module 3 bio
1/126
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
127 Terms
Diffusion
Movement of particles or molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration
Osmosis
Diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane
Selectively pemeable membrane
A membrane that allows certain materials to pass through, but not others
Tonicity
A description of the relative solute concentration in a solution as compared to another solution.
Equilibrium
The condition that exists in system when there is a relatively equal distribution of a particular molecule
Hypertonic
A solution that has a higher concentration of solutes than another.
Hypotonic
A solution that has a lower concentration of solutes than another.
Isotonic
Two solutions that have an equal concentration of solutes.
Solute
substance that is dissolved in a solution
Solvent
the liquid that contains the dissolved solute in a solution.
Cell Membrane
regulates and controls what enters or leaves the cell
Facilitated Diffusion
this form of diffusion is regulated by protein channels in the membrane and requires no energy input from the cell
Active Transport
movement of molecules or ion into or out of the cell against its concentration gradient (from low to high) and requires an input of energy.
Endocytosis
movement of substances into the cell by creating a new vacuole at the cell membrane. requires energy.
Exocytosis
movement of substances out of a cell by merging a vacuole with the cell membrane. requires energy.
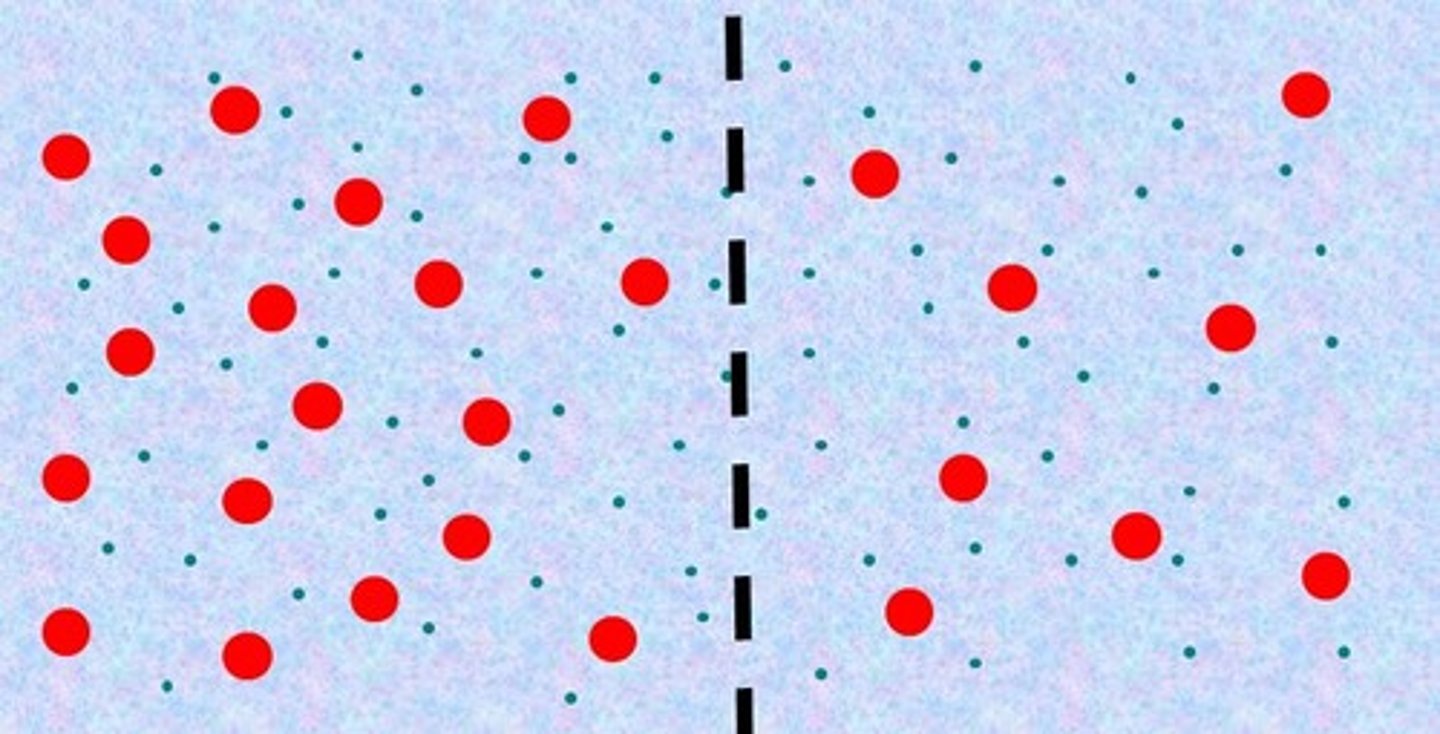
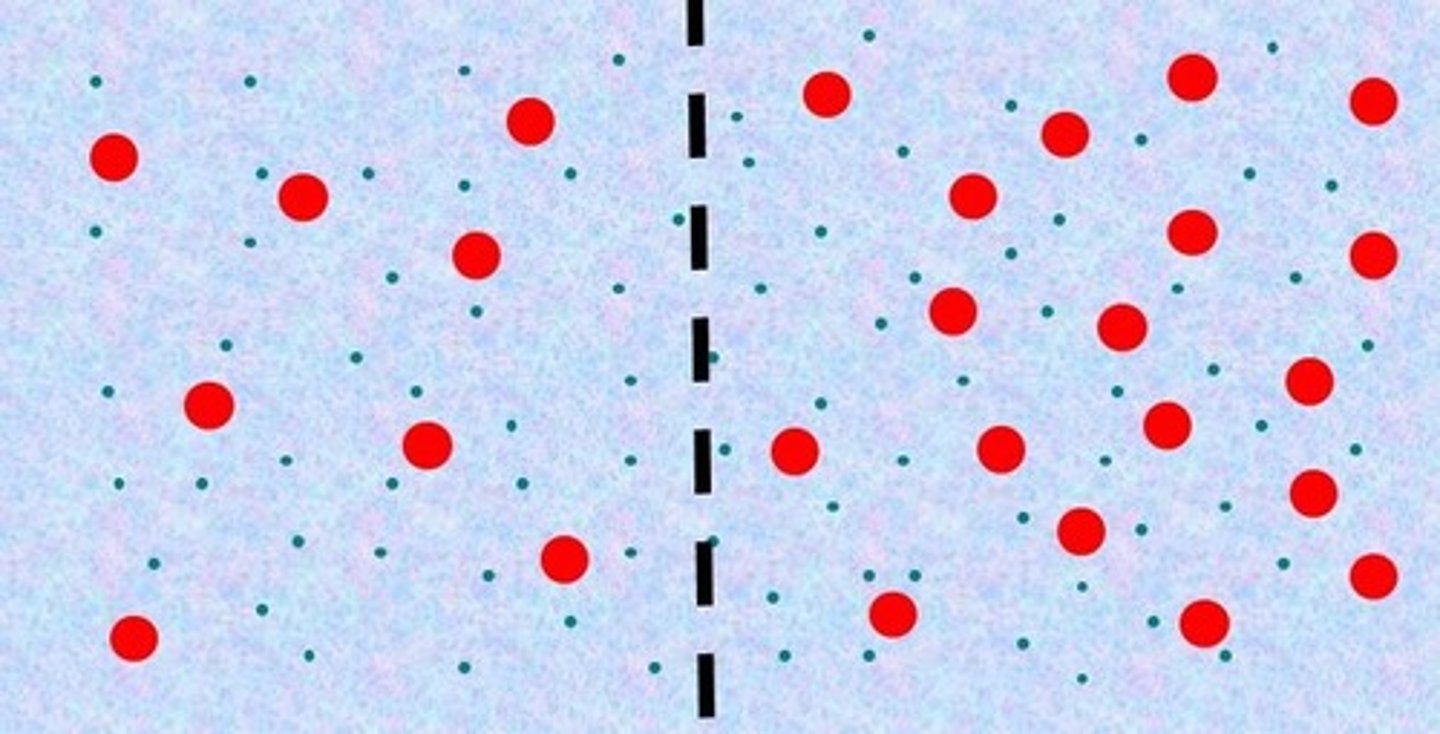
Hypertonic
the left side is _____ compared to the right side.
