Launching a New Nation
4.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/75
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:00 PM on 11/7/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
76 Terms
1
New cards
Judiciary Act of 1789
Established structure/jurisdiction for federal court system (Supreme Court, 3 federal courts of appeals, 13 federal district courts), federal laws are "the Supreme Law of the Land"

2
New cards
# of justices originally in Supreme Court
1 chief justice, 5 associates

3
New cards
Cabinet
group of department heads who act as advisors to president

4
New cards
Washington's Secretary of State
Thomas Jefferson

5
New cards
Washington's Secretary of the Treasury
Alexander Hamilton

6
New cards
Washington's Secretary of War
Henry Knox

7
New cards
Secretary of State
Foreign affairs

8
New cards
Secretary of the Treasury
Financial Obligations

9
New cards
Secretary of War
Deals with global conflicts

10
New cards
Hamilton's plan to deal with debt
Accept debt of states, pay off all other debt to citizens at face value of bonds sold during American Revolution ($40 million), Excise Tax on Whiskey, Bank of the United States
11
New cards
Excise Tax
tax on luxury product's manufacture within the US

12
New cards
What caused Whiskey Rebellion
Excise Tax on whiskey

13
New cards
Who was responsible for the Whiskey Rebellion
Western Pennsylvania Farmers
14
New cards
What did whiskey rebels do?
Attack & destroy home of tax inspectors

15
New cards
How did Hamilton want to respond to Whiskey Rebellion?
Send military
16
New cards
Washington's response to Whiskey Rebellion
Go to Pennsylvania and threaten rebels with military

17
New cards
Bank of the United States (B.U.S.)
National bank to manage nation's debts and issue bank notes/national currency

18
New cards
Who opposed the National Bank
Southerners
19
New cards
Why did people oppose the National Bank?
It was not among the federal government's powers in the Constitution

20
New cards
Justification for BUS
Elastic Clause (make all laws which are necessary and proper)

21
New cards
What did creating the BUS do?
gave the federal government implied powers to do what was necessary for carrying out its delegated powers
22
New cards
Implied powers
powers not listed in Constitution but necessary for federal government to do its job
23
New cards
Federalist leaders
Alexander Hamilton, John Adams, John Jay

24
New cards
Democratic-Republicans leader
Thomas Jefferson

25
New cards
Two main parties
Federalists & Democratic-Republicans
26
New cards
What led to the creation of political parties?
The split in Washington's Cabinet

27
New cards
Federalists supporters
middle, upper middle, upper classes (merchants, white collar, and urban professionals)
28
New cards
Democratic-Republicans supporters
lower and lower-middle classes (farmres, Western frontiersmen, blue-collar workers, urban craft-workers, traders)

29
New cards
Federalists view on power of government
Strong federal government

30
New cards
Democratic-Republicans view on power of government
Strong states' rights
31
New cards
Federalists interpretation of Constitution
Flexible
32
New cards
Democratic-Republicans interpretation Constitution
Strict constructionist

33
New cards
Federalists economy
Manufacturing

34
New cards
Democratic-Republicans economy
Agriculture

35
New cards
Did Federalists trust common people in government?
No
36
New cards
Did Democratic-Republicans trust common people in government?
Yes
37
New cards
American stance on French Revolution (1789-1799)
At first supportive, but Americans soon became divided b/c French were fighting British (British wanted to restore French monarchy) & US was trading partners with both France and Britain.
38
New cards
Proclamation of Neutrality (1793)
Signed by Washington, kept US out of foreign affairs

39
New cards
Why didn't Washington support French Revolution?
It was too violent

40
New cards
How did Britain respond to US trade with France
impressment of American sailors & seizure of naval & military supplies bound to France

41
New cards
Jay's Treaty (1794)
- Made by John Jay
- Protected US trade with Britain
- Britain gave up forts in American territory from Revolutionary War
- US accepted British seizure of cargo
- Protected US trade with Britain
- Britain gave up forts in American territory from Revolutionary War
- US accepted British seizure of cargo
42
New cards
Jefferson's response to Jay's Treaty
Thought it was too pro-British, so he resigned as Secretary of State after Senate approved it

43
New cards
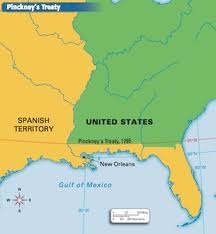
Pickney's Treaty (1795)
- with Spain
- allowed US to use Mississippi River & port of New Orleans for trade
- Spain feared America's contacts with Britain
- allowed US to use Mississippi River & port of New Orleans for trade
- Spain feared America's contacts with Britain
44
New cards
Why didn't Washington run for third term?
thought running for more than 2 terms would be authoritarian
45
New cards
Washington's Farewell Address (1796)
- warned against political parties & geographical divisions
- warned against permanent political alliances with other countries
- urged fairness in trade with all countries
warned against geographical divisions
- warned against permanent political alliances with other countries
- urged fairness in trade with all countries
warned against geographical divisions

46
New cards
Which party did Washington side with?
Federalists (although he did not want to associate himself with any political parties)

