Retrosynthesis and Protecting Groups
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
As discussed in the lectures, differentiate the three primary types of organic syntheses: linear synthesis, convergent synthesis, and retrosynthesis.
Linear synthesis: Forward process, constructing from simpler compounds to build a complex molecule.
Convergent synthesis: Multiple compounds are built separately and then combined in a final step.
Retrosynthesis: Backward process, deconstructing from complex molecule to simpler compounds or commercially available starting materials.
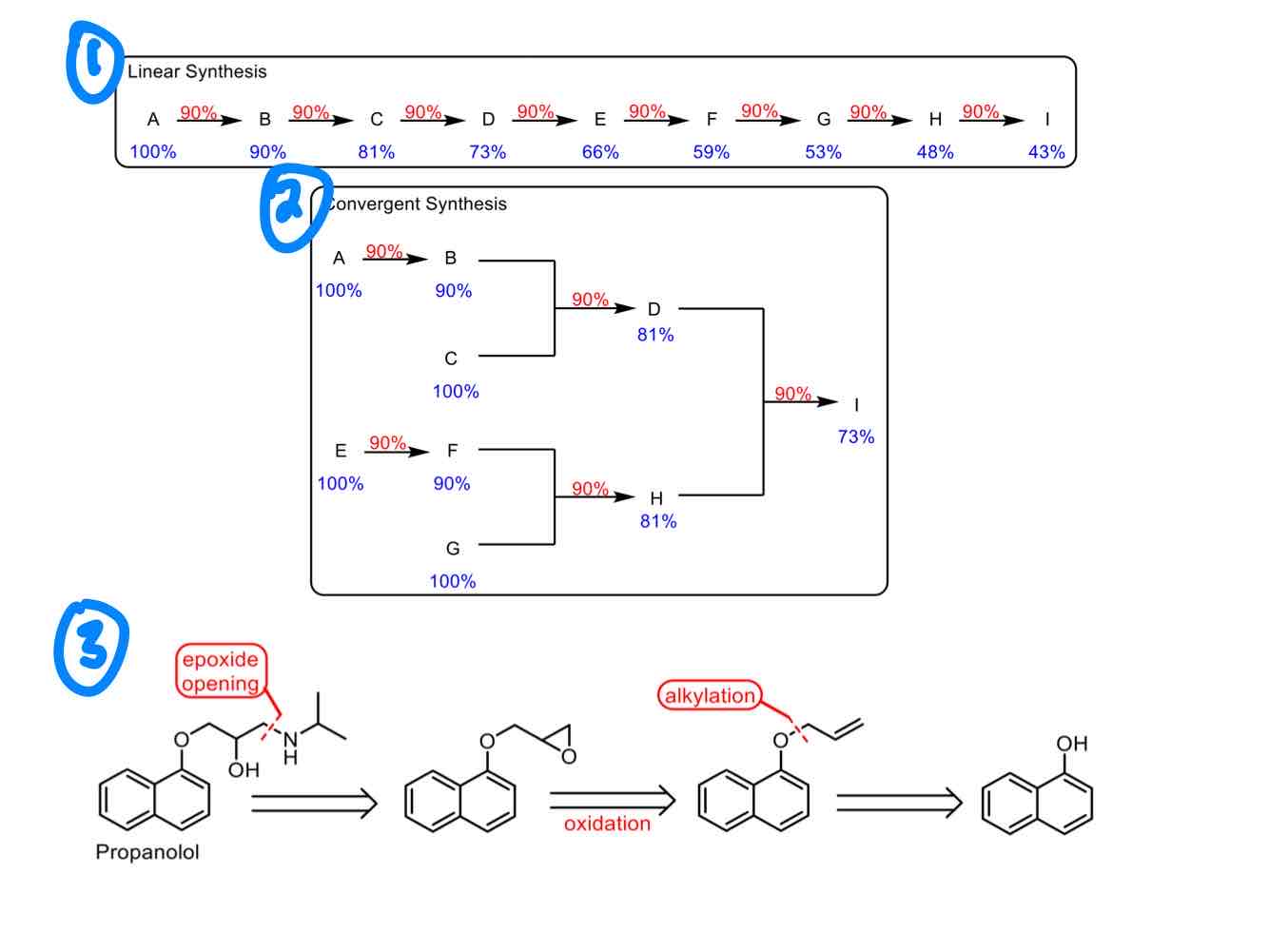
Why are linear and convergent synthesis generally not as good as retrosynthesis?
Efficiency: Decreasing yields with each step.
Flexibility: Each step depends on the previous one.
What are Dr. Walsh’s two “rules” when it comes to retrosynthesis?
Never cut benzene.
Never cut cyclic systems.
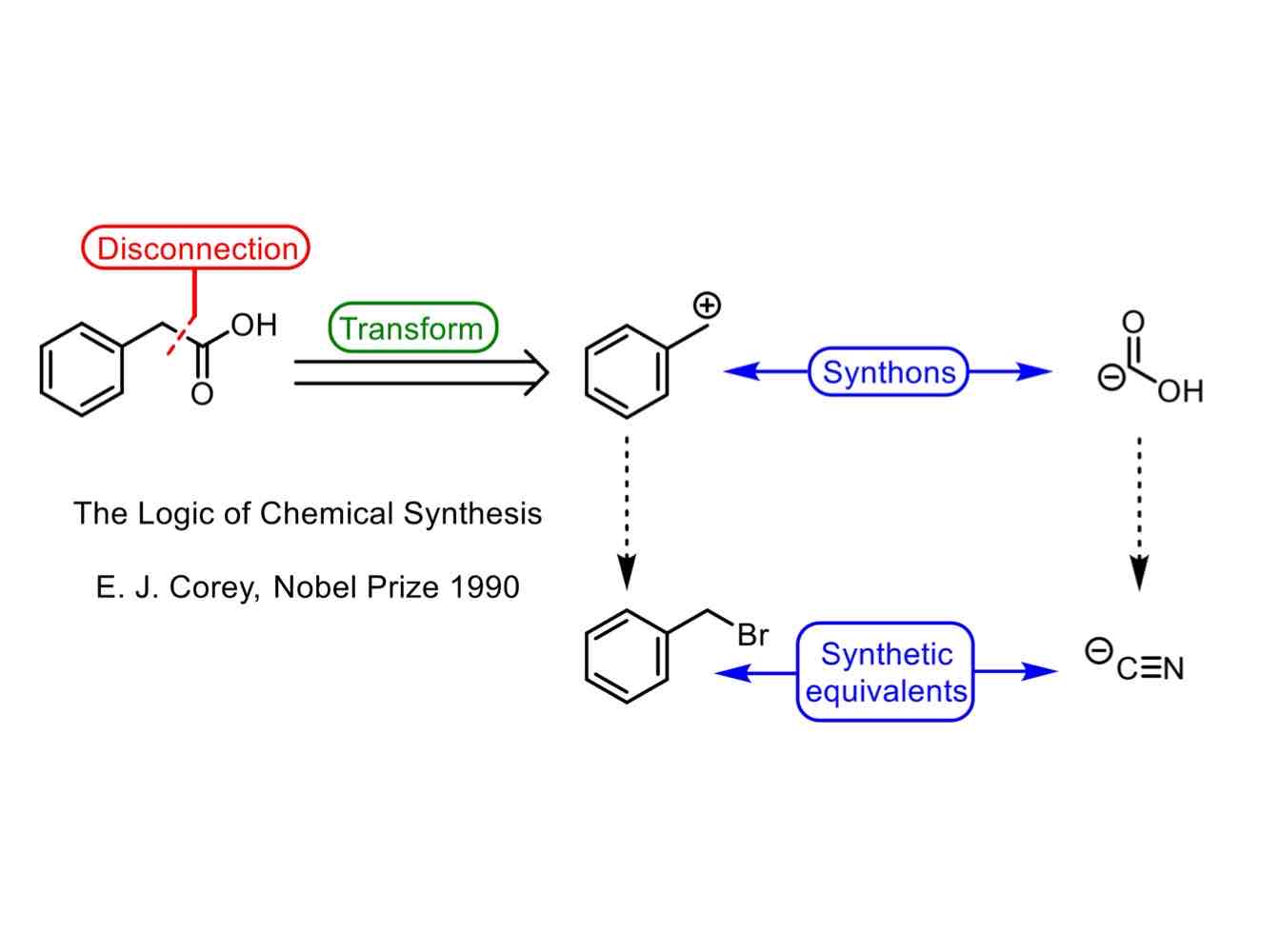
Before getting into retrosynthesis, define these terms:
Transformation.
Retrosynthetic cut or disconnection.
Synthons.
Synthetic equivalents.
Transformation: A reaction of changing a molecule, either going either forward or backward.
“Retrosynthetic cut” or disconnection: Breakage of a bond, converting a molecule into a possible starting material.
Synthons: A generalized fragment, usually an ion, produced by a
disconnection, which cannot itself be used, often because it is too unstable
Synthetic equivalent: A reagent carrying out the function of a synthon.
What are the three considerations for using protecting groups (PGs) for functional groups (FGs)?
