B7: Non-communicable diseases
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
Communicable diseases
Can spread from person to person
Spread by a pathogen
Non-communicable disease
Can’t be passed from person to person
Health
State of physical + mental well being
What are non-communicable diseases caused by?
Risk factors
Edpidemiology
Study of the patterns of disease to determine its risk factors
How can different types of disease may interact?
4
Defects in IS → individual more likely to suffer from infectious diseases
Viruses living in cells trigger cancers
Immune reactions initially caused by a pathogen trigger allergies eg skin rashes + asthma
Severe physical ill health can lead to depression + other mental illness
Risk factors
Factors linked to an increased rate of a disease
What are many diseases caused by?
Interaction of a number of factors
What can risk factors be?
Aspects of a person’s lifestyle
Substances in the person’s body or environment
Correlation
A link between two factors
Eg non-communicable disease + lifestyle factors
How to determine if there is a correlation between 2 factors?
Plot scatter graph
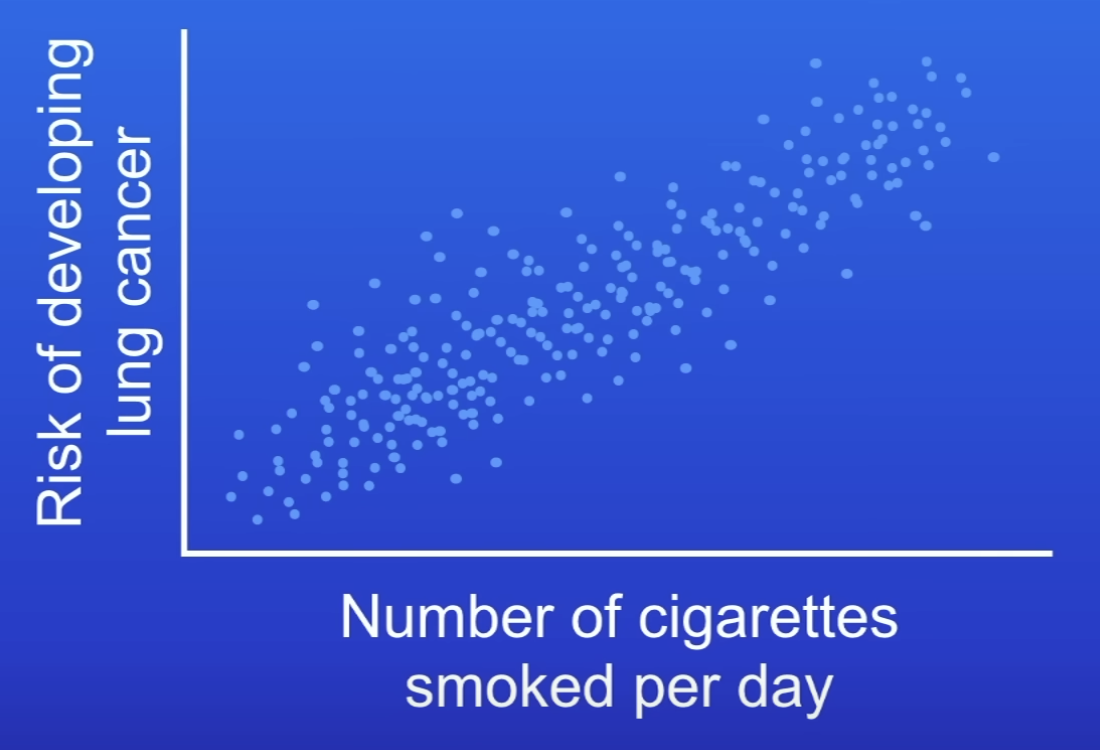
Positive correlation
When 2 variables move in the same direction
As 1 increases, the other also increases
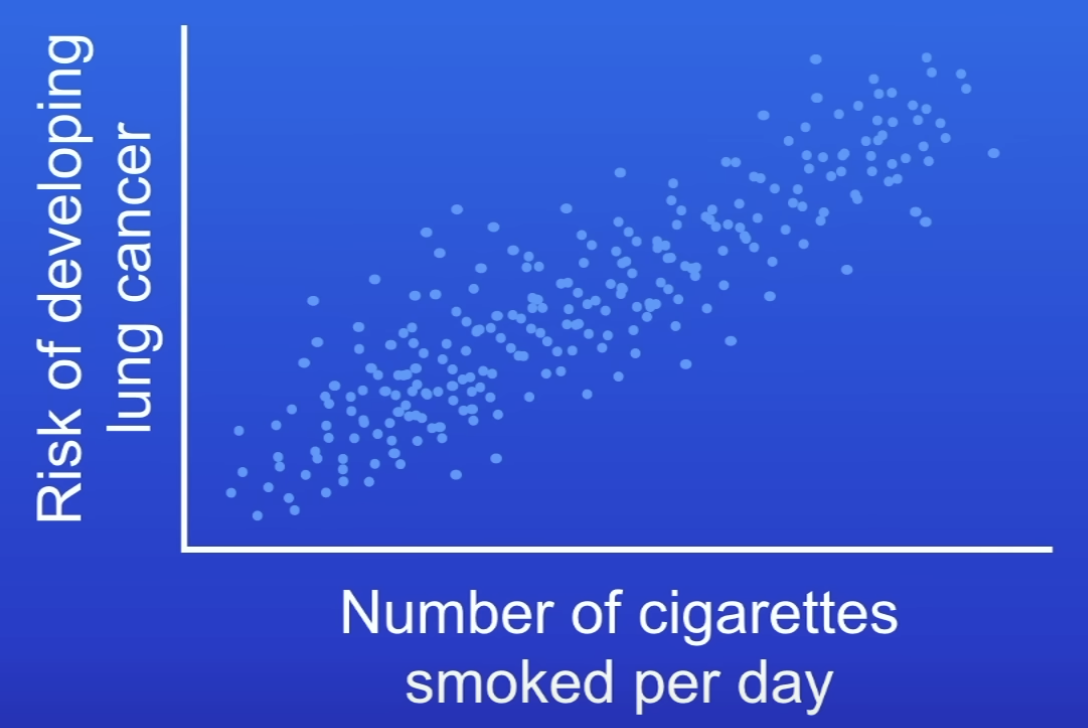
Correlation doesn’t prove…
Cause
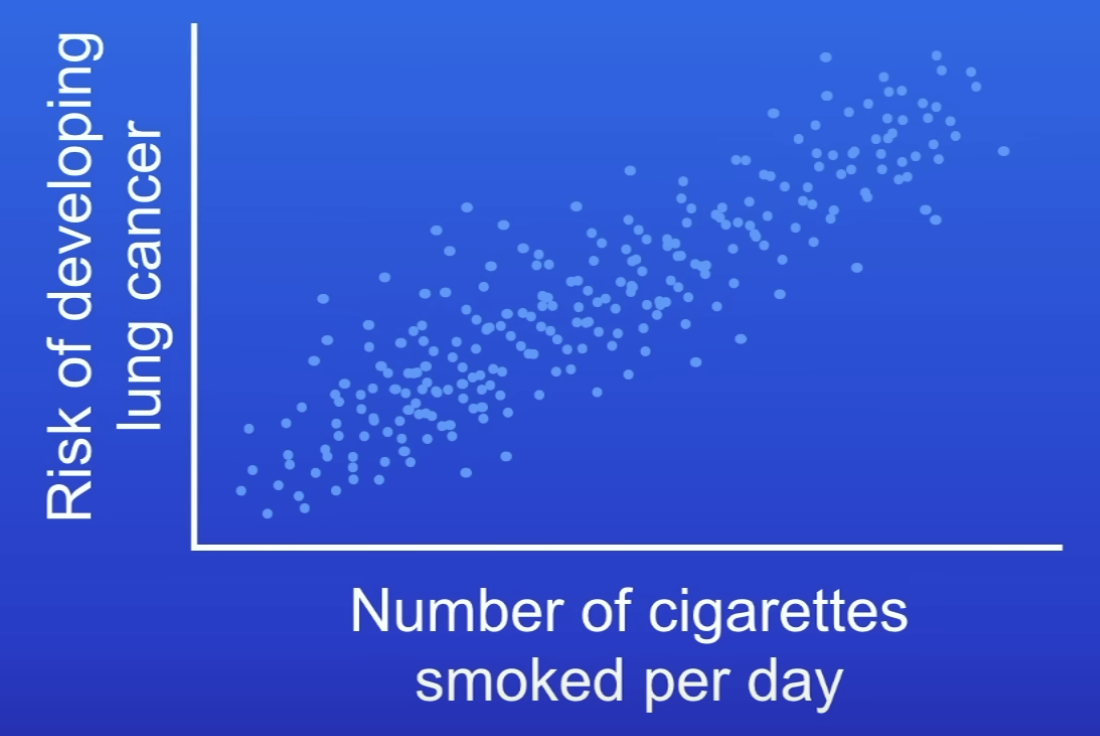
What does this graph show?
