PPCP Final
1/130
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
131 Terms
Evidence Based Medicine (EBM)
1) convert our info needs into answerable questions
2) track down the best evidence to answer these questions
3) appraise evidence critically to assess validity and usefulness
4)implement the results of this appraisal in clinical practice
5) evaluate our performance
14-65%
Proportion of physicians’ clinical decisions that were based on strong research evidence varied from ____________ depending on discipline.
18%
What % of decisions were based on strong research evidence in primary care?
Decision-making by anecdote
storytelling, personal-experiences, and past successes
Decision-making by press cutting
chasing new articles and editorials to replace standard practice
Decision-making by GOBSAT "good ole boys sat around a table"
consensus statements and expert opinions (key opinion leaders)
Decision-making by cost-minimization
cheapest option no matter how effective it is
Drug Information (DI)
one of the most fundamental responsibilities of pharmacists
DI examples
-patient specific (counseling)
-population specific (treatment guidelines or national quality initiatives)
-adverse event specific (health-system or global efforts reporting and monitoring)
-cost savers
-decision tools (med selection/policy decisions)
-patient educators or advocates
What do pharmacists serve as when it comes to providing drug information (DI)?
•Supporting clinical services
•Answering patient questions
•Coordinating P&T committee
•Developing in-service and education
•Critical evaluation of literature for formulary and patient decisions
•Poison control
•Publishing (local or globally)
•Research-efforts (clinical or economic outcomes)
•Developing criteria/policy for medication use
•Quality assurance and improvement activities
•Managing drug shortages
•Serving on Institutional Review Boards
•Coordinating ADE/medication error reporting and monitoring
Consulting in pharmacy informatics initiatives
What are some of the specific functions you may see in drug information (DI)?
-access information
-assess urgency
-formulate questions
-systematic search approach
-evaluate info critically
-develop, organize, and summarize response
-communicate clearly, effectively, and at an appropriate level
-anticipate follow-up needs
List the general DI skills for pharmacists:
-primary
-secondary
-tertiary
-"other"
What are the different types of information sources?
primary info source
-clinical research and reports, both published and unpublished
-original research
-current and original info
-knowledge of research and statistical methods to interpret
-MOST UP TO DATE info is needed
secondary info source
-searchable databases that enable primary/tertiary resource retrieval
-indexing/abstracting services
-provides efficient access to primary literature
-knowledge of search terms and Boolean operators to maximize efficiency
-need to find breadth and depth of most up to date info
tertiary info source
-information that has been summarized by the author to provide an overview
-convenient, well-established, easy to use info
-info may be dated or have gaps from our current understanding
-background info or quick answer
other info sources
online news and consumer health information
primary research
original, first-hand, the author of the source generated the research data they are using
secondary research
second-hand, the author of the source did not generate the research data that they are using
-basic research
-clinical research
-epidemiological research
What are the different types of primary research?
basic research
Basic medical research including animal experiments, cell studies, biochemical, genetic and physiological investigations, and studies on the properties of drugs and materials
Clinical research
Any study performed with the purpose of studying or demonstrating the clinical or pharmacological effects of drugs (or other treatment) , to establish side effects, or to investigate absorption, distribution, metabolism or elimination, with the aim of providing clear evidence of the efficacy or safety of the drug
Epidemiological research
Investigates the distribution and historical changes in the frequency of diseases and the causes for these
meta analysis and systemic review
What are the types of medical research that fall under secondary research?
meta analysis
-is a statistical analysis that combines the results of multiple quantitative studies
-Using statistical methods, results are combined to provide evidence from multiple studies
Systemic review
-A systematic search for data, using a repeatable method
-It includes appraising the data (for example the quality of the data) and a synthesis of research data
-abstract
-intro
-methods
-results
-discussion
-references
What are the elements of a basic publication?
Abstract
-Brief overview of the research product
-Generally the last thing written by the author
Introduction
-Research background, but never assume a COMPLETE review
-What is already known
-Rationale for study
-Objective/hypotheses
Methods
-should be detailed enough to be reproducible
-Study design
-Study setting
-Population to be sampled
-Inclusion/exclusion criteria
-Intervention and control groups
-Randomization
-Blinding
-Endpoints/outcomes
-Follow-up procedures
-Sample size calculations/power analysis
-Statistical analysis
Results
-data without interpretation
-Subject characteristics
-Subject dropouts/adherence
-Endpoints quantified
-Statistical significance
-Safety Assessments
Discussion
-Interpretation of results
-Clinical significance
-Other study results compared
-Limitations
-Conclusion/application to practice
References
Citations for information included from other resources
yes
Can plagiarism occur without being intentional?
