BioE 002 Lecture Notes 21 4/21/25
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
Activated Receptor Tyrosine Kinases
Needs ATP
Ras genes
According to the NCI, drives over 30% of all human cancers
Activated by Tyrosine Kinase Receptors
PI-3 Kinase pathway
JAK-STAT pathway
Different pathways based on their receptors
Pathway A and Pathway B
Pathway A
Activation of transcription factors such as CREB
Pathway B
Contains serine-threonine kinase, which directly phosphorylates and activates a member of the Smad class
Some ion channels
Controlled by electrical currents instead of ligands and are called voltage0gated ion channels. Ligand binds to a channel and opens it by changing conformation.
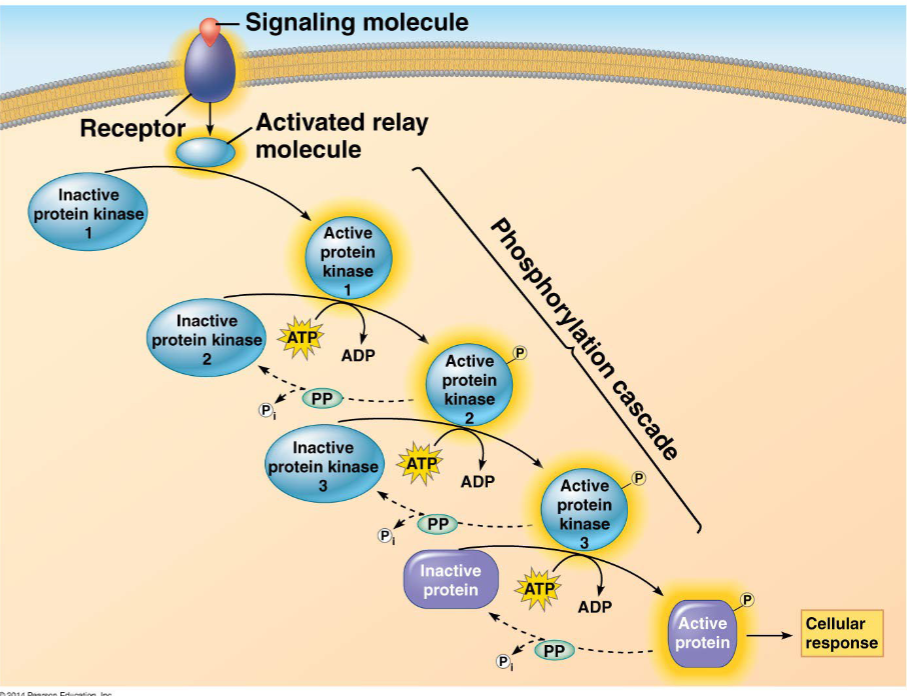
Signal Transduction
Is a multi step process
Cytokinesis
Broad category of small proteins (~5 - ~25 kDa) important in cell signaling. They are peptides and can’t cross the lipid bilayer
Examples:
Chemokines
Interferons
Interleukins
Lymphokines
Tumor necrosis factors
Transforming growth fator
Cell signaling
Can lead to the regulation of the activity of proteins. After the response, the signal is terminated. A process by which cells communicate
Cell signaling amplification
Occurs in small steps. Process where a small initial signal is transformed into a larger, more powerful response within a cell.
Autocrine
Type of signaling where the cell that expresses the messenger molecule also produces the receptors for that messenger
Hormones
AKA endocrine messengers
Conformation
Protein kinases and phosphates act by altering _________ of the signaling proteins
Cell adhesion
Process by which extracellular messages translate into a cascade of intracellular changes
G-protein couple receptors
Contains 7 transmembrane alpha helices
Cyclic AMP
Signal molecule not used for extracellular signaling
False
In endocrine signaling, the signal molecules act on the target cell only in close proximity
First messenger
A hormone or ligand can be considered as a ______________
Receptor Tyrosine Kinases
Family of receptors that mediates the biologic actions of a wide variety of ligands, including insulin, and other growth factors
Dimerization
Occurs when a ligand binds to the receptor tyrosine kinase
Cells with low cell division
Nerve cells
Muscle cells
Red blood cells
Cells with inducible cell division
Liver cells
Lymphocytes
Cells with high cell division
Hematopoietic stem cells. Has asymetric cell division
Stem cells
Precursors to all kinds of cells
Quiescent cells (G0)
Terminally differentiated and lost the ability to receive signals to initiate division.
Gap Stage 1
The initial stage of the cell cycle, where the cell grows, increases its organelles, and prepares for DNA replication
Synthesis
Where DNA replication occurs, creating a complete copy of the genetic material
Gap Stage 2
A period in the cell cycle where the cell continues to grow and prepare for cell division
Mitosis
Cells divide
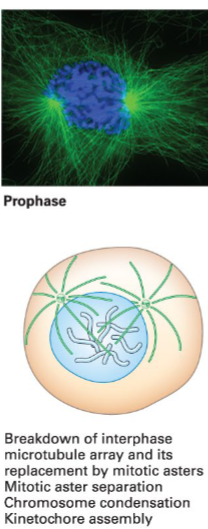
Prophase
Chromosomes condense, nuclear envelope breaks down by retracting into the ER, spindle poles duplicate, microtubules form the mitotic spindle apparatus, and kinetochore assembles.