Suggests smoking cigarettes + lung cancer linked
Doesn’t prove smoking causes lung cancer
Causal mechanism
Scientific explanation of how 1 factor causes another thru a biological process
Causal mechanism of how cigarette smoking causes cancer
Cigarette smoke contains chemicals that damage DNA + increase risk of cancer
Carcinogen
Cancer causing chemical
When will scientists accept that 1 factor increases the risk of another factor?
Strong correlation betw 2 factors
Causal mechanism proved
Has a causal mechanism been proven for all risk factors?
No- only some
Issue with studying patterns of disease to determine risk factors?
Sampling- not possible to sample every single person
Ideally how would you investigate if a disease is linked to diet?
Look at every single person in population
Look at what they ate + chances of them developing the disease
What do scientists do instead of sampling every single person in the population?
Sample a group of people
Then try to draw conclusions abt the whole population
Issue with sampling
Can get biased sample → can’t use results to draw conclusions abt whole country
Example of biased sample
Sample selected from only 1 town → may not represent entire pop of country
Eg ppl in the town may do less exercise than average or be exposed to certain type of pollution only there in that town
How to avoid bias when sampling?
Use large sample
Must be as random as possible
What can’t conclusions be drawn from?
Small / non-random sample
What do scientists need to prove a correlation?
Causal mechanism
Is the human and financial cost of non communicable diseases high or low?
High
Human cost of non communicable diseases (individual, local community)
Lots of people die per year from NCD:
Individual- emotional
Financial effect on family / local community (support people who are ill)
Financial effects of NCDs on nations
Expensive to:
Treat ill people
Research into disease
Financial effects of NCDs globally
Disease affects working age population
What happens in cell division by mitosis?
1 cell copied into 2 identical cells
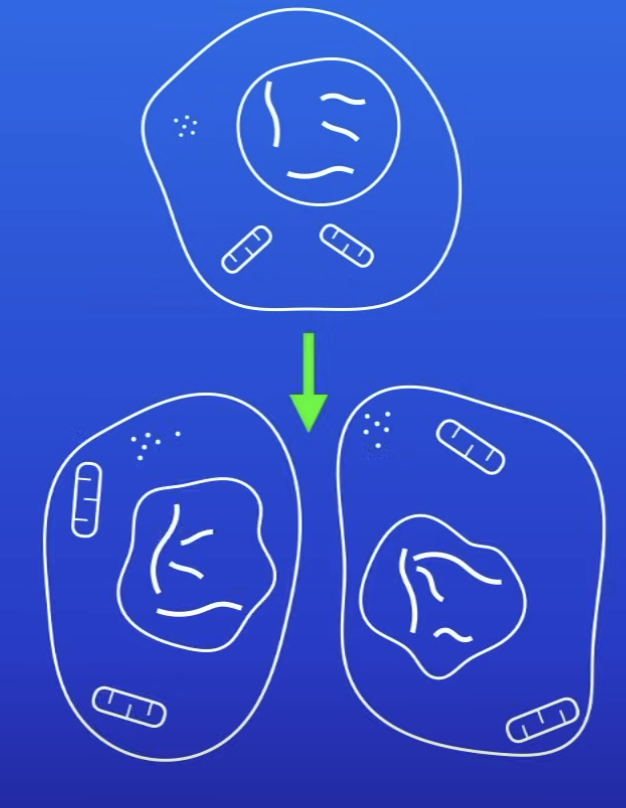
Where does cell division by mitosis in the body occur?
All over the body
When are rates of mitosis high in the body?
During growth + repair
Key feature of mitosis
Tightly controlled process
How is mitosis a tightly controlled process?
Genes in nucleus tell cells when to divide + when to stop dividing
What do changes in genes (that control mitosis) lead to?
Uncontrolled growth + mitosis
What produces a tumour?
