Blood Bank
1/405
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
406 Terms
Which of the following set of conditions would NOT allow HDN to occur as a result of Rh incompatibility:
Mother Rh-negative, father Rh-negative
What is the purpose of a major crossmatch?
Verify donor ABO packed-cell compatibility
The use of cells with known blood groups to confirm ABO typing is known as:
Reverse grouping
Fresh frozen plasma :
Should be transfused within 24 hours of thawing
What is the proper storage temperature for thawed Cryoprecipitate?
20 - 24 ºC.
Most antibodies present in cord blood are of ________ origin.
maternal
What are the possible ABO genotypes of offspring from parents whose genotypes are OO and AB:
OA
OB
An aliquot of AS-1 red blood cells is being prepared from an intact packed cell unit using a sterile connection device.
During the process of preparing an aliquot, the sterile device fails and blood drips onto the counter from the product tubing. What should be done with the primary unit?
Change the expiration date to 24 hours
Kernicterus due to high levels of unconjugated bilirubin can cause brain damage in newborns suffering from severe HDFN.
True
The parents' blood types were AB and O. The blood group of any of their children could ONLY be:
Group A or B only
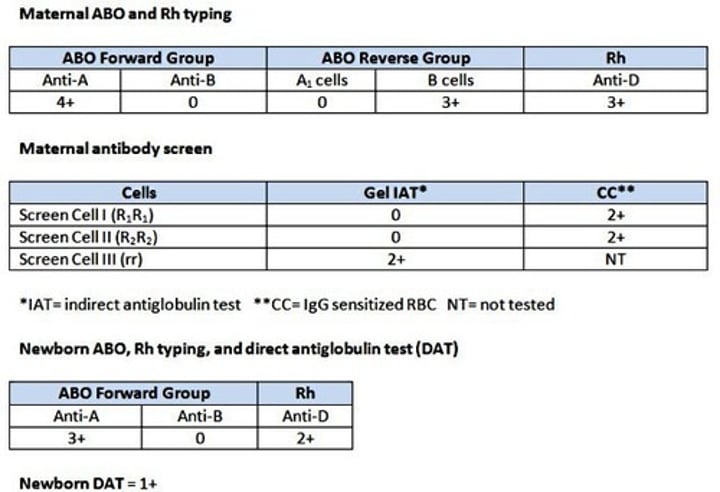
For the test results shown above, which of the following antibodies is most likely to be causing the newborn's positive DAT?
anti-K
The correct answer is anti-K.
Both the mother and infant are group A, eliminating ABO HDFN.
We are given the cell ID information for each of the screening cells. Screen cell 1 is R1R1. Therefore these antigens are present: D,C, e.
Screen cell 2 is R2R2. Therefore these antigens are present: D,E,c
Screen cell 3 is rr. Therefore these antigens are present: c,e
The only cell that reacted was Screen cell 3. Both c and e are also present on the nonreactive cells. The only choice that has not been eliminated is anti-K.
Also, the antibody screen reaction pattern (only cell 3 positive) is typical of anti-K.
An urticarial transfusion reaction is characterized by:
Rash and hives
Which one of the following is NOT a cause for donor deferral?
Weighs 115 pounds
Why do so few patients transfused with un-crossmatched red cells in an emergency experience a hemolytic transfusion reaction? Select the one best reason.
The incidence of unexpected red cell antibodies is relatively low.
What is the first step a transfusionist should take when a transfusion reaction is suspected?
Stop the transfusion, but keep the intravenous line open with saline.
What is the fundamental purpose of the full, pre-transfusion crossmatch?
Detect antibodies in recipient serum/plasma that react with donor red cells.
At what phase of antibody screen testing is it most important to read the reactions in order to detect clinically significant antibodies?
AHG
Which of these methods is the MOST accurate and reliable for determining the volume of fetal whole blood or red blood cells in the maternal circulation in order to evaluate fetomaternal hemorrhage?
Flow cytometry
What is the first line treatment for moderate to severe hemophilia A?
Lyophilized Factor VIII concentrate
For infants born to Rh negative females, a test for weak D is optional when initial D typing shows the newborn to be Rh negative.
False
The statement is false. For such infants, blood safety standards require a weak D test to be performed when initial D typing shows the newborn to be Rh negative.
For transfusion services in the United States, which of the following incidents must be reported to the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) because of a biological product deviation?
Incident C: The wrong specimen was used to crossmatch a unit and the unit was issued.