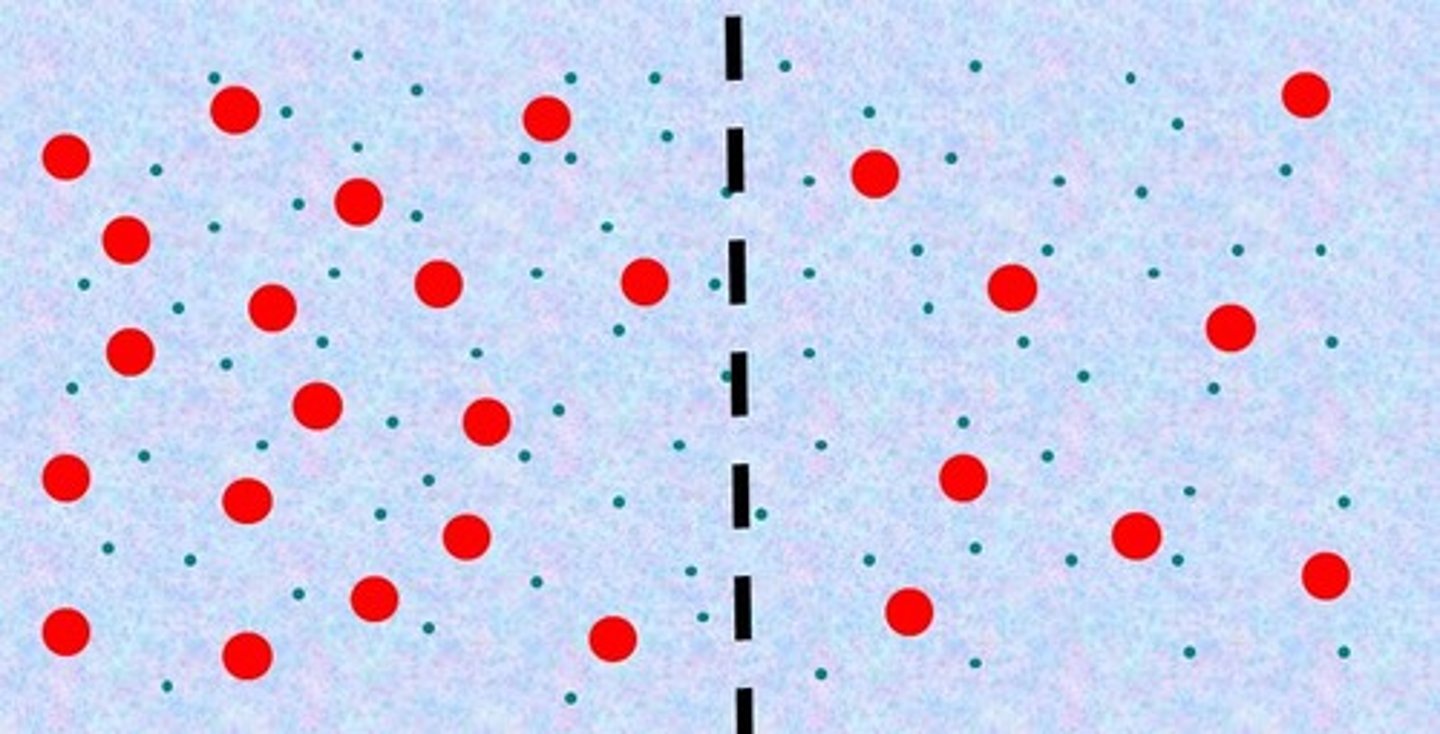
Hypotonic
The right side is _____ compared to the left side.
right, left, osmosis
Water will move from the _____ to the _____ by _____.
