Business Associations
1/341
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
342 Terms
What is the structure of a sole proprietorship?
Single owner
What is the structure of a partnership?
Two or more owners
What is the structure of a limited liability partnership?
Two or more owners who have filed a statement of qualification with their respective state agency

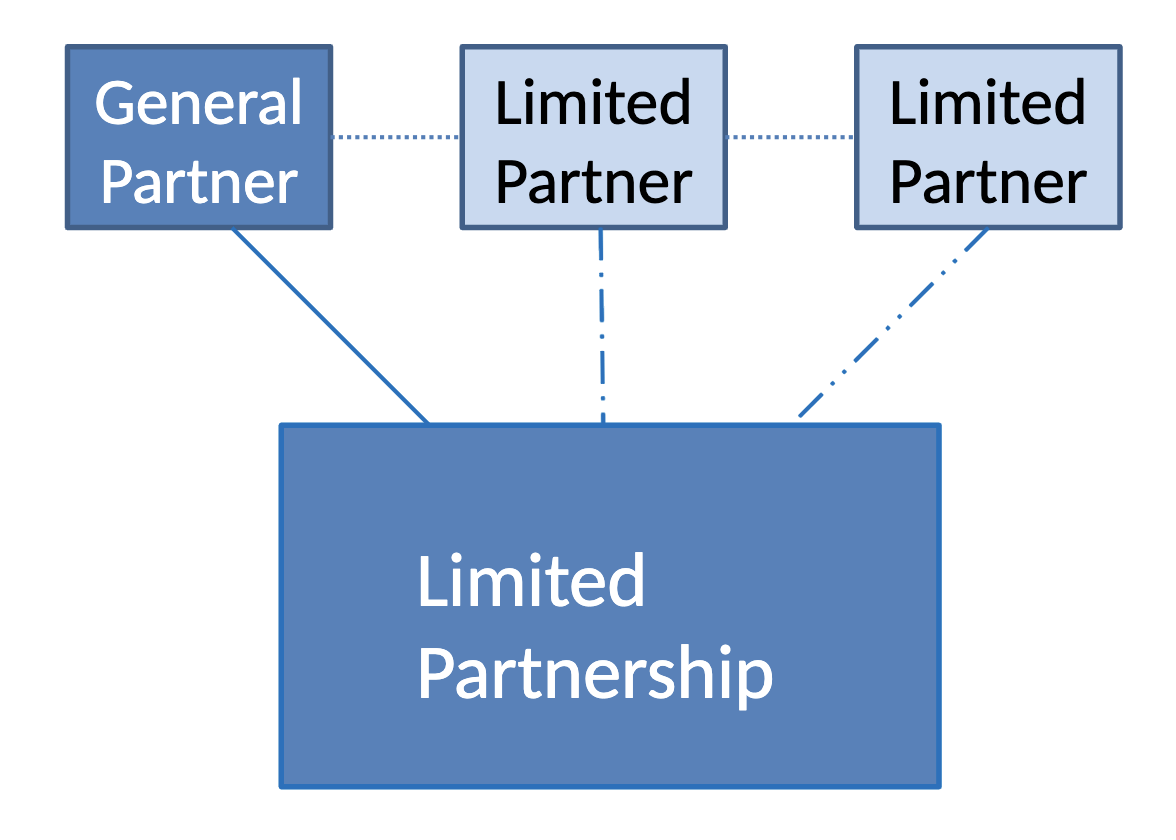
What is the structure of a limited partnership?
