Raven Biology of Plants, Chapter 14
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
What are fungi?
They are eukaryote decomposers that are important in nutrient cycling; they are Janus-faced or two-faced (enable life & yet cause massive amounts of destruction
-ex. penicillin, pneumonia, yeast, Dutch elm disease, Bioremediation, food spoilage
What are the characteristics of fungi?
fungi: single celled (yeasts) or multicellular (fungal molds). Eukaryotic cells that are heterotrophic (they grow on organisms and absorb their nutrients) and cell walls are made of chitin.
What are hyphae and mycelium?
Hyphae are individual filaments that make up a fungus. Mycelium is a mass of hyphae.
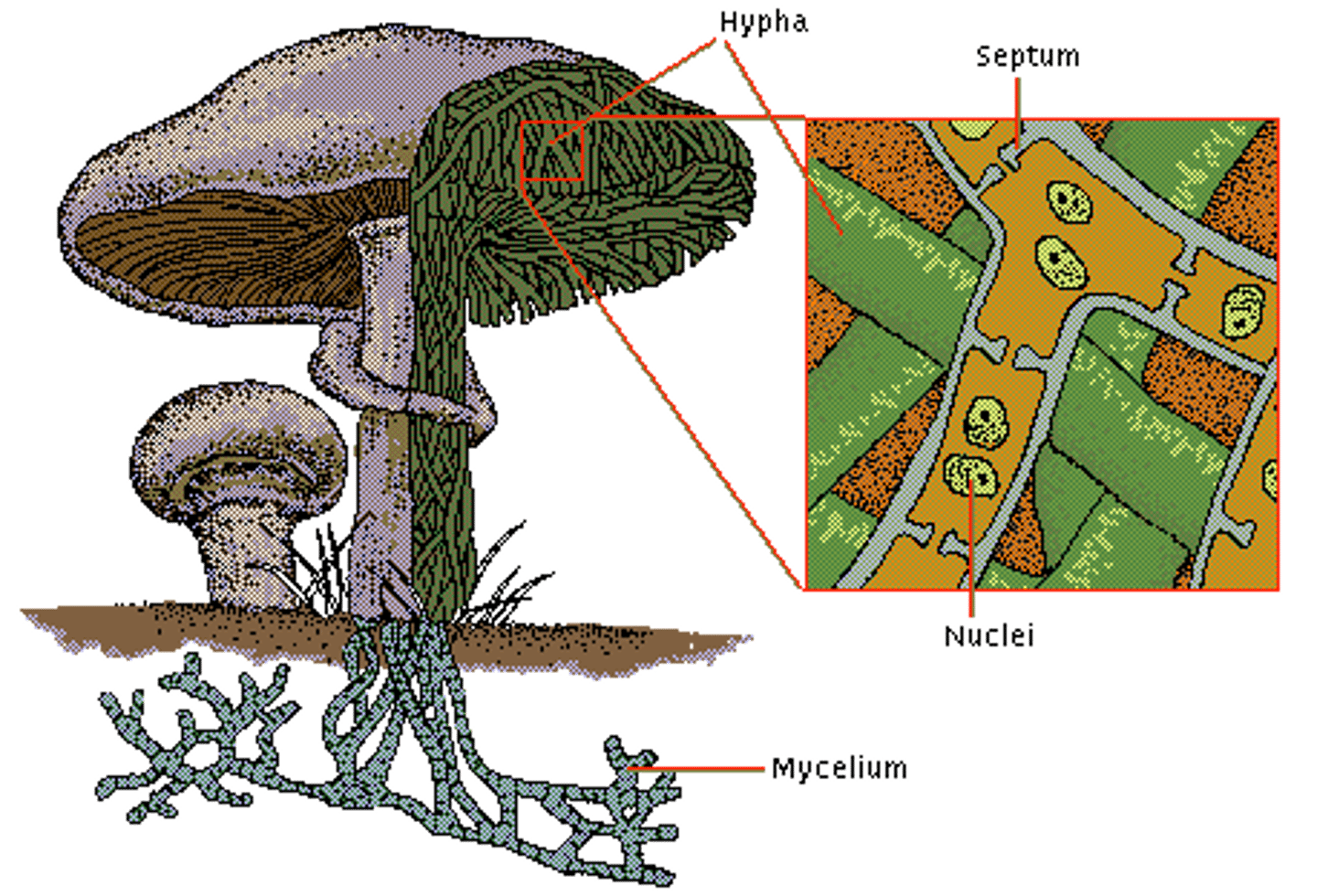
What are haustoria and what are they used for?