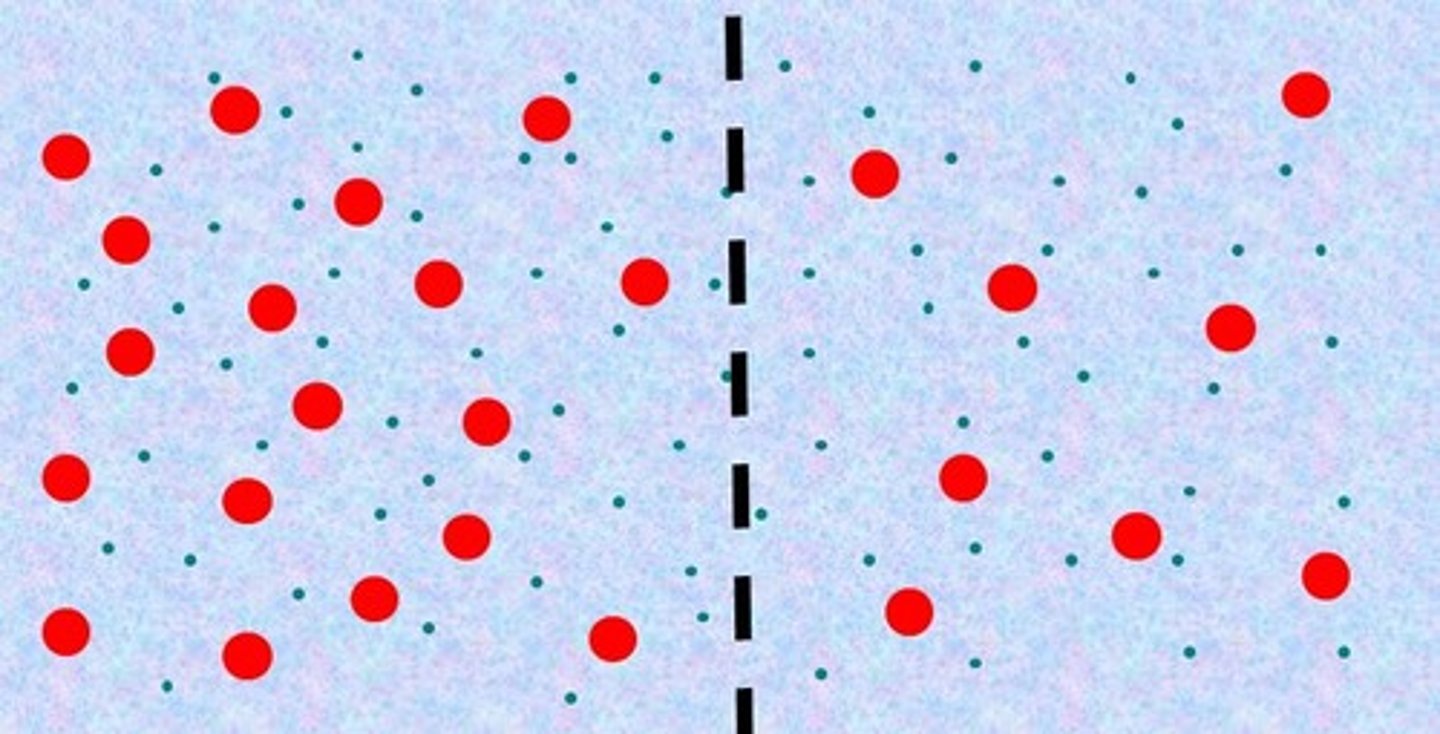
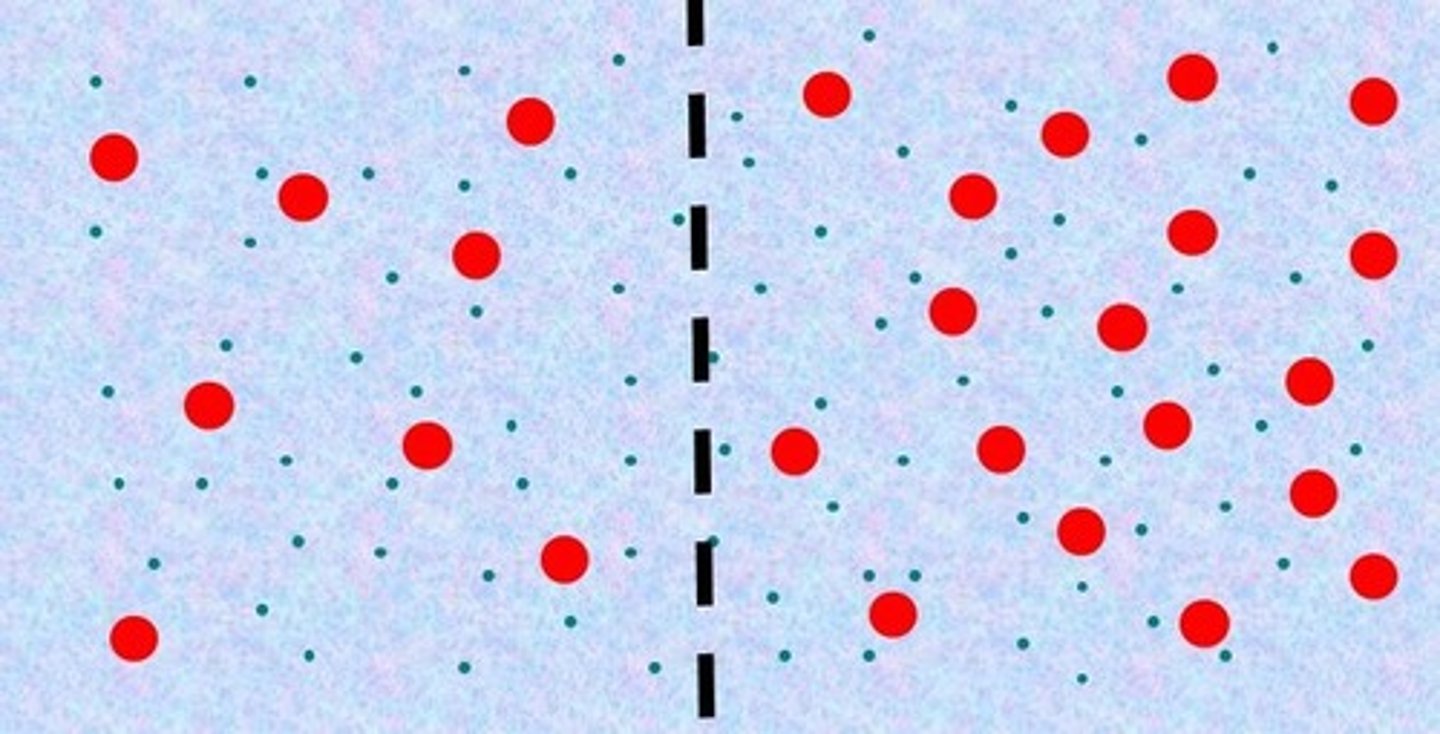
Hypotonic
The left side is _____ compared to the right side.
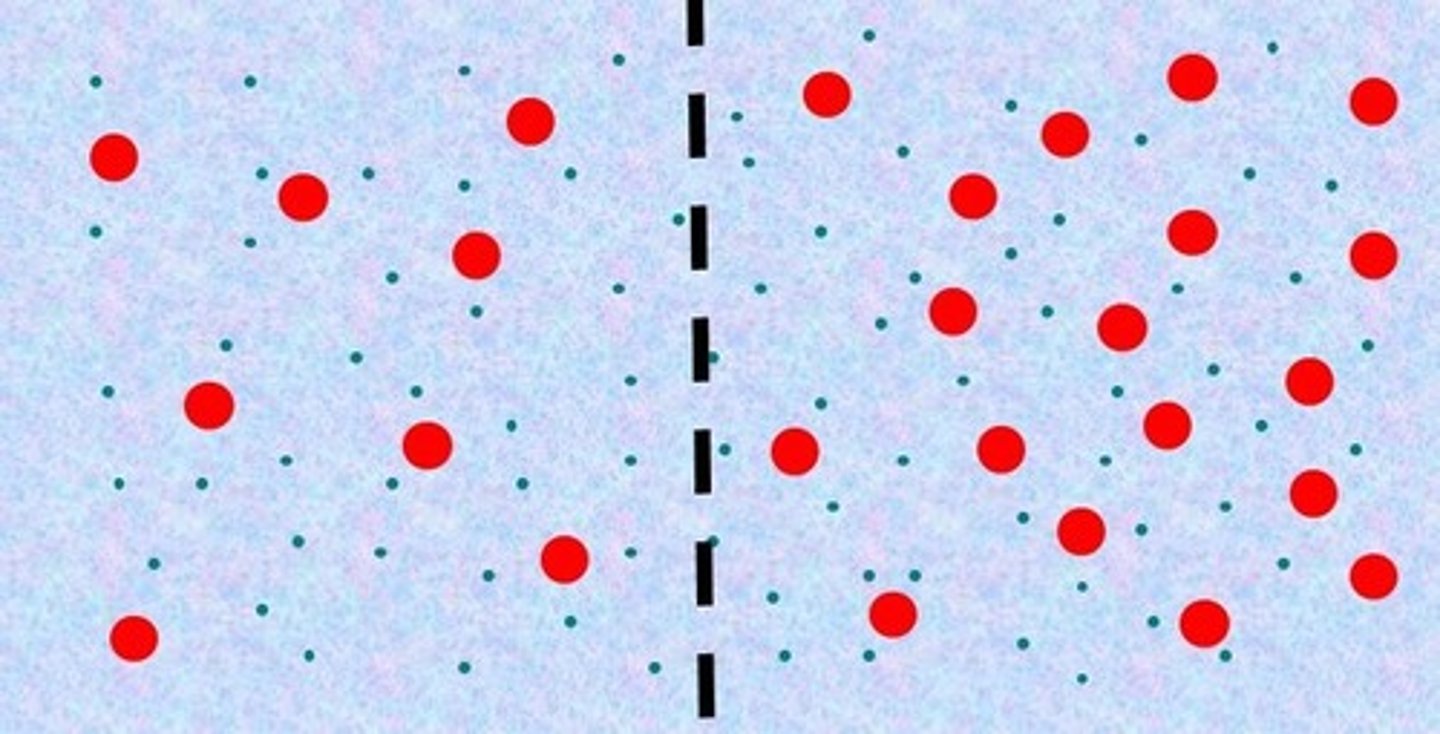
Hypertonic
The right side is _____ compared to the left side.