Prometaphase
Spindle microtubules from each pole attach to chromosome kinetochores and center sister chromatid pairs in the spindle.

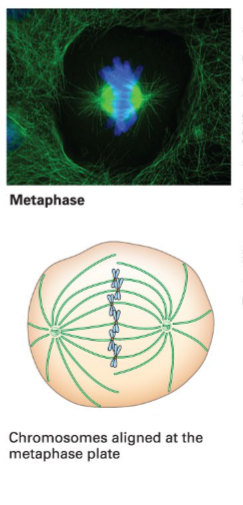
Metaphase
Chromosomes align at the metaphase plate.
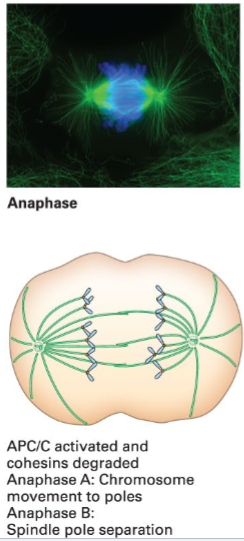
Anaphase
Spindle microtubule shortening and microtubule-based motors pull each sister chromatid toward an opposite spindle pole
Telophase
Chromosomes decondense, and each presumptive daughter cell reassembles a nuclear membrane around its chromosomes.
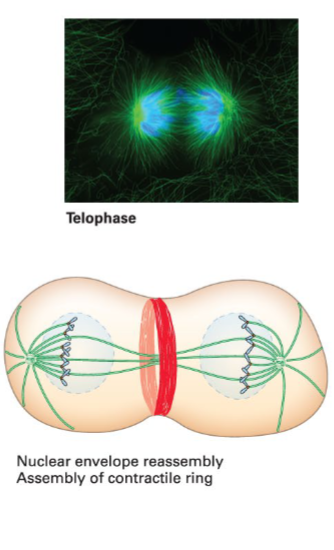
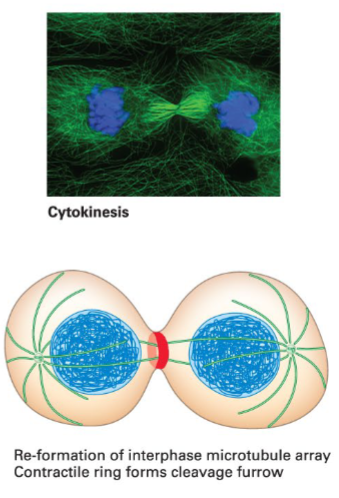
Cytokinesis
Cell division into two separate daughter cells. Contractile ring (actin and myosin) forms the cleavage furrow to split the cell.
Centrosome
A cellular structure involved in cell division that produces microtubules.
Before cell division, it duplicates and then, as the division begins, the 2 centrosomes move to opposite ends of the cell.
Microtubules
Assemble into a spindle between 2 centrosomes and helps separate the 2 identical sister cells
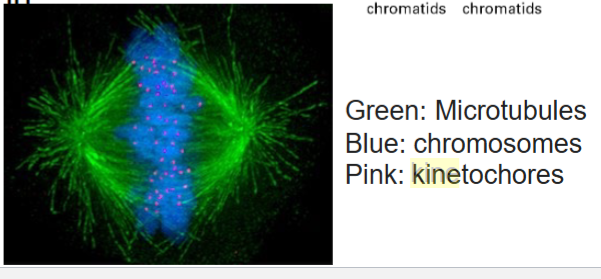
Kinetochore
A multilayer protein structure located at or near the centromere of each mitotic chromosome from which microtubules
extend toward the spindle poles of the cell; plays an active role in movement of chromosomes toward the poles during anaphase.
Cylin-dependent kinase activation
Initiates centrosome splicing during mitosis
Interphase
Chromosome/centrosome duplication and cohesion
Types of microtubules
Astral MTs
Kinetochore MTs
Polar MTs
Astral Microtubules
Extends from the centrosome to the cell cortex during cell division, forming part of the mitotic spindle
Kinetochore Microtubules
Connected to the chromosomes
Polar Microtubules
Originates from opposite poles in the cell and overlaps in the middle of the spindle apparatus
Cell cycle model organisms
Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Schizosaccharomyces pombe
Xenopus laevis
Drosophilia melanogaster
Human tissue culture cells
At the checkpoint
The cell makes decisions to enter the next phase
Performs replicating organelles in preparation for M phase. Monitors to see if it works before entering the next phase
Cells monitor the fidelity of the various processes required for cell division
This system is deeply conserved in eukaryotes
Cell cycle checkpoints
Cyclin-dependent kinases require association with other proteins (cyclins(
Multiple biochemical mechanisms ensure that the CDKs are active only in the stages that they need to be
Mechanisms involved in regulating CDKs
Cyclin binding
CDK phosphorylation state
CDK inhibitors
Controlled proteolysis
Subcellular localization
Cyclin A
Forms an activating complex with CDK2 in S phase with CDK1
Cyclin B
Only forms a complex with CDK1
Phosphatase Cdc25
Activates when DNA replication is done
Activation of Mitotic CDKs
Promotes mitosis and the breakdown of lamins
CDK1
Triggers chromosome condensation by initiating phosphorylation events on key proteins.