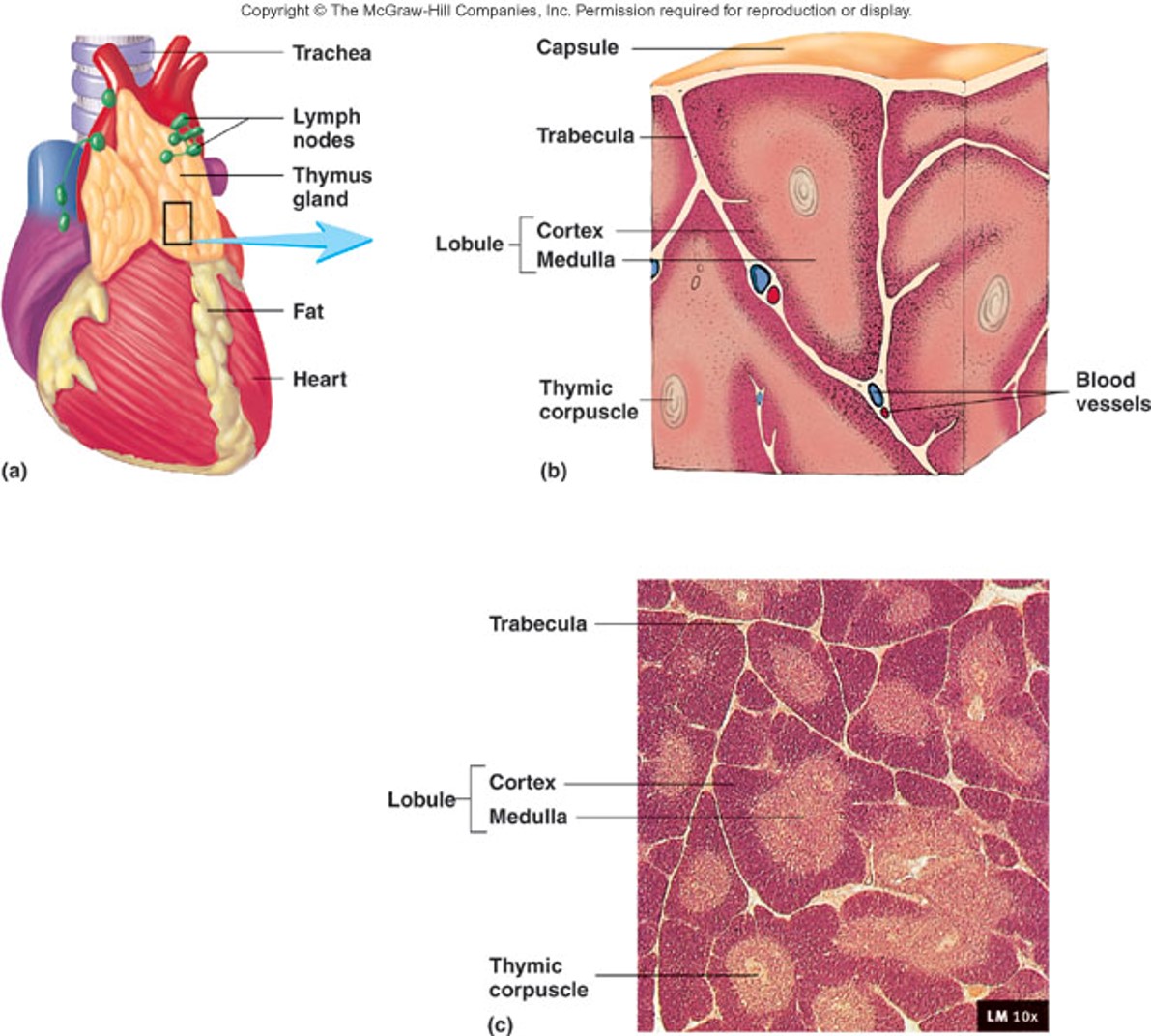
What is the thymus?
a bi-lobed gland in the superior mediastinum made up of cortex and medulla that grows in size during the first year then decreases after 60 years old
63
New cards
Which has more lymphocytes, the cortex of the thymus or the medulla?
the cortex
64
New cards
Where are thymic corpuscles found?
the medulla of the thymus
65
New cards
What is the function of thymic corpuscles?
to develop regulatory T cells that suppress the immune response and protect against autoimmune diseases
66
New cards
The thymus is the _____ site of T cells.
maturation
67
New cards
Thymosin plays an important role in _____.