A partnership consisting of one or more general partners and one or more limited partners who contribute capital and share profits but have limited liability
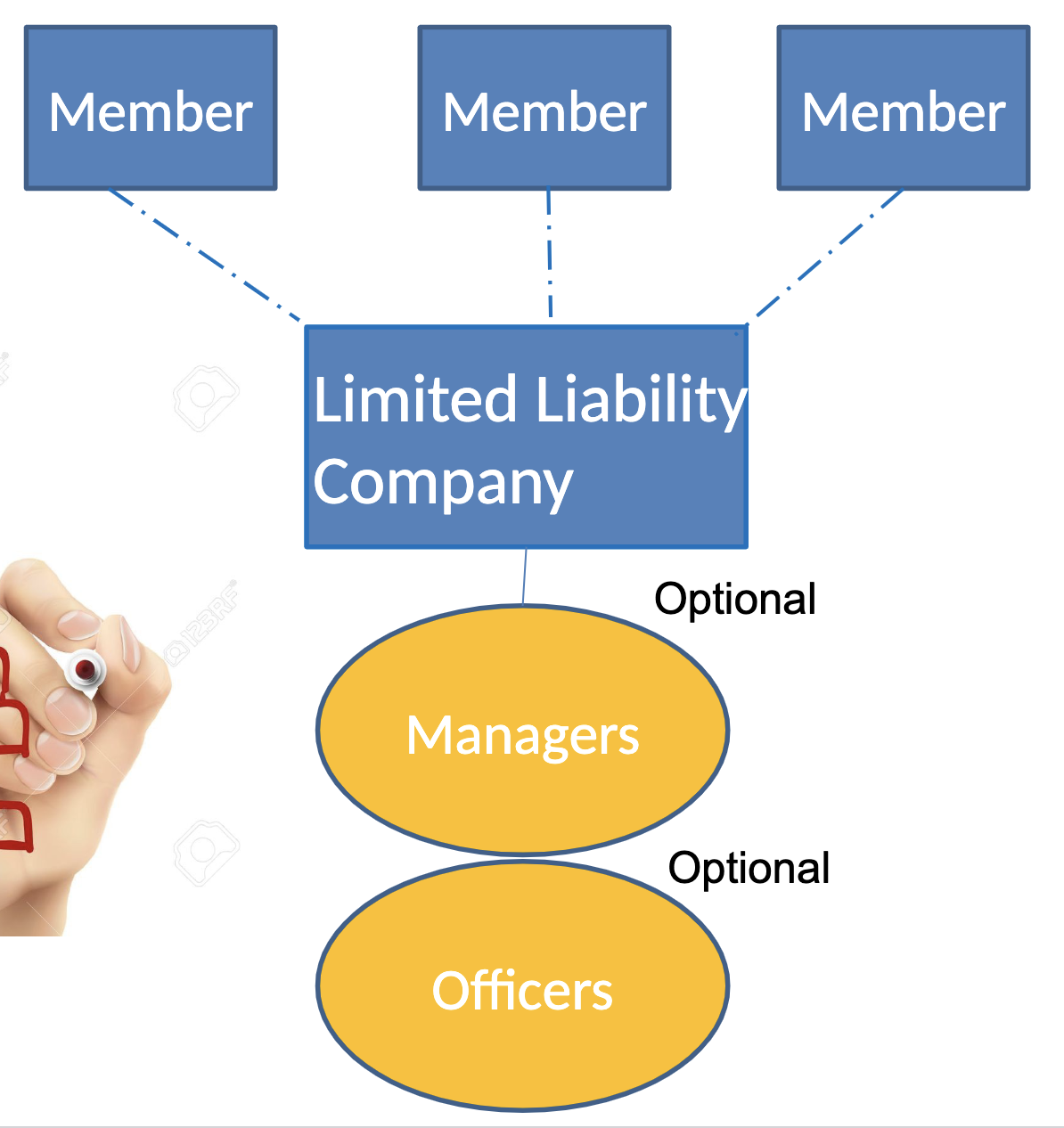
What is the structure of a limited liability company?
Comprised of “members” with with OPTION of adding managers and officers
What is the structure of a corporation?