Nature of the functional group requiring protecting group.
Conditions for stability of protecting group.
Conditions for removal of protecting group.
In total synthesis, it is a bad idea to carry through reactive _________. If you have a functional group in your final product, you don’t want your functional group in your ____ step in your 20-step synthesis.
In total synthesis, it is a bad idea to carry through reactive intermediates. If you have a functional group in your final product, you don’t want your functional group in your first step in your 20-step synthesis.
In total synthesis, it’s a much better idea to keep _____ intermediates as ________ intermediates. Keep the reactive stuff towards the end.
In total synthesis, it’s a much better idea to keep reactive intermediates as protected intermediates. Keep the reactive stuff towards the end.
You don’t need to take your protecting group on and off _________.
You don’t need to take your protecting group on and off immediately.
When protecting a group, when I say that “any acid can be used” or “any base can be used,” what is the one thing that the acid or base has to be in order to protect?
The acid must be more acidic than the molecule that you’re reacting it with. p-TsOH is everyone’s favourite acid.
The base must be more basic than the molecule you’re reacting it with.
Name the four primary protecting groups for alcohols, as discussed in lectures.
Tetrahydropyran group. (THP).
Allyl groups.
Methoxymethyl (MOM).
Silyl ethers.
How to install and remove THP?
Any acid can be used.

