Topic 9
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
What are the main divisions of the pulmonary system?
Upper Airway and Lower Airway.
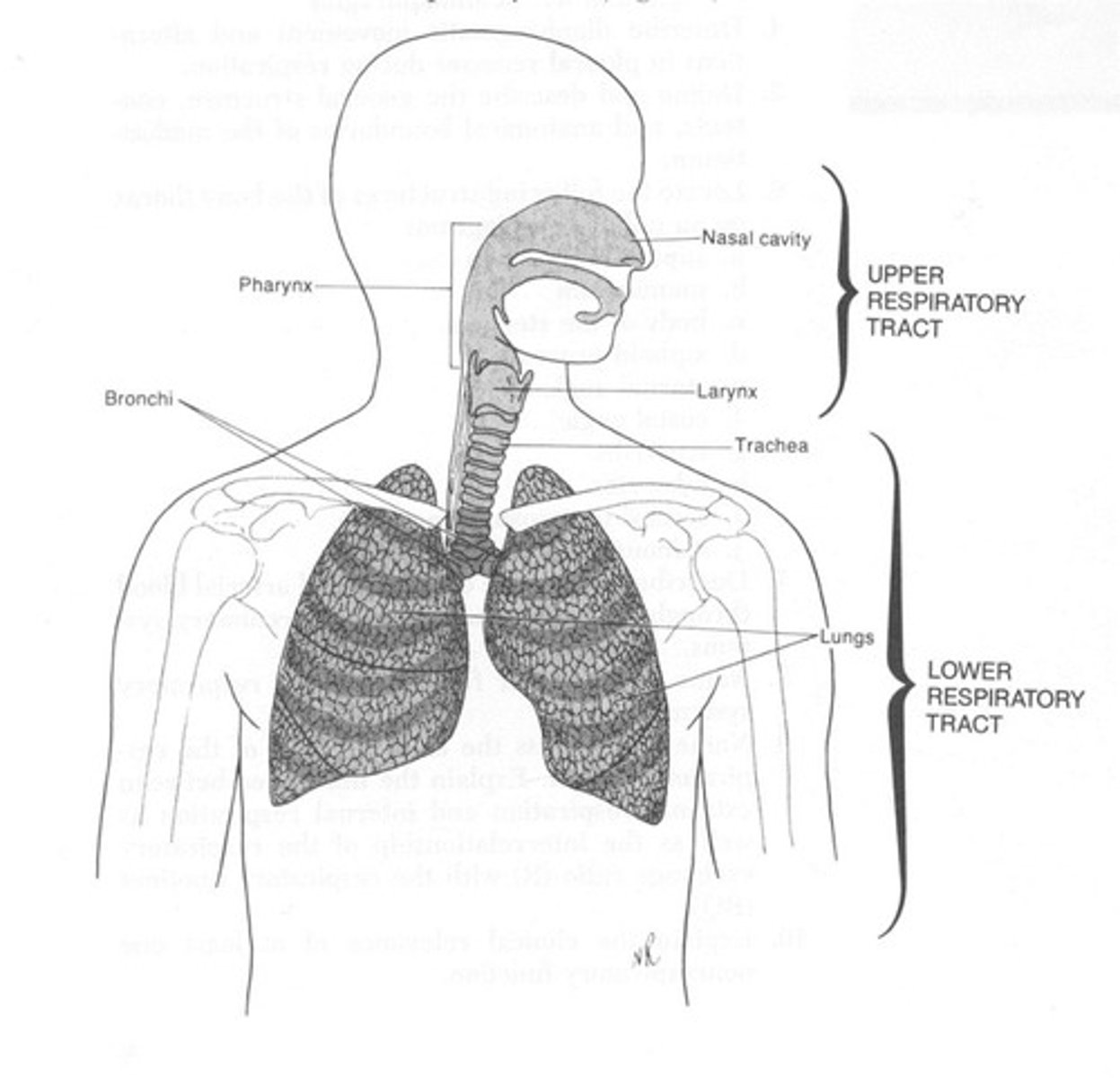
What structures comprise the Upper Airway?
Nose, Oral Cavity, and Pharynx.