left, right, osmosis
Water will move from the _____ to the _____ by _____.
Cell Membrane
Composed of a phospholipid bilayer
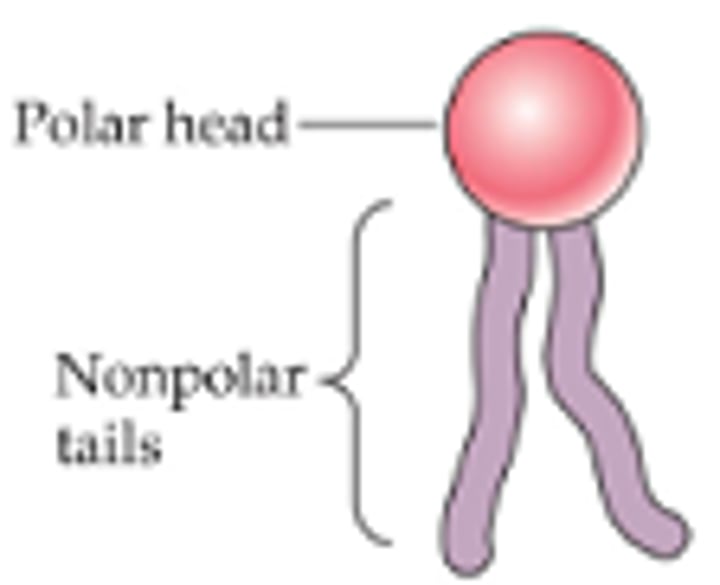
Phospholipid
molecule that makes up cell membranes. It has a hydrophilic "head" and two hydrophobic "tails".
Hydrophilic
water loving. substances that easily mix with water.
Hydrophobic
water hating. substances that will not mix with water.
Transport Protein
Proteins within the cell membrane that function to move substances into or out of the cell.
Cell Membrane
Controls the movement in and out of the cell
Cytoplasm
Watery material which contains many of the materials involved in cell metabolisim
Endoplasmic reticulum
Serves as a pathway for the transport of materials throughout the cell; also associated with synthesis and storage
Nucleus
Serves as the control center for cell metabolism and reproduction
Ribosomes
Sites of protein synthesis
Lysosome
Involved in the digestion of food within the cell
Mitochondria
Powerhouse of the cell
Golgi Apparatus
Packages and secretes the products of the cell
Centriole
Involved in cell division in animals
Vacuole
Fluid-filled organelles enclosed by a membrane; contains stored food or wastes
Nucleolus
Site of production of ribosomes
Nuclear Membrane
Controls movement in and out of the nucleus
Cell Wall
Only in plant cells; Gives the cell its shape and provides protection
Nucleolus
Found inside the nucleus and produces ribosomes
Eukaryotic cells
Contain a nucleus and other organelles that are bound by membranes.
prokaryotic cell
cell that does not have a nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles.
Cytoskeleton
A network of fibers that holds the cell together, helps the cell to keep its shape, and aids in movement
cell theory
idea that all living things are composed of cells, cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things, and new cells are produced from existing cells
Robert Hooke (1665)
Studied cork and and named the structures he saw "cells".
Levels of organization
atom, molecules, organelles, cell, tissue, organ, organ system, organism
Robert Hooke
1665 -English scientist that cut a thin slice of cork and looked at it under his microscope. To him, the cork seemed to be made up of empty little boxes, which he named cells.
Anton Van Leewenhoek
1673 Dutch naturalist who created a very powerful (for the time period) single lens microscope, He observed pond water. In pond scum he discovered small animals he called animalcules,or little animals (protists),and also discovered bacteria while examining scraping of crud from his teeth.

Matthias Schleiden
1838 German botanist who determined plants are composed of cells.

Theodor Schwann
German physiologist and histologist who in 1838 and 1839 identified the cell as the basic structure of plant and animal tissue (1810-1882)

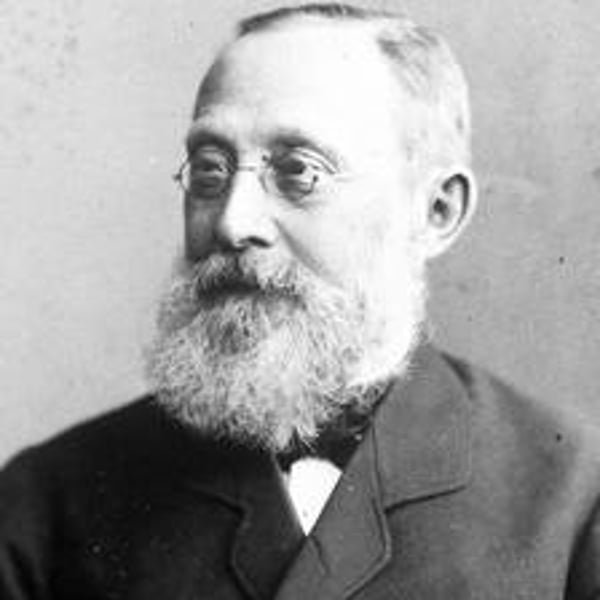
Rudolph Virchow
1858 - A doctor who stated that all living cells come from other living cells (part 3 of the cell theory)

The Cell Theory (ABC)
Three parts -
A. ALL organisms are made up of
one or more cells.
B. BASIC unit of life.
C. CELLS come from other living
cells
Carl Braun
1845 - He reworks the cell theory, calling cells the basic unit of life.
