Unit 4: Earth Systems and Resources
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
earthquakes
occurs on a fault, pressure caused by extreme stress in Earth's crust (stress caused by tectonic plates, volcanoes, or man-made), sudden and powerful release of energy, shock waves cause intense vibrations
volcanoes
plates are pushed together, magma is pushed together or pulled apart, pressure explodes, then the pressure forces magma to the top
mountains, atmosphere
how volcanoes formed our current environment
1. form ____ (by becoming not active)
2. formed Earth's ____ (contribute to the carbon cycle by releasing carbon)
gases, forests, lakes, life, die
ways that volcanic eruptions affect the environment, natural ecosystems, and humans:
1. ___ released into air (ash, poisonous steam)
2. ___ are flattened
3. ___ are drowned
4. all ___ is distinguished
5. people can ___
igneous
type of rock formed by magma cooling and hardening, either cools inside or outside Earth (lava), bubbles form from air caught inside
granite, basalt, obsidian
3 examples of igneous rocks
sedimentary
type of rock formed by particles of sand, shells, pebbles, and other fragments, gradually forms layers, is fairly soft/crumbles easily, sometimes contains fossils
conglomerate, limestone
2 examples of sedimentary rocks
metamorphic
type of rock formed under the surface from intense heat and pressure, has ribbonlike layers and shiny crystals
gneiss, marble
2 examples of metamorphic rock
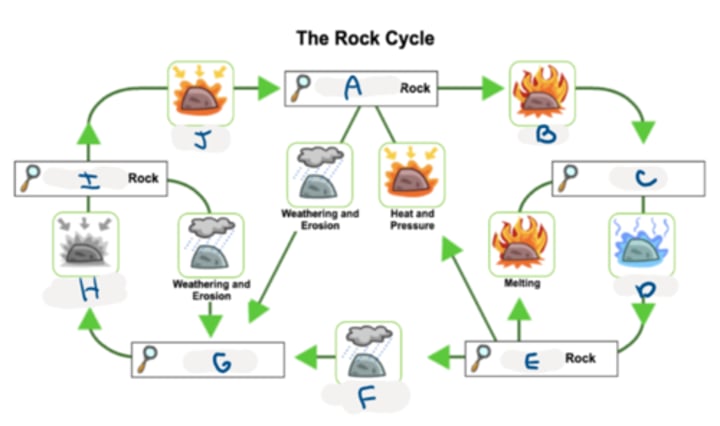
metamorphic, melting, magma, cooling, igneous, weathering, sediment, compacting, sedimentary, heat
label the rock cycle
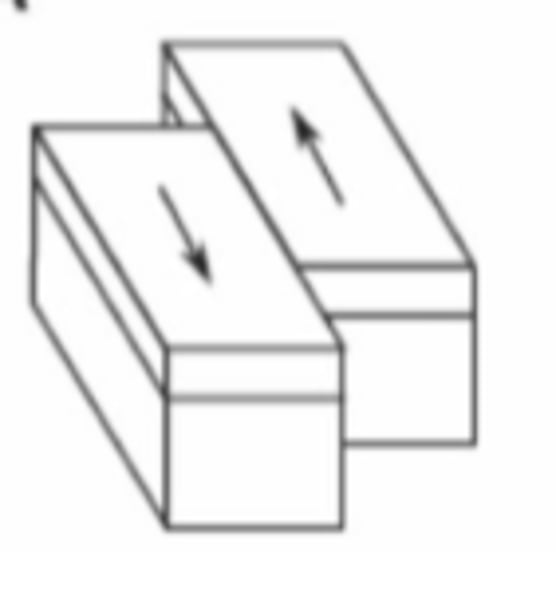
transform
what type of fault is this?
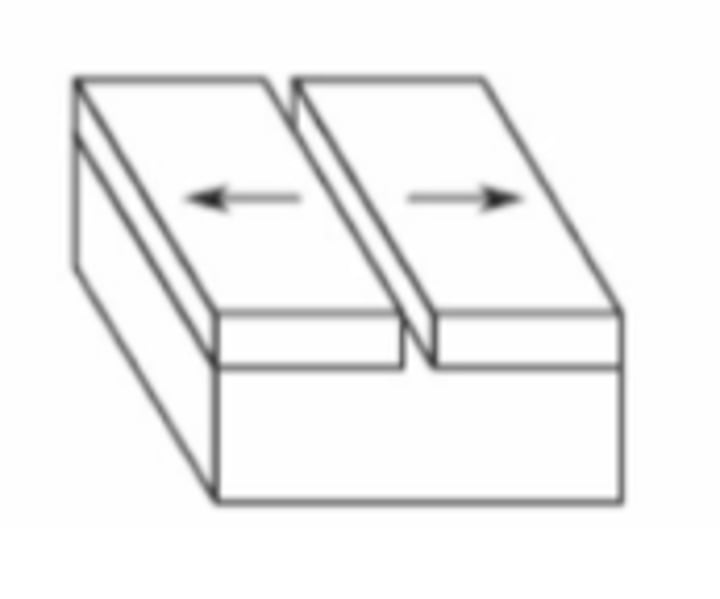
divergent
what type of fault is this?
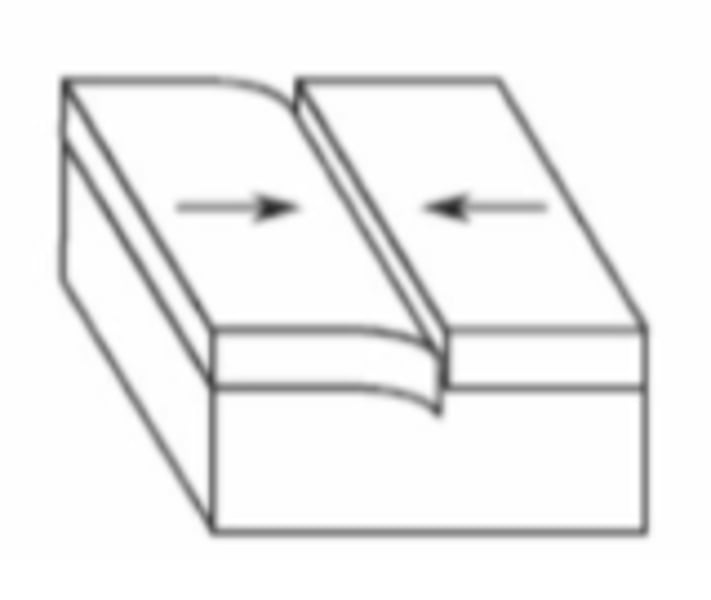
convergent
what type of fault is this?
physical weathering
mechanical breakdown of rocks and minerals
water, wind, temperature
abiotic causes of physical weathering
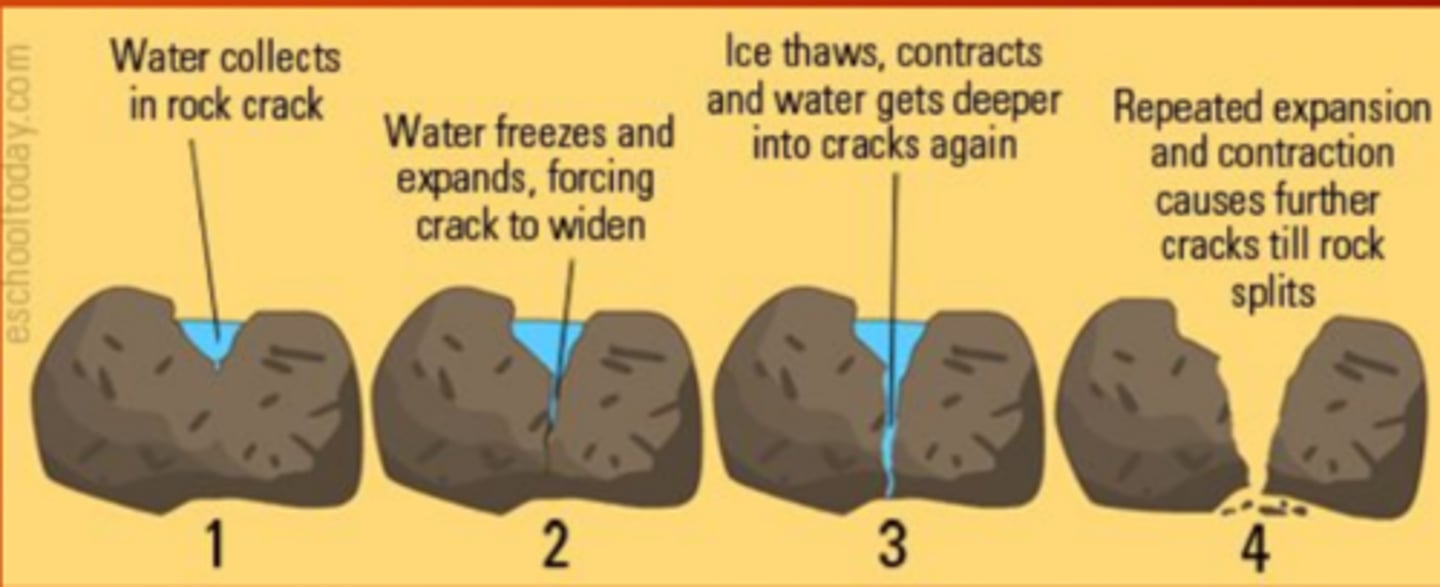
plant roots, animal burrowing
2 biotic causes of physical weathering
chemical weathering
