Cell motility
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
What basic structure enables swimming type cell mobility? What are the 2 subtypes of this structure?
microtubules
cilia and flagella
What kind of cargo do cilia move?
surrounding molecules while the cells are stationary
What kind of cargo do flagella move?
the cell itself
Example of cell driven by cilia
cells in respiratory tract
Example of cell driven by flagella
spermatozoid
What structure allows the movement of fluid relative to static cells?
cilia
What are 3 key characteristics of microtubules’ structure?
hollow
alpha and beta tubulin ie tubulin dimer
cross section made up of 13 protofilaments
What size are microtubules?
large - 24 nm
What is the main structural difference between cilia and flagella?
length - flagella much longer
What is the functional structure of the microtubule?
the axoneme
Describe the 9 + 2 microtubule assembly of an axoneme
9 outer doublets of tubules connected to a singular pair of tubules inside
What is the structural difference between A and B fibres within axonemes and explain this difference
A is complete with 13 protofilaments // B incomplete with only 10 protofilaments
B piggy back on A so uses A to close the gap
How is polarity/asymmetry established in the axoneme?
contact between adjacent fibres on one side vs farther apart and not touching on the other = polarity
What does the polarity/asymmetry of a microtubule’s axoneme allow?
different functions for each side ie one side moves the other doesn’t = motility
What is the protein dynein’s role in the axoneme?
allows motion by stopping fibres from slipping off each other
What are 4 essential aspects of a microtubule’s axoneme?
type A fibres - 13 filaments
type B fibres - 10 filaments
polarity - between opposing sides
dynein - allows fibres to not just slide off each other
What are the two types of cellular motility?
swimming and climbing
What type of motion do microtubules do thanks to dynein?
flex and bend = wave like motion
Is dynein present in cilia or flagella?
both
How is waveform motility dependent on the inner and outer arms of dynein?
Inner arm: waveform // outer arm: power
At what point does the inner pair of the axoneme disappear?
Once it enters the plasma membrane in the basal body of the microtubule
What is a centriole made up of?
9 groups of 3 microtubules and one group of two microtubules in the middle
What are the roles of centrioles and centrosomes?
allow the mitotic spindle to form during mitosis vs area of the cell next to the nucleus where the centrioles normally live when the cell is not undergoing mitosis
How many centrioles does a centrosome contain?
2
Why is the basal body of the axoneme/microtubule anchored into the cell through the plasma membrane?
allows motion without tearing away of microtubule from the cell
What are two essential components to the climbing motion of a cell?
adhesion and actin
How do proteins drive actin based motility?
motor proteins and polymerisation of ends of proteins ie turnover
Where is the actin’s source of energy found and what is it?
heart of the actin molecule, ATP hydrolised
Where is the microtubule’s energy source found and what it it?
2 GTPs - one buried in centre not hydrolised, the other is at the positive end
Which end of the microtubule is stable, grows quickly and can therefore drive motility?
positive end
Explain actin treadmilling
monomers added on one end and disassembled on the other, so moves but don’t move laterally - called treadmilling bc of this lack of actual mvt, even though there is overall mvt
What establishes the polarity of a microtubule and an actin filament?
based on the directionality of subunit addition (tubulin dimers for microtubules, actin monomers for actin filaments)
Give the two main fates for monomers
sequestering
nucleating
What are the different types of fates for nucleated monomers?
all polymerised then:
membrane binding
depolymerising
filament-severing
bundling
cross-linking
end-blocking (capping)
What are the filaments and the motor proteins for cilia vs cell cytoskeleton/muscle?
microtubule and dynein (cilia) vs actin and myosin (cytoskeleton/muscle)
What is at the 2 extremities of myosin and what makes up the myosin body?
C-terminus, N-terminus at the head side then body made up of coiled-coil of 2 alpha helices
Which is the business end of myosin and what types of chains are there?
