A&P Cell Structures and Organelles
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
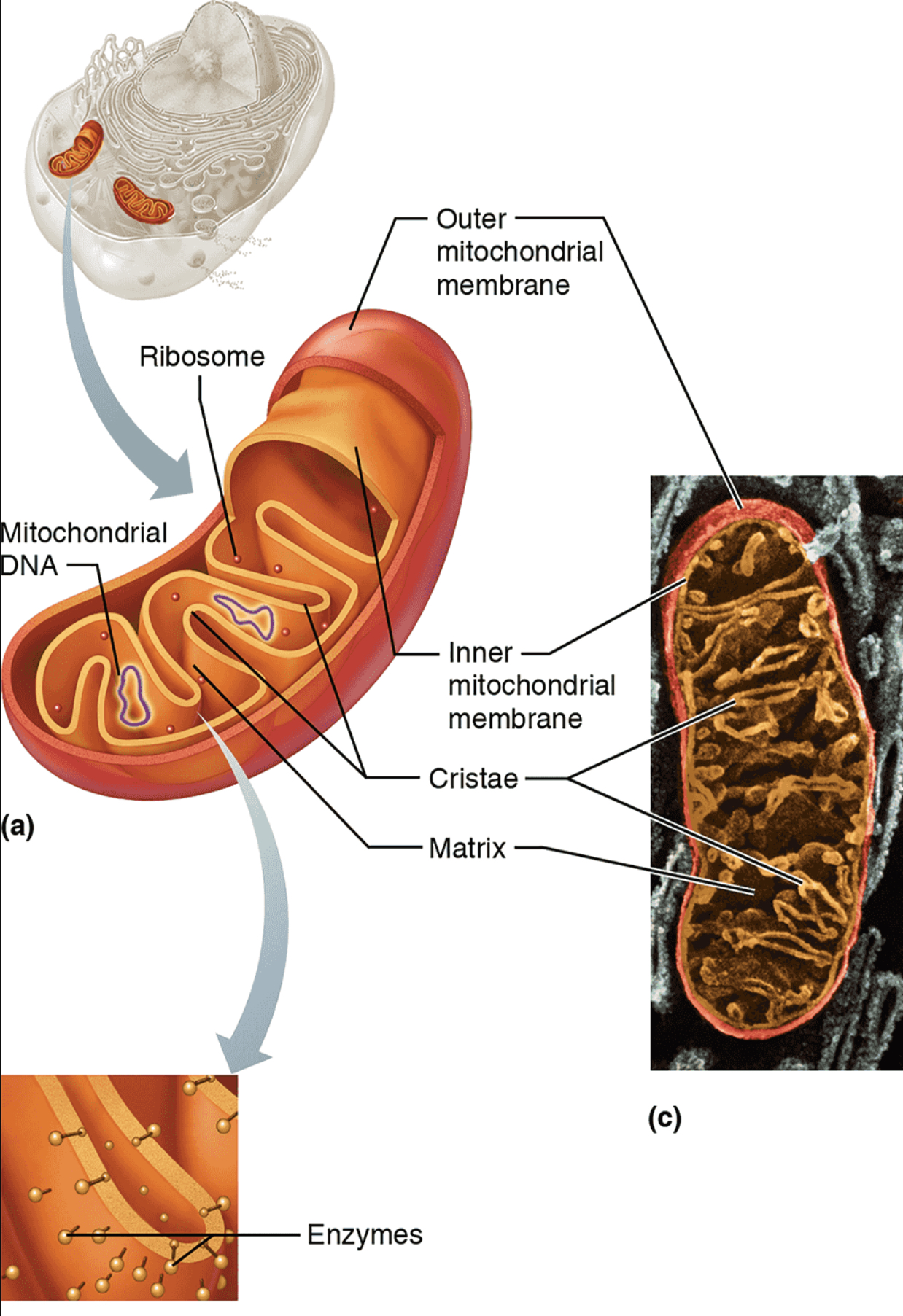
Mitochondria
Structure: Rodlike, double-membrane structures; inner membrane folded into cristae
Function: Site of ATP Synthesis; powerhouse of the cell
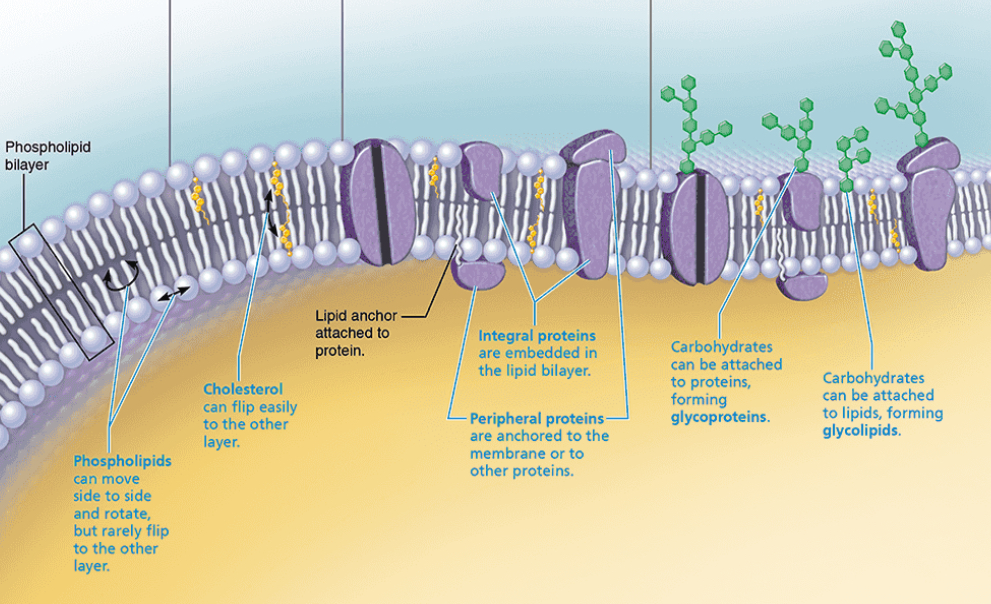
Plasma Membrane
Structure: Made of phospholipid bilayer within which proteins and cholesterol are embedded. Sugars can be found attached to most external facing proteins and some lipids.