increased surface area (from physical weathering) leads to a change in chemical composition of mineral compounds
carbonation, hydrolysis, oxidation
3 types of chemical weathering
chemical weathering
releases essential nutrients from rocks, important part of the phosphorus cycle
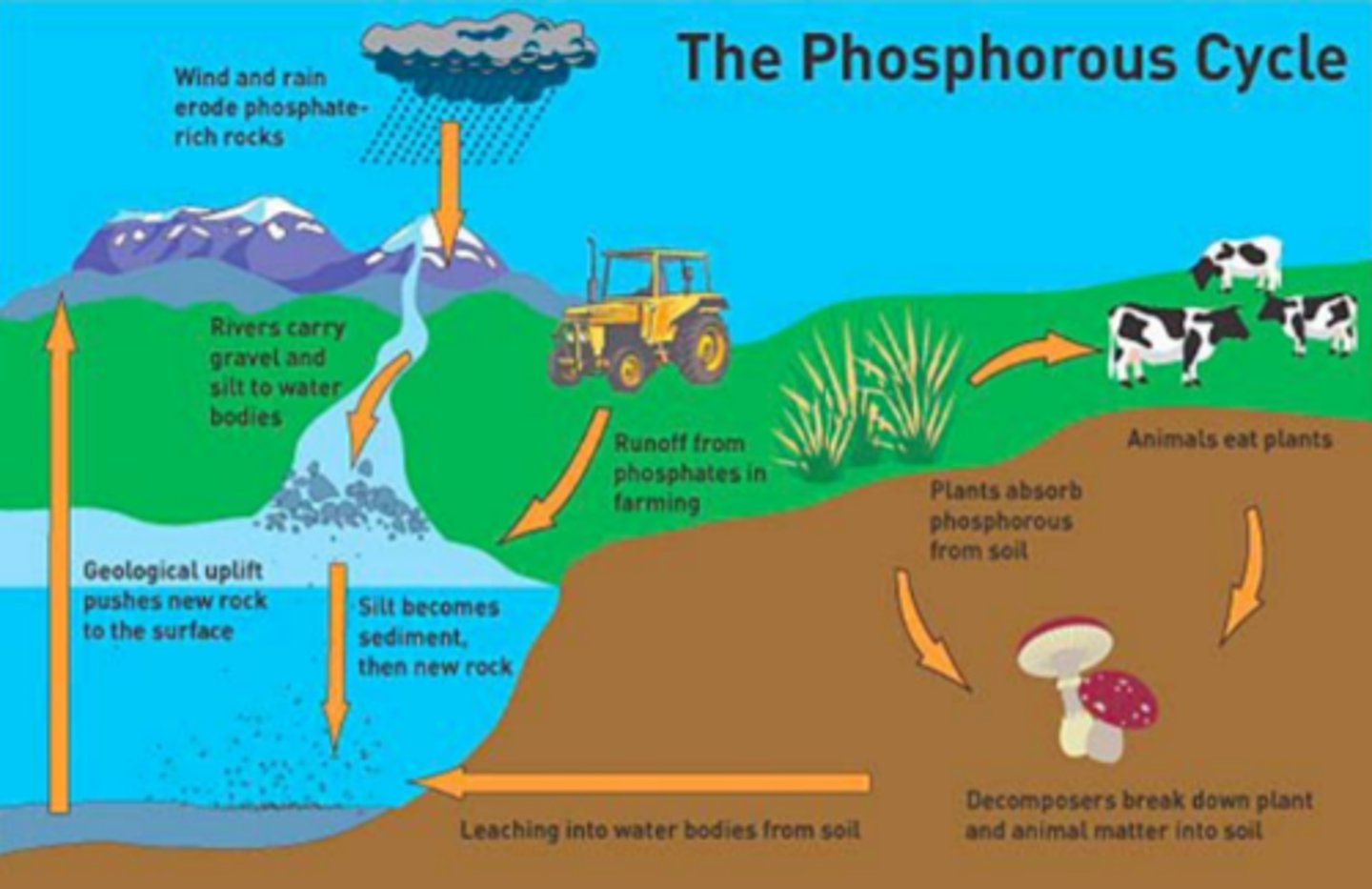
anthropogenic chemical weathering
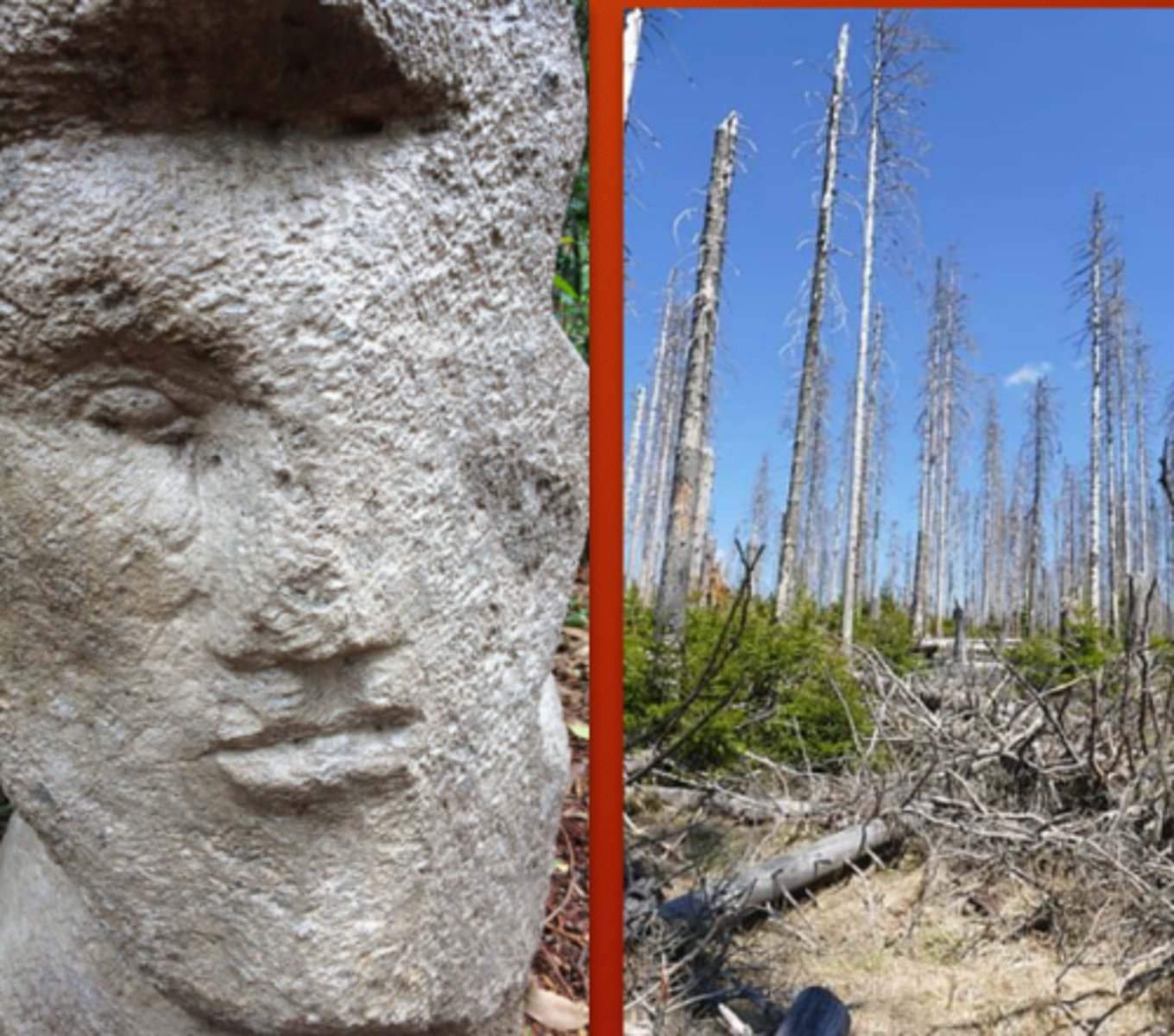
____ ____ ____: fossil fuel combustion --> sulfur and nitrogen oxides --> react with water vapor --> sulfuric acid --> acid precipitation (rain)
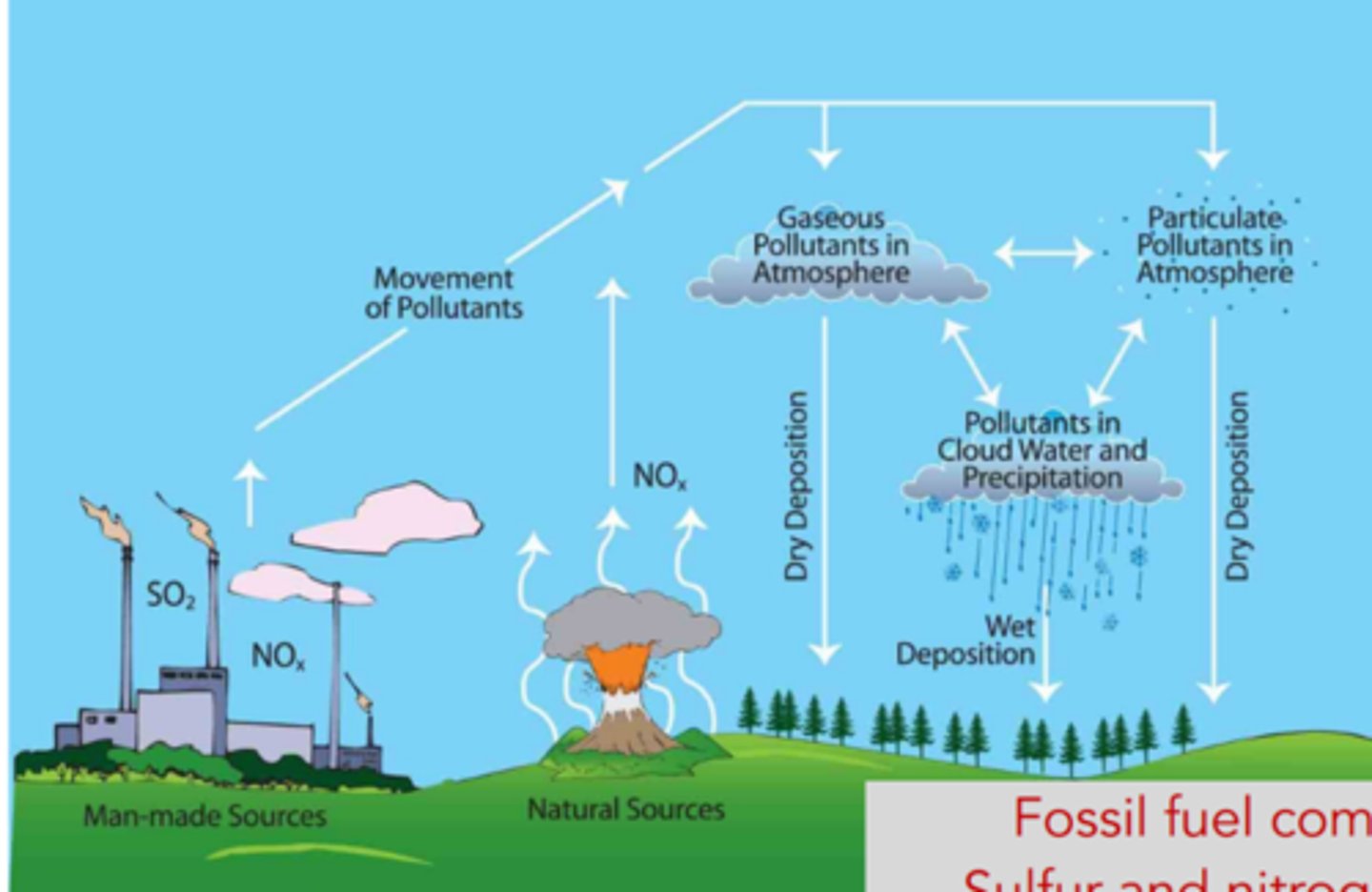
acidification, vision, human health, decay
acid rain effects:
1. _____ of soils/trees
2. impaired ____
3. ____ ____ (asthma, bronchitis, emphysema)
4. ____ (limestone, marble statues, gravestones, buildings, and bridges)

raw materials, organic materials, mature soil, nutrient poor
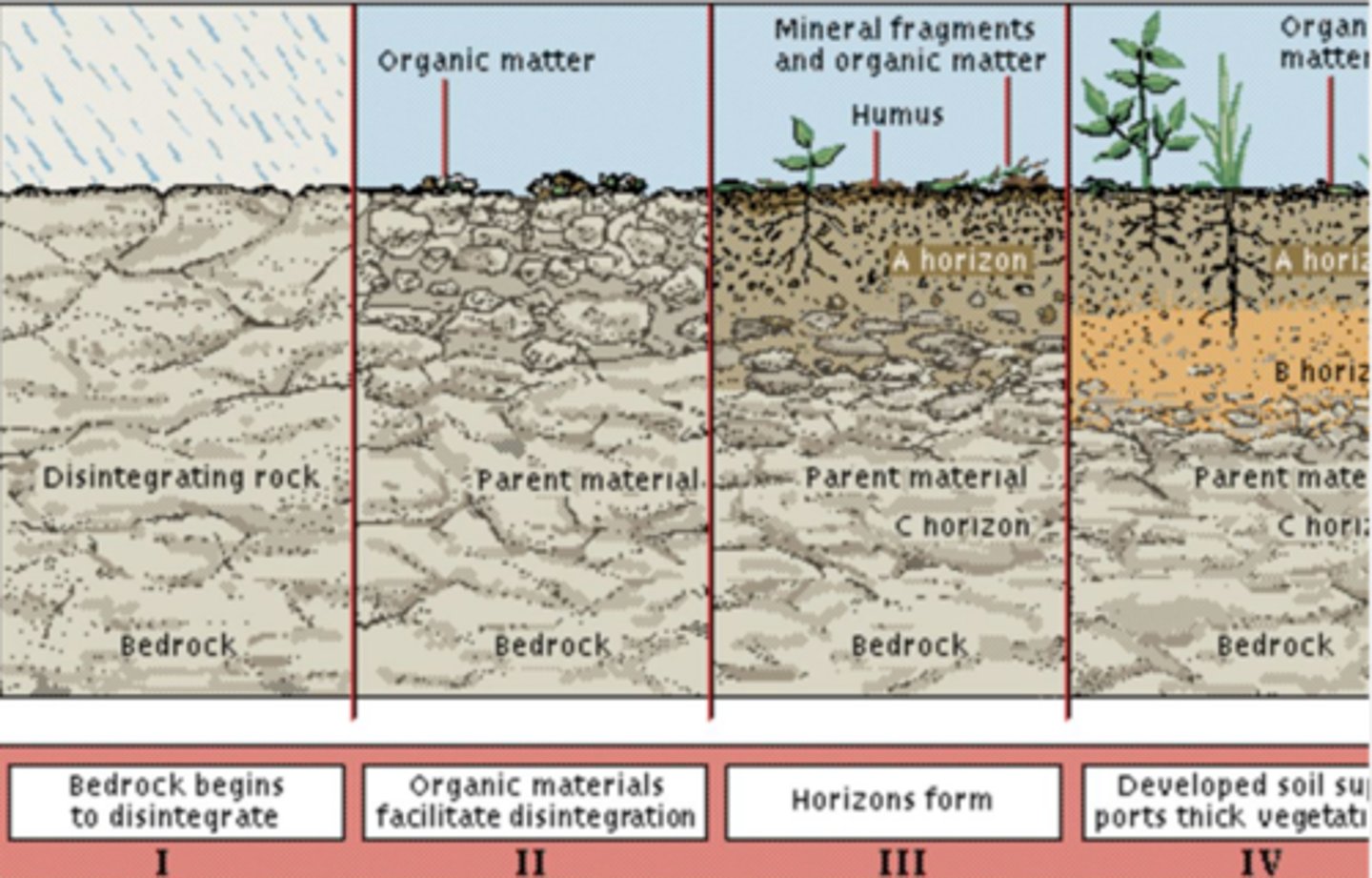
soil development stages:
1. from below: physical breakdown of rocks and primary materials (newly exposed minerals) provide ___ ____
2. from above: deposition of ____ ____ from dead organisms and their waste