T cell maturation.
68
New cards
How does thymosin play an important role in T cell maturation?
Large numbers of lymphocytes are produced in the thymus, but most degenerate. The lymphocytes that survive the maturation process live to react to foreign substances
69
New cards
The thymus
A. decreases in size in older adults.
B. produces neutrophils that move to other tissues.
C. produces a hormone called lymphopathin.
D. all of these
A. decreases in size in older adults.
B. produces neutrophils that move to other tissues.
C. produces a hormone called lymphopathin.
D. all of these
A. decreases in size in older adults.
70
New cards
Overview of the Lymphatic System (diagram)
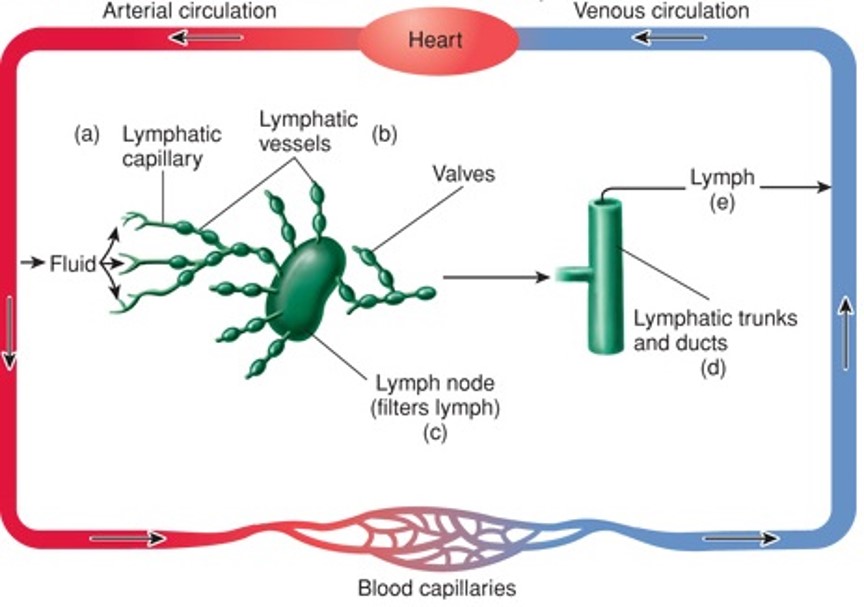
71
New cards
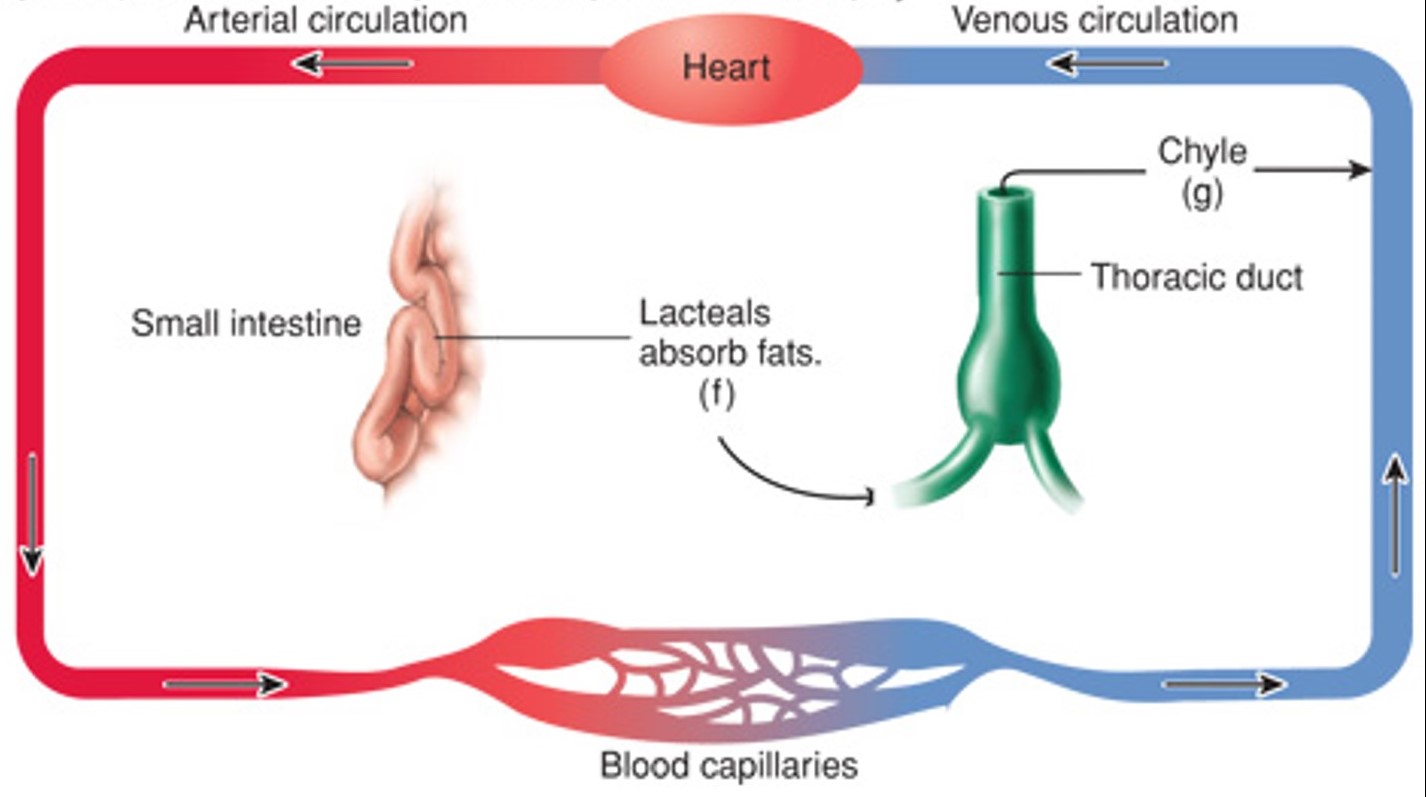
How is the small intestine important to the lymphatic system?
Lacteals absorb lipids, forming chyle (lymph + lipids), which then passes through the thoracic duct or right lymphatic trunks before entering the blood.
72
New cards
How is the spleen important to the lymphatic system?
It filters blood and is a site where lymphocytes respond to infections.
73
New cards
How is red bone marrow important to the lymphatic system?
Pre-B cells mature into B cells and are released with Pre-T cells into the blood.
74
New cards
How is the thymus important to the lymphatic system?
Pre-T cells mature into T cells in the thymus and are released into the blood.
75
New cards
What happens to B and T cells once they enter the blood?
They populate all lymphatic tissues and either remain there or pass through back into the bloodstream to respond to infections
