Part-4-1A-Auditing-Computer-Based-IS-Risk-Based-Audit-Approach
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
The Risk-Based Audit Approach
is a four-step approach to internal control evaluation that provides a logical framework for carrying out an audit.
provides auditors with a clear understanding of the errors and irregularities that can occur and the related risks and exposures.
This understanding provides a basis for developing recommendations to management on how the AIS control system should be improved.
Four steps of Risk-Based Audit Approach
Determine the threats (errors and irregularities) facing the accounting information system
Four steps of Risk-Based Audit Approach
Identify control procedures implemented to minimize each threat by preventing or detecting such errors and irregularities.
Four steps of Risk-Based Audit Approach
Evaluate the control procedures
Four steps of Risk-Based Audit Approach
Evaluate weakness (errors and irregularities not covered by control procedures) to determine their effect on the nature, timing, or extent of auditing procedures and client suggestions.
The Information System Audits
The purpose of an information system audit is to review and evaluate the internal controls that protect the system.
Security provisions protect computer equipment, programs, communications, and data from unauthorized access, modification, or destruction
When performing an information system audit, auditors should ascertain that the following objectives are met:
Program development and acquisition are performed in accordance with the management’s general and specific authorization
When performing an information system audit, auditors should ascertain that the following objectives are met:
Program modifications have management’s authorization and approval
When performing an information system audit, auditors should ascertain that the following objectives are met:
Processing of transactions, files, reports, and other computer records is accurate and complete.
When performing an information system audit, auditors should ascertain that the following objectives are met:
Source data that are inaccurate or improperly authorized are identified and handled according to prescribed managerial policies.
When performing an information system audit, auditors should ascertain that the following objectives are met:
Computer data files are accurate, complete and confidential.
When performing an information system audit, auditors should ascertain that the following objectives are met:
Overall Security
Program Development and Acquisition
Program Modification
Computer Processing
Source Data
Data Files
Each description includes an audit plan to accomplish the objective, as well as the techniques and procedures to carry out the plan.
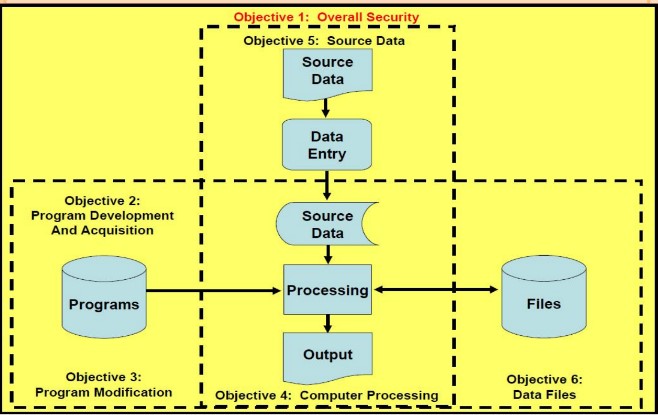
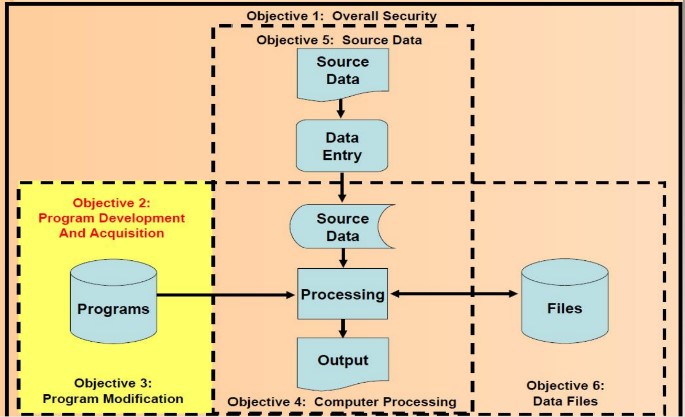
Information System coponents and audit objectives
Accidental or intentional damage to system assets
Unauthorized access, disclosure, or modification of data and programs
Theft.
Interruption of crucial business activities.
OBJECTIVE 1: OVERALL SECURITY
Types of security errors and fraud faced by companies:
OBJECTIVE 1: OVERALL SECURITY
Control procedures to minimize security errors and fraud