3. ___ ___ has more organic material and more nutrients
4. very old soils may be ___ ___ due to plants and water leaching nutrients
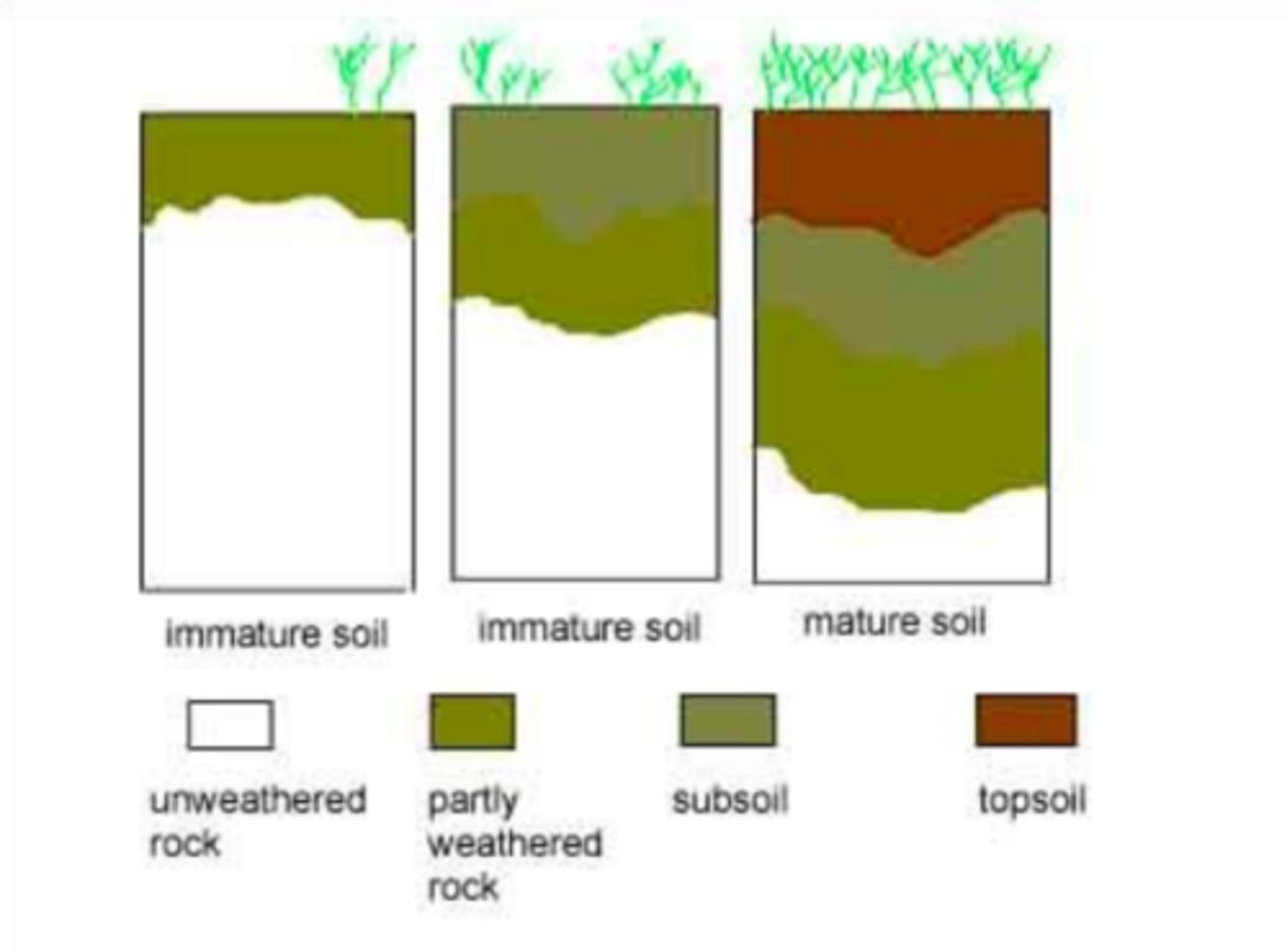
organic, topsoil eluviated, subsoil, C horizon, R horizon
label the soil layers (names)
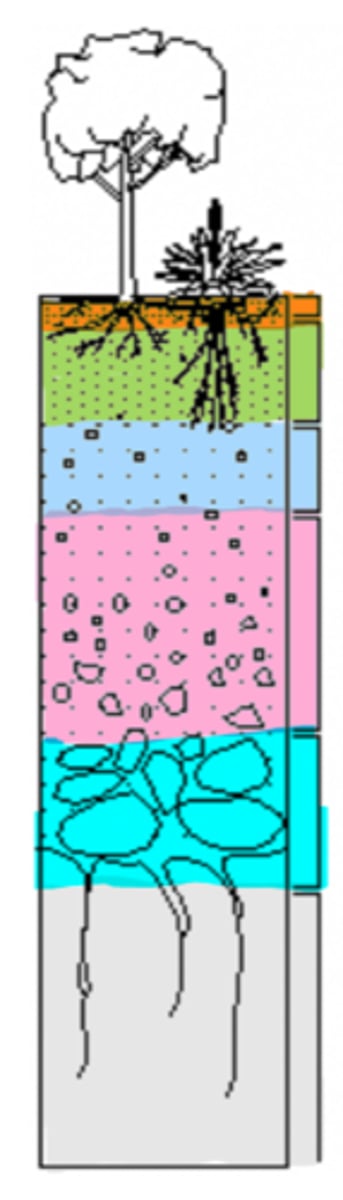
O A E B C R
label the soil layers (letters)
organic
soil layer with decomposed organic material, the lower, most decomposed part is called humus, most pronounced in forest
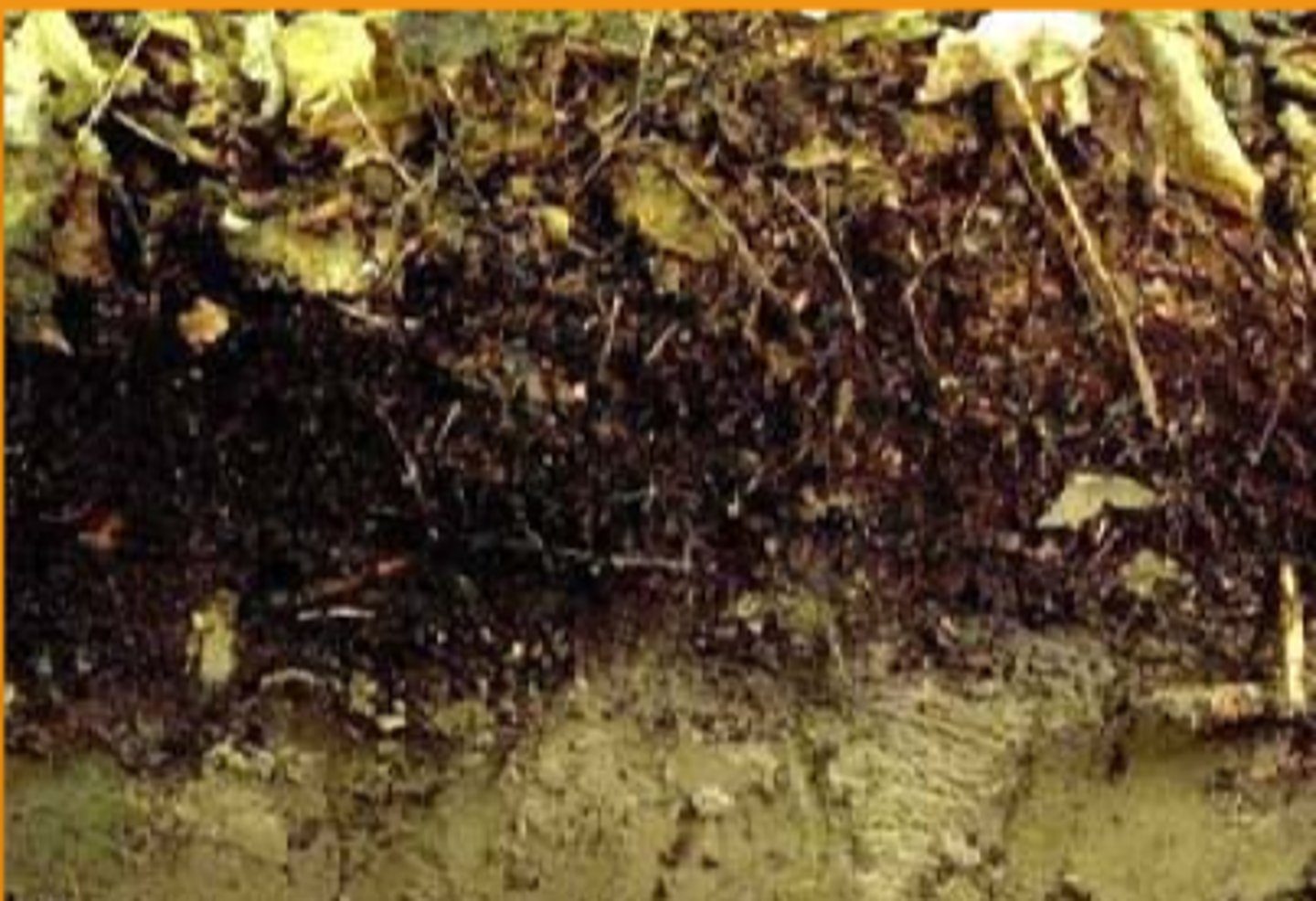

topsoil
soil type with surface soil, organic material mixed with mineral material most biological activity
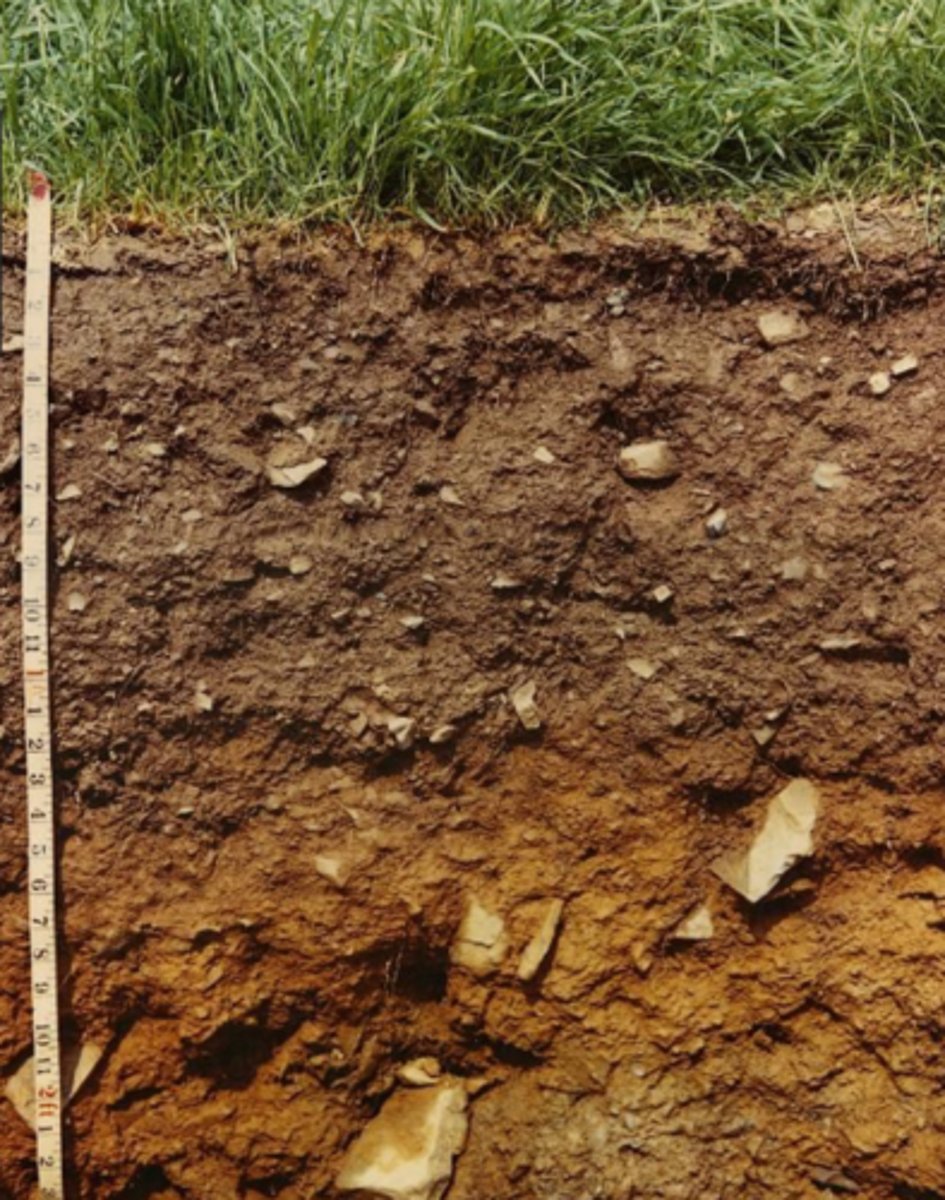

eluviated
soil type, in some acidic soils, metals and nutrients (iron, aluminum, organic acids) are leached from above

subsoil
soil type with mineral material, zone of accumulation or metals and nutrients
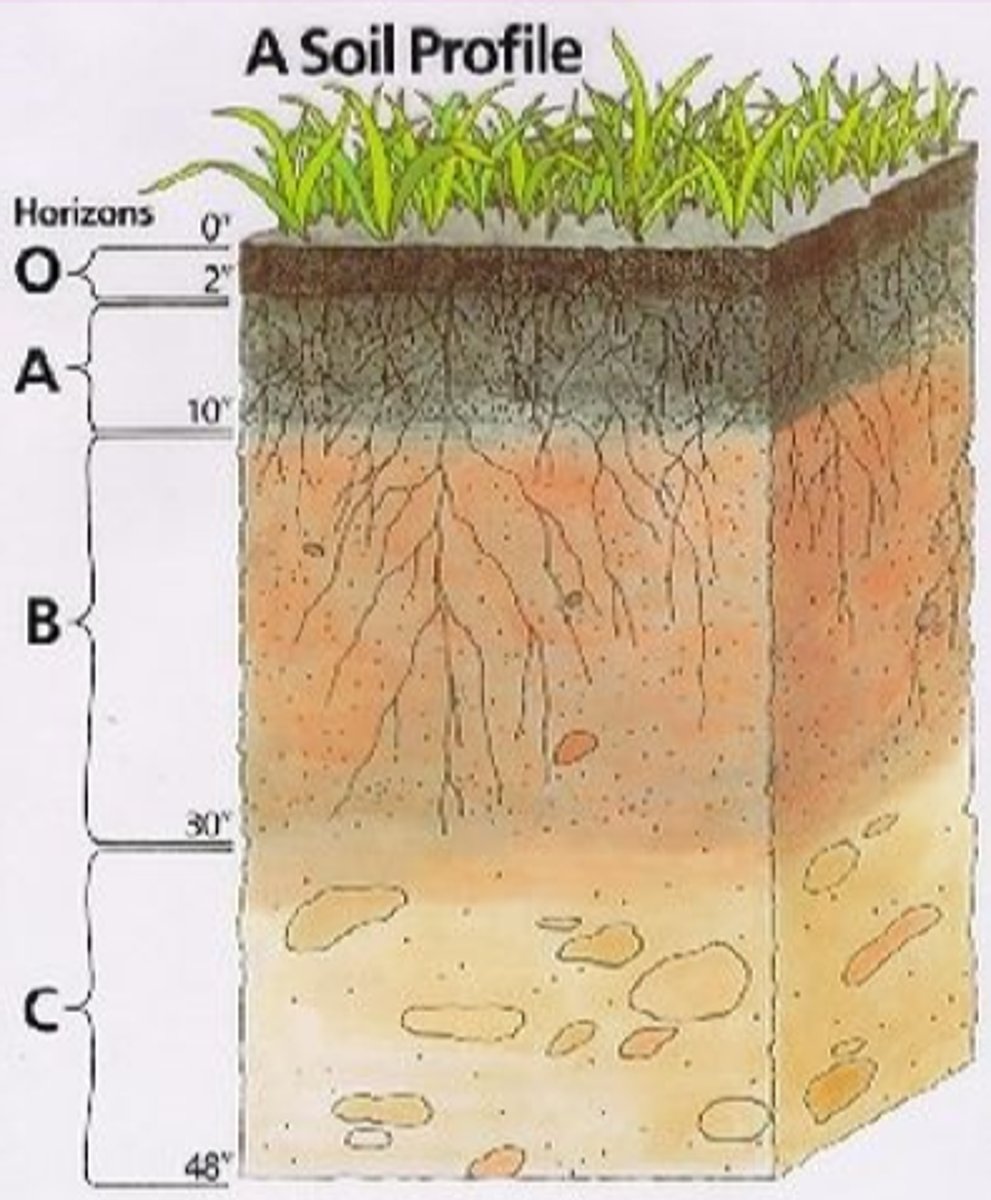
C horizon
soil type that is least weathered, similar to parent material
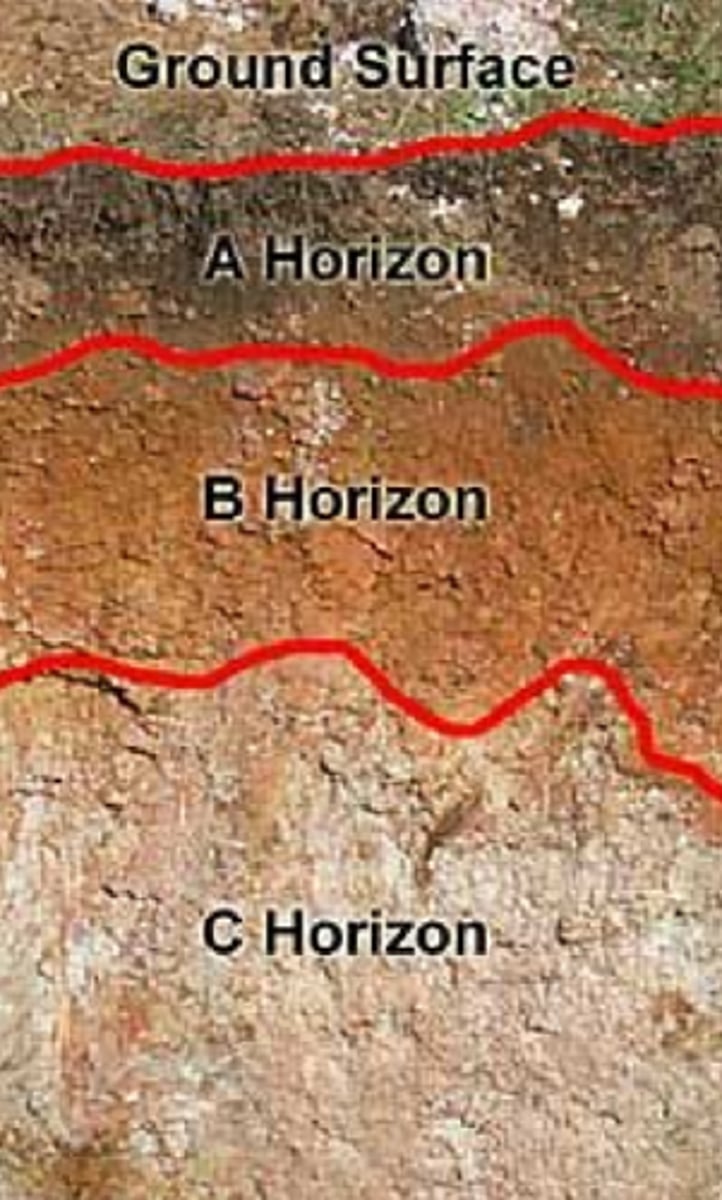

R horizon
soil type made of unweathered parent material (rock)