Function: Control what comes in and out of cell; maintains cell’s boundaries

Ribosomes
Structure: Consists of 2 subunits (large and small), each composed of rRNA and protein; can be free-floating or found attached to Rough ER
Function: Sites of protein synthesis
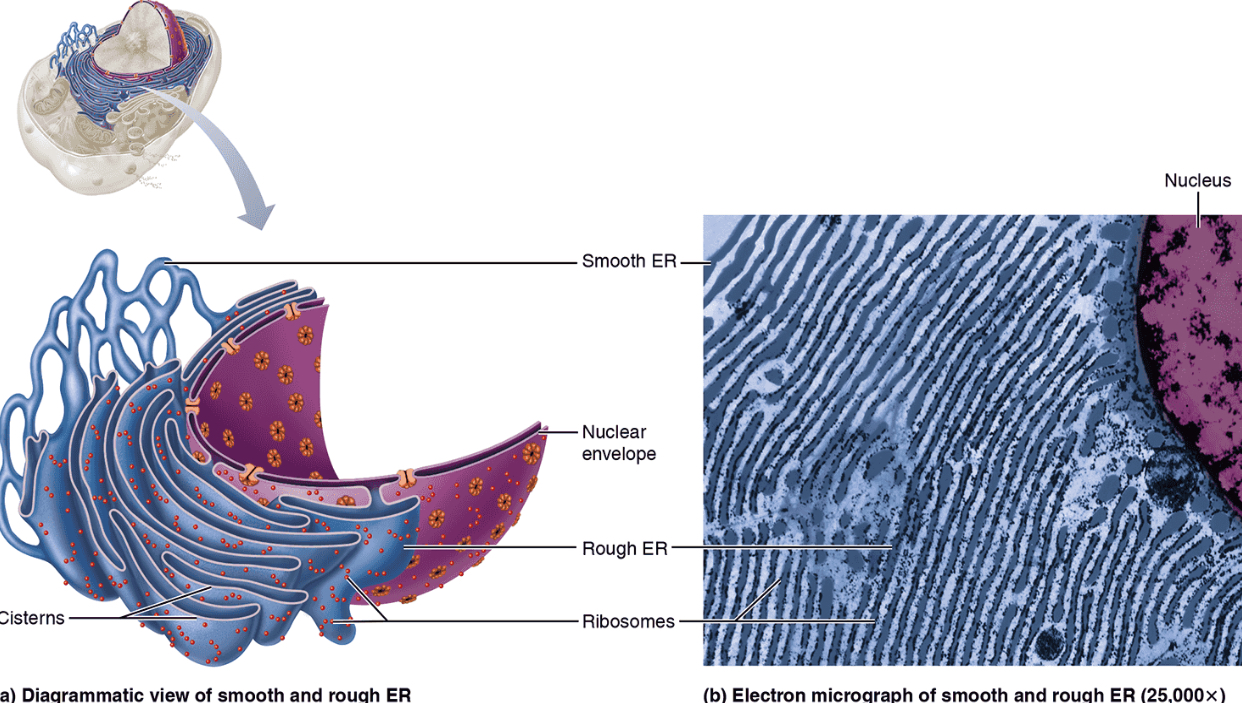
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER)
Structure: Membranous system enclosing a cavity (called cistern) and coiling through cytoplasm; externally studded with ribosomes