SHAREHOLDERS create a BOARD OF DIRECTORS which then elect OFFICERS
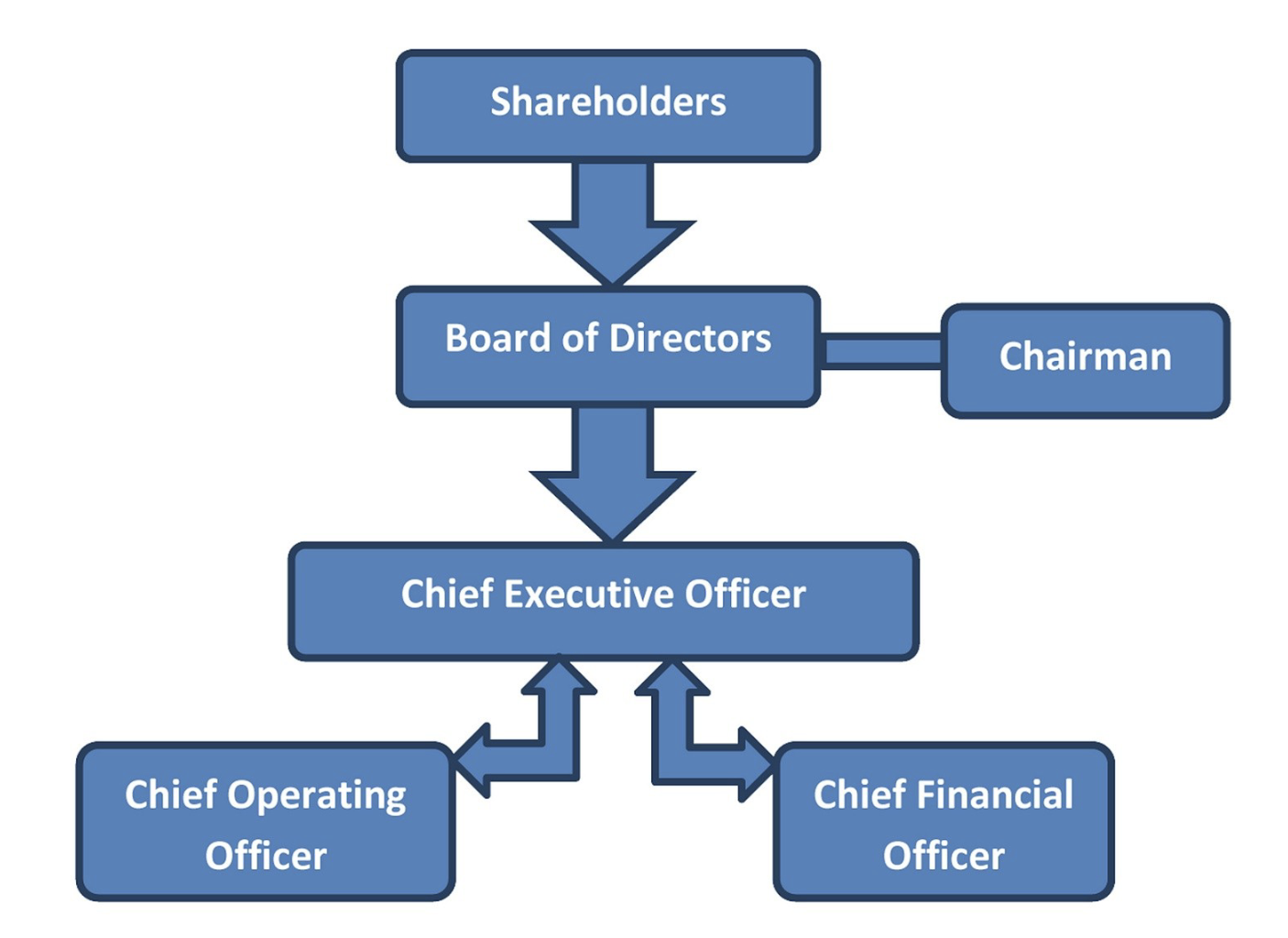
How do business entities interact with the world?
Business entities interact with the world through agents.
What is the rule to determine whether there is an agency relationship? 🏫
An agency relationship arises when (1) a principal manifests assent that an agent (2) act on the principal’s behalf and subject to the principal’s control, and (3) the agent consents to so act.
What is the rule statement for manifestations?
Manifestations are written words, spoken words, or other conduct
What are all the ways a principal can be bound to a contract? 🍺👂
Actual authority (express or implied), apparent authority, ratification, estoppel, and inherent agency power
What is the rule statement for actual authority? 💛🏈💚
Actual authority means the authority granted by a principal to an agent, enabling the agent to act on the principal's behalf. Actual authority can either express or implied.
What is the rule statement for express authority? 💦
Express authority is the authority the principal explicitly gives the agent.
What is the rule for implied authority? 👶
Implied authority is the authority the agent has for acts necessary or incidental to the express authority.
What is the rule statement for apparent authority? 📱⛪️
Apparent authority is when the agent has the appearance of authority, such that the law deems the principal bound to a contract signed by the agent. Apparent authority exists when a third-party (1) reasonably believes the author has authority and (2) that belief is traceable to the principal’s manifestations.