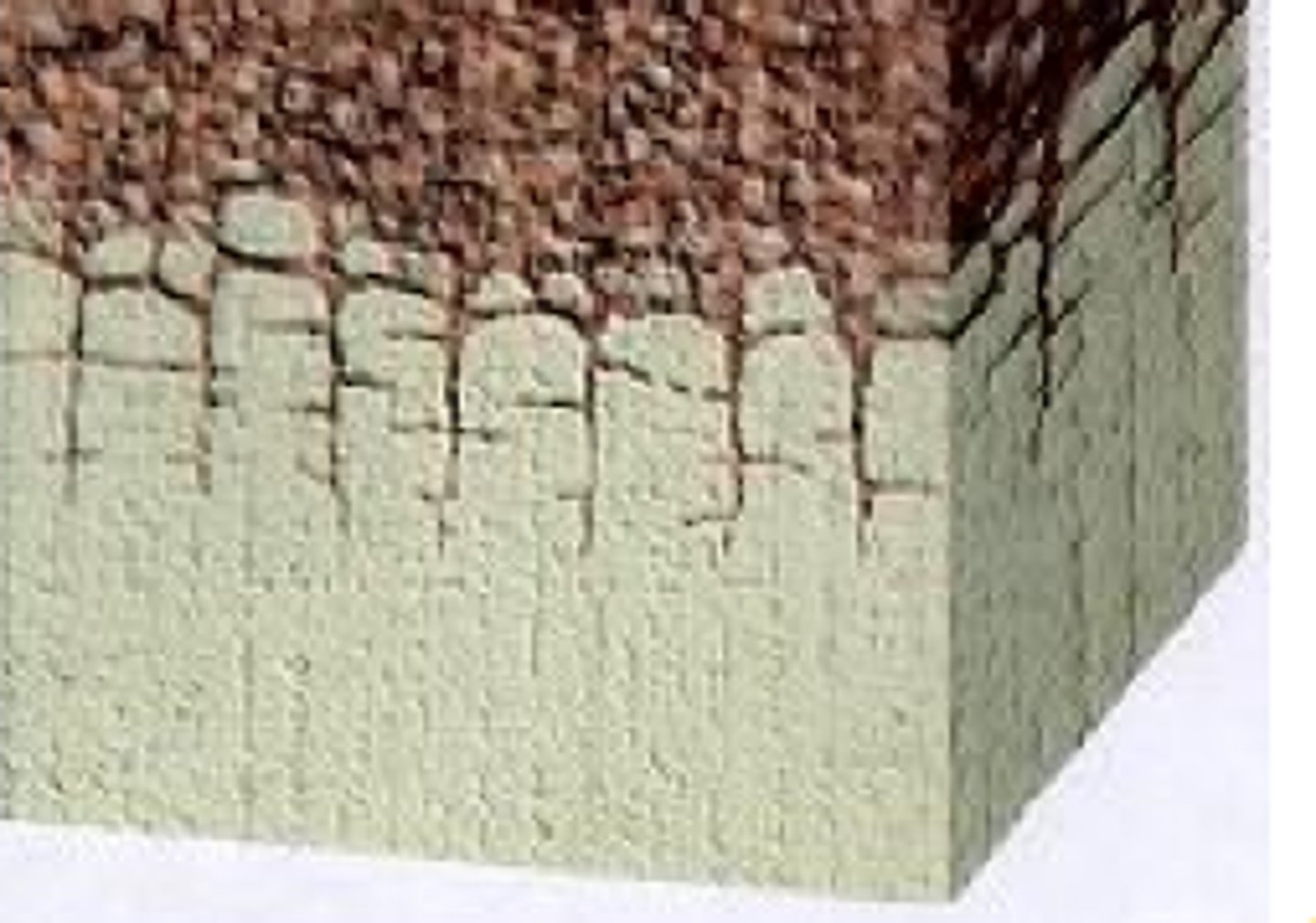

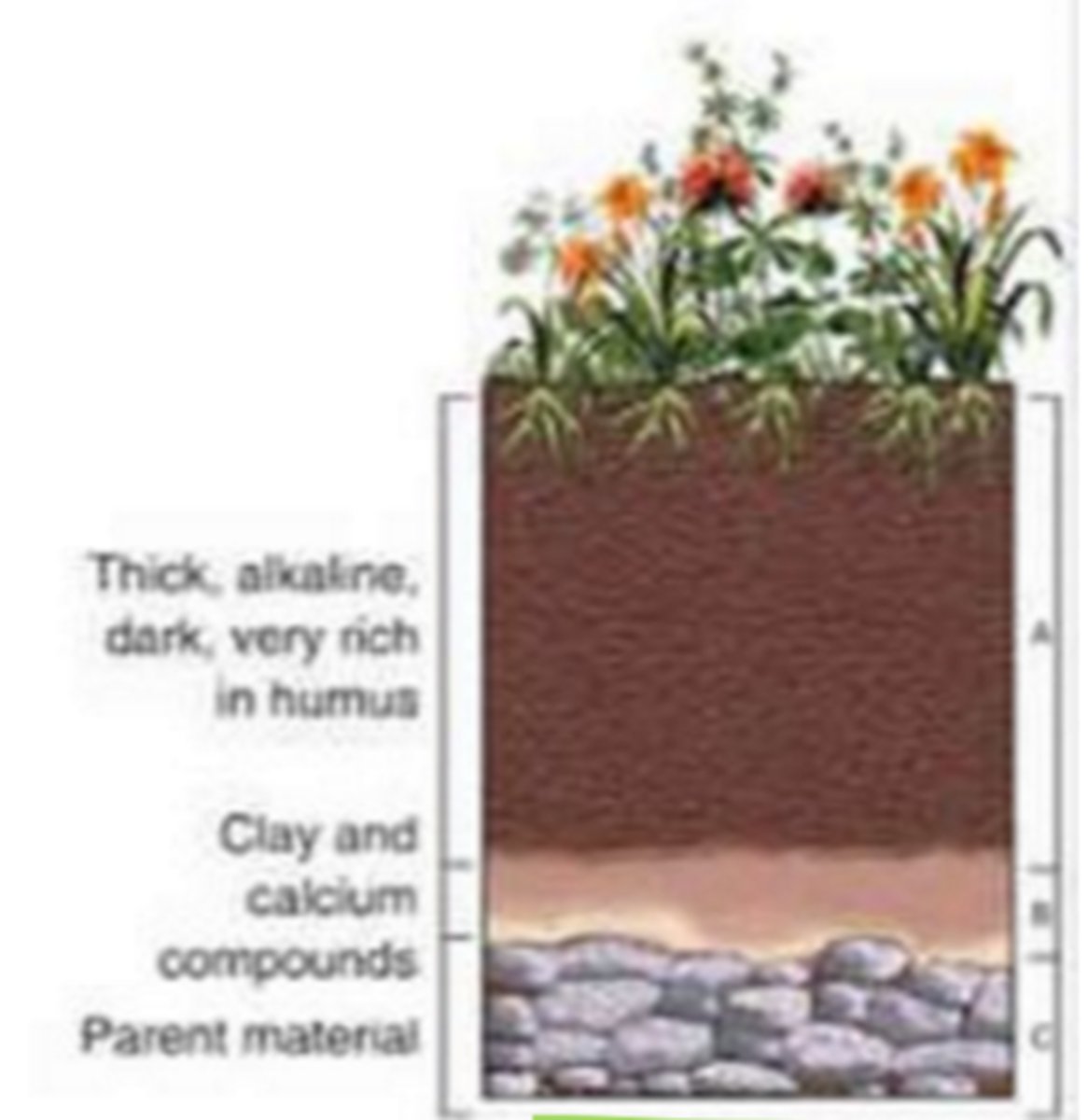
forest
biome with lots of humus (organic soil), thick O layer (because of leaves), and bleaching E layer
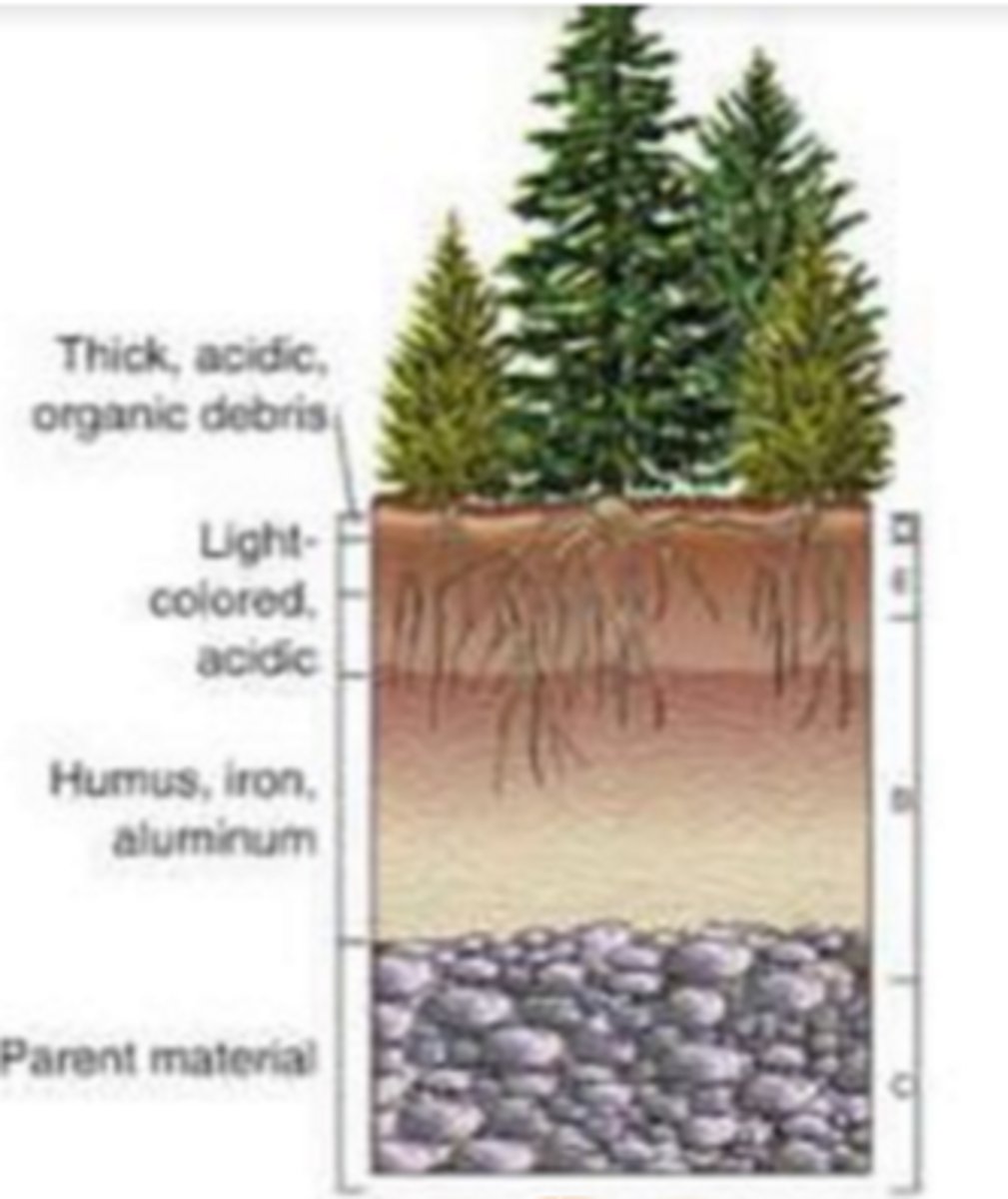
grassland
biome with very thick topsoil
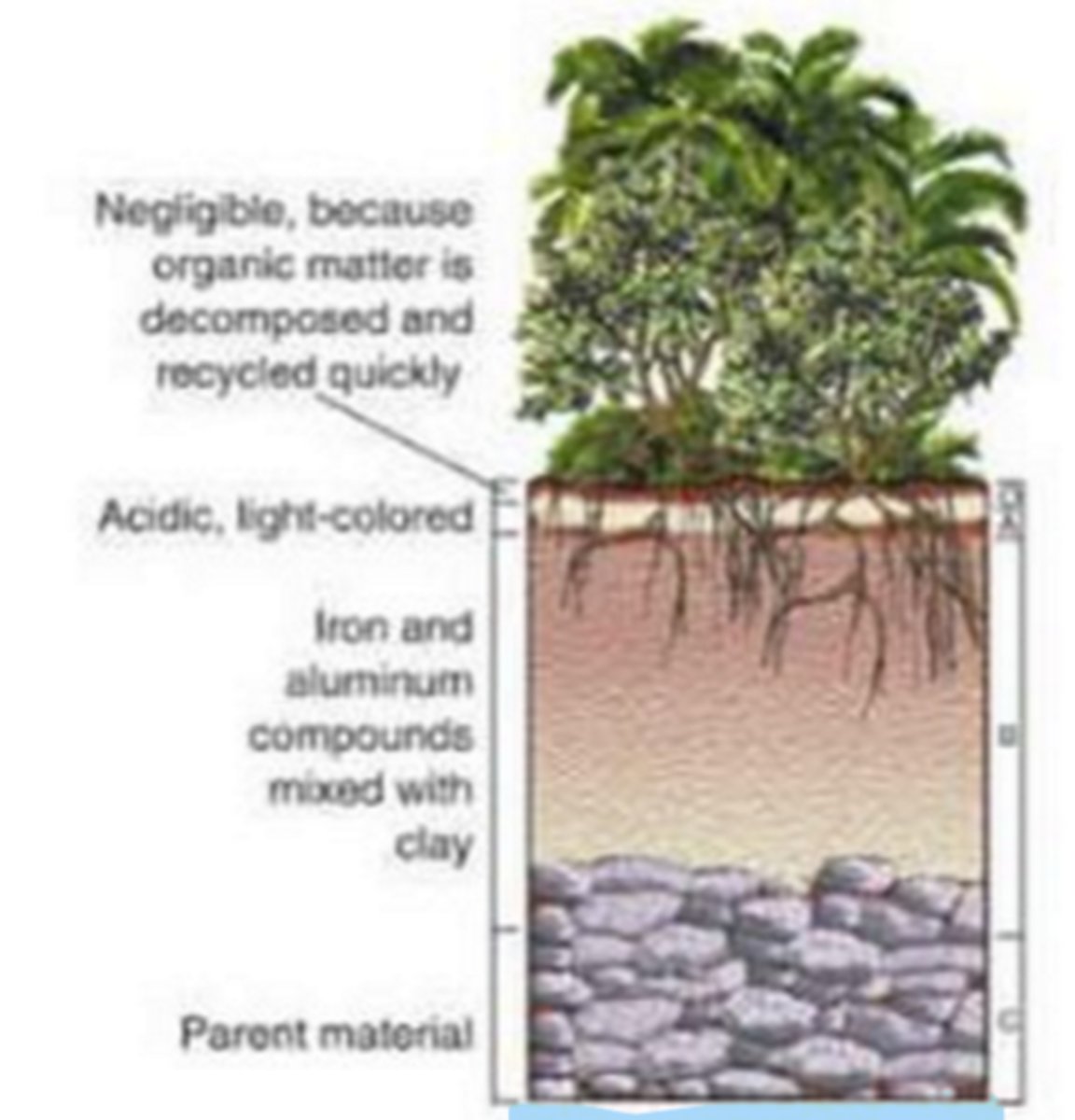
rainforests
biome with thin O and A layer (no topsoil), uses a lot == not very healthy soil
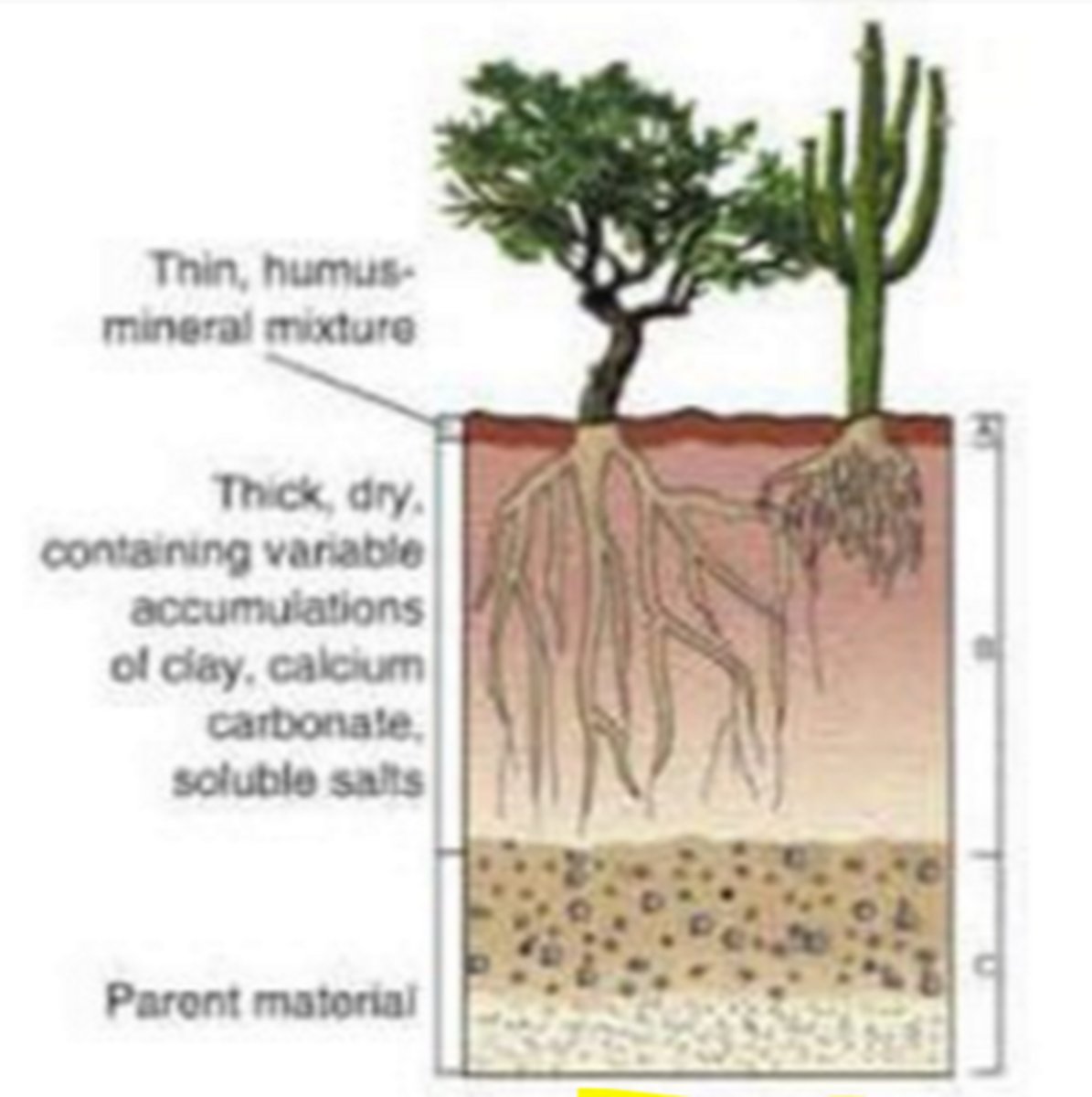
desert
biome with no O layer, a thin A layer (little topsoil), large B layer
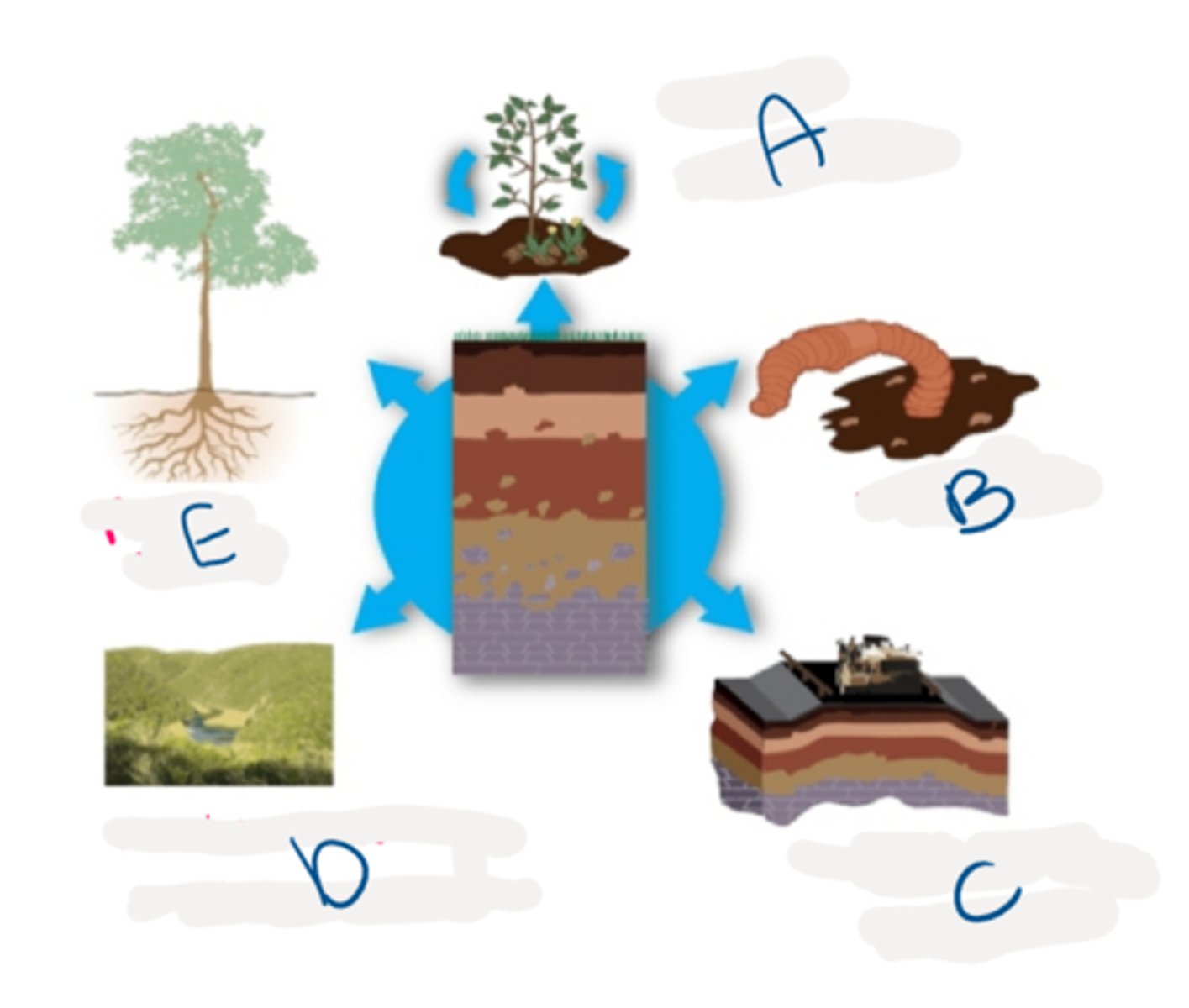
cycle nutrients, habitats, engineering medium, water storage/filtration, plant growth
label the diagram of ecosystem services provided by soil
parent material, climate, topography, organisms, time
5 soil properties are determined by
parent material
a property soil is determined by, rocks, quartz = nutrient poor, calcium carbonate = high calcium, high pH, high crop productivity
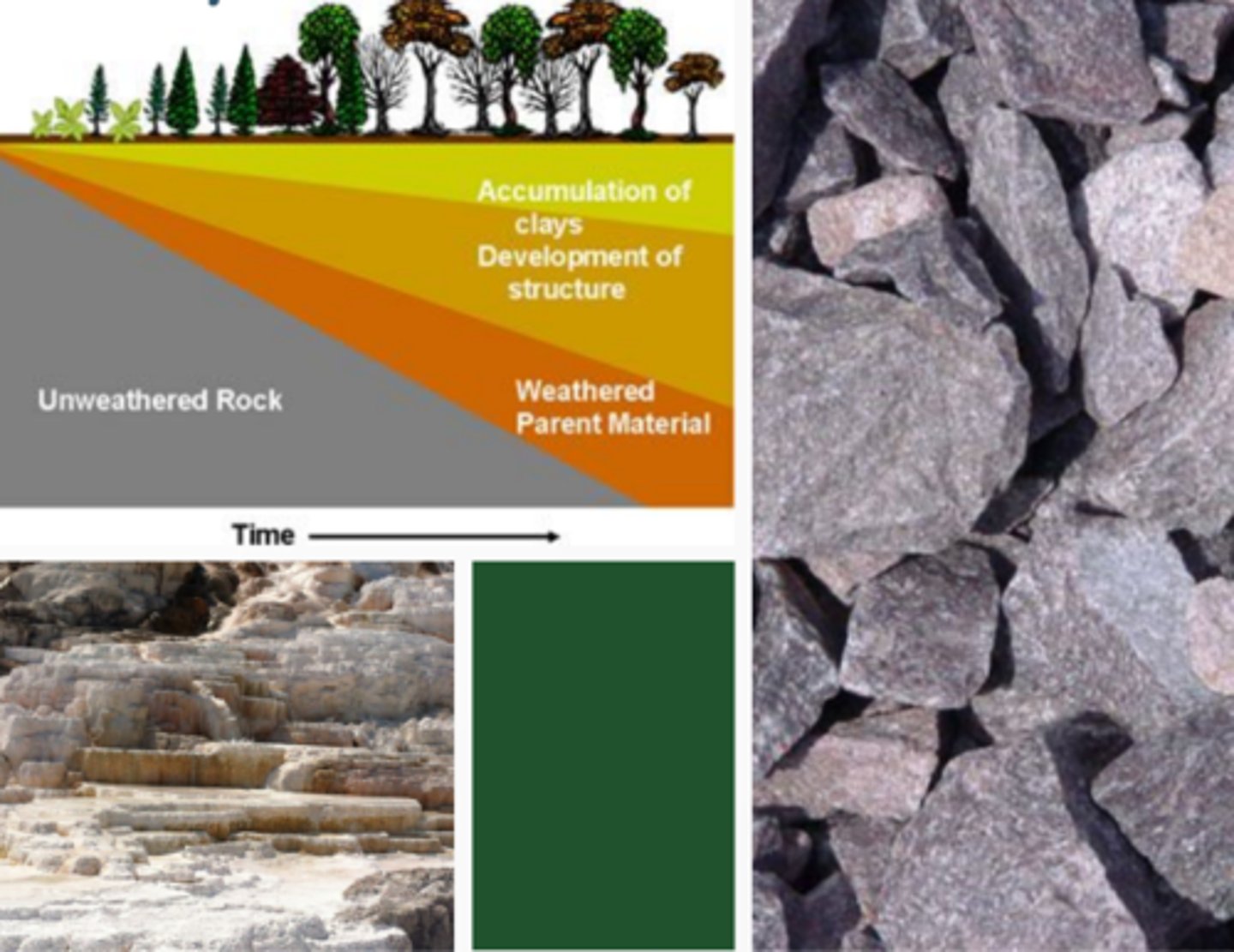

climate
a property soil is determined by, too cold = much undecomposed organic material, humid tropics = rapid weathering leaching of nutrients, decomposition of organic detritus