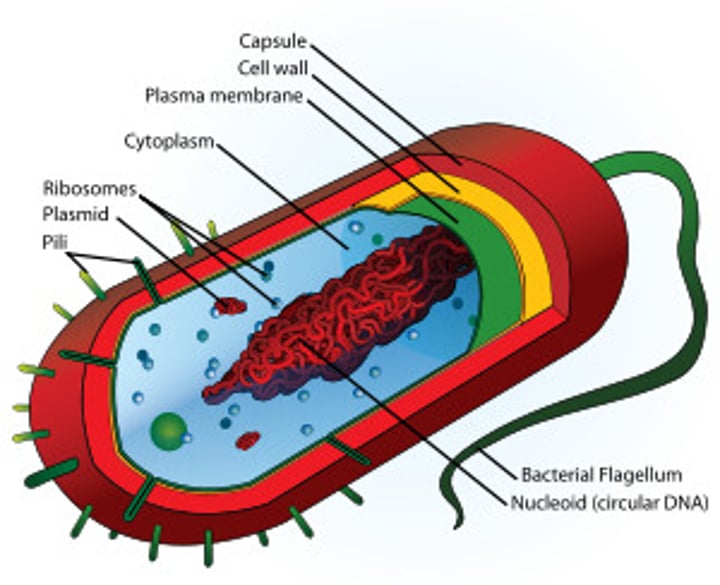
Prokaryotes
Bacteria
No nucleus
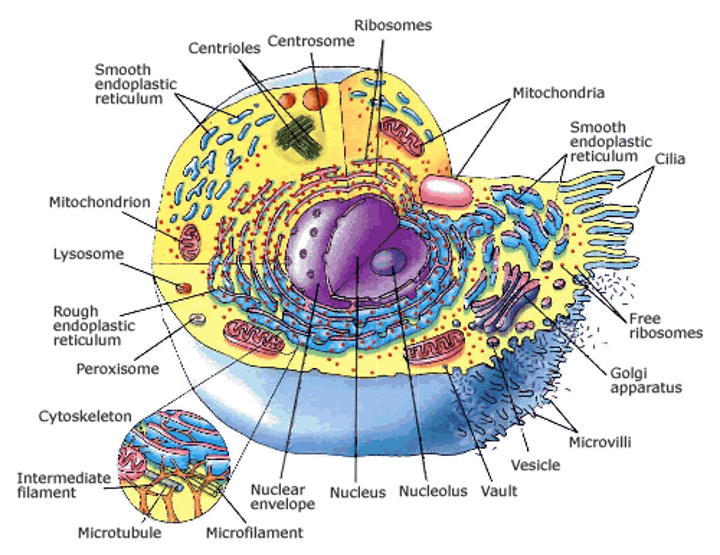
Eukaryotes
Cells with a nucleus
All organisms in the kingdoms Protista, Plantae, Fungi, and Animalia are Eukaryotes
Cells
Basic unit of life
The basic unit of structure and function in all living things
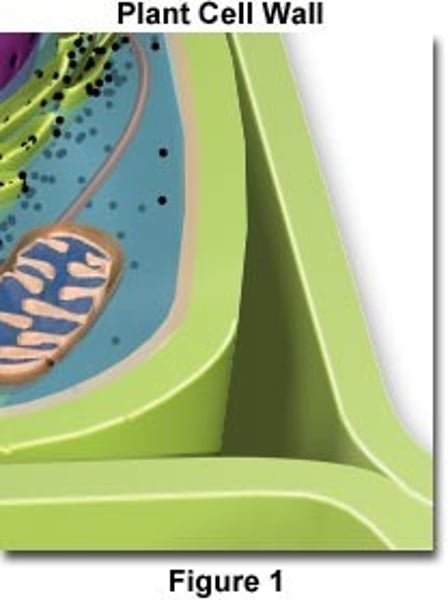
cell wall
An inflexible barrier that provides support and protects the plant cell
cell membrane
A cell structure that controls which substances can enter or leave the cell.
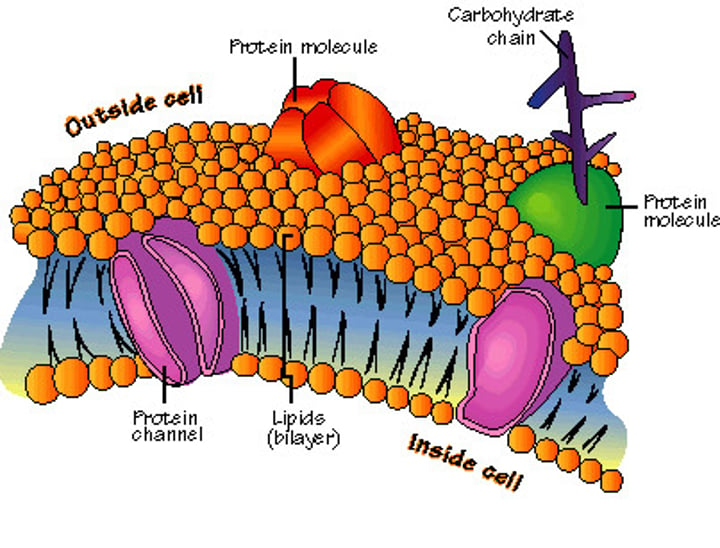
organelle
A tiny cell structure that carries out a specific function within the cell
A subunit within a cell that has a specialized function.