What is the rule statement for estoppel? ➡❌
Estoppel applies where a third party detrimentally changes their position because (1) a principal carelessly or intentionally causes a third-party to reasonably believe the actor had authority; or (2) having notice of such belief, the principal fails to notify the third-party of the facts.
What is the rule statement for inherent agency power? 🍆🍑
Inherent agency power is the power to bind a principal to a contract, derived solely from the agency relation itself, typically where an employee engages in an act customary for the employee’s position.
What is the rule statement for ratification? ⬅
Ratification is when a principal affirms a prior act done by another, giving the act the same effect as if it were originally authorized. A principal affirms a prior act through written or spoken words or other conduct.
What is the specific agency law applicable to partnerships? 💼
(1) Each partner is an agent of the partnership. (2) Each partner can bind the partnership to contracts in the ordinary course of business. (3) A partner has authority for a non-ordinary course act only if all the partners authorize it.
In partnerships, what is a statement of authority?
A statement of authority is a document filed with the Secretary of State, or DFI in Wisconsin, specifying a partner’s authority.
What is the specific agency rule applicable to corporations? 👤👤👤👤
(1) Shareholders are not agents of the corporation. (2) Individual directors are not agents of the corporation. (3) Officers are agents of the corporation. (4) The Board of Directors can authorize people to act on behalf of the corporation.
What is a secretary’s certificate?
A secretary’s certificate is a document signed by a corporation’s secretary certifying certain actions were approved.
What is an opinion letter?
An opinion letter is a document from a law firm opining on authority.
What is the RULLCA agency rule applicable to LLCs?
A member is not an agent of an LLC solely by reason of being a member—they must be granted such authority.
What is the DLLCA agency rule applicable to LLCs?
Unless otherwise provided in an LLC agreement, each member and manager has the authority to bind the LLC.
What is a statement of authority in LLCs?
A statement of authority is a document filed with secretary of state, or DFI in WI, specifying a partner’s authority.
What is the rule for respondeat superior? 👷
A principal is liable for a tort committed by an agent if (1) the agent is an employee of the principal and (2) the agent committed the tort while acting within the scope of
employment.
What is an employee? 🩷💚
An employee is an agent whose principal controls or has the right to control the manner and means of the work. A principal is generally not liable for torts of a non-employee agent or independent contractor.
What is “scope of employment”? 💍
An employee is acting within the scope of employment when either (1) performing work assigned by the employer or (2) engaging in conduct subject to the employer’s control.
What is the duty of loyalty? 👮
An agent must be loyal and act in the principal’s best interests. This means the agent must not (1) be or act for an adverse party in a transaction related to the agency relationship, (2) compete with the principal during the agency relationship, (3) use the principal’s property for personal purposes, or (4) disclose the principal’s confidential information to third parties.
What is the duty of performance and disclosure? 🧑🏻💼👱🏻♀️
An agent has duties to (1) act with care and competence, (2) act within the scope of the agent’s actual authority, and (3) provide information the principal would wish to have.
What is the rule statement for the termination of fiduciary duties?
An agent’s fiduciary duties to a principal generally end on termination of the agency relationship.
What is the rule statement for restrictive covenants?
Breach of restrictive covenants between the principal and agent may entitle the principal to injunctive relief.
What are some examples of restrictive covenants?
Non-disclosure agreements/provisions, non-compete agreements/provisions, non-solicit agreements/provisions
What is inside liability?
Inside liability is the owners’ personal liability for business obligations.
What are some examples of inside liabilities?
Breach of contract, torts, business debts
What is the rule statement for inside liability applicable to LLCs?
Owners have a full shield against all inside liability.
What is the rule statement for inside liability applicable to corporations?
Owners in a corporation have a full shield against all inside liability.
What is the rule statement for inside liability applicable to LLPs?
Owners in an LLP have a full shield against all liability EXCEPT for a few states.
What is the rule statement for inside liability applicable to an LP?
Limited partners in an LP have a full shield against all inside liability; general partners in an LP have no shield.
What are outside liabilites?
Outside liabilities are a company’s exposure to an owner’s personal liabilities.
What are some examples of outside liabilities?
Medical debt, tort judgements, credit card debt, mortgages
What are the five typical factors of the “piercing the veil” doctrine?
