tutorial 1: Autism spectrum disorder
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
what does autism spectrum disorder include?
Autism, Rett’s disorder, childhood disintegrative disorder and Asbergers syndrome
why is autism a neurodevelopmental biogenetic condition?
because its something you are born with
what are the two key features of autims?
severe impairment in social interaction and severe impairment in communication
how does the impairment of reciprocal social interaction manifest itself?
no interets in making friends and soializing
no eye contact
lacking theory of mind
in what other diseases is there a lacking theory of mind?
schizophrenia, ADHD, brain injury, poor emotional attachement in childhood
which brain part is mostly associated with the lacking theory of mind?
medial prefrontal cortex
how does lack of ToM manifest itself at 14 months?
difficulty following a pointing finger (eg. looking at finger instead of the object)
how does lack of ToM show at 24 months?
struggling to play pretend games
how does lack of ToM show after 4 years?
failing to take other peoples perspective
what shows ToM at 9 years?
failing the “Faux pas- test” => not noticing when someones feelings might be hurt
what is the “awkward moment test” ?
people with aspergers cant remember the mental states of people in commercials as well
What is the “sally -Anne false belief task”?
autistic children fail to answer correcty, they think she will look in the box
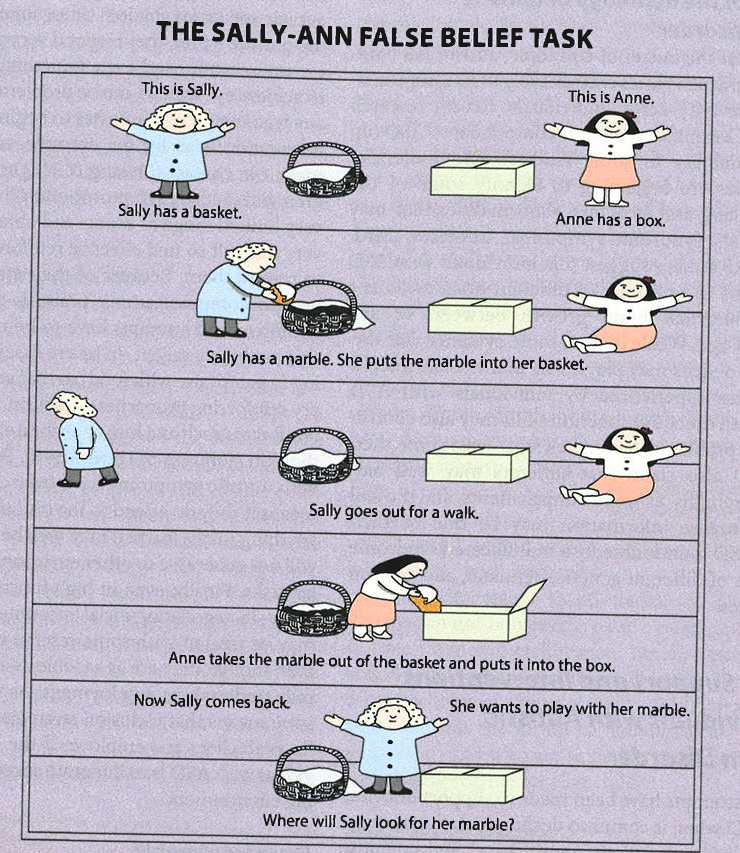
what is the weak central coherence theory?
not seeing the whole but instead all te small details
→ difficulty connecting, integrating, making meaning, answering specific questions about the whole, difficulty generalizing
do autistic people use “bottom up” or “top down” processing?
they use “bottom up” processing → from details to the big picture
how do autistic people cope with the detail overload?
they prefer routines, rules, being very systematic => makes them feel more in control and more safe
What does Monotropism refer to?
there is only one single channel of attention in autistic people
→ acounts for their hyperfocus and specialized interests
→ combinatio of eye contact, spoken words and body language is already so challenging that they cant pick up hidden meaning as well
“what is weak executive functioning theory”?
autistic people struggle to be flexible, multitask, plan and divide their attention
How is frontal lobe dysfunction associated with autism?
usually frontal lobe is synchronizing all brain activity like the director of an orchestra
→ in people with autism that director isnt as effective and the individual parts cant come together as harmoniously
what is Baron-Cohens “Empathizing-systemizing” theory?
people are either better at emphasizing or systemizing
systemizing = analyzing, finding rules, spot patterns and predictability, wanting to know how things work
empathizing= understanding other peoples emotions etc
=> people with autism are extreme systemizers
what causes the sex differences in systemizing and empathizing?
prenatal levels of sex hormones like testosterone and oestrogen
more testosterone = more systemizing
more oestrogen= more empathizer
what are the two components of empathy and which do autistic people lack?
cognitive
affective
=> autistic people lack cognitive empathy
what are the key features of the impaired communication in autistic people?
delay in learning how to communicate
Echolalia
pronoun reversal
monotonous speech
immature grammar use
how many autistic people approx have an intelellectual disability?