76
New cards
T cells
A. are processed in the thymus.
B. are responsible for antibody-mediated immunity.
C. originate in the spleen.
D. produce antibodies when activated.
A. are processed in the thymus.
B. are responsible for antibody-mediated immunity.
C. originate in the spleen.
D. produce antibodies when activated.
A. are processed in the thymus.
77
New cards
DO:
* Define the concepts of specificity and memory as they apply to immunity
* Distinguish between the general characteristics of innate immunity and adaptive immunity
* Define the concepts of specificity and memory as they apply to immunity
* Distinguish between the general characteristics of innate immunity and adaptive immunity
78
New cards
Adaptive immunity (specific)
can recognize a particular substance and remember previous encounters with it to respond stronger and more rapidly with each encounter
79
New cards
Innate immunity (nonspecific)
can recognize and destroy certain foreign substances, but the response to them is the same each time the body is exposed
80
New cards
3 classes of innate immunity with functions
1. Physical barriers: prevent entry & remove microbes
2. Chemical mediators: kill bacteria, promote phagocytosis and inflammation
3. Cells: phagocytosis and production of chemicals
81
New cards
7 examples of physical barriers
1. Skin
2. Mucous membranes
3. Tears
4. Saliva
5. Urine
6. Cilia (in respiratory tract)
7. Coughing & sneezing
82
New cards
6 examples of chemical mediators
1. Lysozymes
2. Sebum
3. Mucus
4. Histamines
5. Complement proteins
6. Interferons
83
New cards
What is complement?