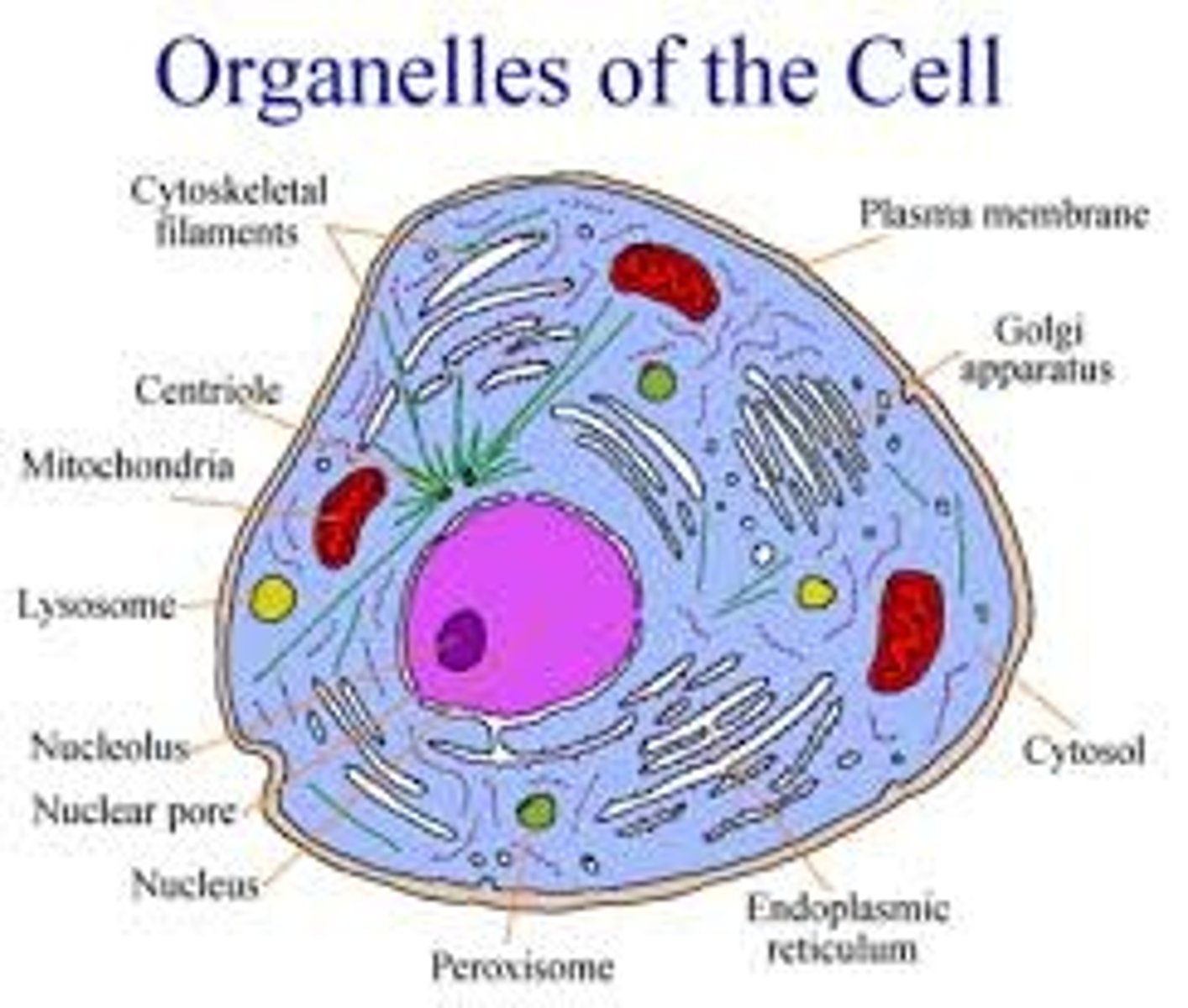
nucleus
A part of the cell containing DNA and RNA and responsible for growth and reproduction
endosymbiotic theory
theory that eukaryotic cells formed from a symbiosis among several different prokaryotic organisms
Ribosomes
site of protein synthesis
Flagella
Whip-like tails found in one-celled organisms to aid in movement. This structure can be found in eukaryotes and prokaryotes
phospholipids
A molecule in cell membranes
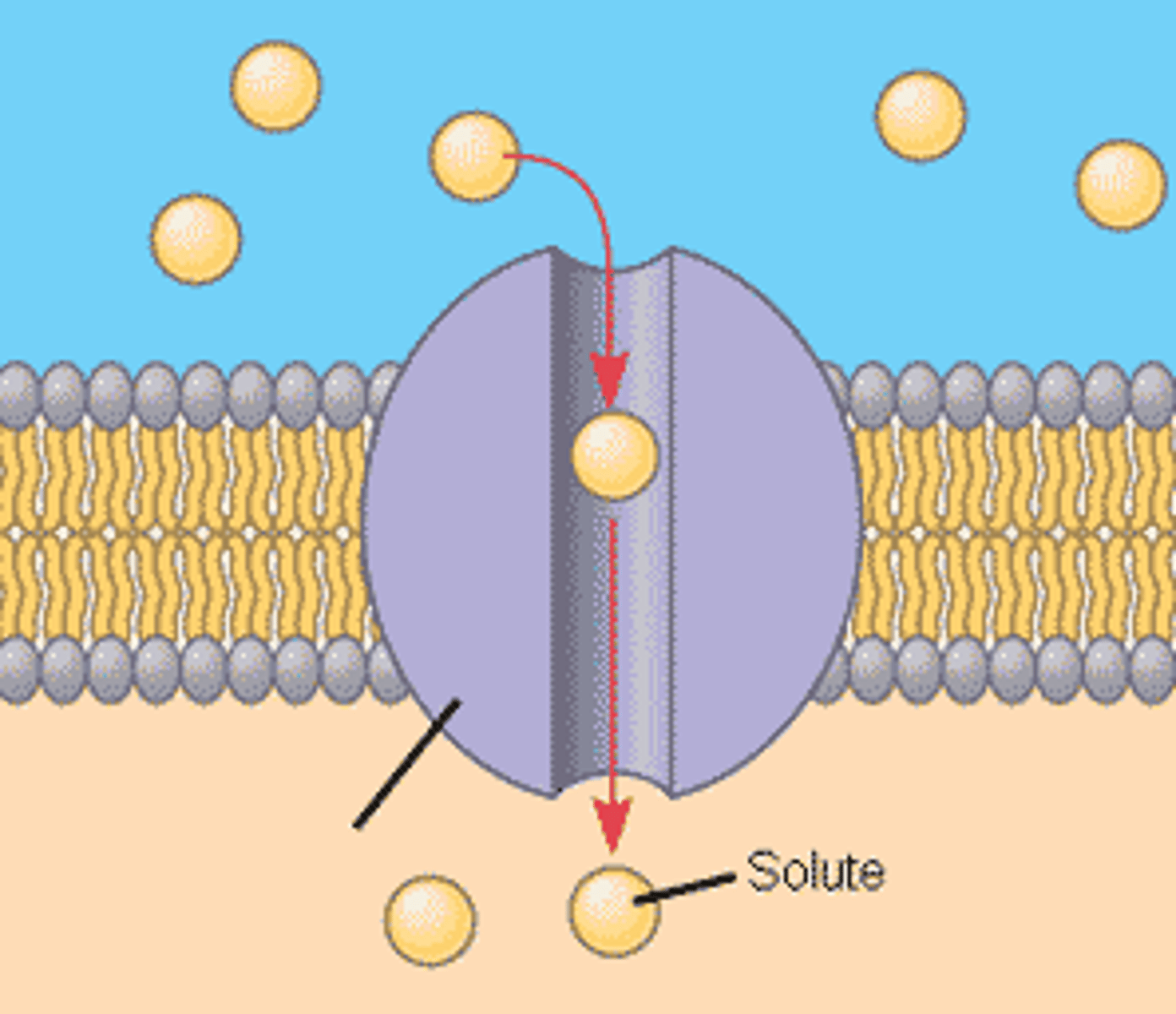
cell membrane
A cell structure that controls which substances can enter or leave the cell.