To detect the presence of blocking antibodies fixed on the red cells of a newborn infant:
Use the direct antiglobulin test
When given during pregnancy, RhIg may cross the placenta and sensitize fetal D-positive RBCs.
True
Because RhIg contains IgG anti-D, it can cross the placenta and sensitize fetal Rh positive red cells. Affected infants may be born with a weakly positive DAT, but significant hemolysis does not occur.
Which one of these Lewis blood group system phenotypes usually produces anti-Lea?
Le(a--b-)
This antibody is found in the serum of Le(a-b-) secretors.
Which organism is MOST likely responsible for septic reactions associated with Red Blood Cell transfusions?
Yersina entercolitica
A febrile nonhemolytic transfusion reaction is characterized by which of the following?
An increase in temperature of >1 degree C above 37 degrees during transfusion
Which type of blood component is most implicated in bacterial contamination?
platelets
IgM antibodies produced against red blood cells generally:
React best at room temperature
The hh genotype gives rise to:
Bombay phenotype
Which of the following antigen groups is closely related to the ABO antigens on the red cell membrane?
I, i
Today, amniocentesis is preferred to Doppler sonography for monitoring the severity of hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn (HDFN).
False
Because Doppler sonography is noninvasive, it is a safer alternative to amniocentesis for fetal monitoring and has largely replaced serial amniocentesis for predicting severity of HDFN.
If an Rh negative patient is administered a unit of R1R1 packed red cells, which one of the following antibodies would be most likely to develop:
Anti-D
R1R1 (DCe/DCe) cells are positive for the D antigen, which is the most immunogenic antigen of the Rh system, followed by c and E.
Which symptom of HDFN does phototherapy help prevent?
Kernicterus
Which of the following statements about high-frequency antigens is correct?
High-frequency antigens are common, but it's difficult to identify their corresponding antibodies
The cause of the most severe life-threatening hemolytic transfusion reactions is:
Anti-A, Anti-B, Anti-A, B
If the mother is a Rh immune globulin (RhIg) candidate, blood safety standards mandate that a test for weak D is compulsory when initial D typing shows a newborn to be Rh negative.
True
Weak D red cells can stimulate production of anti-D. Therefore, infants born to mothers who are RhIg candidates must be tested for weak D.
RhIg is given to Rh negative women who deliver infants who are Rh positive or weak D.
All of the following cellular antigens are important to an immunohematologist except:
Haptens
A hapten is an incomplete antigen.
Which one of the following blood groups usually reacts LEAST strongly with anti-H?
A1
Of the blood groups that are listed, A1 has the least amount of H antigen and therefore would react least strongly with anti-H.
Unexpected positive reactions encountered during forward ABO typing may be due to:
Acquired B antigen due to intestinal cancer
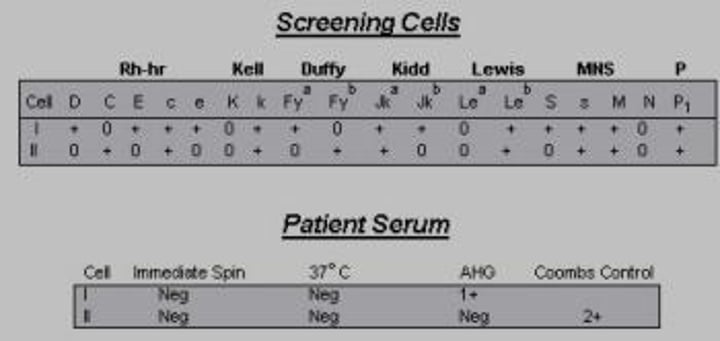
Based on the phenotype of the RBC screening cells, and patient results shown on the right, which of the following antibodies CANNOT be ruled out?
Anti-C
Anti-Fya
A 300 µg dose of RhIg can suppress immunization to how many mL of D-positive whole blood?
30 mL
One vial of 300µg RhIg can suppress immunization to a fetomaternal hemorrhage of approximately 30 mL of D+ whole blood
At what frequency should quality control testing be performed on each lot of anti-human globulin to be in compliance with the FDA's current good manufacturing practices requirements?
B. Each day of use
For which of the following antibodies is the DAT most likely to be negative when testing a newborn for possible HDFN?
anti-A
The DAT is most likely to be negative in ABO HDFN. It's possible that the washing done as part of the DAT may break the bonds between anti-A (or anti-B) and the newborn's poorly developed A (or B) antigens.