topography
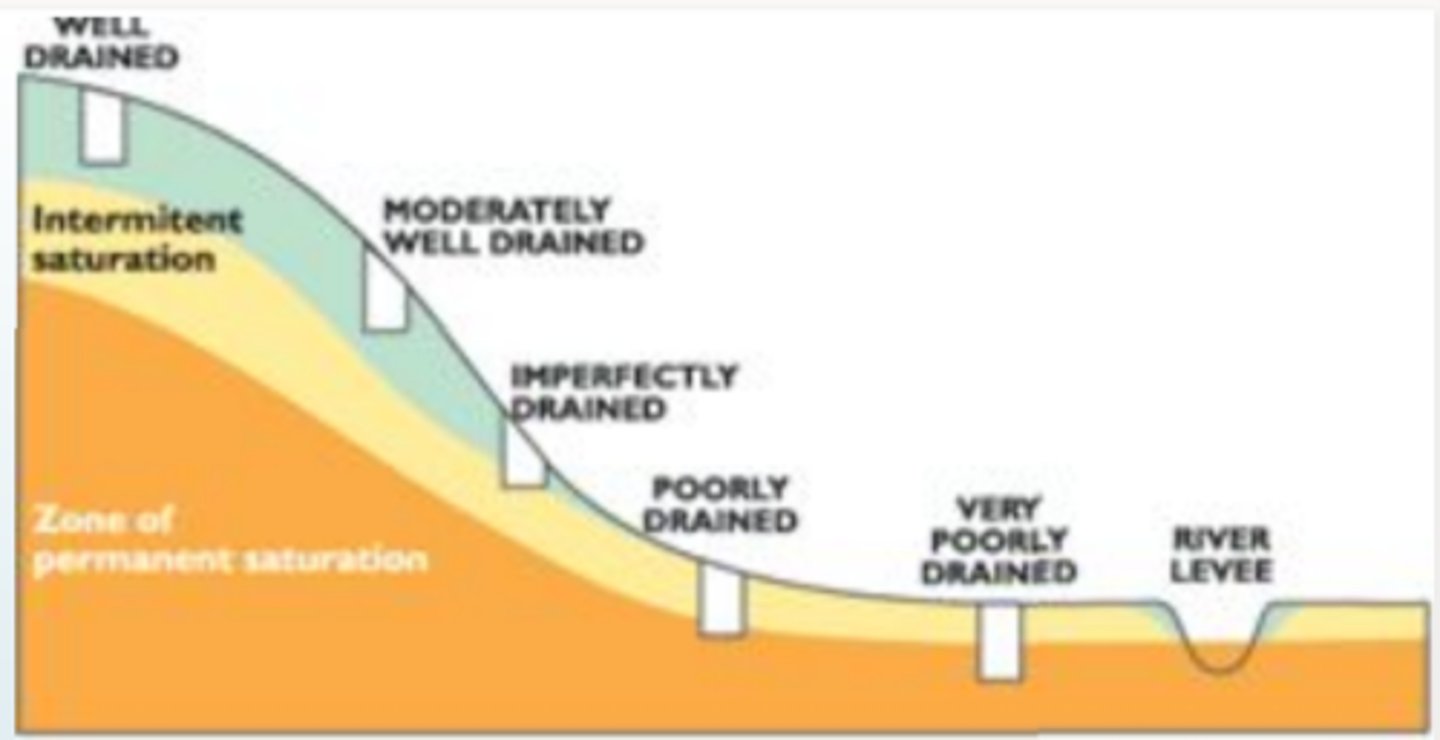
a property soil is determined by, slope and arrangement of landscape, amount of erosion, depth of soil, soil quality)
organisms
a property soil is determined by, plants = nutrient removal, excretion of acids, animals = tunneling and burrowing by earthworms, gophers, and voles, all organisms = cycling of nutrients by fungi and bacteria, humans = using/walking on soil
time
a property soil is determined by, young vs. mature soils, soil formation over time
topsoil compaction, vegetation
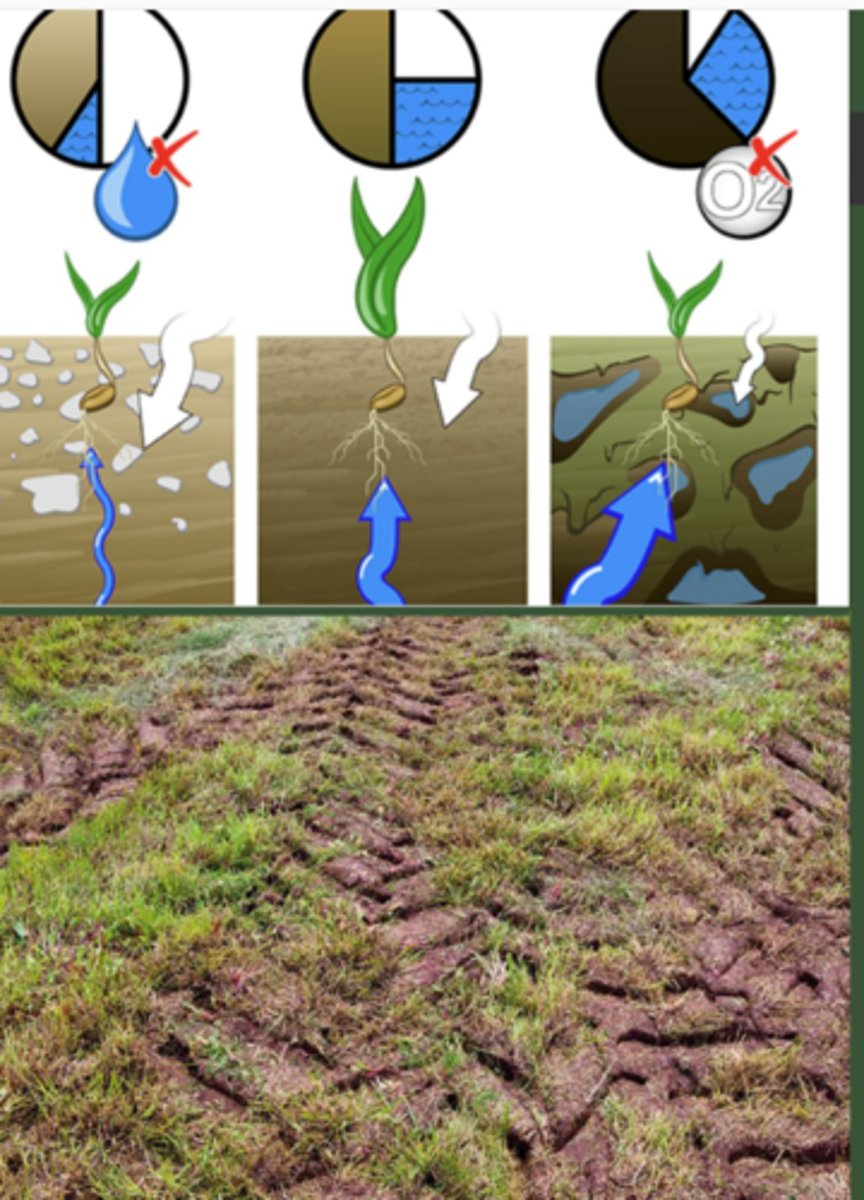
anthropogenic soil degradation:
1. ___ plowed/removed = increased erosion
2. ____ of soil by machines, humans, and livestock
3. less ___ = more erosion

drying, waterlogging, root
compaction of soil by humans:
1. ___ (water won't circulate)
2. _____ (water stays in top layer and oxygen won't circulate)
3. more mechanical/physical resistance to ___ development
positive
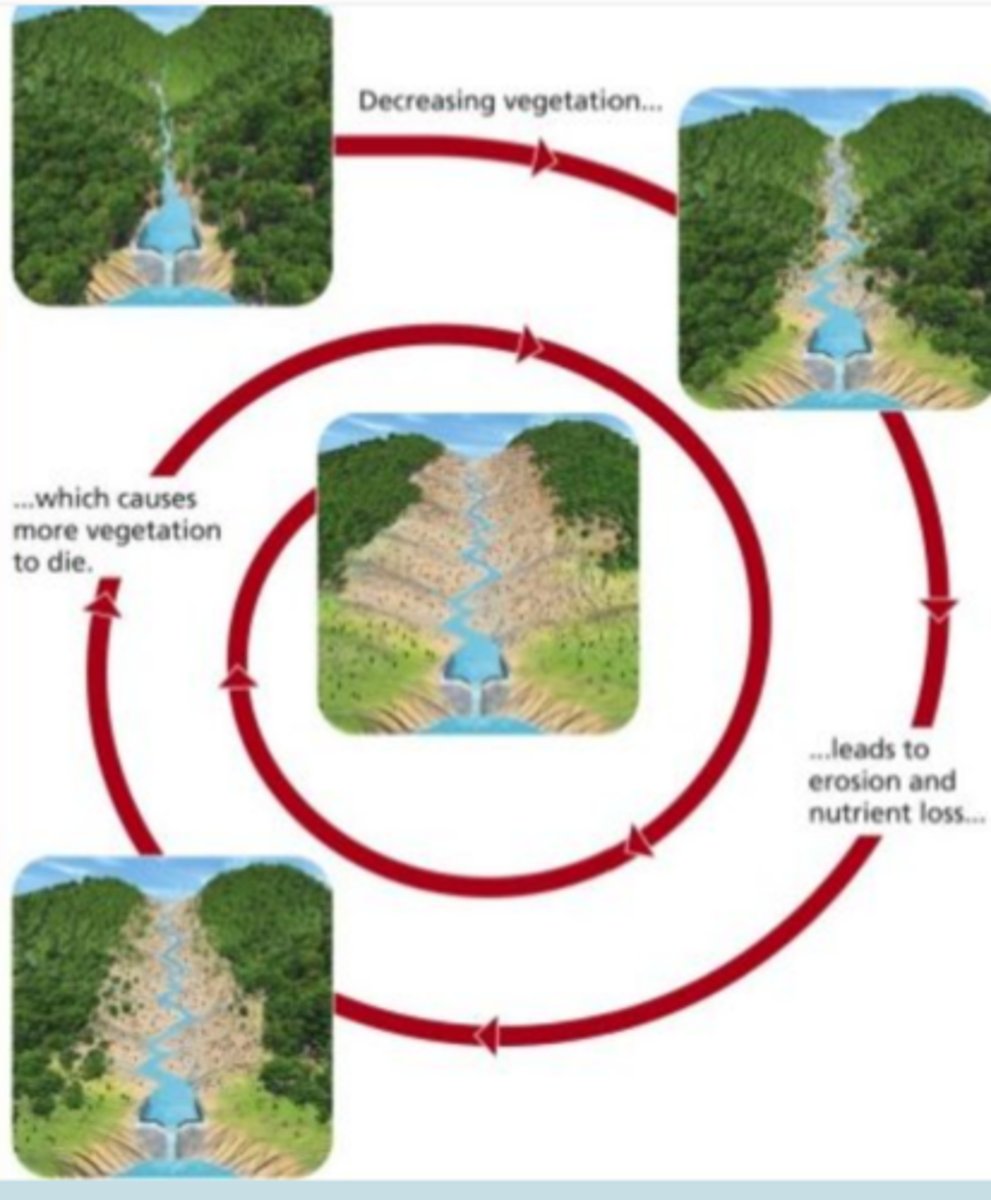
what type of feedback loop is this?