a group of 20 inactive plasma proteins in the blood that form a cascade when activated
84
New cards
2 complement pathways
1. Alternative pathway: C3 binds with foreign substance
2. Classical pathway: C1 binds to an antigen-antibody complex, which then activates C4
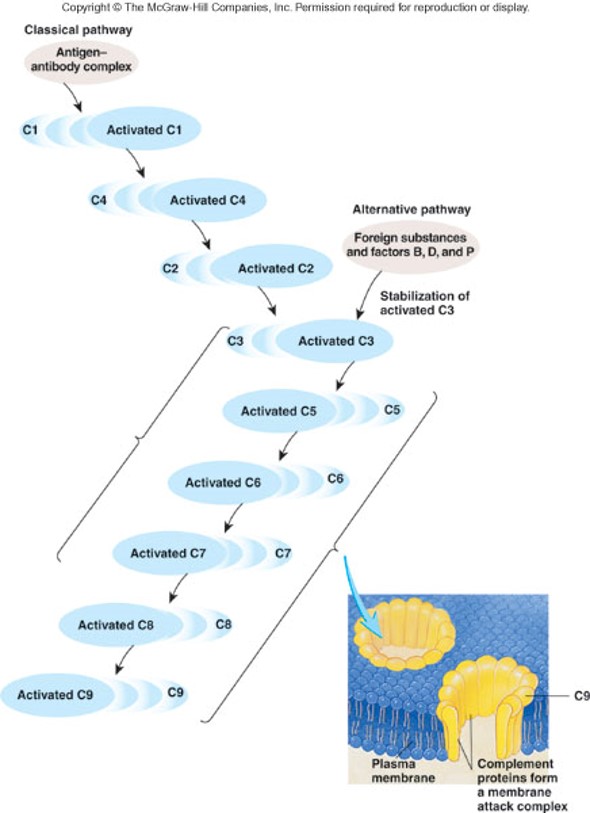
85
New cards
Which immunity is the alternate pathway a part of?
innate immunity
86
New cards
Which immunity is the classical pathway a part of?
adaptive
87
New cards
Activated complement proteins can: (3 things)
1. C3–C7 promote phagocytosis, inflammation, & chemotaxis at the site of infection
2. C5–C9 combine to form a membrane attack complex (MAC) which forms a channel through a cell’s plasma membrane, resulting in the lysis of that cell
3. Opsonization
88
New cards
What is opsonization?
when complement proteins attach to the surface of bacteria to stimulate macrophages and phagocytize the bacteria
89
New cards
What are interferons?
proteins that protect the body against viral infection and perhaps some forms of cancer
90
New cards
How do interferons work in the immune system?
Interferons are produced by the infected cell, paracrinely causing neighboring cells to produce antiviral proteins, which prevents viral replication in neighboring cells.
91
New cards
Is interferon viral resistance innate or adaptive?
innate
92
New cards
Which of the following is a protein that disrupts virus production, and is produced by most cells in response to a viral infection?
A. complement
B. interferon
C. lysozyme
D. mucus
A. complement
B. interferon
C. lysozyme
D. mucus
B. interferon
93
New cards
DO:
* Describe the three components of innate immunity
* Describe the chemical mediators and cells involved with innate immunity
* List the events of the inflammatory response and explain their significance
* Describe the three components of innate immunity
* Describe the chemical mediators and cells involved with innate immunity
* List the events of the inflammatory response and explain their significance
94
New cards
6 examples of cells used in innate immunity
1. White blood cells
2. Neutrophils
3. Macrophages
4. Basophils and mast cells
5. Eosinophils
6. Natural killer (NK) cells
95
New cards
Where are white blood cells produced?
red bone marrow and lymphatic tissue
96
New cards
What is the function of white blood cells?
travel in blood to infected tissues to destroy infections via phagocytosis (chemotaxis)
97
New cards
Where are neutrophils produced?
red bone marrow
98
New cards
What is the function of neutrophils?
one of the most important phagocytic cells that is the first responder to foreign substances
99
New cards
How many neutrophils leave the blood and pass through the wall of the digestive tract to provide phagocytic protection to the GI tract?
approximately 126 billion per day
100
New cards
Where do macrophages come from?
they are derived from monocytes and enter tissues