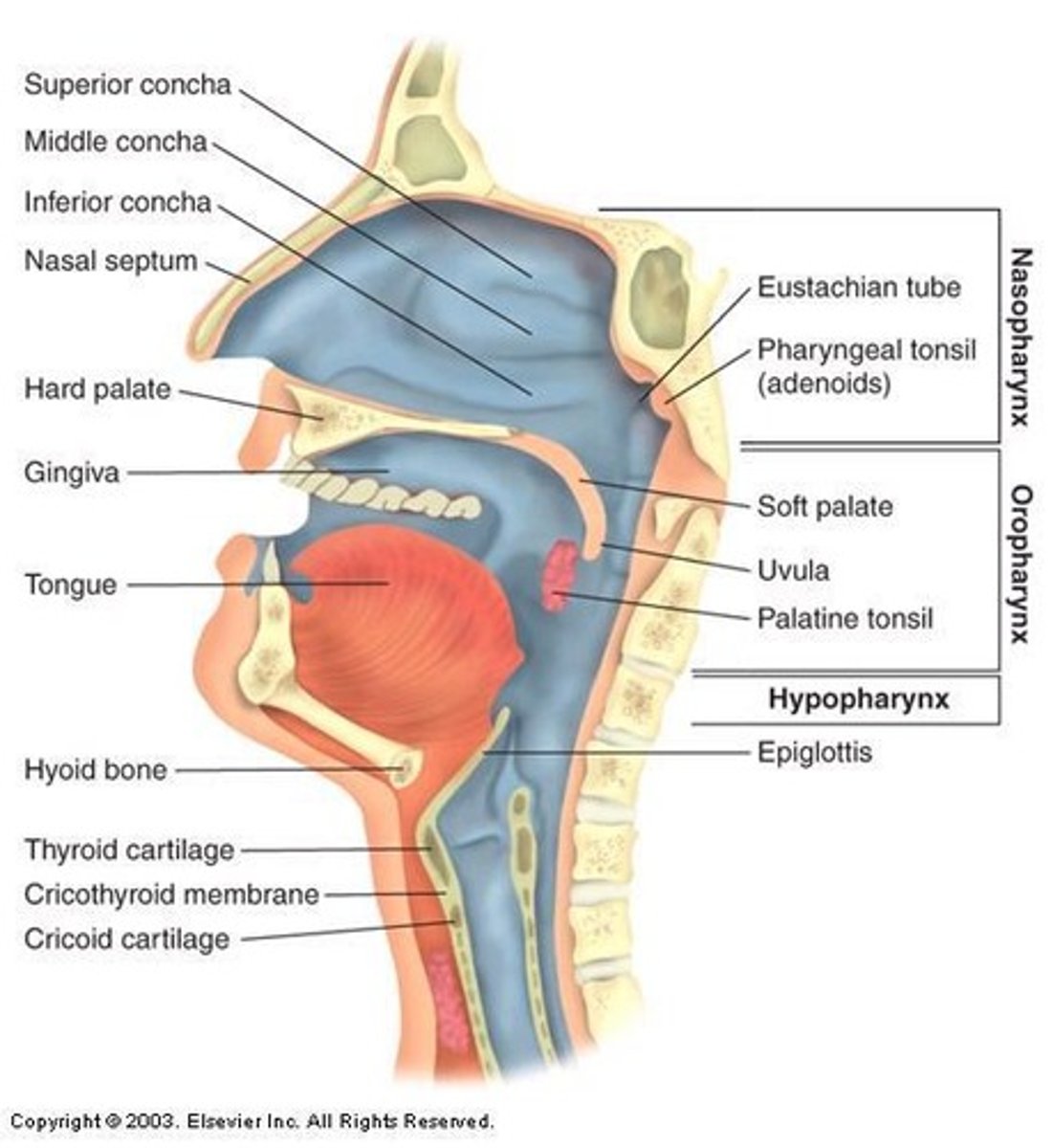
What are the three parts of the pharynx?
Nasopharynx, Oropharynx, and Hypopharynx (Laryngopharynx).
What are the primary functions of the Upper Airway?
To conduct air, humidify and warm inspired air, prevent foreign materials from entering the tracheobronchial tree, and serve as an area involved in speech and smell.
