Types of Organizational Structure
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Types of organization charts (5)
Flat (horizontal
Tall (vertical)
By product
By function
By region
Organization by product
structuring a workfor
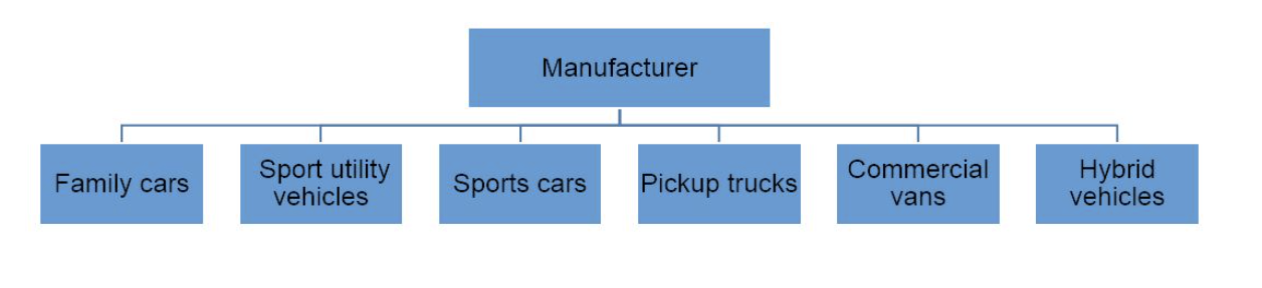
ce according to the goods or services sold. Each department focuses on a different product within the organization’s overall product portfolio.
ADVs of Organization by product (3)
Organization by product enables specialisation as workers focus on a specific market segment related to the product. This helps to ensure the business meets the needs of its customers more effectively, such as improved product knowledge and marketing activities.
It can also encourage healthy internal competition between departments to produce ever-more appealing products.
It is suitable for large organizations with a broad product portfolio.
DIS of organization by product (2)
the duplication of work done by each department, such as different marketing and sales personnel in the various departments.
associated with decentralized decision-making, so it can be difficult for the senior executives to maintain overall control of the various separate divisions of the business.
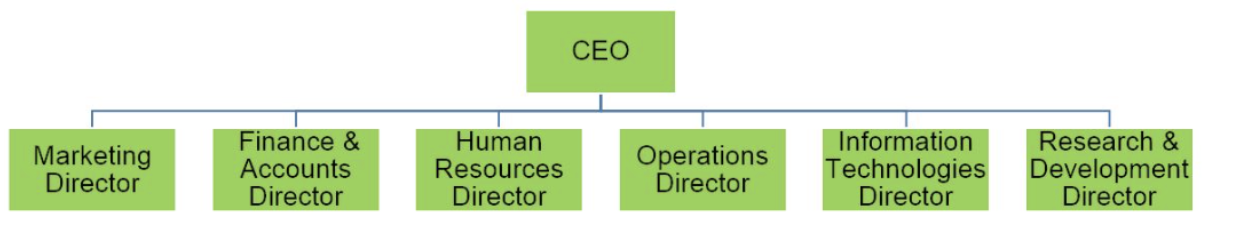
organization by function
structuring a workforce according to business functions. It will involve staff working together but from different departments, such as marketing, human resources, production (operations), and finance. Each department has a manager or director who is in charge of the assigned functional area of the business.
ADVs of organization by function
roles and tasks are carried out by experts and specialists. Hence, productivity and output are both higher.
Organization by function
departments tend to work in isolation by focusing only on their area of responsibility.
slower decision-making, limited cross-functional collaboration, and potential stifling of innovation.
Organization by region
structuring a workforce according to different geographical areas based on where the firm’s operations are. It is suitable for large businesses with operations in different geographical locations, such as global multinational companies.
ADVs of organization by region
This form of organization enables businesses to focus better on the specific needs and wants of their customers in markets in indifferent geographical regions of the country or the world.
suitable for large businesses that operate across the globe. Whilst most multinational companies have their headquarters in a single location, having regional offices helps the organization to adapt to regional differences in demand and exploit local knowledge, despite the benefits of globalization
DIS of organization by region
the difficulty in controlling a decentralised organization that operates across numerous regions of the country or the world.
costly
flexible organizational structures (2)
project-based organization
- the Shamrock organization.