(1) The entity was the “alter ego” of another person or entity. This means the entity was misused and not treated as a separate entity. (2) The entity was used to commit a fraud. (3) The owners/managers failed to observe company formalities. (4) The company was inadequately capitalized. (5) The owner(s) commingled personal and business assets.
How does a creditor collect on a debt from an owner of a corporation? 🔪🍑
A creditor obtains a court judgement affirming the debt, then obtains a writ of execution allowing the creditor to seize the debtor’s assets (shares). The creditor then sells the shares, unless otherwise prohibited by governing documents.
How does a creditor collect on a debt from an owner of an LLC, LP, or Partnership? 🍆💦
A creditor gets a charging order, which is a lien on the debtor’s ownership interest and gives only a right to receive distributions with no other rights. If distributions will be insufficient, the director can seek judicial foreclosure, forcing sale of the ownership interest.
What is traditional veil piercing?👫
Under traditional veil piercing, the business lacks assets, so the veil is pierced outward to hold the owner liable for business’ debts.
What is reverse veil piercing? 👭
Under reverse veil piercing, the owner lacks assets, so the veil is pierced inward to hold the business liable on the owner’s debts.
What is the definition of income?
Income can be wages, interest on savings, dividends, or business income.
What is self-employment tax?
This tax is a separate tax on income from wages or self-employment.
What is a capital gains tax?
A capital gains tax is a tax on qualified dividends and sale of stock held longer than one year.
What is a deduction?
A deduction is a subtraction from income subject to tax.
What is a credit?
A credit is a direct reduction in the taxes owed.
In partnerships, what is a contribution?
Contributions are assets or services that partners provide to the partnership.
In partnerships, what are distributions?
Distributions are payments or property transfers from the partnership to the partners.
In partnerships, what are allocations?
Allocations are how the partnership’s income, gains, losses, deductions, and credits are allocated to each partner.
In partnerships, what is pass-through taxation?
Under pass-through taxation, profits and losses pass through to each partner, and the partnership itself does not pay any income tax.
What are single-member LLCs taxed as by default?
Sole proprietorship.
What is a sole proprietorship’s taxation scheme?
The owner reports all income or losses on his or her personal income tax return. The owner also pays a self-employment tax.
What is the taxation scheme for a partnership under Subchapter K?
Pass through — profits and losses pass through to each partner, and the partnership itself does not pay income tax.
What entities are taxed as partnerships by default?
LLPs, LPs, and multi-member LLCs are taxed by default as partnerships.
In partnerships, what are special allocations?👭
Special allocations are when the partnership allocates income or losses different than the partners’ ownership percentages. A special allocation is valid for tax purposes only if it has “substantial economic effect,” which means it must reflect the economic reality of the relationship and not just be a way to avoid taxes.
Under a sole proprietorship, what is the rule for income tax?
The owner of a sole proprietorship must report all income or losses on his personal income tax return.
Under a sole proprietorship, what is the rule for self-employment tax?
The owner of a sole proprietorship must pay a 15.3% self-employment tax.
What entity are single-member LLCs taxed as?
Single-member LLCs are taxed by default as a sole proprietorship.
What is the rule for C-Corporations?
A C-Corp annually files IRS Form 1120 and pays taxes on its taxable income at a flat rate of 21%. If the corporation has excess earnings, it may pay dividends to its shareholders.
What can single and multi-member LLCs elect to be taxed as by filing certain forms?
Single and multi-member LLCs can elect C-Corp taxation through filing certain forms.
What is the rule statement for S-Corporations? 🙏
In an S-Corp, income and losses pass through to each shareholder. Restrictions include (1) no special allocations, (2) 100 or fewer owners, (3) owners can be individuals, estates, certain types of trusts, or tax-exempt organizations, but no corporations or LLC owners, (4) no nonresident alien owners, and (5) one class of ownership interests only.
Which entity is best for employment tax savings and why?
S-Corps — the shareholder-employee of an S-Corp will likely pay lower employment taxes than a similar owner of a partnership, if the business will generate earnings in excess of a reasonable salary for that employee.
What is the main benefit of partnership taxation?
Partnership taxation is better if the owners want to change how profits or losses are allocated.
Which entity has the potential issue for double taxation, and how can they avoid it?
C-corps — don’t issue dividends.
What is an angel investor, and who do they normally invest in?