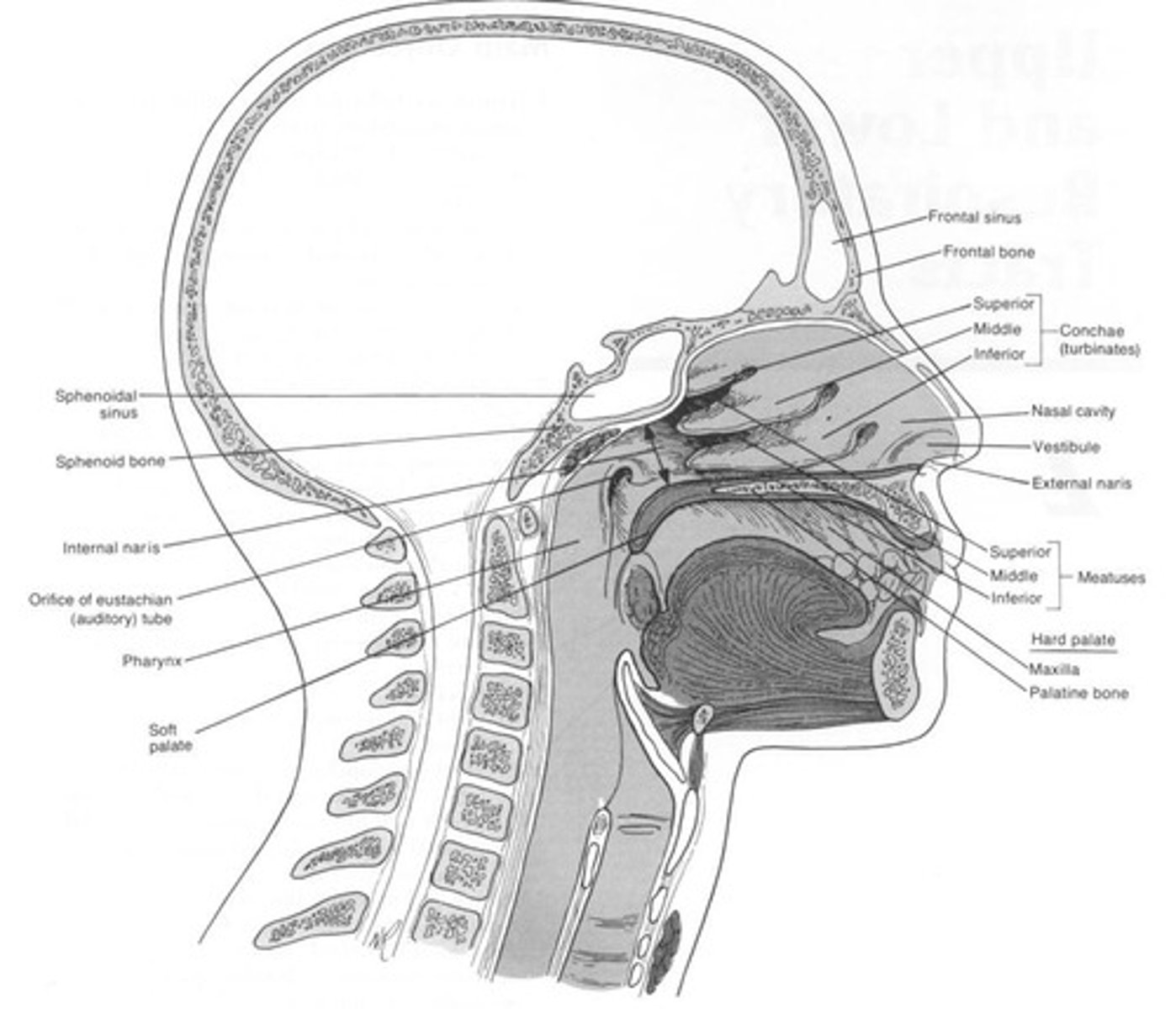
What is the anatomical structure of the nose?
A hollow structure in the skull consisting of hyaline cartilage and bone.
What are the openings of the nose?
Anterior nares (external naris) and internal nares (posterior nares or choana).
What is choanal atresia?
A condition where the anatomical opening of the nose is small, which may require surgery.
List the functions of the nose.
Filter, warm, humidify air; olfaction; and phonation (resonance).
What are the bones that form the nose?
Nasal bone, nasal septal cartilage, perpendicular plate of ethmoid bone, and vomer.
What is the function of the nasal septal cartilage?
To divide the nose into right and left halves.
What are turbinates (conchae) and their functions?
Three bony structures that increase the surface area of the nose, create turbulent airflow, filter air, humidify inspired gases, and warm inspired gases.