Function: Binds proteins synthesized by ribosomes within vesicles for transport to Golgi; synthesizes lipids on external face; manufactures integral proteins and phospholipids; attaches sugars to external facing membrane proteins within cistern
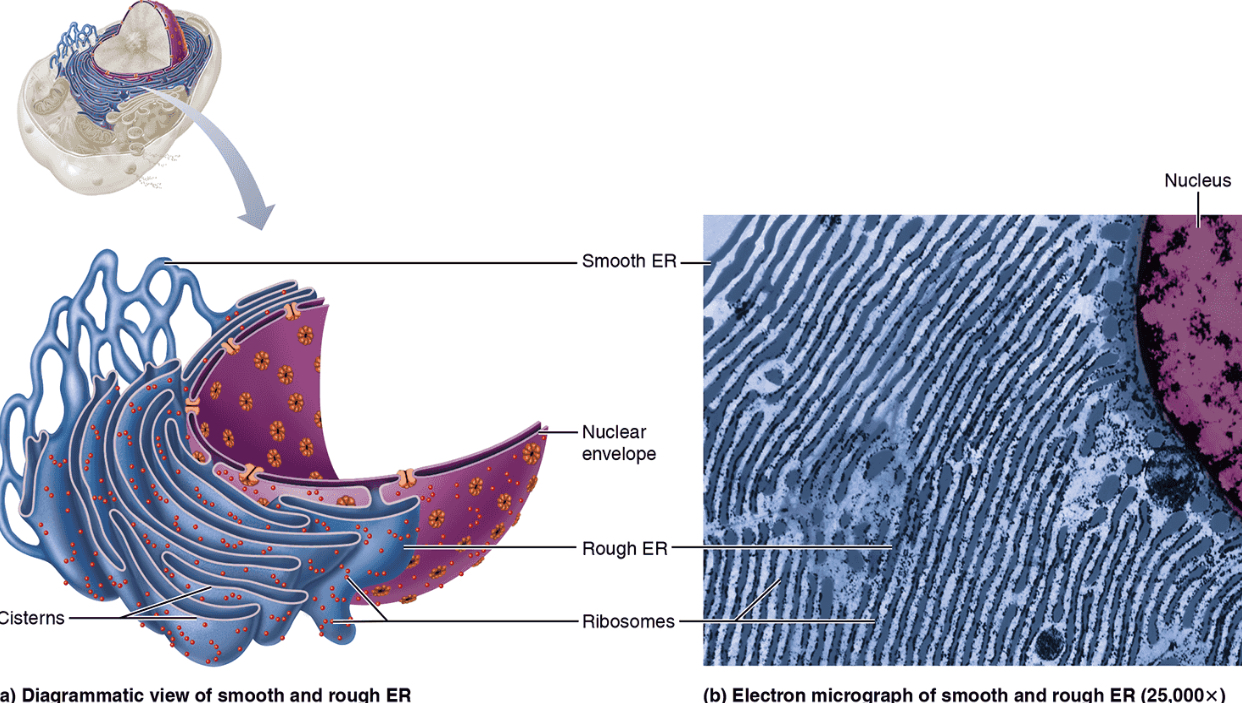
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER)
Structure: Membranous system of sacs and tubules; free of ribosomes
Function: Site of lipid and steroid synthesis, lipid metabolism, drug detoxification, andCa^{2+} storage
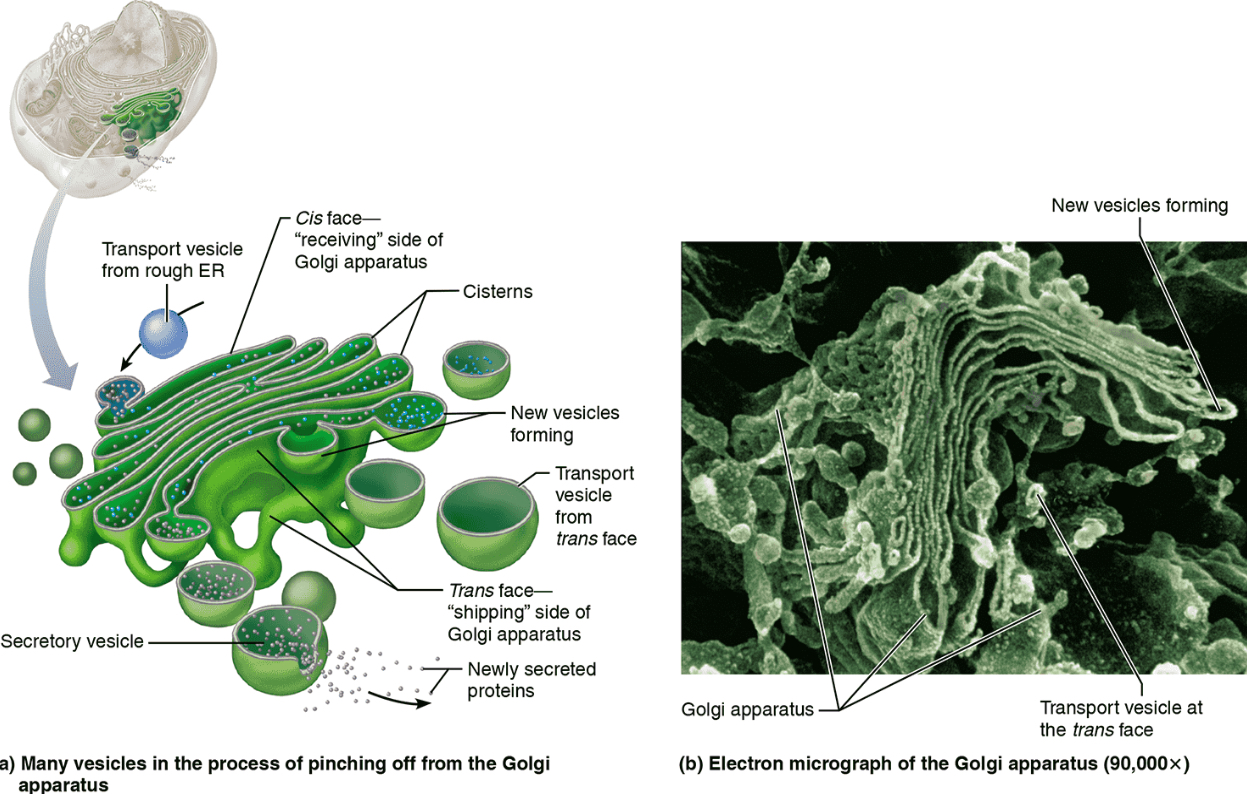