What is the MAXIMUM interval during which a recipient sample may be used for crossmatching if the patient has recently been transfused or was pregnant within the past 3 months?
3 days
Which of the following is the MOST likely discrepancy seen when a person demonstrates an "acquired B-like" phenomenon?
Forward typing appears to be AB, but reverse groups like A
What should be the first step performed to resolve a case where all forward and reverse ABO typing results are negative on a patient?
Incubate all testing tubes at 22ºc
Which of the following steps should be taken in the IMMEDIATE investigation of a potential hemolytic transfusion reaction? (choose all that apply)
ABO and DAT on the post-transfusion patient sample
Check for a clerical error
Visual examination of the post-reaction and pre-reaction (if available) plasma for hemolysis
Essential components of compatibility testing include all of the following except :
Direct Antiglobulin Test (DAT)
Which one of the following blood group antigens is not expressed, or only weakly expressed on cord blood cells?
Leb
Newborns are phenotypically Le(a-b-).
What action should be taken if a large clot is noticed in a red blood cell unit while the product is being prepared for release to the patient?
Do not issue the product.
Which of the following antigens are well developed on fetal cells?
Kell
Which of the procedures listed below will increase the platelet concentration in the preparation of platelets?
Centrifuge the blood at a low speed, remove the plasma and spin the plasma again at a high speed.
Which of the following consequences of severe hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn (HDFN) is most associated with neonatal death before or shortly after birth?
Hydrops fetalis
The concentration of sodium chloride in an isotonic solution is :
0.85 %
Reconstituted deglycerolized Red Blood Cells that have been prepared in an open system must be used within _______.
24 hours
The seeds of the Dolichos biflorus plant will agglutinate A2 cells but not A1 cells.
False
Anti-A1 lectin is extracted from the seeds of Dolichos biflorus. This reagent will agglutinate A1 cells, but not A2 cells.
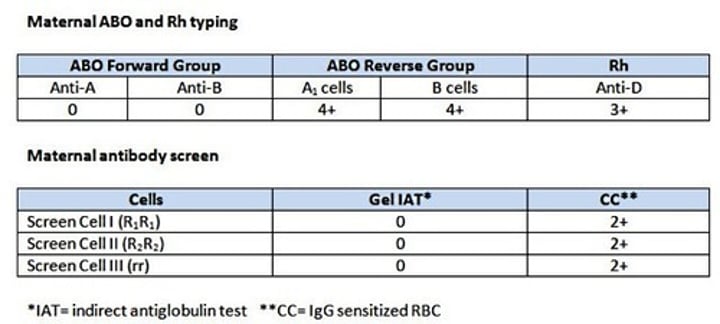
A mother's serologic results are shown above. Her newborn types as group A Rh positive with a (1+) positive direct antiglobulin test (DAT).
Which of the following investigative tests would be most useful to resolve the cause of the positive DAT and should be done FIRST?
Test newborn's plasma against group A1 red cells and group O antibody screen cells by IAT.
Which D variant has a qualitative difference in the D antigen that allows individuals with the D variant to produce anti-D? Select all that apply.
partial D
partial weak D
Which one of the following blood components would be MOST appropriate for a 9-yr old girl, with a low hemoglobin and low platelet count, who has bleeding gums?
Platelet Concentrate
RhIg prevents anti-D production mainly by clearing antibody-sensitized D-positive rbc from maternal circulation.
False
Initially researchers thought that RhIg prevented anti-D production by clearing the infant's D-positive rbc sensitized with maternal anti-D, but we now know this is not true.
Currently, the mechanism by which RhIg prevents immunization to the D antigen is poorly defined. However, research shows that it likely involves down-regulation of antigen-specific B cells, ie., the B cells do not differentiate into antibody-excreting plasma cells as they normally would when presented with foreign antigens.
In the Coombs phase of a crossmatch, what is the proper procedure to follow if the Check Cells give a negative reaction?
Repeat procedure with new AHG reagent and check the cell washer
Which of the following patients are at risk for transfusion-associated graft versus host disease (TA-GVHD) and require irradiated cellular blood products? (Choose all that apply)
Neonates less than 4 months of age
Recipients of donor units known to be from a blood relative.
Patient receiving chemotherapy who are immunocompromised.
Red blood cells with a positive DAT cannot be tested accurately with blood typing reagents that require an indirect antiglobulin technique unless they have been treated with ___________________ to dissociate IgG from the RBC membrane.