Project-based organization
flexible organizational structure based on the specific needs of a particular project or business venture. Each project is run by a project manager (PM), who is in charge of the team involved in the particular project. Decision making is centralized in project-based organization, although the dedicated team works on the designated project to achieve a common goal.
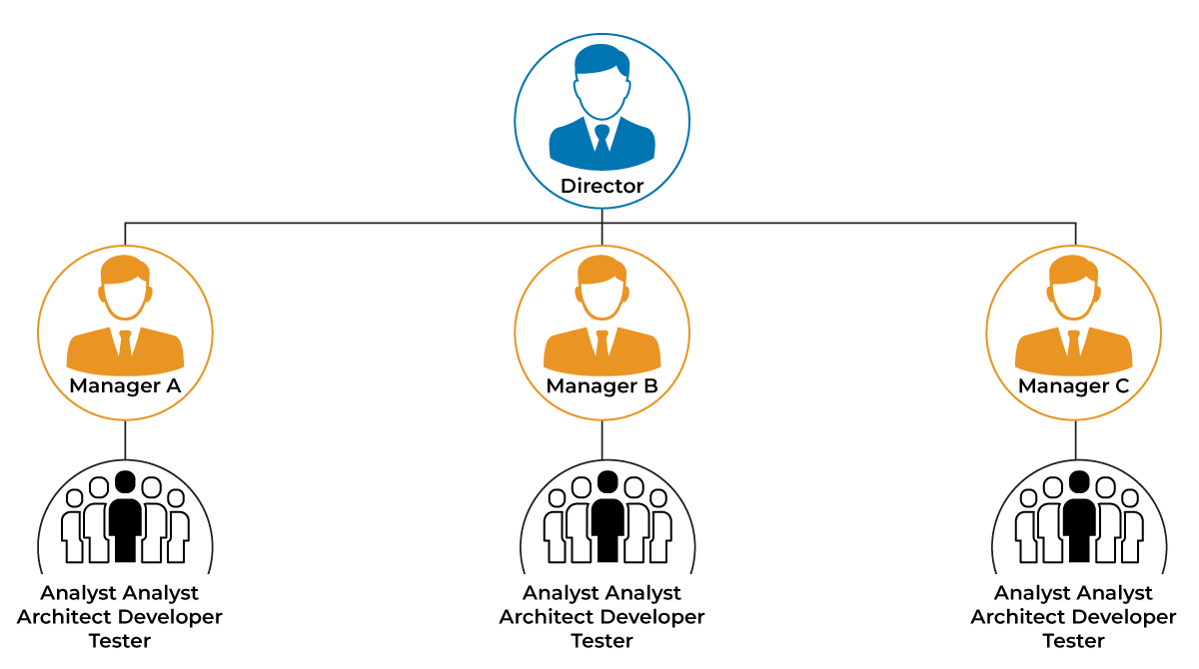
ADVs of Project-based organization (3)
This type of organizational structure is designed to allow firms to be responsive to changes in market demand for goods and services.
As a temporary and flexible organizational structure, it can be used by any type of business.
- Using experts from across the organization in a matrix structure can help to generate new and creative ideas, as well as improve productivity.
DIS of Project-based organization (3)
can isolate group members who work outside of their normal functional areas.
Cultural differences may exist between the various members of the project who have been put together from other sections of the organization.
—> less productivity, efficiency
Matrix structure
An organisational structure that creates project teams that cut across traditional functional departments.