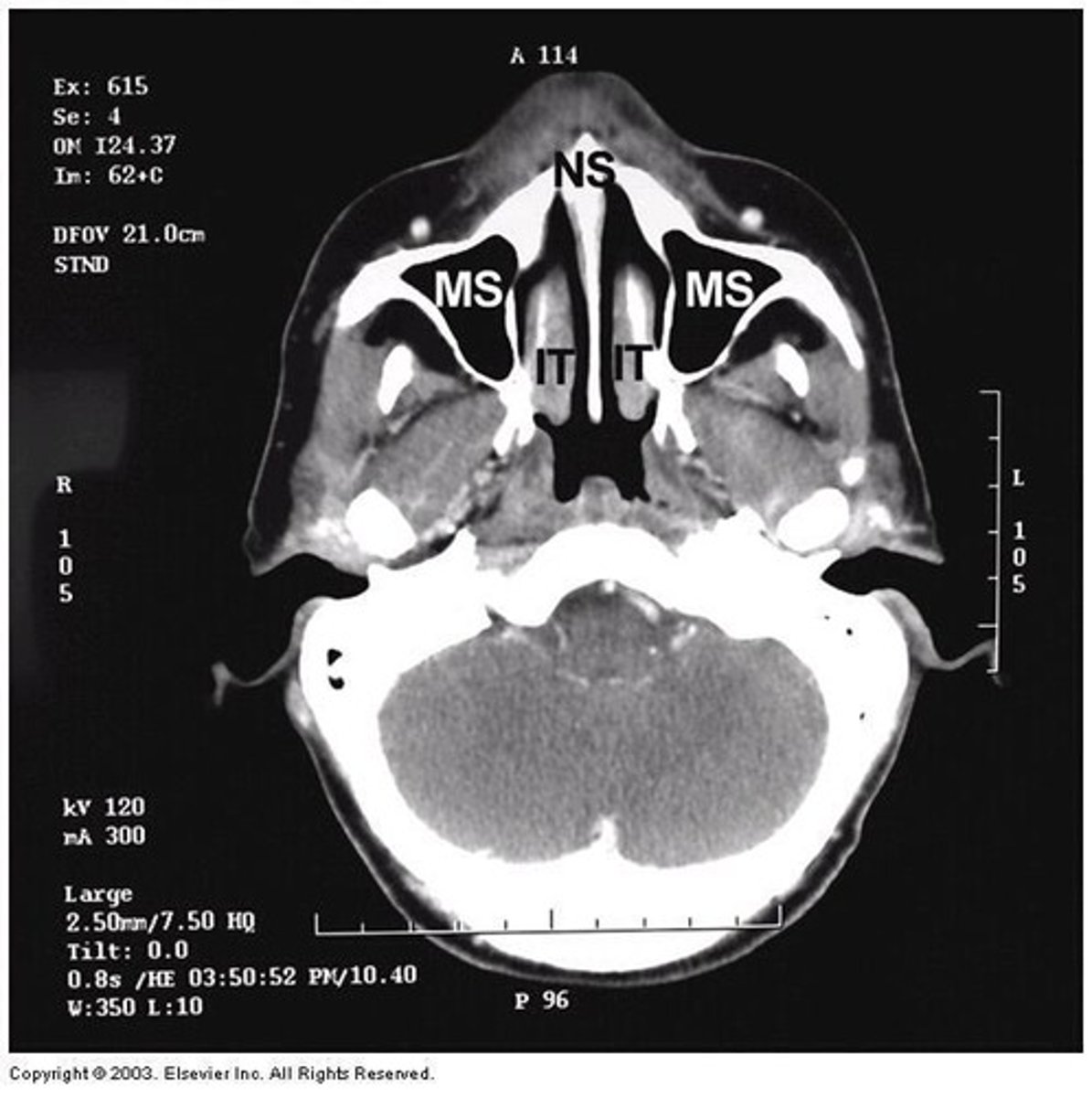
What types of epithelium are found in the nose?
Respiratory epithelium, stratified squamous epithelium, and olfactory epithelium.
