1.1 Nature of Economics
1/69
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
What do economists do?
Develop models to explain how the economy works
Whats the difference between a theory and a model?
A theory is often expressed in words whereas a model is expressed in mathematical terms
Define ceteris paribus
‘All other things being equal’
Why is it difficult to set up experiments to test hypothesis?
Other variables are always changing in the everyday world
What is a positive economic statement?
It is an objective statement made without value judgemtns or emotion.
They can be tested to be proven or disproven.
A positive statement is usually expressed in what form? And why?
As a hypothesis becaue they ca be analysed and evaluated.
What type of statement is 'Raising taxes will lead to an increase in tax revenue' ?
Positive statement
What type of statement is 'Warm weather will lead to an increase in ice cream sales'?
Positive statement
Define a normative statement
Subjective statements that contain value judgement.
Based on an opinion therefore cannot be proven or disproven.
Says one action is better than another. ‘Should’, ‘
What words are normative statements most likely to include?
‘Ought’, ‘maybe’, ‘unwise’, ‘should’
What type of statement is 'The free market is the best way to allocate resources'
Normative statement
What type of statement is 'The government should increase taxes'
Normative statement
'The government should increase the interest rate' and 'The rate of inflation is at 5%'. Is an example of what economists do. What is this ?
Economists use positive statements to back up normative statements
What is the economic problem?
Scarcity
Define scarcity
Infinite wants and limited resources
What is an evaluation point about normative statements?
As they are value judgements they can influence economic desicion making ad policy
State examples of scarcity
Water in India and China, food shortages around the world
How do economies try and solve the basic economy problem?
By working out
a) what to produce
b) how to produce it
c) for whom production should take place for.
How do economies try to solve the basic economic problem?
Work out what to produce, how to produce it and for whom production should take place.
Define renewable resource
A natural resource that can be replaced or replenished on a level equal to consumption.
Examples of a renewable resource
Oxygen
Solar power
Fish
Describe how stock will not decrease.
As long as the rate of consumption are less than or equal to the rate of replenishment
Define non-renewable resource
A resource of economic value that cannot be replaced when used up.
Examples of non-renewable resources
Fossil fuels, coal, oil and gas
Define opportunity cost
The cost of the next best alternative forgone when making a decision.
How do consumers make choices?
Based on what gives them the greatest level of satisfaction, using their limited income
How do producers make decisions?
They must choose what to do with their limited resources and their desicions will be based on profit.
How does the government make decisions?
They make decisions on where they should spend their limited tax revenues based on what will maximise their social welfare.
What are tax revenues?
Limited amount of money raised primarily through taxes from individuals and businesses
How can the government maximise social welfare?
Allocating their tax revenues efficiently, investing in public goods (clean air, infrastructure).
What are the 4 factors of production?
Capital, enterprise, land and labour
How will consumers make choices using theier limited income?
By what gives them the greatest level of satisfaction while maximizing their utility.
How will producers choose what to do with their limited resources?
Producers will allocate their limited resources to maximize profit by analyzing costs, potential revenue (profit) , and consumer demand.
When is there no opportunity cost?
When there are free resources available for use without sacrificing alternatives.
What does the government spend tax revenues?
Health care, unemployment benefits, education, infrastructure development, national security, public sector salaries (teachers, healthcare workers)
Define land as a factor of production
Land refers to all natural resources used in the production of goods and services
What is an example of ‘land’
Natural resources eg. soil, minerals, water, and forests.
Define ‘labour’ as a factor of production
Labour refers to:
All productive human effort, skills, and abilities used in the production of goods and services
Both physical ad mental
Paid or unpaid work
Define ‘capital’ as a factor of production
Capital refers to:
All man-made resources that are used to produce goods or services in the future
Define entrepeneurship as a factor of production
Mangers willingness and ability to take the risks of combining the other 3 factors of production in order to make a product or service.
Organise and make decisions about production methods, product design and market strategies
What is the basic economic problem?