selective permeability
condition or quality of allowing some, but not all, materials to cross a barrier or membrane
hydrophilic
water loving
hydrophobic
Water fearing
protein channels
proteins in the membrane whose role it is to pass molecules that cannot go through the membrane
cholestrol in membrane
Adds stability; keeps the tails from sticking together
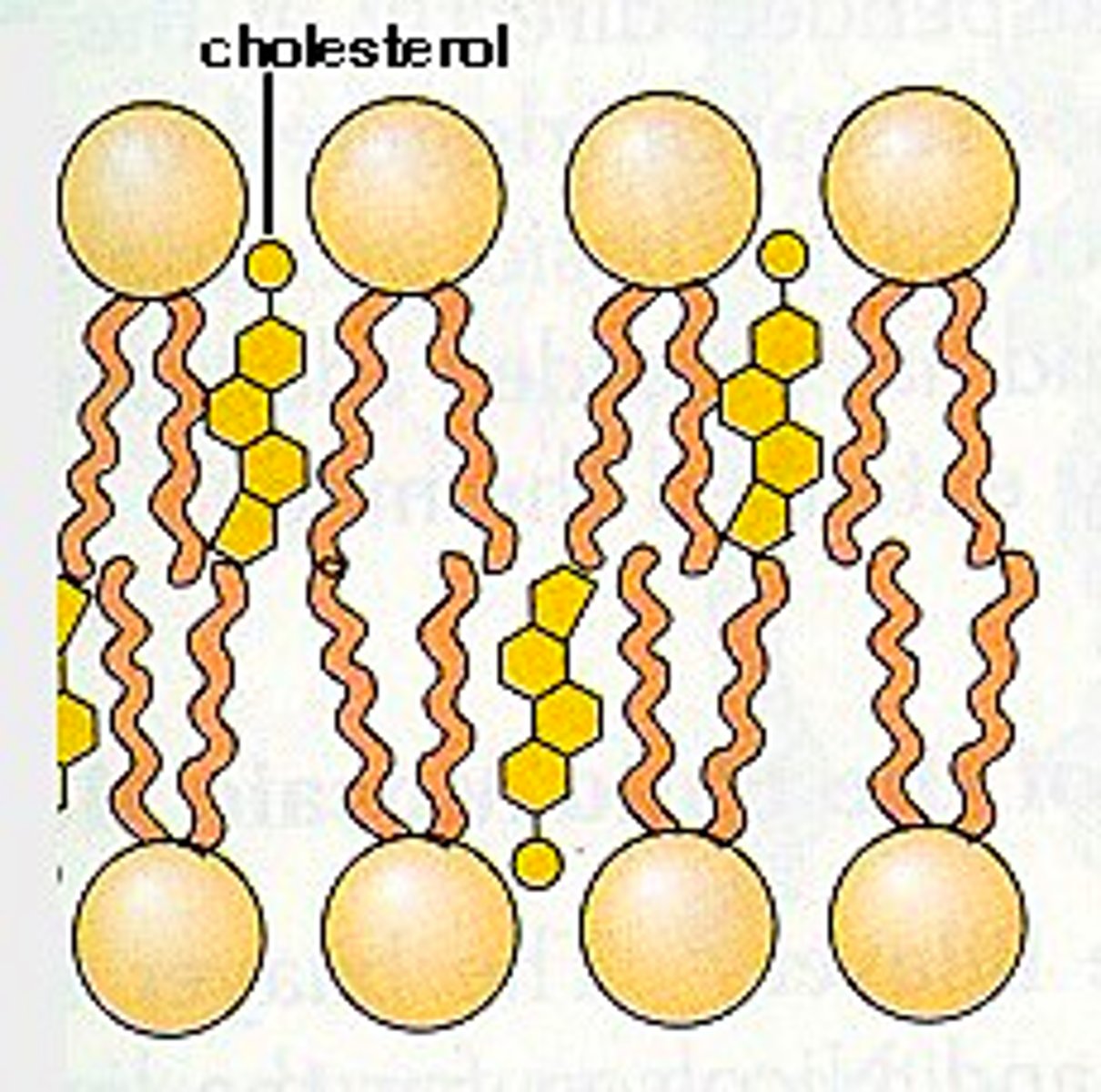
hydrophilic heads are found
facing the outside of the membrane
hydrophobic tails are found
touching each other inside the membrane
polar molecule
a molecule in which one side of the molecule is slightly negative and the opposite side is slightly positive
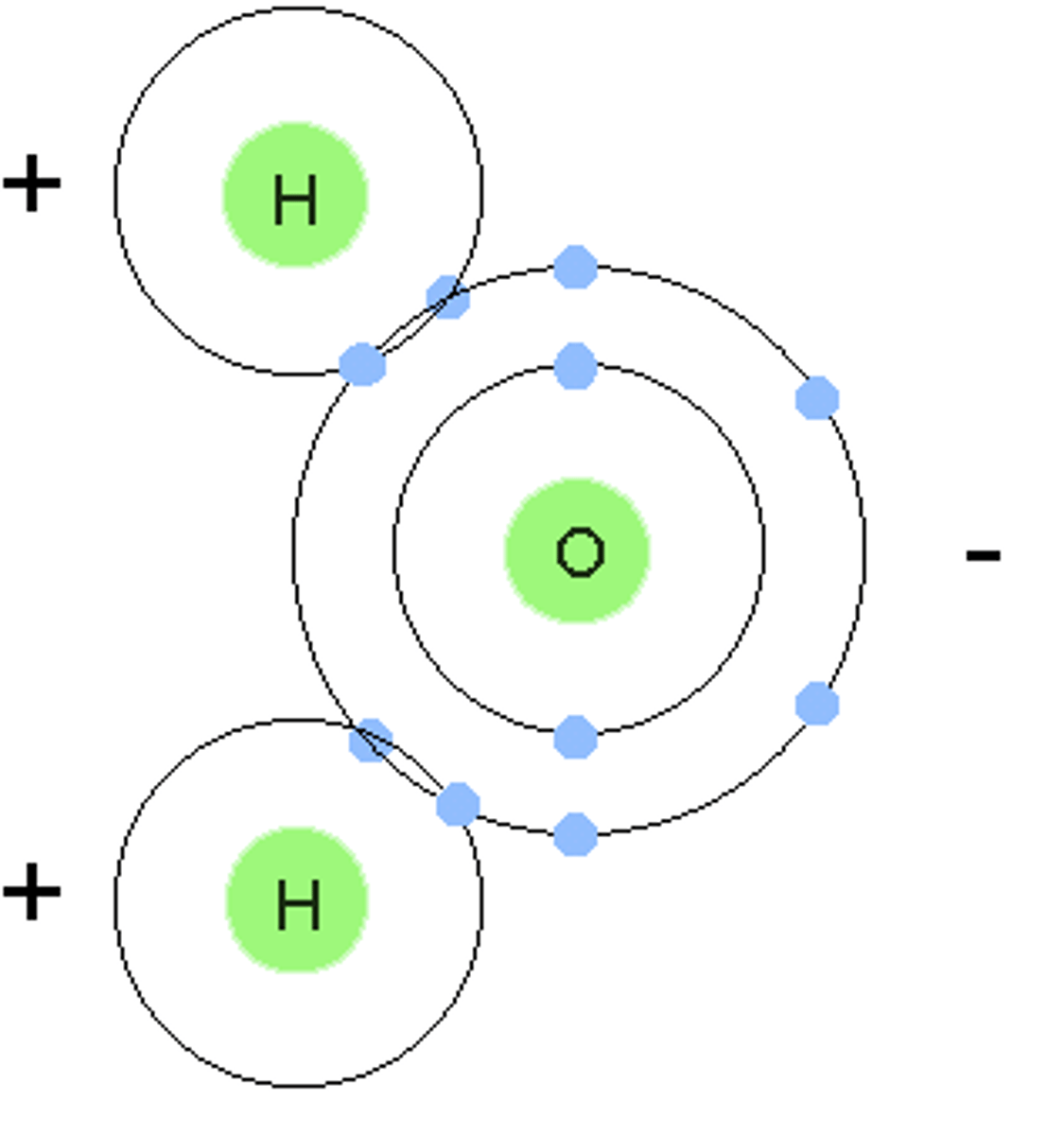
nonpolar molecule
a molecule that does not have oppositely charged ends
Cell Membrane
surrounds cell parts; controls materials in & out of cell
Cytoplasm
protects all the organelles in the cell
Nucleus
control center of the cell; contains DNA
organelles
A tiny cell structure that carries out a specific function within the cell
chromatin
thin strands of material that fill the nucleus
nucleolus
small round structure in the nucleus, where ribosomes are made
Mitochondria
powerhouse of the cell; converts energy stored in food
ribosomes
organelle that makes proteins
Endoplasmic Reticulum
helps ribosomes make proteins
Golgi apparatus
packages and transports proteins from ER to other parts
cell wall
provides rigid structure and protection
large central vacuole
found in plants, this organelle stores water for the cell
chloroplasts
Capture energy from sunlight and use it to produce food for the cell
chlorophyll
Green pigment in plants that absorbs light energy used to carry out photosynthesis