Uncontrolled growth + mitosis
Tumour
Mass of abnormally growing cells formed when control in cell cycle is lost
2 types of tumor
Benign
Malignant
Benign tumors
Growths of abnormal cells contained in 1 area, within a membrane
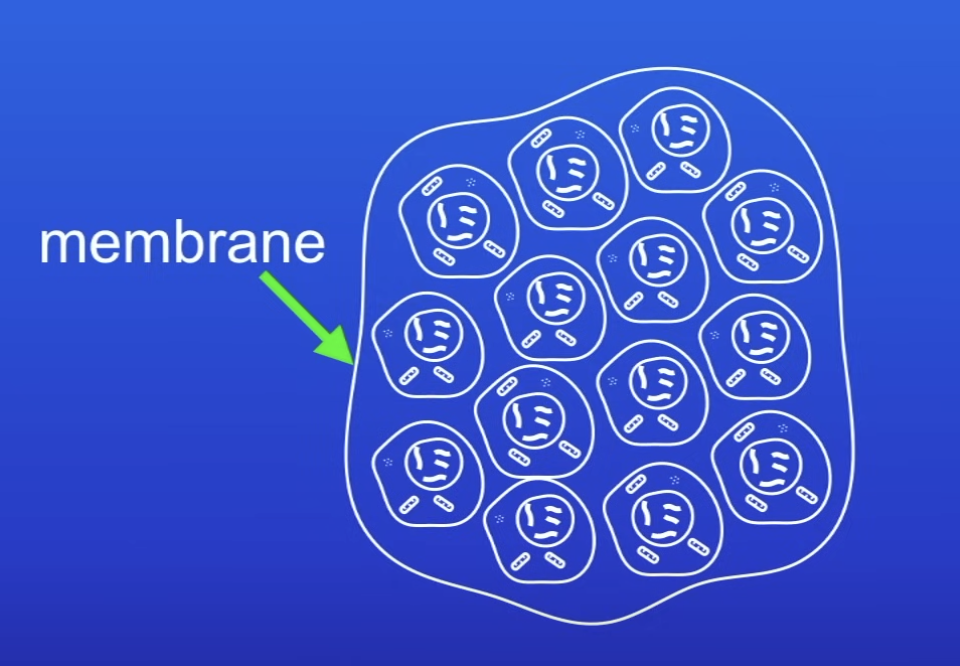
Features of benign tumours
Don’t invade other parts of the body
Are benign tumors cancerous?
No
When can benign tumors be dangerous?
When it causes pressure / damage to an organ
Malignant tumour cells
Cancers
Malignant tumours
Mass of abnormal cells that invade neighbouring tissues + move into BS
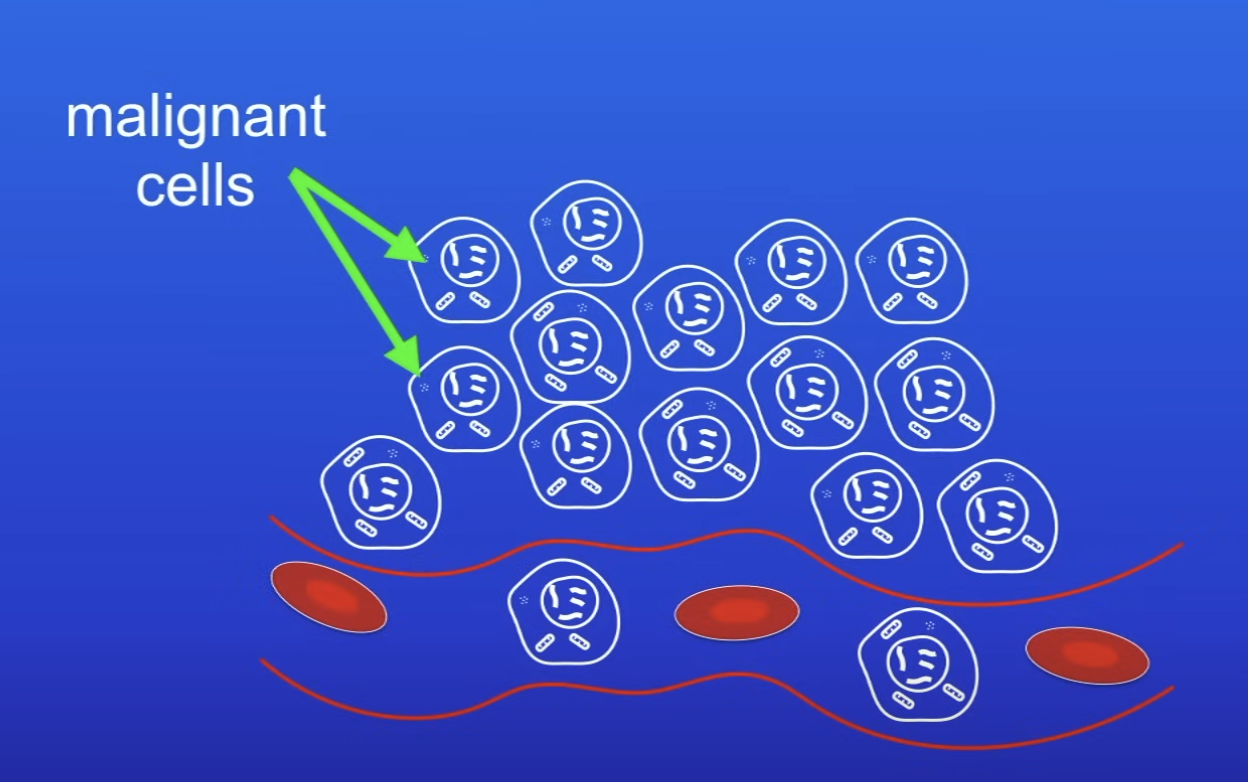
Features of malignant tumours (cells)
Once in BS, MC spread to diff parts of body + form secondary tumours
How are secondary tumours formed?