The basic economic problem is the issue of scarcity
Define scarcity
Where limited resources are insufficient to satisfy unlimited human wants and needs, leading to the necessity of making choices about resource allocation.
What is the reward of land?
Rent
What is the reward of labour?
Wages
What is the reward of capital?
Interest
What is the reward of enterprise?
Profit
What are the 3 combinations of factors of production
Labour-intensive industries
Capital intensive industries
Land intensive industries
Define labour-intensive industries
Example (agriculture or retail)
They might rely on human labour more than the other factors of production
Define capital-intesive industries
Example: manufacturing, energy or technology
They would typically use more machinery, equipment and technology
Define land intensive
Example: farming
What afctor of produciton is essential in all industries
Entrepeneurship, involves organising and co-ordinating the other factors to respond to market demands
What does a PPF show?
Maximum possible combinations of capital and consumer goods that the economy can produce with its current resources and technology.
Define intermediate goods
Goods that are used by businesses to produce other goods and services
They are not consumed in the final product but are essential for creating other products or services
Why is a PPF drawn as a curve?
To illustrate the law of increasing opportunity costs, showing that producing more of one good requires larger sacrifices of another good.
The PPF tends to be drawn as a curve because the firs resources switched from captial to consumer good production are resources that are not adding much to capital goods but will be muchmore productive in the production of consumer goods, and vice versa
What is a disadvantage of a PPF?
Gives no indication of which combination of goods is best for economic efficiency or societal welfare. A PPF
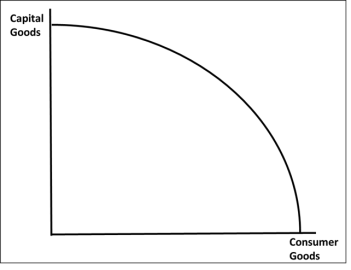
What does this diagram show?
A PPF
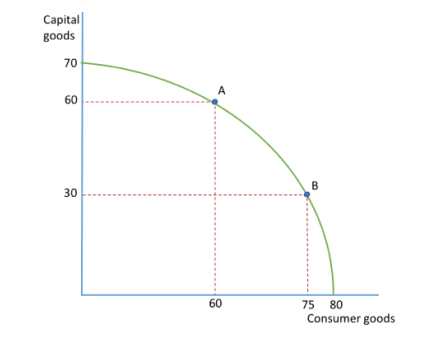
Moving from A to B, what is the opportuntiy cost of producing an extra 15 consumer goods
30 capital coods
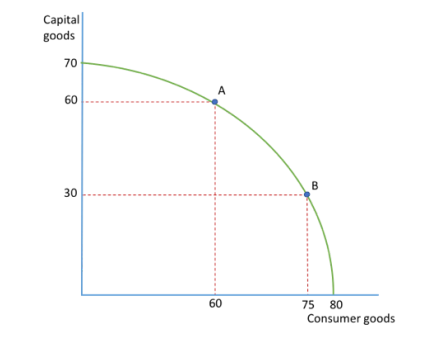
If they produced 0 capital goods, how many consumer goods could be produced?
80 consumer goods
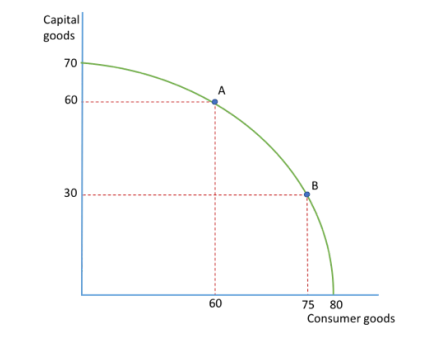
By producing 60 capital goods, how many consumer goods are lost?
20 consumer goods are lost.
Factors that can cause an economics decline (shown on a PPF)
Natural disasters
Natural resources running out
Decrease in quantity/quality of labour
War
Migration
Fall in spending on education