Haustoria are modified hyphae, and are used to penetrate the cells of their host and absorb nutrients directly from cells
What are saprotrophs?
heterotrophs that obtain organic nutrients from dead organisms
What are predators?
animals that kill and eat other organisms
What are parasites?
Protists that live in or inside other organisms and cause damage. They are transferred by a vector
What is symbiosis?
Any relationship in which two species live closely together
What is mutualism?
symbiosis in which both organisms benefit
What kinds of relationships do fungi have?
1-some are saprophytes
2-some are parasites
3-others are mutualistic
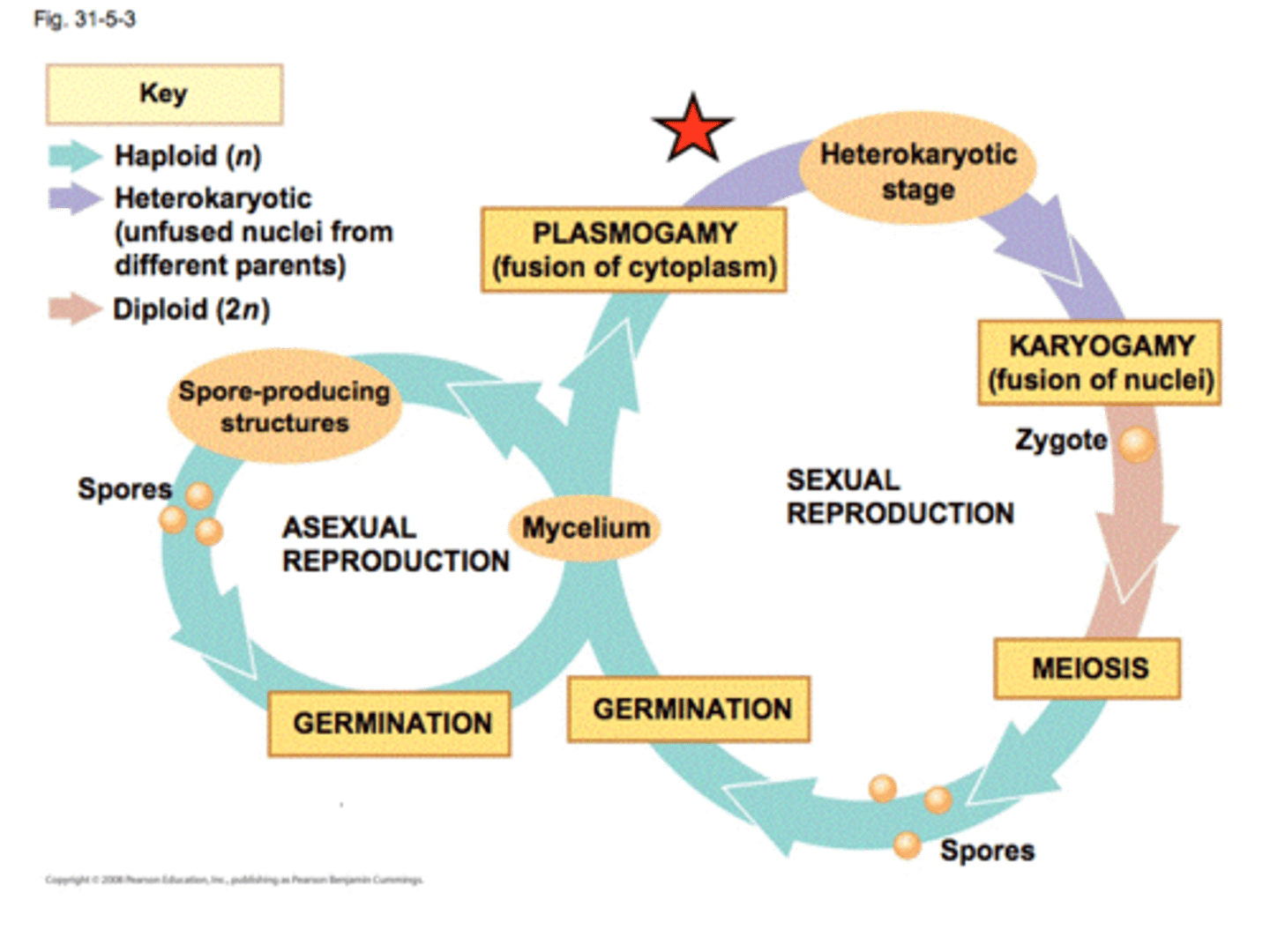
How do fungi reproduce?
sexually and asexually (budding)
What are sporangia?
multicellular organs that produce spores
How are sporangia produced?