MC invade neighbouring tissue + move into BS
MC spread to diff parts of body → undergo uncontrolled cell division → forms ST
How are cancer cells different to normal cells?
Divide quicker
Live longer
What is cancer the result of?
Changes in the DNA of cells (mutations)
That lead to uncontrolled growth + division
Results in the formation of a malignant tumour
Cancer
Result of mutations in cells, leading to uncontrolled growth + division, forms MT
Risk factors for developing cancer
Genetics- (breast, prostate, LI)
Lifestyle (eg substances in enviorment)
What does it mean if the risk factor for cancer is genetic?
Can inherit genes from our parents that increase the risk of these cancers
Cancers linked to lifestyle
Smoking → lung
Ultraviolet → skin
Alcohol → mouth + throat
What substances in the environment can cause cancer?
Radon → lung cancer
Radon
Radioactive gas
Increases risk of developing lung cancer
How does radon increase the risk of lung cancer?
Releases ionising radiation, which damages DNA in cells
Causes uncontrolled cell division in cells → cancer
Example lifestyle factors that can increase risk of NCD
Diet
Alcohol
Smoking
Risk factors for cardiovascular diseases
Diet
Smoking
How does a high fat diet increase risk of cardiovascular disease?
↑ cholesterol level in blood → ↑ rate fatty materials build up in arteries
How does a diet high in salt increase risk of cardiovascular disease?
↑ blood pressure
What decreases risk of developing cardiovascular diseases?
Regular exercise
What does smoking increase the risk of?
Lung cancer
Lung diseases (emphysema)
Miscarriage
How does smoking increase the risk of lung cancer?
Cigarette smoke contains carcinogens
Carcinogens
Chemicals that can trigger cancer
Effects of NCD
Poor life quality
Reduced life span
Effects of smoking when pregnant on unborn baby?
↑ risk of
Miscarriage
Premature birth
Baby born w low body mass
After smoking, why do you feel breathless?
CO binds to haemoglobin instead of O2
How does smoking increase risk of infections?
Cilia move mucus + bacteria away from lungs
Chemicals in smoke paralyzes cilia in trachea + bronchi
So pathogens enter the lung
What does smoking do to blood vessels?
Narrows it
What does drinking alcohol while pregnant cause?
Fetal alcohol syndrome
What do children born with FAS have?
Learning difficulties
Mental + physical problems
Pregnant women shouldn’t
Drink alcohol
Smoke
Example carcinogens
Ionising radiation
Tar (in smoke)
Alcohol
What does drinking alcohol increase the risk of?
Fetal alcohol syndrome
Liver cirrhosis
Liver cancer
Memory loss
What organ can alcohol affect?
Liver
Brain → leads to addiction + memory loss
What can’t people with type 2 diabetes control?
Their blood glucose levels
What can type 2 diabetes lead to?
Blindness
What may type 2 diabetes require?
Amputation of limb
Risk factor for type 2 diabetes?
Obesity
Risk factors interacting: how does drinking alcohol increase risk of type 2 diabetes?
Drink excess alc → obesity (increase risk of T2D)
What happens if you eat more food than you need?
Excess stored as fat
What does the food you eat transfer?
Energy to muscles
What does the amount of exercise you do affect?
Amt of respiration in muscles
Hence amt of food you need