-stealing
-insufficient paraphrasing
-self-plagairism
What are the various forms of plagiarism?
stealing form of plagiarism
direct coping for a resource without citation
insufficient paraphrasing form of plagiarism
changing author's words slightly without direct quote or citation
self-plagiarism form of plagiarism
recycling without reference
-Ideas from other materials
-Exact wording or unique phrasing
-Diagrams, charts, or pictures
-Facts and statistics
What should your cite?
National Library of Medicine (NLM) Format
What referencing format should you follow?
unique
Each number is _______ to that reference source in NLM in-text citations.
superscript
Each information source should be cited in the body of the text using a __________ arabic number, outside the punctuation mark in NLM in-text citations.
based on the order in which you use them
How should you number your references using NLM?
secondary sources
"aka databases" provide access to primary and some tertiary resources even gray literature
when hoping to stay up to date on recently published literature or to find literature on a specific topic
When should you consider secondary resources?
indexing
providing bibliographic citation information (title, abstract, citations)
abstracting
provides bibliographic citation information and a brief description
1) formulate a clear, well defined, answerable search question
2) identify primary concepts and gather synonyms
3) locate subject headings
4) combine concepts using Boolean operators
5) refine search terms and search in PubMed
6) apply limits (if necessary)
How to use secondary searching:
P-patient
I-intervention
C-comparator
O-outcome
What is PICO?
developing answerable questions
What is PICO used for?
MeSH headings
medical subject headings
Boolean operators
adding terms or combine search terms with connector words: AND, NOT, OR
AND
used between terms returns only records that contain all of the search terms
OR
used between terms all records that contain any of the search terms
NOT
used between search terms returns only records that contain the first term and not the second term
-search by phrase
-search for words in the title
-search for author
-view related articles
How can you refine search terms?
-language of publication
-publication types
-year of publication
-age group
-country of origin
What are limits that you can apply in your searches?
-CDC website
-FDA website
-ClinicalTrials.gov
-Health.gov
-KidsHealth.gov
-MedlinePlus
-established medical centers
-disease or professional societies
Where can you point patients to reliable information?
1) Tertiary
2) Secondary
3) Primary
What are the steps for diving into research?
citation-sequence and citation-name sequence
number refers to items in reference list
name-year
parenthetical statement including author last name and publication year
CMM
comprehensive medication management that assesses of each medication to identify potential and actual medication therapy problems (MTPs)
optimize medication use and improve quality of healthcare
What is the goal of the Pharmacist's Patient Care Process?
Pharmacist's responsibilities in Collect
-Collect necessary subjective and objective patient info
-Patient interview
-Medical records
-analyze collected info to understand med history and patient's clinical status
1) gather relevant patient info
2) review meds, med history and history
3) analyze info in preparation for formulating an assessment of MTPs
What are the steps in collec?
relevant patient info
-demographics
-PMH
-immunizations
-lab values
-diagnostics tests and meds
review of meds, med history, and history
-Social history (i.e., alcohol, tobacco, substance use)
-Social determinants of health (i.e., transportation)
-Complete medication reconciliation (and medication experience)
-Review indication, effectiveness, safety, adherence
-Address any patient questions / concerns / therapy goals
collect, assess, plan, implement, follow up
What are the steps of PPCP in order?
key
Collaboration, communication, and DOCUMENTATION are ____________ foundational components occurring during each step
(1) meet professional standards and legal requirements
(2) establish accountability for medication-related aspects of direct patient care
(3) communicate with other health care professionals
(4) strengthen transition and continuity of care
(5) create your record of critical thinking and judgment
(6) provide evidence of your value and workload allocation
(7) justify reimbursement for cognitive services; billing requirements
(8) provide needed information and data for tracking of patient health outcomes and evaluation of progress
Why do we document?
-SOAP/SOAR notes
-FARM notes
-MTM/CMM documentation
-letters to providers
-patient records, med lists
-informal messages and phone notes
-verification logs
What are some different types of documentation that pharmacists do?