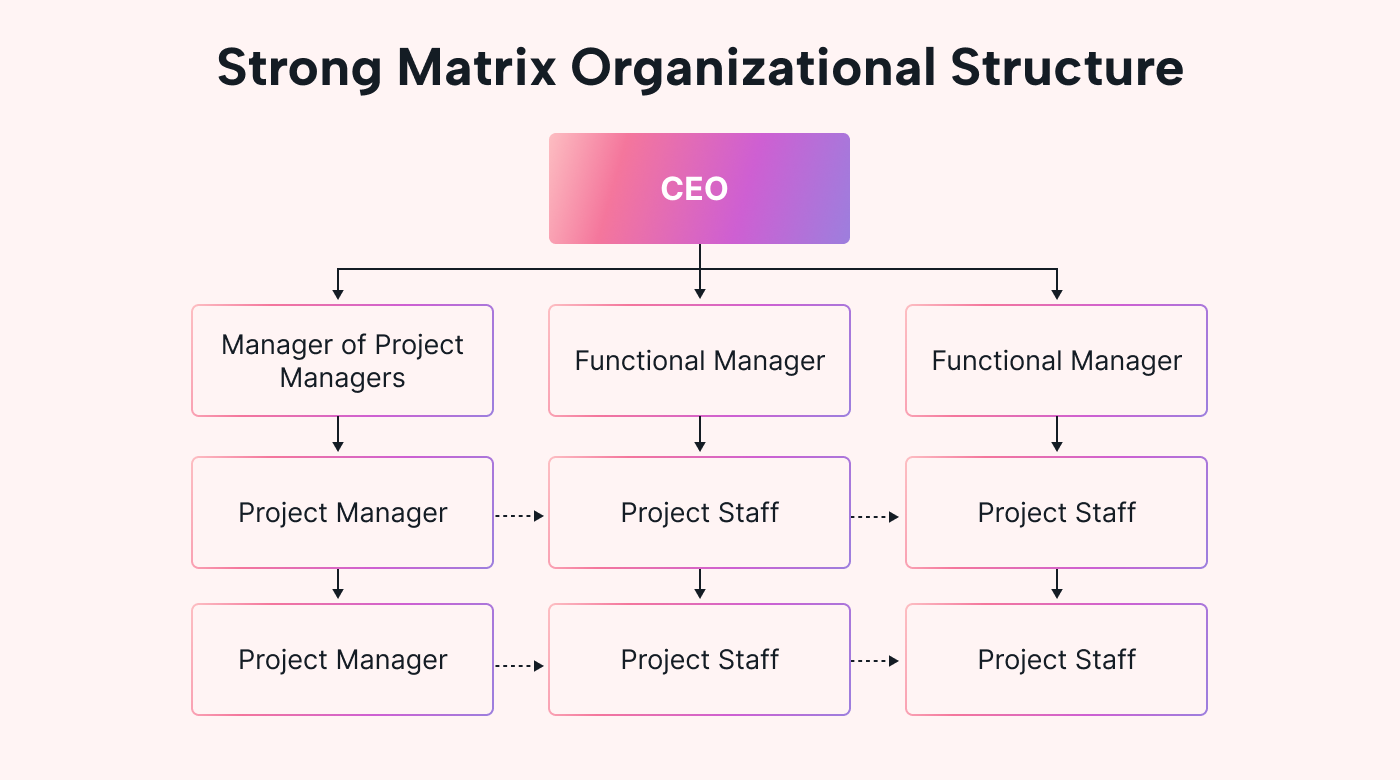
Differences between matrix structure and organization by function (4)

matrix structure advs
increased flexibility, efficient resource utilization, and enhanced collaboration
matrix structure dis (4)
confusion about roles and responsibilities, slower decision-making, increased costs, and potential power struggles
Professional core (core workers)
full-time experts who are vital for the organization’s operations and survival. They are essential for the business to meet their organizational objectives, mission and vision. Hence, the professional core is considered as the most significant group of workers in an organization
The contingent workforce
temporary staff hired by the organization. It is made up of portfolio workers, part-time staff, seasonal workers, and those on flexitime or flexible hours. Contingent workers perform routine jobs.
Outsourced vendor
individuals or other organizations hired on a contract basis to carry out a specific but non-core role. They mainly consist of self-employed professionals and contractors who are hired on flexible and project-based terms. As outsourced workers are not managed directly by the business. Their pay is negotiated and often based on performance rather than time commitments.
ADVs of shamrock organization (3)
It allows firms to have greater flexibility and ability to change the number of employees as and when the organization’s needs change.
Retaining only a multi skilled group of core workers enables the workforce to concentrate on their core activities
Non-core functions can/should be outsourced to specialists and to gain cost advantages.
This also helps to cut costs further as only full-time workers are entitled to fringe benefits (perks).
DIS of shamrock organization (3)
flexible structures like the Shamrock organization can create uncertainties and therefore anxieties for workers. Also, flexible contracts can be a legal minefield in some countries or regions of the world where labour laws are particular stringent.