The are produced from sporangia (spores). They can also be produced from hyphae cells called conidiophores (also called conidiogenous cells) at the tip or side of the hyphae
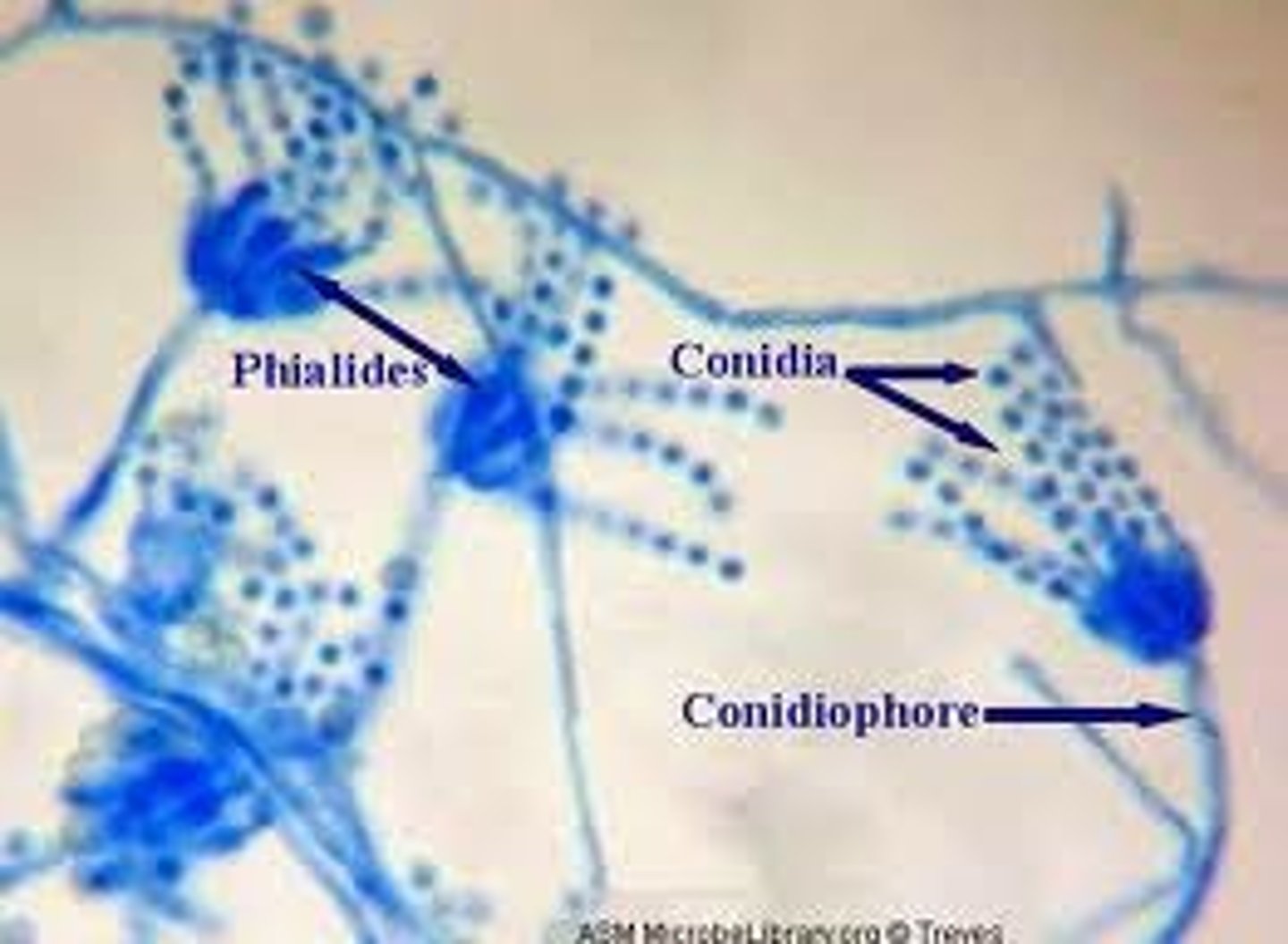
What are the benefits of budding in fungi?
1-maintains genetic information
2-easy & cheap
What is the benefit of sexual reproduction in fungi?
introduces genetic variation into a population
What are the three distinct phases of sexual reproduction in fungi?