47
New cards
2nd president
John Adams (1795-1800)

48
New cards
Who did Washington urge to run for president?
John Adams

49
New cards
When was Adams elected?
1796
50
New cards
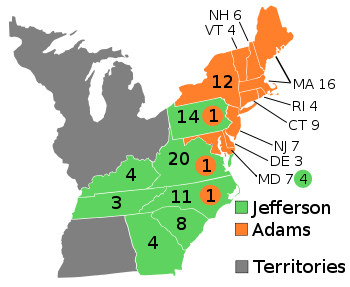
Sectionalism
-Placing the interests of one's over those of the nation
- In election of 1796, all of the North voted for Adams (Federalist) & all of the South voted for Jefferson (Democratic Republican)
- In election of 1796, all of the North voted for Adams (Federalist) & all of the South voted for Jefferson (Democratic Republican)
51
New cards
France's response to Jay's Treaty
- Didn't like US siding with Britain
- Captured American ships
- Captured American ships
52
New cards
XYZ Affair (1797-1798)
- 3 American diplomats sent to meet French foreign minister
- France sends 3 random government individuals (X, Y, and Z)
- X, Y, and Z ask for $10 million dollars
- Americans refused
- France sends 3 random government individuals (X, Y, and Z)
- X, Y, and Z ask for $10 million dollars
- Americans refused

53
New cards
Quasi War (Winter 1798)
- XYZ affair led to demand for war
- slogan: "millions for defense, but not one cent for tribute"
- Congress prepares 20,000 man-army & calls Washington out of retirement as Commander in Chief
- navy sent by Adams to defend from France
- Undeclared naval war took place between France & US.
- 14 American warships backed by 200 armed merchant ships captured 80 French vessels and forced French warships out of American waters.
- "Quasi War" because war not declared by Congress
- US held their ground against France
- slogan: "millions for defense, but not one cent for tribute"
- Congress prepares 20,000 man-army & calls Washington out of retirement as Commander in Chief
- navy sent by Adams to defend from France
- Undeclared naval war took place between France & US.
- 14 American warships backed by 200 armed merchant ships captured 80 French vessels and forced French warships out of American waters.
- "Quasi War" because war not declared by Congress
- US held their ground against France
54
New cards
Alien and Sedition Acts (1798)
- raised residency requirements for citizenship from 5 to 14 years
- authorized President to deport aliens
- permitted arrest, imprisonment, &deportation of aliens during wartime
- Sedition Acts prevented Americans from writing, saying, printing, or publishing things against government
- Only Democratic-Republican newspapers were attacked
- Tested limits of freedom of speech & press
- authorized President to deport aliens
- permitted arrest, imprisonment, &deportation of aliens during wartime
- Sedition Acts prevented Americans from writing, saying, printing, or publishing things against government
- Only Democratic-Republican newspapers were attacked
- Tested limits of freedom of speech & press

55
New cards
Virginia and Kentucky Resolutions (Jan 1800)
- made by Jefferson and Madison
- denounced Alien & Sedition Acts as infringement on freedom of expression
- states have right to declare laws null and void
- denounced Alien & Sedition Acts as infringement on freedom of expression
- states have right to declare laws null and void

56
New cards
Who controlled Congress during Adams Administration?
Federalists

57
New cards
3rd president
Jefferson

58
New cards
When was Jefferson elected?
1800
59
New cards
Significance of 1800 election
Successful transition of power from federalist to democratic-republican

60
New cards
Judiciary Act of 1801
- "Midnight judges"
- Adams worked with Federalist-controlled Congress to pack supreme court with federalist judges
- reduced # of justices from 6 to 5
- expanded judgeships (in Court of appeals & District courts) to 16
- John Marshall appointed as Chief Justice
- Adams worked with Federalist-controlled Congress to pack supreme court with federalist judges
- reduced # of justices from 6 to 5
- expanded judgeships (in Court of appeals & District courts) to 16
- John Marshall appointed as Chief Justice

61
New cards
What did John Marshall do?
strengthen federal government power over states' rights

62
New cards
Jefferson's Secretary of State
James Madison

63
New cards
What did Jefferson tell Madison not to do?
deliver commissions to judges appointed by Adams

64
New cards
Who was William Marbury
One of the "midnight judges"

65
New cards
Marbury v. Madison (1803) cause
Sec. of State Madison didn't give Marbury his commission, so Marbury sued Madison

66
New cards
Marbury v. Madison (1803) ruling
- Marbury had right to his commission
- Judiciary Act of 1789 declared unconstitutional b/c it gave SCOTUS greater power than Constitution allowed
- Judiciary Act of 1789 declared unconstitutional b/c it gave SCOTUS greater power than Constitution allowed

67
New cards
Significance of Marbury v. Madison (1803)
First time SCOTUS used judicial review

68
New cards
Who made the Louisiana Purchase?
Jefferson

69
New cards
What did the Louisiana Purchase do?
gave US Louisiana Territory, previously owned by France
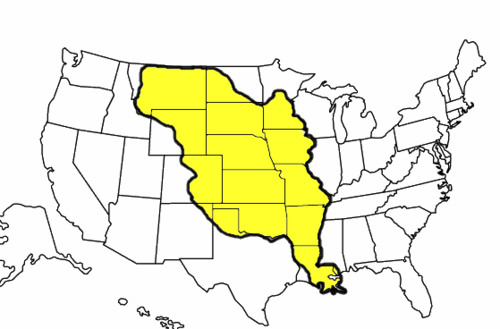
70
New cards
What was the problem with the Louisiana Purchase?
Congress (mostly federalists) didn't approve, but Jefferson bought the Louisiana Territory anyways (unconstitutional)

71
New cards
Why was the Embargo Act (1808) passed?
British impressment of American ships during Napoleonic Wars (1803-1815)

72
New cards
Embargo Act (1808)
blocked trade with Britain & France

73
New cards
Problem with Embargo Act
very costly, ended up being a failure

74
New cards
Macon's Bill (1810)
France agrees to stop impressing ships, and in return, trade with France continued

75
New cards
Who passed Macon's Bill
Madison

76
New cards
What did Macon's Bill lead to?
War of 1812