An angel investor is a wealthy individual who invests their own personal money directly into startups, often at a very early stage. They often prefer to invest in C-Corps, buT some are okay investing in an LLC taxed as a partnership.
What is a venture capital firm, and what entity do they prefer to invest in and why? 🫖
A venture capital firm is a company, usually an LP, that manages money from investors in a fund and uses it to invest in startups, aiming for high growth. They strongly prefer to invest in C-Corps because (1) they want preferred stock, (2) they want to avoid pass-through taxation, which can create tax problems for the investors, and (3) they want the tax benefits of qualified small business stock.
What is qualified small business stock?
Qualified small business stock is stock under IRC 1202 that has (1) tax-free gains, which means no tax on some or all profit if the stock is held for more than five years, and (2) an exclusion cap.
Which entity has the most formalities?
Corporations
Which entity has fewer formalities, compared to corporations?
LLCs
Which is the most expensive entity?
Delaware C-Corps are generally the most expensive entity.
What is the rule for continuity of existence applicable to corporations?
Corporations can exist in most states perpetually.
What is the rule for continuity of existence applicable to LLCs?
LLCs can exist in most states perpetually.
What is the rule for continuity of existence applicable to sole proprietorships?
Sole proprietorships terminate on the death of the owner.
What is the management structure for LLCs?
By default, LLCs have a flat management structure, but this can be changed to a corporate structure.
What is the management structure for corporations?
Corporations have centralized management in a board of directors, with daily operations run by officers.
What is the general rule for fiduciary duties?
Owners generally owe fiduciary duties to the business entity and other owners.
What is the rule for waiving fiduciary duties, generally?
It is generally easier to waive duties for LLCs than for corporations.
What is conversion?
Conversion is changing a business from one entity type to another. Most states allow statutory conversion by filing the proper forms with the Secretary of State (or in WI, the DFI).
What is the rule for converting an LLC taxed as a partnership to a C-Corp?
This is the more common conversion; it has generally minimal tax consequences if the LLC has no debt.
What is the rule for converting a C-Corp to an LLC taxed as a partnership?
This is the more rare conversion; it often triggers a large tax bill.
What is equity?
Equity is ownership stake in a business.
What is the obligation of good faith and fair dealing?
Every contract has an implied duty of good faith and fair dealing. The parties must act honestly and fairly and not undermine the contract’s purpose. Where a contract is silent or ambiguous, courts examine if reasonable parties, at the time of contracting, would have agreed to the conduct in question.
What are the purpose, key components, and focus of an income statement?
An income statement shows a company’s profitability over a specific period. They key components are revenues, expenses (cost of revenue), and net income (profit or loss). It tracks how much revenue the company earned and what it spent, resulting in the net profit or loss.
What are the purpose, key components, and focus of a balance sheet?
A balance sheet provides a snapshot of the company’s financial position at a specific point in time. The key components are assets, liabilities, and owners’ equity. It reflects what the company owns (assets), what it owes (liabilities), and the residual value (owners’ equity) at a particular moment.
What are the purpose, key components, and focus of a cash flow statement?
A cash flow statement shows the company’s cash inflows and outflows over a specific period. The key components are cash flows from operating activities, investing activities, and financing activities. It tracks how cash is generated and used, providing insight into the company’s liquidity and cash management.
What is the key equation for a balance sheet and cash flow statement?
Owners’ Equity = Assets - Liabilties OR Assets = Owners’ Equity + Liabilties
What is debt?
Debt is borrowed money the corporation must pay back with interest, documented by a promissory note.
What is credit risk?
Credit risk is the risk that a borrower will not be able to repay a loan.
What is the rule statement for credit risk?
The interest rate charged on a loan correlates with the credit risk of the buyer—the higher the risk, the higher the interest rate.
What is a representation?
A representation is (1) a statement of fact (2) made to induce a party into a contract. Representations are grounded in tort law.
What is a warranty?
A warranty is (1) a statement of fact (2) a party promises to be true. Warranties are grounded in contract law.
What are covenants?
Covenants are obligations.
What is a lien?
A lien is either (1) a mortgage on real property or (2) a security interest on a real property.
What is a guarantee?
A guarantee is a contractual promise made by a third party to pay amounts owed on the loan if the borrower defaults.
What is a qualifier?
Qualifiers soften representations and warranties a corporate client is making to protect them in contracting.