1-plasmogamy
2-karyogamy
3-meiosis
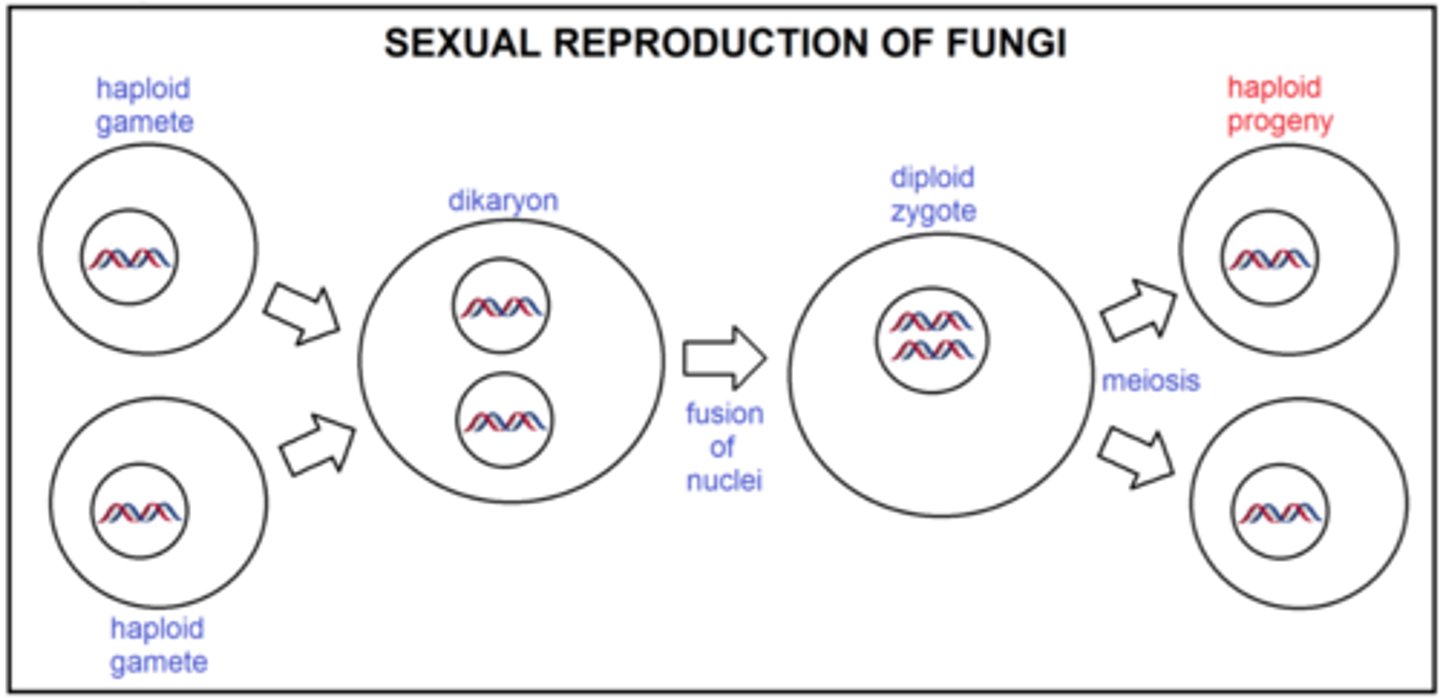
What is plasmogamy? Karyogamy? Meiosis?
1) Plasmogamy- union of cytoplasm-A haploid nucleus of a donor cell (+) penetrates the cytoplasm of a recipient cell (-).
2) Karyogamy- nuclear marriage-The (+) and (-) nuclei fuse to form a diploid zygote nucleus (2n)
3) Meiosis: The diploid nucleus gives rise to haploid nuclei (sexual spores)-causes genetic diversity; 2n-->n
What is a lichen?
symbiotic association between a fungus and algae (photosynthetic organism)
Describe Dutch elm disease.
-1st discovered in 1930s
-lethal fungal disease of American elm trees
-found across USA
Discuss Ergot.
-fungal disease of Rye & other cereals (genus Claviceps)
-called ergotism in humans
Describe mycorrhizae
-Mutualistic relationship between plants and fungi: Web of hyphae penetrates soil around roots & increase the plant root surface area (called fungus roots)
-Plants receive increased supply of water and mineral nutrients; fungi get organic food molecules (carbohydrates from photosynthesis) from the plants