How to install allyl groups?
Any base can be used.

How to remove allyl group?

How to install MOM?
Any base can be used. Base is used to catalyze the reaction.

How to remove MOM?
Any acid can be used.

Why are silyl ethers used instead of regular carbon ethers?
It is difficult to cleave the ether bond, as carbon is not a good leaving group.
What are the four silyl ethers that we have discussed so far? Order them in increasing reactivity to install and remove and briefly explain why.
TIPS. (least reactive)
TBDMS.
TES.
TMS. (most reactive)
Sterics - as reactivity increases, less steric hinderance is involved, and better chance at installation (Oxygen attack) and removal (Fluoride attack).
How to install any of the silyl ethers?
Any base can be used.

How to remove any of the silyl ethers?

Why would you use TBAF to remove silyl ethers?
Si-F bond is very strong.
Generally, what are the three amino-PGs?
Phthalimide.
A carbamate commonly called Boc.
A carbamate commonly called Fmoc.
How would you install phthalimide on an amino group?
Any base can be used. Base catalyzes the reaction.

How would you remove phthalimide on an amino group?

How would you install Boc on an amino group?
What does the installation reagent look like?
Any base can be used. Base catalyzes the reaction.

How would you remove Boc from an amino group?
What does the removal reagent look like?

How would you install Fmoc on an amino group?
What does the installation reagent look like?
Any base can be used. Base catalyzes the reaction.

How would you remove Fmoc on an amino group?
What does the removal reagent look like?

How would you protect and install a PG on a diol group? On that note, how would you remove it?
Any acid can be used.

How would you install a dithioacetal on a carbonyl group efficiently?
Any acid can be used.

How would you remove a dithioacetal on a carbonyl group?
Any mild proton source can be used.

What are the two ways of protecting carboxyls?
Via oxazoline.
Via OBO.
How would you protect a carboxyl via oxazoline?
Any acid can be used.

How would you deprotect a carboxyl via oxazoline?
Any acid and mild proton source can be used.

How would you protect a carboxyl via OBO?
DMAP is used for catalysis.

How would you deprotect a carboxyl via OBO?
Any acid can be used.
Any base and mild acid can be used.