N-terminus, light chains
At which end of a myosin is energy spent?
head ie N-terminus
How does exposure of binding sites for myosin by calcium allow faster and more efficient myosin power strokes ie contractions/movements?
much faster and less energy consummation - calcium reveals troponin binding sites means we can have this structure already ready to react to ATP/calcium - doesn’t have to be built any time we need to move
Explain the stages of myosin power stroke
ATP Binding: Myosin binds ATP, causing the head to detach from actin.
ATP Hydrolysis: ATP is hydrolysed to ADP and Pi, causing myosin to "cock" and store energy.
Cross-Bridge Formation: Myosin head binds to actin, forming a cross-bridge.
Power Stroke: Myosin head pivots, pulling actin toward the centre of the sarcomere.
ADP and Pi Release: Myosin releases ADP and Pi, completing the power stroke.
ATP Rebinds: Another ATP binds, causing myosin to detach and reset.
List the essential ingredients for myosin power stroke allowing mvt/contraction
ATP
Myosin
Actin
Calcium ions (for actin exposure)
What are the 4 essential structures in a cell that allow for actin-based motility?
Filopodium
Lamellipodium
Stress fibres
Cortical actin
What gives a cell direction during actin-based mvt?
growth factor or cytokine
What are the 5 steps of actin-based motility?
growth factor or cytokine give direction
formation of filopodia moving it in that direction
then lamellipodium = network of actin
adhesion: protrusion so finally need to grab onto what we’re reaching out
stress fibres disassemble the back, contract the cells in middle = mvt by one step
repeat
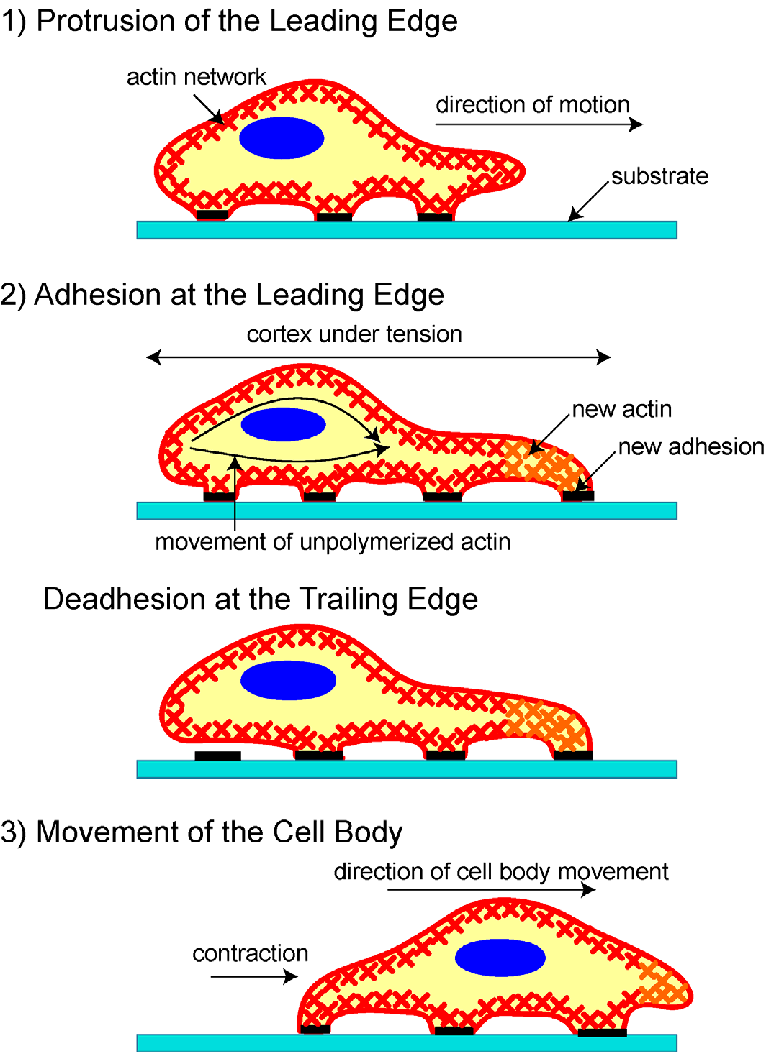
What is this diagram depicting?
actin-based motility