lysosomes
breaks down worn out or damaged organelles
Compound Microscope
Microscope that allows light to pass through a specimen and uses two lenses to form an image.
-2 lenses, ocular and objective
-2-d image

Dissecting Microscope
This is also known as the Dissecting Microscope, and uses two separate optical shafts (for both eyes) to create a three-dimensional image of the object through two slightly different viewpoints. This kind of microscope conducts microsurgery, dissection, watch-making, small circuit board manufacturing, etc.
Provides three-dimensional images at lower magnifications.
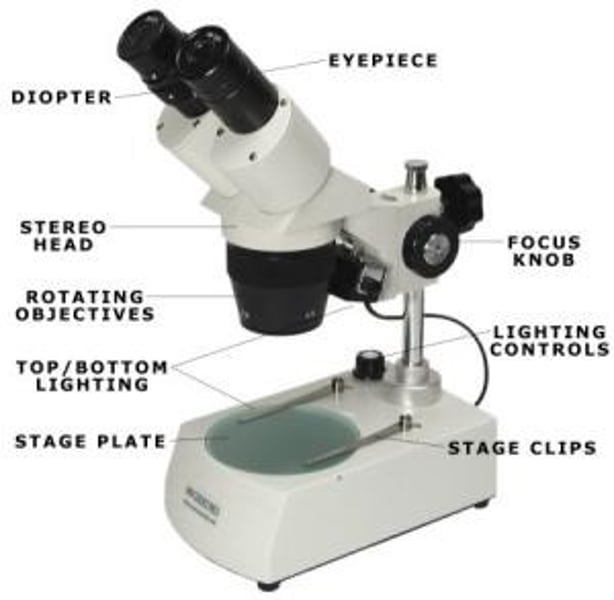
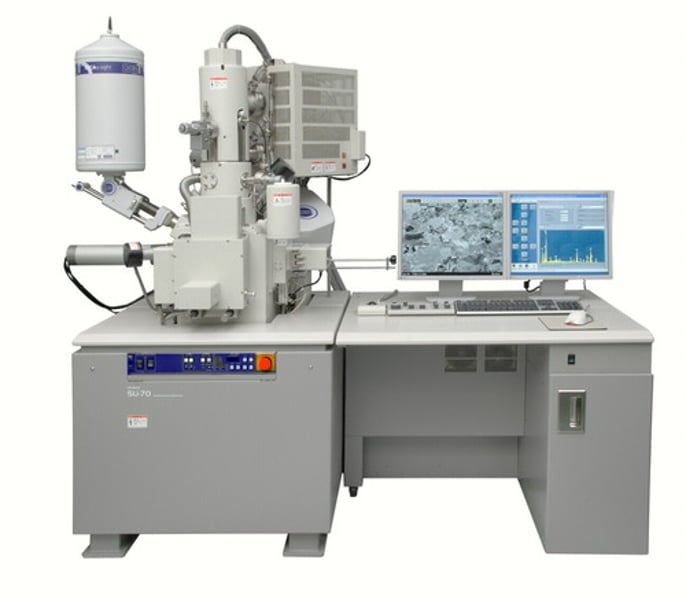
Scanning Electron Microscope
a microscope that produces an enlarged, three-dimensional image of an object by using a beam of electrons rather than light (Kills the specimen)

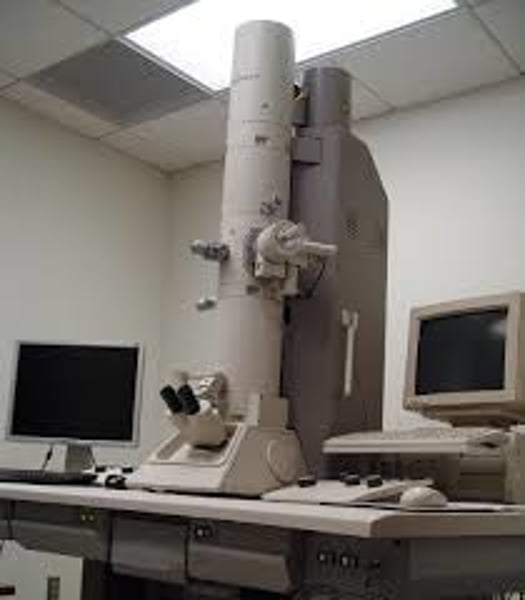
Transmission Electron Microscope
A microscope that transmits a beam of electrons through a very thin slice of specimen and that can magnify up to 200,000 times (abbreviation, TEM)
Maximum resolution of 0.0002 micrometres. Magnification of x 1,000,000.
Only dead cells can be observed.

Produces 2D images
Compound microscope and TEM
Produces 3D Images
Dissecting microscope and SEM
Uses light
Dissecting and compound microscope
Cell membrane
A cell structure that controls which substances can enter or leave the cell and helps the cell communicate with other cells.
Nucleus
Control center of the cell that has the DNA of the cell.
Ribosomes
Makes proteins for the cell
Cytoplasm
A jellylike fluid inside the cell in which the organelles are contained