Chloroquine diphosphate
Ficin
ZZAP
Any of the above
Which of the following is NOT a possible type for an offspring from the mating of an O and an AB (non-cis) individual?
AB
The AB inheritance is not possible. In this case, the parents' genotypes are OO and AB, therefore one parent can only pass on the O gene.
Most blood group antibodies belong to which immunoglobulin classes?
IgG and IgM
When given during pregnancy, RhIg may cross the placenta and cause a positive DAT in the newborn.
True
Because RhIg contains IgG anti-D, it can cross the placenta and sensitize fetal Rh positive red cells. Affected infants may be born with a weakly positive DAT, but significant hemolysis does not occur.
Antibodies to which of the following are the most frequent cause of febrile transfusion reactions:
Granulocytes
The Kidd antibody is MOST commonly associated with:
Delayed hemolytic transfusion reactions
Delayed hemolytic transfusion reactions (DHTR) usually occur within which time period?
3-10 days after transfusion
Which of the following blood group antigens are most susceptible to destruction by the action of enzymes:
Fya
Duffy, or Fya and Fyb antigens, are most sensitive to enzyme treatment since they will be destroyed during this process. Enzyme panels can be helpful when multiple antibodies, including duffy, are present in a patient sample. With the duffy antigens destroyed, the panel can be performed to identify the remaining antibodies present.
HLA-A and HLA-B antigens can be detected using which of the following techniques?
Lymphocyte cytotoxicity
A 40-year-old female receives two units of Red Blood Cells during a surgical procedure. The patient has no prior history of transfusions. Seven days later, she presents with extensive bruising of the extremities and bleeding of the gums, with no additional symptoms. Her platelet count is 5 x 109/L ( reference interval 150 - 400 x 109/L). What is the most likely diagnosis?
Post transfusion purpura (PTP)
Based on the following results obtained against a patient's red cells, what will the genotype look like in this example?
Anti-C = 4+
Anti-c = 4+
Anti-E = 0
Anti-e = 4+
Anti-D = 0
r'r
Based on the positive antigen results given, the most likely Fisher-Race phenotype is Cde/cde. It is necessary to convert between Wiener system shorthand nomenclature to Fisher-Race nomenclature in order to make this determination. For example:
Wiener Fisher-Race
Ro Dce
R1 DCe
R2 DcE
Rz DCE
r dce
r' dCe
r" dcE
ry dCE
Which one of the ABO groups listed below has the MOST H-antigen?
O
The amount of H antigen varies depending on the ABO group that is inherited. Group O has the greatest amount of H antigen, followed by A2 then B, and then A1. A1B has the least amount of H antigen.
The BEST way to thaw Fresh Frozen Plasma is to thaw it by:
placing the FFP in a 37º C or lower in a water bath
What should be done with a box of 10 Red Blood Cell units that was received with a measured temperature inside the box at 15ºC.
Quarantine and destroy the products.
Blood safety standards such as AABB Standards directly specify that an electronic crossmatch cannot be done when an Rh negative female has an anti-D consistent with antenatal RhIg administration.
False
The statement is false. Current blood safety standards do not directly address whether an electronic crossmatch is contraindicated when anti-D consistent with antenatal RhIg administration is present. Laboratories are left to develop their own policies.
Why is it dangerous to transfuse a person with type O blood with a unit of A blood?
The patient's anti-A would destroy the donor's cells with severe consequences to the patient.
Which of the following is generally considered equivalent to CMV seronegative RBC for use in an exchange transfusion to a newborn?
Leukoreduced RBC
In order to prevent a loss of viability in platelet concentrates during storage the pH must be maintained above:
6.2
The term "allogenic blood" is synonymous in meaning with blood that is:
donated by a donor for a recipient other than the donor to use
Which one of the following blood group systems may show a cell typing change during pregnancy?
Lewis
Which of the following are not appropriate indications for the use of fresh frozen plasma:
Volume expansion
The most recent algorithm for HIV confirmatory testing in patients who are positive by ELISA is the:
HIV-1/HIV-2 antibody differentiation immunoassay
A patient with Multiple Myeloma has the following reactions in the ABO typing:
Anti-A= w+
Anti-B = w+
Anti-A,B = w+
Auto control = w+
A1 Cells = 4+
B cells = 4+
What is probably causing these results?