70%
what is the so called “Savant syndrome”?
excelling at one specific ability while having multiple cognitive impairments
what are the requirements for being diagnosed autistic?
strong social and communicative deficits
restrictive, repetitive and stereotyped behaviour patterns
strong need for sameness and routine
hyper or hyporeactive to sensory input
symptoms must be present since early development
symptoms mus cause severe impairment in daily life
what is the estimates prevalence of autism?
1.1%
what is the estimated ration of autism between boys and girls?
4:1
what are the gender differences in autism?
females seem to be more innately social
girls are better at masking, pretending to be normal
girls have stronger verbal and language skills than boys
girls have better eye contact, more imaginative, more socially interactive
less likely to cope by isolation
special interests of girls focuses more on people and animals vs. for boys its more objects
girls are less likely to be involved in conduct problems
girls have less obvious motor problems, fewer repetitive behaviours
girls have more sensory issues (more easily overstimulated)
what is the approximate heritability of autism?
80%
what three other genetic diseases does autism often co-occur with?
PKU, fragile x syndrome and tuberous sclerosis
what is the association between older fathers and autism?
increases risk of autistic offspring due to increased mutation in sperm (over 40 years means six times as likely)
what is the association between IQ of father and autism?
very high IQ of father increases risk of autism (over 111 32% more likely)
what is the association between prematurity and autism?
being born premature increases risk of autism
how much is the cooccurence rate between autism and gastrointestinal dysfucntion?
80%
what disease is especially often co-occuring with autism in girls?
PCOS
how much more likely areautistic people to have sleep problems?
twice as likely
what are three other disease/defects often co-occuring with autism?
deafness, tuberous sclerosis, hypermobility and Ehlers-Danlos syndrome
what ar four ways the genetic effects occur?
→ code number variations
→ epigenetics
→ “double hit mutations” (mutations in two genes)
→ sex linked genes
what are some perinatal rism factors for autism?
maternal infections
(intrauterine) drug intake
maternal bleeding in first trimester
depressed immune function
what are some postnatal events that have been linked to ASD?
inflammatory bowel disease
admniniatration of MMR vaccine (measles, mumps, rubella)
what is the connection between brain growth and autism?
unusual brain growth in first 4 years
rapid grow from 12-24 months
decline in growth in adolescence → very slow
=> the rapid growth period leads to poorer neural connectivity
what can be said about neural connection in the autistic brain ?
poorer connection
connections arent as selective bc of the period of rapid growth
poor synaptic pruning between 2 and 4
information going from frontal lobes to more distant parts is small
how do fmri scans show the lacking theory of mind in the autistic brain?
decreased activity in the prefrontal cortex and amygdala
what do EEG scans of autistic brains show?
abnormal patterns in temporal lobes
sometimes even seizures
what do ERP studies reveal about autistic brain activity?
abnormal reaction to novel and language stimuli
what does sensory amplification refer to ?
increased connection causes sensory overload and reduced ability to filter out information
How can different brain activity account for the difficulty to shift attention quickly?
in autistic brain it takes longer for the connections to be disconnected again, the neurons stay synchronized about 20 seconds longer
what did autopsies reveal about the cerebellum of autistic people?
abnormal
smaller and less connections
reduced number of Purkinje cells
=> affects motor, balance and social cognition
what did autopsies reveal about the corpus callosum?
smaller and different shape
=> affects amount and velocity of transmission, problems in integrating information
what is different in the amygdala of autistic people?
either under or over connected
where did autopsies reveal abnormalities in the autistic brain?
frontal lobe
limbic system
basal ganglia
cerebllum
amygdala
ventricles
corpus callosum
what is one very interesting thing about autistic brains?
they have been found to often be unsymmetrical
what has been found in einsteins brain (apparently)?
larger parietal lobes
more glial cells
which brain circuits are less connected in autistic brains?
mpfc (comparing perspectives)
right temporal parietal junction (processing gaze)
right fusiform area (processing faces)
insula (interoception and self-awareness)
what are some cognitive functions that are impaired in autistic people?
problem solving
attention
ability to plan actions
impulse control
inhibition of inappropriate behaviour
short and long term memory
phonological and visiosparial working memory
what is often one strength of autistic people?
systemizing information
which drugs are mostly prescribed to autistic people?
antipsychotic drugs (haloperidol, risperidone, naltrexone)
what do the drugs reduce?
repetitve and stereotyped behavior
aggression
social withdrawal
tantrums
hyperactivity
mood changes
self abusive behaviours
what are some serious side effects of the drugs?
sedation
increased hunger
dizziness
weight gain
jerky movement disturbances
how can behavioural training be used to treat autism?
learning self help, communication and social skills
conditioning and modellingbehavior modification techniques to improve functioning.
“ parent implemented early intervention”
“supported employment”
What is the triad of impairment in autism?
impairment in:
impairment in social reciprocity
communication
imagination and fexibility
what is the “double-empathy theory”?
communication difficulties arise from mismatch in neurotype
what did the study by cromton et al. find out about the communication struggles of autistic people?
communication difficulties are increased when its a mixed pair and communication between two autistic people showed much less complications