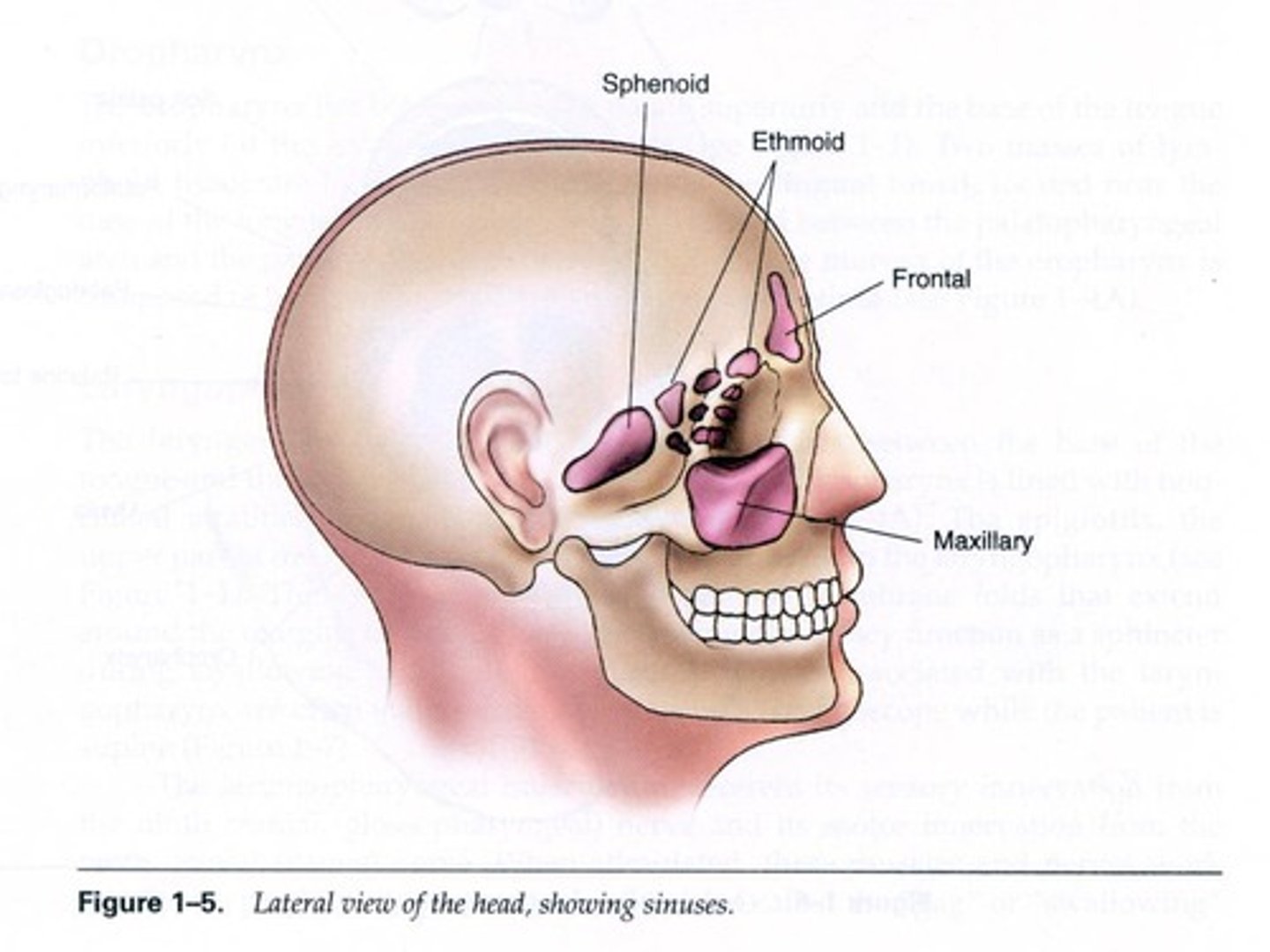
What is the role of the sinuses?
To produce mucus for the nasal cavity, act as a resonating chamber, provide temperature insulation for the head, and lighten the head.
How many groups of sinuses are there, and how are they categorized?
Four groups: three paired (Frontal, Sphenoid, Maxillary) and one that varies in number (Ethmoid).
What is the vestibule of the oral cavity?
The portion between the teeth (and gums) and lips.
What forms the roof of the oral cavity?
Hard palate (palatine process of maxilla and palatine bones) and soft palate with uvula.