-anticoagulation management
-antibiotic mangement
-diabetes management
-annual wellness visits
-transitions of care
-chronic care management
-immunizations
What are services that pharmacists offer?
subjective
What does the S in soap stand for?
objective
What does the O in soap stand for?
assessment
What does the A in soap stand for?
plan (or R for recommendation)
What does the P in soap stand for?
collect (subjective)
-obtained verbally from the patient or caregiver (maybe not during this specific encounter, but at some point)
-not directly observed or measured
social history
-pertinent socioeconomic, cultural info
-insurance/financial info
-level of activity, nutrition history
-work schedule
-social history
-transportation
-chief complaint
-history of present illness
-review of systems
-med history
-surgical history
-fam history
-allergies
-social history
What are the parts of collect that are not directly observed?
-PE, vital signs
-lab values
-med levels
-diagnostic tests
-imaging
What are the parts of collect that are objective or directly observed or measured by a pharmacists or other healthcare professional?
Assess
pharmacists determines MTP and prioritizes them in problem list; generally grouped by active health conditions requiring med therapy
MTP/problem list
often grouped by health conditions requiring med therapy (ranked based on patient and healthcare provider's perspective)
NO but it is an important aspect of all pharmacists' practice that should be documented
Is there a standardized, universal way to document MTPs?
plan, implement, follow-up
includes a plan for each health condition/MTP that should be addressed
audience
may influence abbreviations, technical jargon used, content included
never be accusatory, judgmental, negative
How can you stay objective when documenting?
only included relevant information which could be positives and negatives
Should you include all information in your documentation?
assess
To identify and prioritize problems and achieve optimal care, the pharmacist assesses the collected information and analyzes the clinical effects of the patient’s therapy in the context of the patient’s overall health goals
1) Indication
2) Effectiveness
3) Safety
4) Adherance
When you assess each medication what do you look at?
-social
-environmental
-fam history/genetic
What are risk factors?
secondary causes of disease/problem
uncontrolled GERD or allergies may worsen control of asthma is an example of what?
complications
Nephropathy and neuropathy are _________ of DM.
1) organize by active medical conditions requiring med therapy
2) organize by med therapy problem
What are the 2 ways to organize the "problem list"?
-clinical goals
-patient goals
-acuity
-level of control
-timeframe to achieve goal
You cannot generally address all problems in one day so what should you look at to prioritize your problem list?
Body Mass Index (BMI)
-body weight in kilograms (kg) divided by the square of height in meters
-correlates with amount of body fat
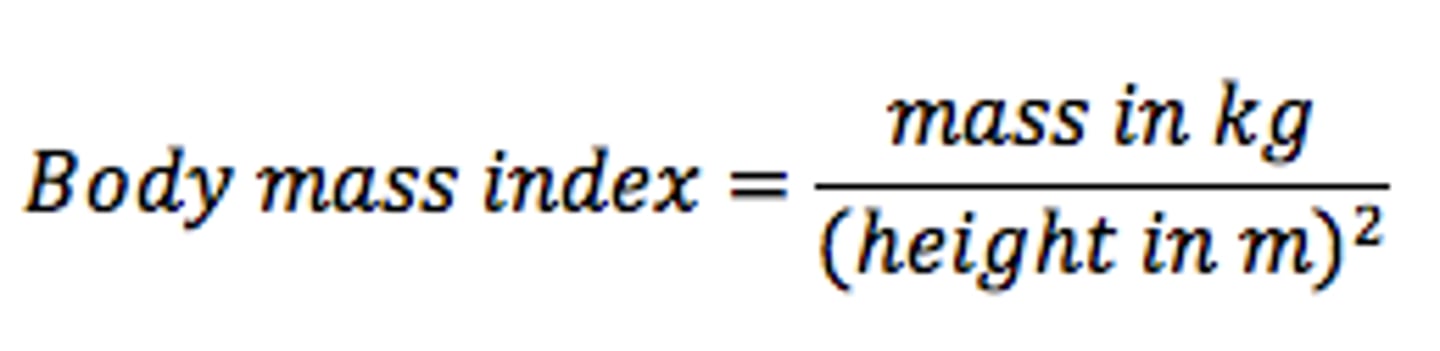
to determine if a patient is underweight, normal weight, overweight, or obese
What is BMI used for?
-can over estimate body fat in ppl who are muscular
-can under estimate body fat in frail old ppl and ppl with lost muscle mass
What are the disadvantages to using BMI?
Underweight
BMI < 18.5
Normal or Healthy weight
BMI 18.5-24.9
Overweight
BMI 25-29.9