Rouleaux
Which one of the following tests BEST correlates with the severity of hemolytic disease of the newborn (HDN).
amniotic fluid bilirubin
What are the possible ABO genotypes of offspring of parents whose genotype is AO and BO:
OO
AO
BO
AB
If a child's phenotype is Group O, the phenotype of the mother of the child is Group A and the phenotype of the father is group B what are the possible genotypes of both parents?
AO and BO
Based on the reactions below, indicate the correct blood group for each patient:
Patient #1
Forward (Cell) Typing Reverse (Serum) Typing
Anti-A Anti-B Anti-A,B A1 Cells B Cells
4+ 4+ 4+ 0 0
Patient #2
Forward (Cell) Typing Reverse (Serum) Typing
Anti-A Anti-B Anti-A,B A1 Cells B Cells
0 0 0 4+ 4+
Patient #3
Forward (Cell) Typing Reverse (Serum) Typing
Anti-A Anti-B Anti-A,B A1 Cells B Cells
4+ 0 4+ 0 4+
Patient #4
Forward (Cell) Typing Reverse (Serum) Typing
Anti-A Anti-B Anti-A,B A1 Cells B Cells
0 4+ 4+ 4+ 0
Group AB Patient #1
Group O Patient #2
Group A Patient #3
Group B Patient #4
Why is Rh immune globulin (RhIG) administered within 72 hours of delivery or miscarriage to an Rh-negative mother if the newborn is found to be D-positive or weak-D positive?
prevent fetal cells from initially sensitizing the mother
FFP that has been thawed at 30 - 37oC and maintained at 1 - 6oC must be transfused within ___________ after it has been thawed.
24 hours
FFP that has been thawed at 30 - 37oC and maintained at 1 - 6oC must be transfused within 24 hours. In contrast, "Thawed Plasma" can be used for up to 5 days as a replacement therapy for patients requiring stable clotting factors. Keep in mind that these are two different component types and you are asked about FFP.
A positive Coombs control test (check cells) in a cross match BEST indicates that the:
negative antiglobulin test was actually negative
The chief purpose of performing a standard crossmatch is to :
Identify recipient antibodies against donor cells
Which term listed below refers to the procedures that must be followed by a transfusion service when notification is received that a donor of a unit sent to the service now tests positive for an infectious disease?
A. Lookback
Match appropriate genotype to its corresponding phenotype
AB - AB
OO- O
AA, AO- A
BB, BO- B
An Rh negative mother has just given birth to an Rh positive baby after 18 hours of strenuous labor. Her rosette test was positive. Upon performing the Kleihauer-Betke stain procedure, the percentage of fetal cells is found to be 1.9%. The mother's total blood volume is 5,000 mL. What dose of Rh Ig (RhoGam) should be administered to the mother?
4 vials
Rh immune globulin, also known as Rh Ig or RhoGam, is used to help prevent an Rh negative mother from becoming sensitized to the D antigen from an Rh positive baby. To do this, vials of Rh Ig must be administered correctly. One full dose vial (300µg or equivalent) per 30 ml of D+ whole blood (15 ml D+ RBCs). To calculate how many vials are needed, the following formula can be employed:
KB% x blood volume = volume of baby blood
In this case: 1.9% x 5,000mL = 95 mL baby blood in maternal circulation
95mL / 30 mL per Rh Ig vial = 3.17 vials
This equals 3 vials (after rounding), with the addition of 1 extra vial = the mother should have 4 vials of Rh Ig administered.
If an average-weight adult male patient with a 7 gram/dL hemoglobin is given two units of packed cells, what would be the approximate new hemoglobin value (assuming there is no active bleeding or other predisposing factors that would shorten the survival of the blood cells
9.0 gm/dL
One unit of Red Blood Cells increases the hemoglobin level by approximately 1g/dL in an adult who is not actively bleeding and has no other predisposing factors that would shorten the survival of the transfused blood cells.
Antihuman globulin (AHG) enables sensitized red cells to cross-link so that agglutination is visible.
True
The mode of action of AHG is to join red cells that have the antigen antibody complex attached to the surface. When AHG is added, the anti human globulin attaches to the antigen-antibody complex and links with other cells that have this attachment. Visible agglutination occurs when they are joined.
Which one of the following may cause a FALSE-NEGATIVE result with antiglobulin techniques?
Addition of AHG is delayed for 40 minutes or more after final saline wash
Antenatal RhIg (1500 IU dose) is typically given at how many weeks gestation?
28
A 1500 IU dose of RhIg is typically given at 28 weeks gestation.