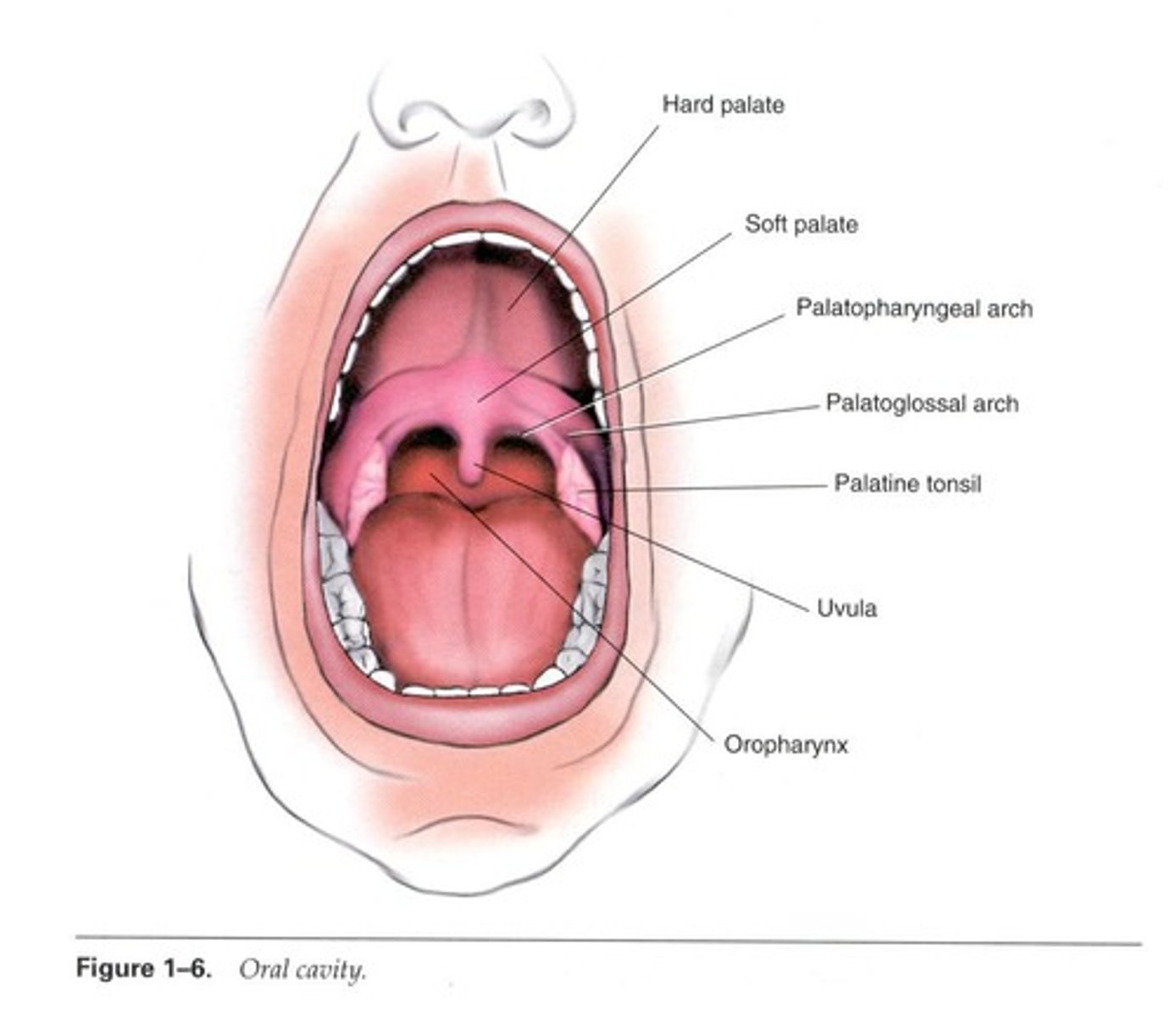
What type of epithelium lines the oral cavity?
Stratified squamous epithelium.
What are the mucous membrane folds in the oral cavity?
Palatoglossal arch, palatopharyngeal arch, and palatine tonsils.
What is the function of the palatine tonsils?
To provide lymphoid tissue for immunity.
What is the role of the respiratory epithelium in the nose?
To warm, filter, and humidify inspired air.
What happens if the holes to the meati are blocked?
It may lead to sinus infections.
What is a deviated septum?
A condition where the nasal septum is shifted to one side.
What is the significance of the olfactory epithelium?
It is specialized for smell and senses chemical changes.
What is the function of the turbinates in terms of air processing?
They increase the surface area for filtering, humidifying, and warming inspired air.