nutrients
traditional agriculture = depletion of soil ____
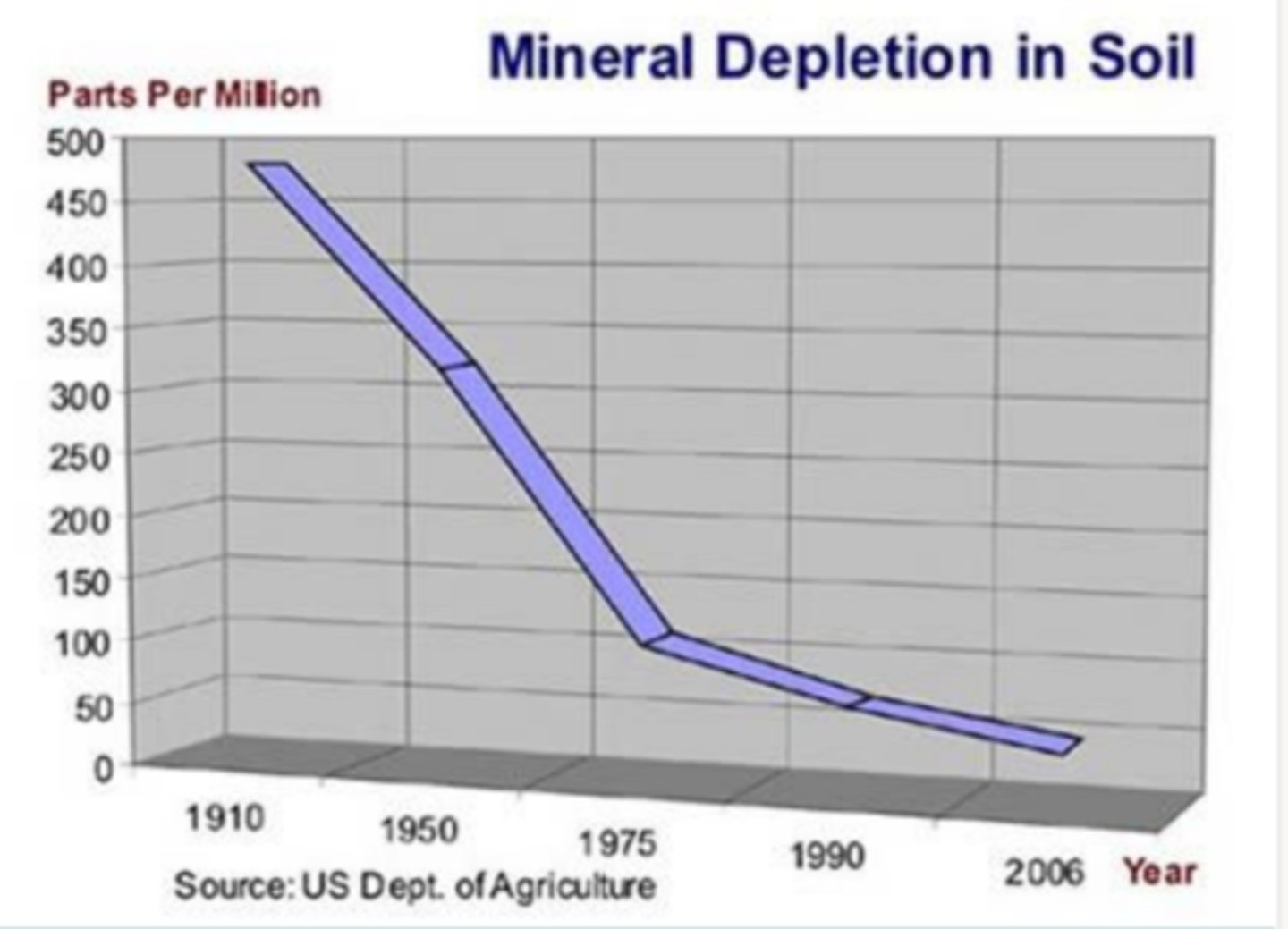
chemical
pesticides = ____ pollution
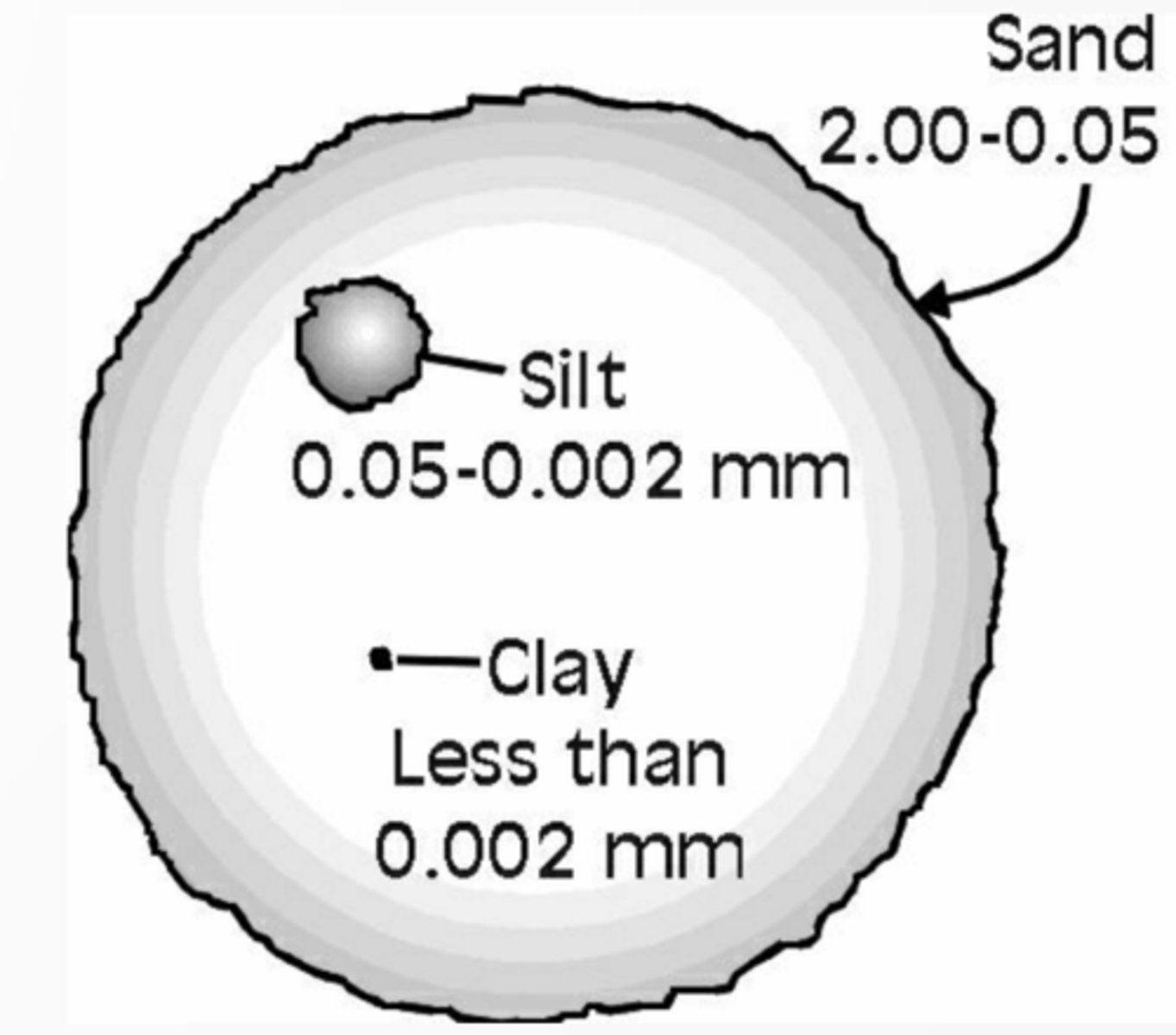
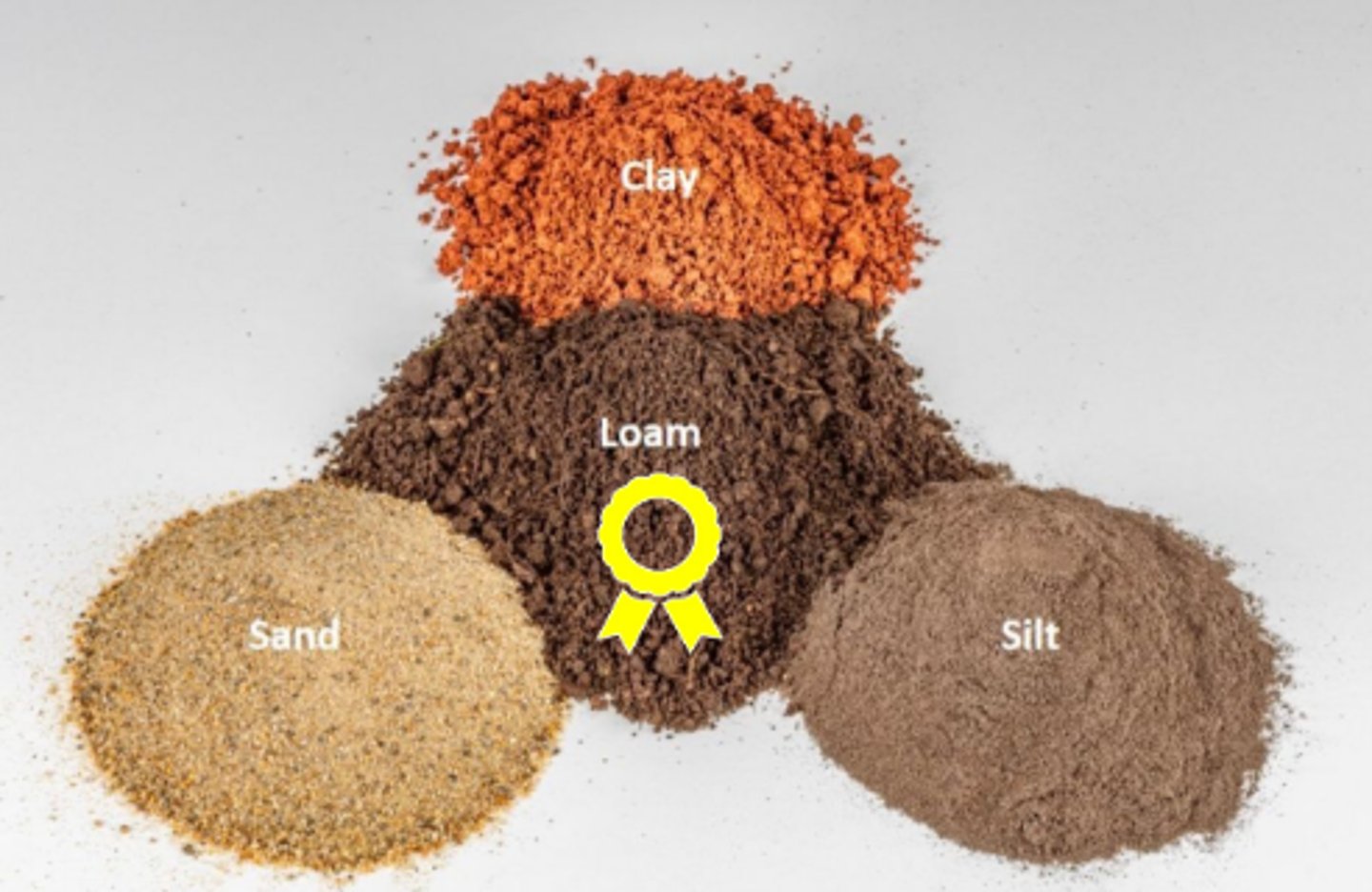
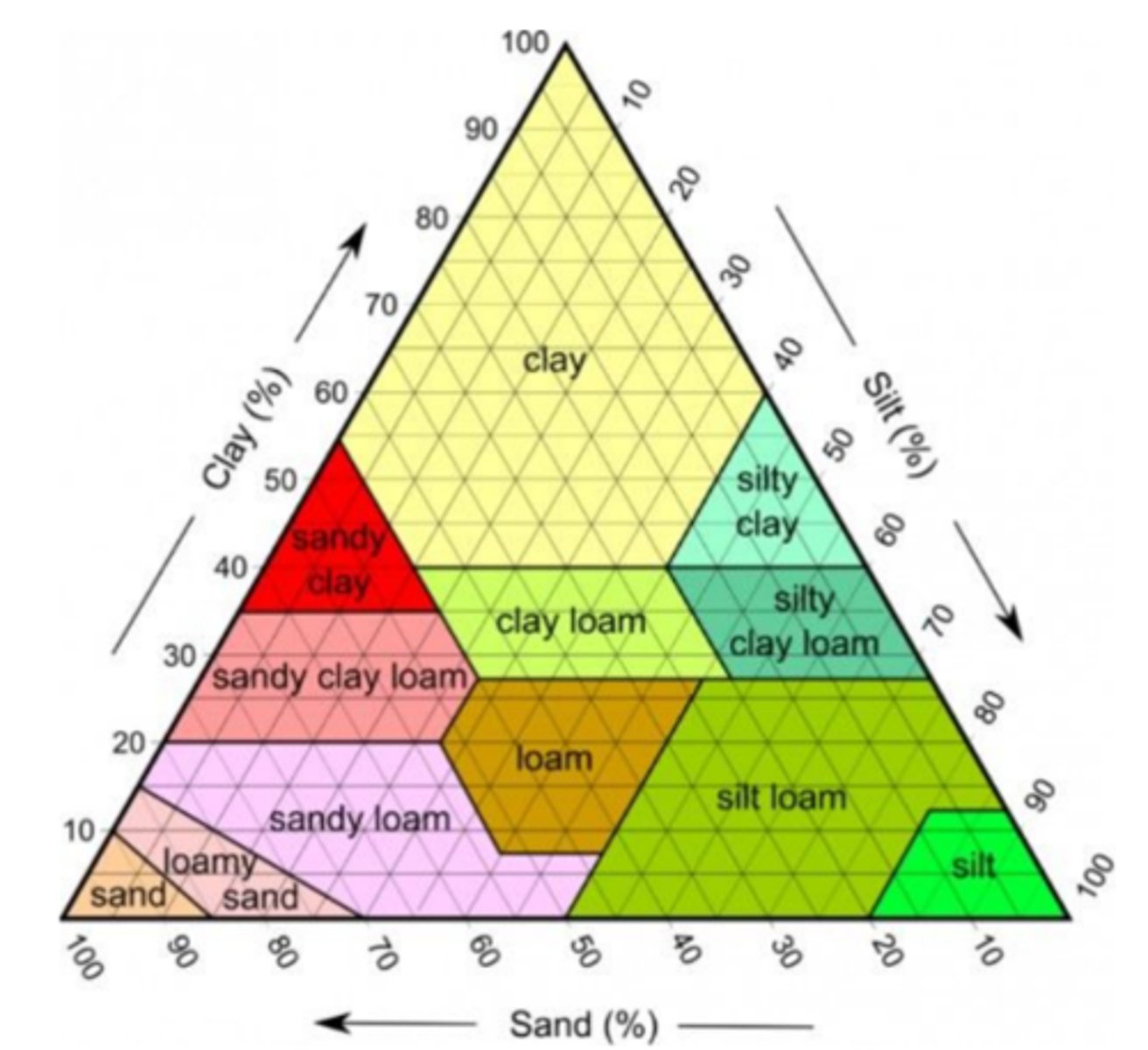
size/weight, permeability, porosity
3 physical properties of soil
sand, silt, clay
list the soil types from least to most size/weight and permeability
porosity
% space in the soil sample
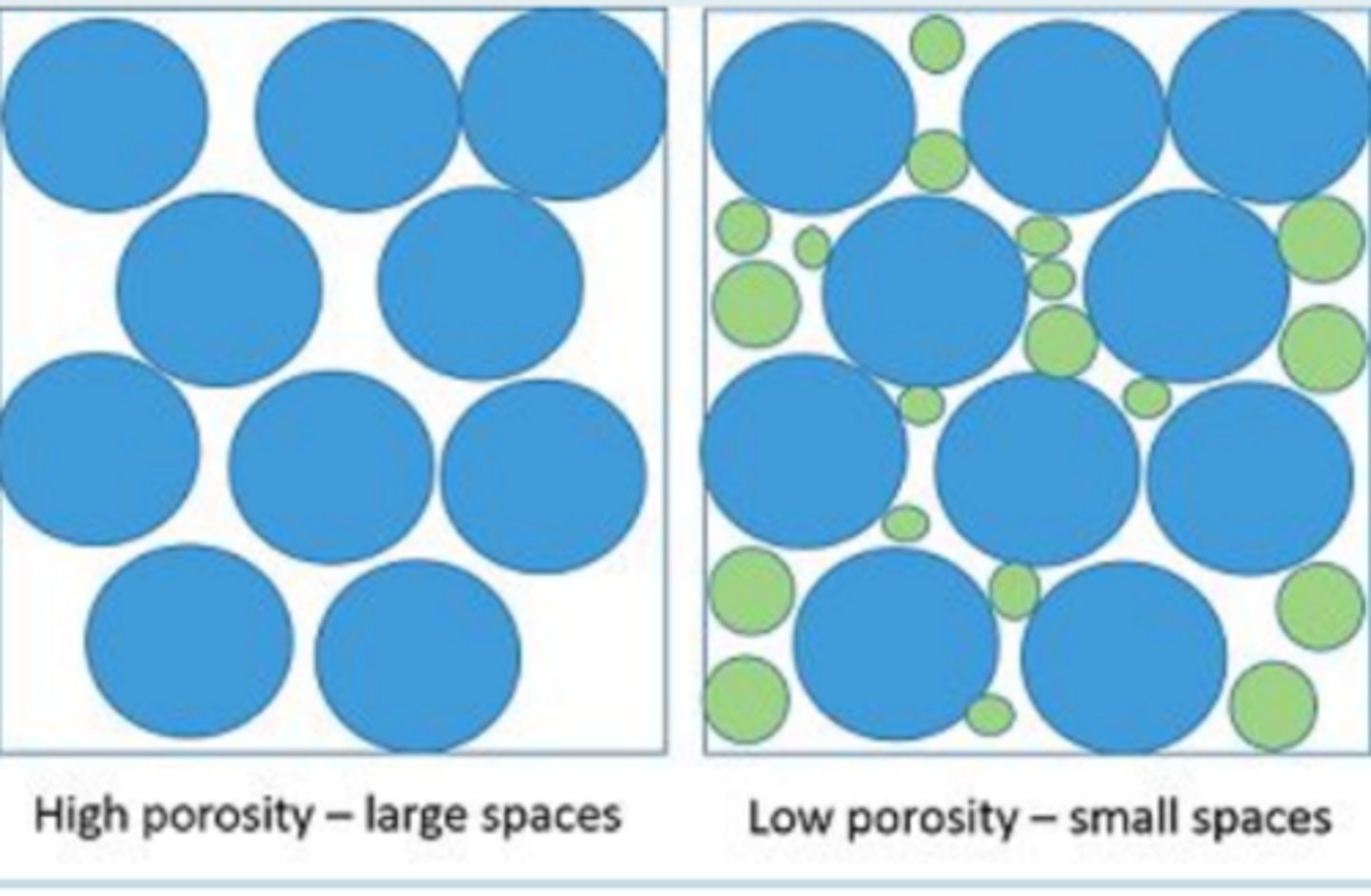
clay is non-porous
why are many landfills lined with clay?
cation exchange capacity (CEC), base saturation
2 chemical properties of soil
cation exchange capacity
chemical property of soil, nutrient-holding capacity, organic material = high
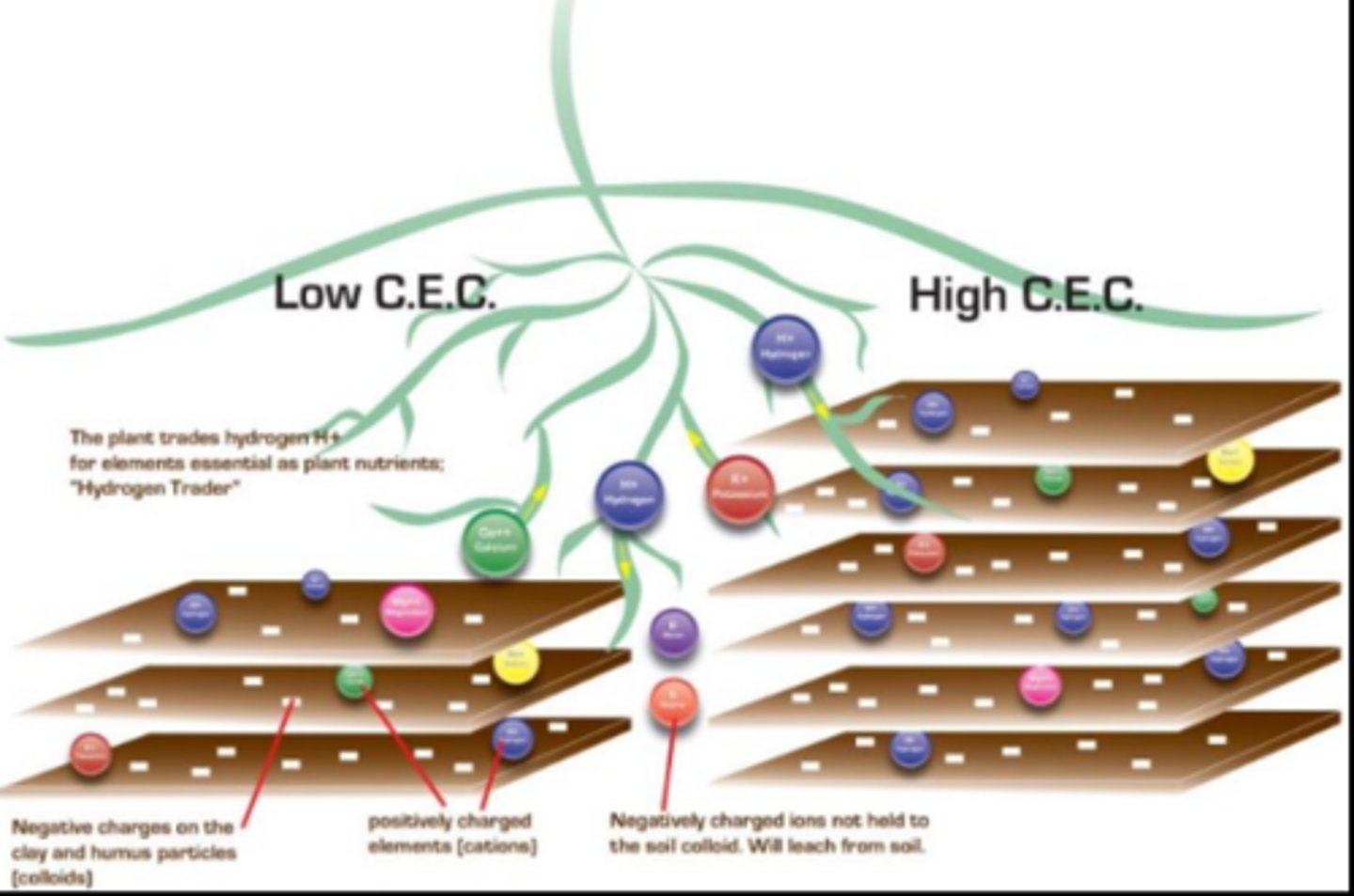
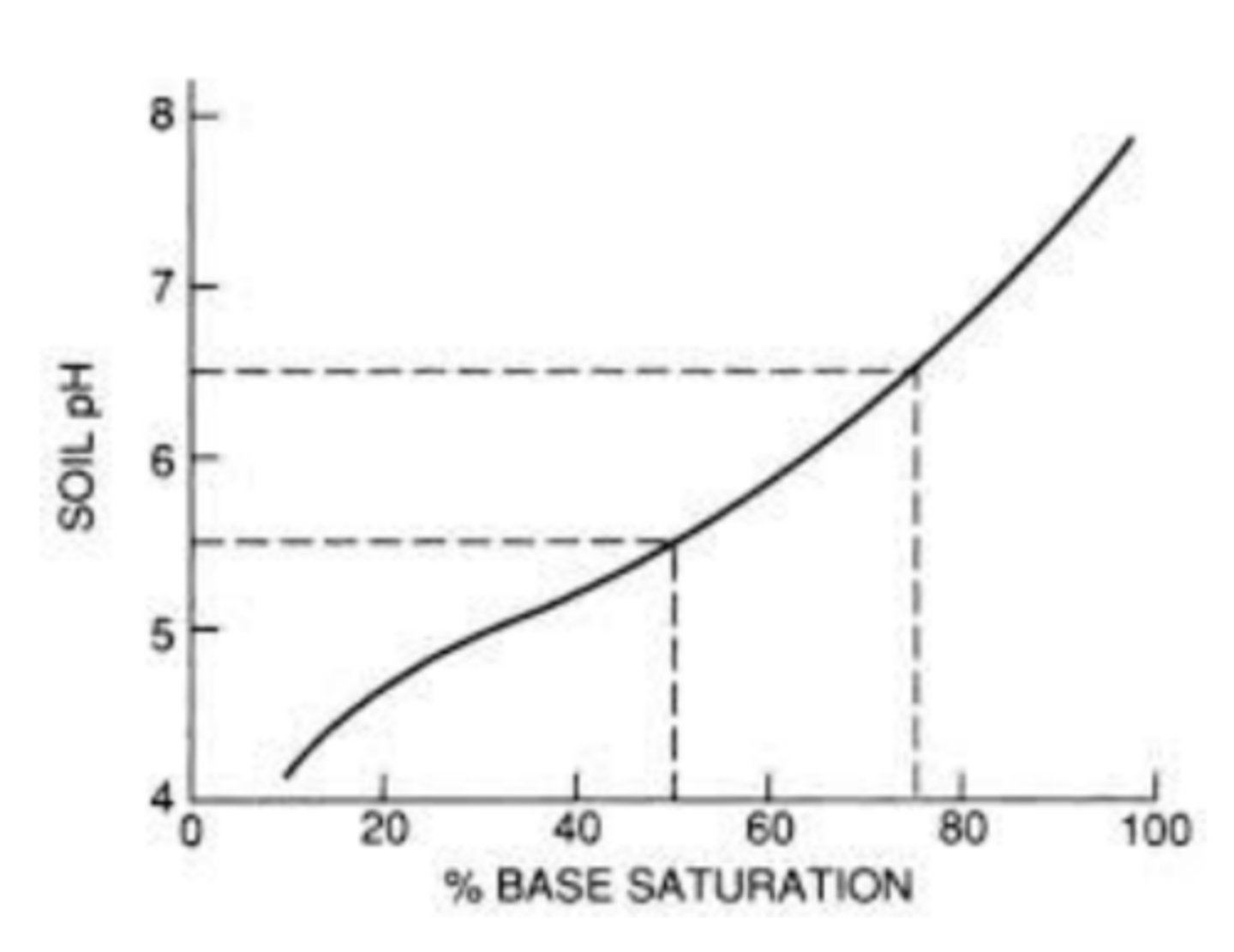
base saturation
chemical property of soil, proportion of bases to acids (as a &), bases are essential for nutrition, acids are detrimental
Ca, K, Mg, Na, and Al, H
4 essential bases for soil nutrition, 2 detrimental acids for soil nutrition
loam
what is the best agricultural soil?