Inspecting computer sites.
Interviewing personnel.
Reviewing policies and procedures.
Examining access logs, insurance policies, and the disaster recovery plan.
OBJECTIVE 1: OVERALL SECURITY
Audit Procedures: Systems Review
OBJECTIVE 1: OVERALL SECURITY
Audit Procedures: Tests of Controls

OBJECTIVE 1: OVERALL SECURITY
Compensating Controls

OBJECTIVE 2: PROGRAM DEVELOPMENT AND ACQUISITION
Two things can go wrong in program development:
Inadvertent errors due to careless programming or misunderstanding specifications; or
Deliberate insertion of unauthorized instructions into the programs.
OBJECTIVE 2: PROGRAM DEVELOPMENT AND ACQUISITION
Types of errors and fraud:
The preceding problems can be controlled by requiring:
Management and user authorization and approval
Thorough testing
Proper documentation
OBJECTIVE 2: PROGRAM DEVELOPMENT AND ACQUISITION
Control procedures:
OBJECTIVE 2: PROGRAM DEVELOPMENT AND ACQUISITION
Audit Procedures: Systems Review

OBJECTIVE 2: PROGRAM DEVELOPMENT AND ACQUISITION
Audit Procedures: Tests of Controls

OBJECTIVE 2: PROGRAM DEVELOPMENT AND ACQUISITION
Compensating Controls

OBJECTIVE 3: PROGRAM MODIFICATION
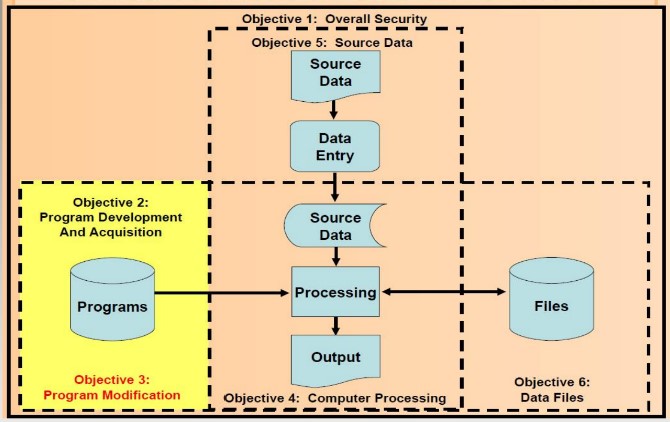
OBJECTIVE 3 : PROGRAM MODIFICATION
Types of Errors and Fraud
Same that can occur during program development:
Inadvertent programming errors
Unauthorized programming code
OBJECTIVE 3 : PROGRAM MODIFICATION
Control Procedures

OBJECTIVE 3 : PROGRAM MODIFICATION
Audit Procedures: System Review

OBJECTIVE 3 : PROGRAM MODIFICATION
Audit Procedures: Tests of Controls

OBJECTIVE 3 : PROGRAM MODIFICATION
Audit Procedures: Tests of Controls

Reprocessing and Parallel simulation
Two additional techniques detect unauthorized program changes:
Reprocessing
On a surprise basis, the auditor uses a verified copy of the source code to reprocess data and compare that output with the company’s data.
Discrepancies are investigated.
Parallel simulation
Like reprocessing except that the auditor writes his own program instead of using verified source code.
Can be used to test a program during the implementation process.
OBJECTIVE 3 : PROGRAM MODIFICATION
Audit Procedures: Tests of Controls

OBJECTIVE 3 : PROGRAM MODIFICATION
Compensating Controls