cecil
in NC we have ____ soil, which is a dark gray sandy loam with a subsoil of red clay loam
decomposition, breakdown, nitrogen
3 biological properties of soil:
1. _____ (fungi, bacteria, protozoans)
2. ____ down of material (rodents, earthworms, snails, slugs)
3. _____ cycle (nitrogen-fixing bacteria)

soil texture chart
what is this? (used for finding types of soil)
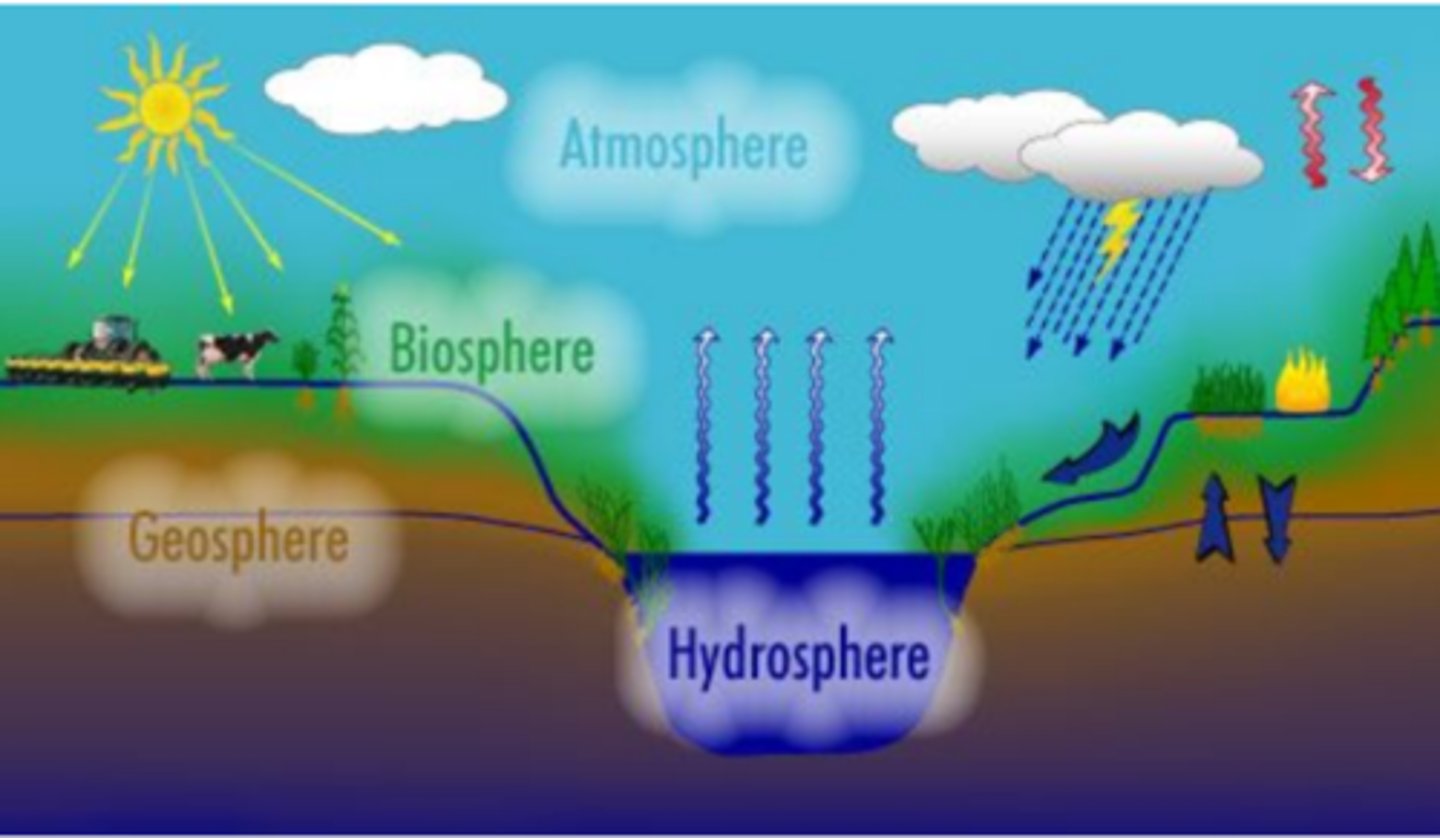
atmosphere, hydrosphere, geosphere, biosphere
the earth's life-support system consists of 4 interacting systems:
1. _____ (air)
2. ____ (water)
3. ____ (rock, soil, sediment)
4. ____ (living things)
atmosphere
a life supporting system, provides O2 and CO2, absorbs solar radiation, moderates climate, transports and recycles water and nutrients
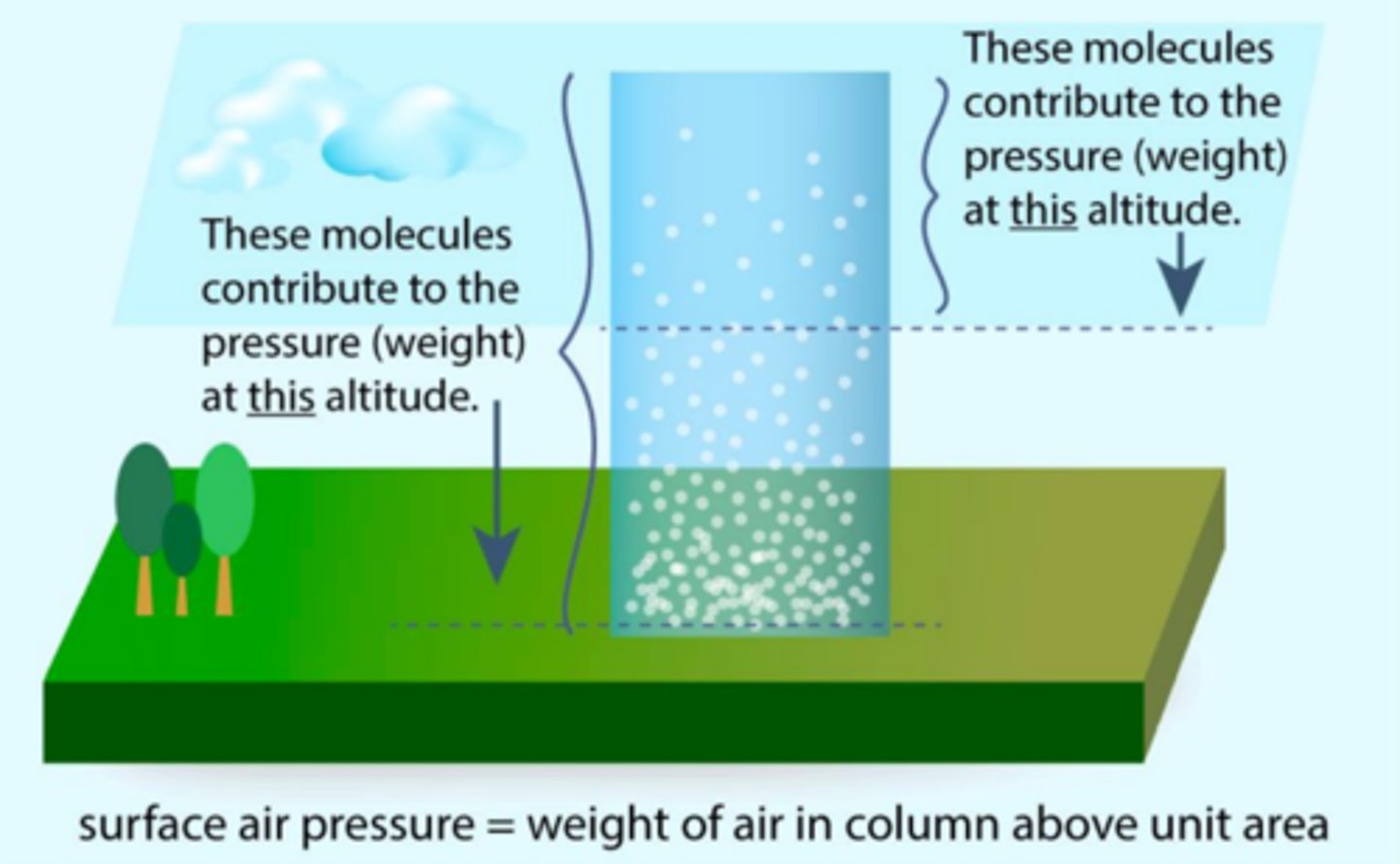
atmospheric pressure
we live at the bottom of an "ocean of air," just as water pressure is caused by the weight of water, _____ _____ is caused by the weight of air
weight/area
pressure formula (column of air from surface to the top of atmosphere)
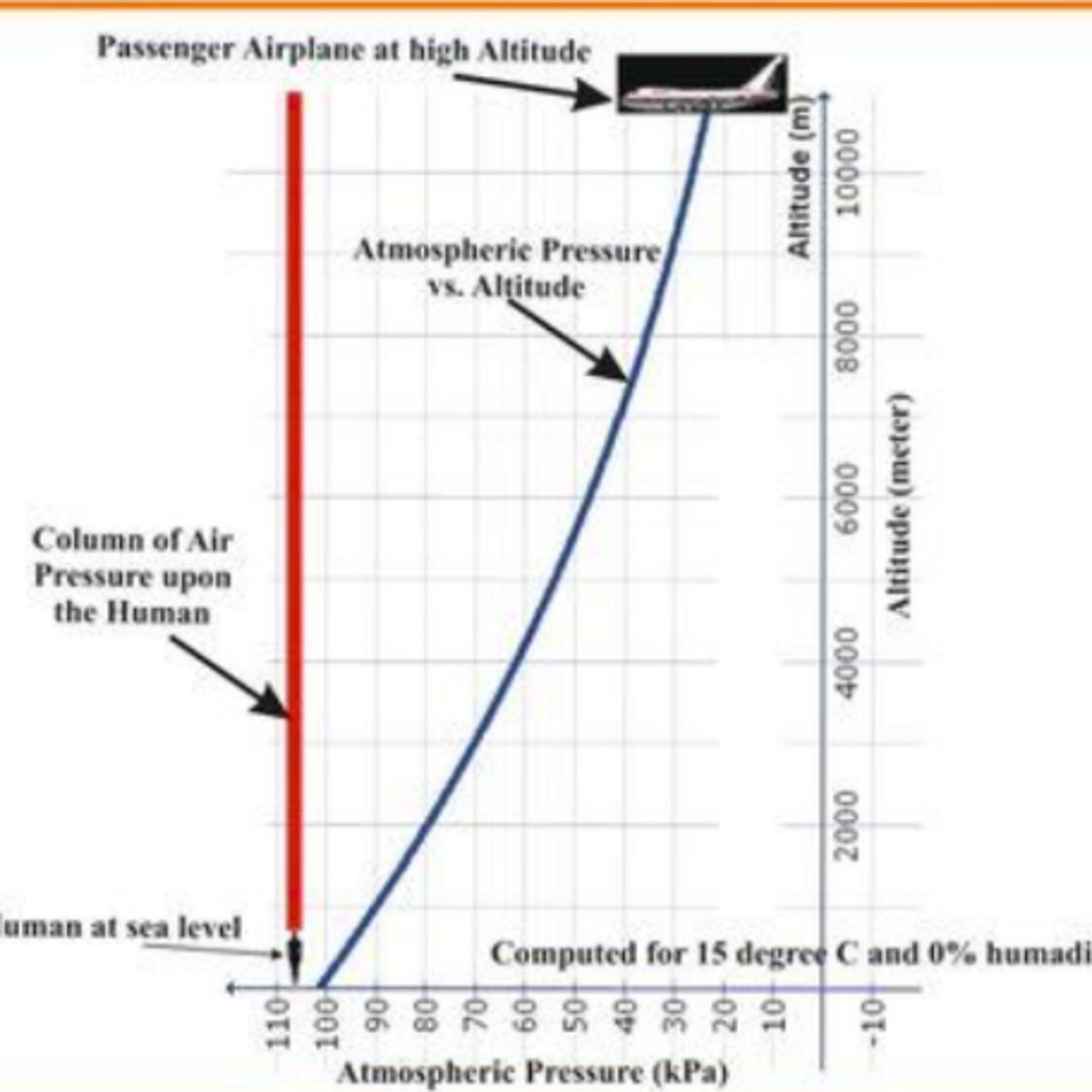
as pressure decreases, altitude increases
pressure and altitude relationship
nitrogen, oxygen, other noble gases
permanent gases in the atmosphere