Golgi Apparatus
Structure: A stack of flattened membranes and associated vesicles close to the nucleus
Function: Packages, modifies, and segregates proteins for secretion from the cell, inclusion in lysosomes, and incorporation into the plasma membrane; modifies carbohydrates on proteins
Peroxisomes
Structure: Membranous sacs containing catalase and oxidase enzymes
Functions: Its enzymes detoxify toxic substances; catalase breaks down hydrogen peroxide

Lysosome
Structure: Membranous sacs containing acid hydrolases
Function: Site of intracellular digestion
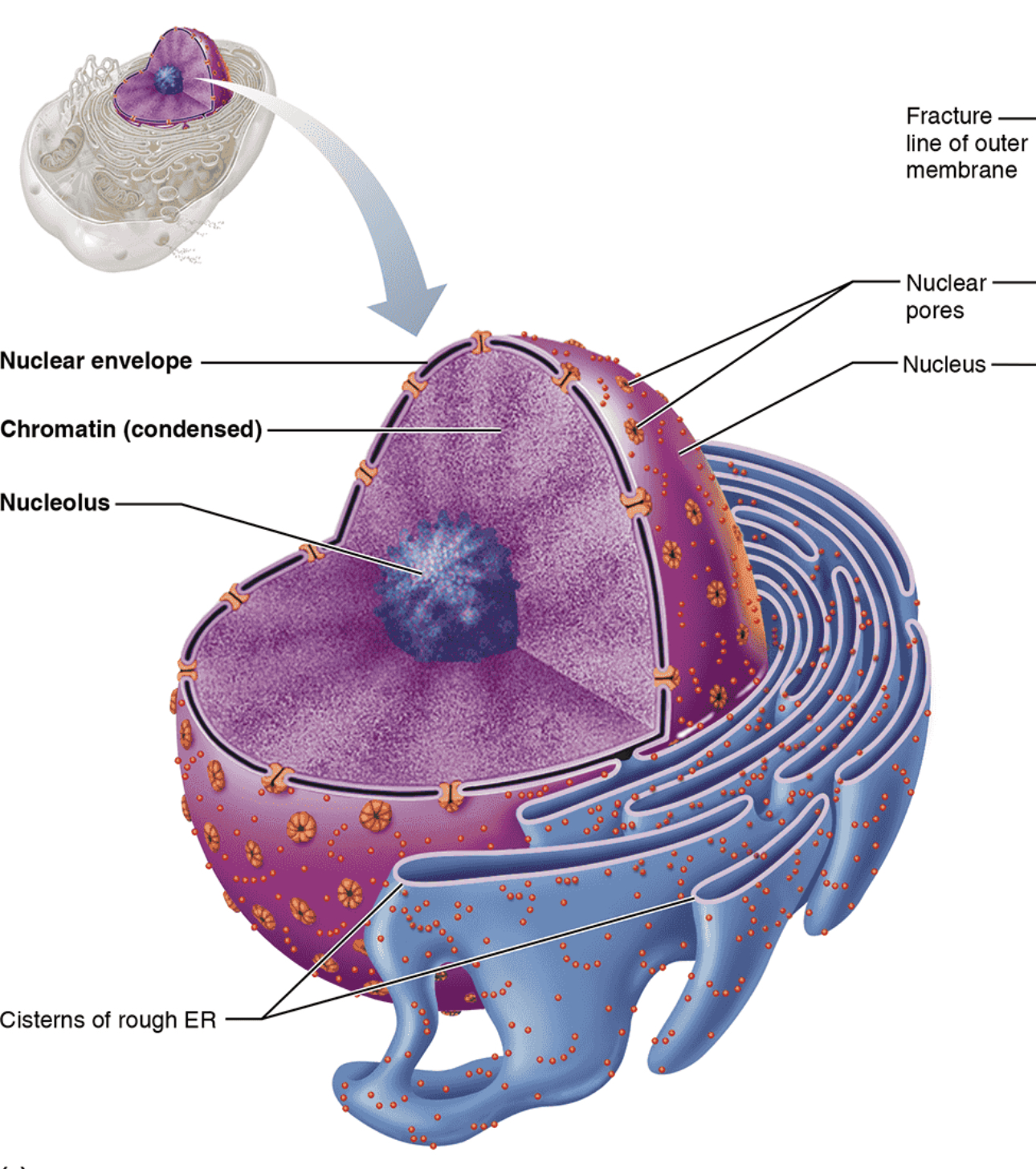
Nucleus
Structure: Largest cytoplasmic organelle at 5\mu m in diameter, and is most often found in spherical or oval shape (but can change to conform to cell’s shape); surrounded by nuclear envelope and contains fluid nucleoplasm, nucleoli, and chromatin
Function: Control center of the cell; responsible for transmitting genetic information and providing the instructions for protein synthesis (houses DNA)
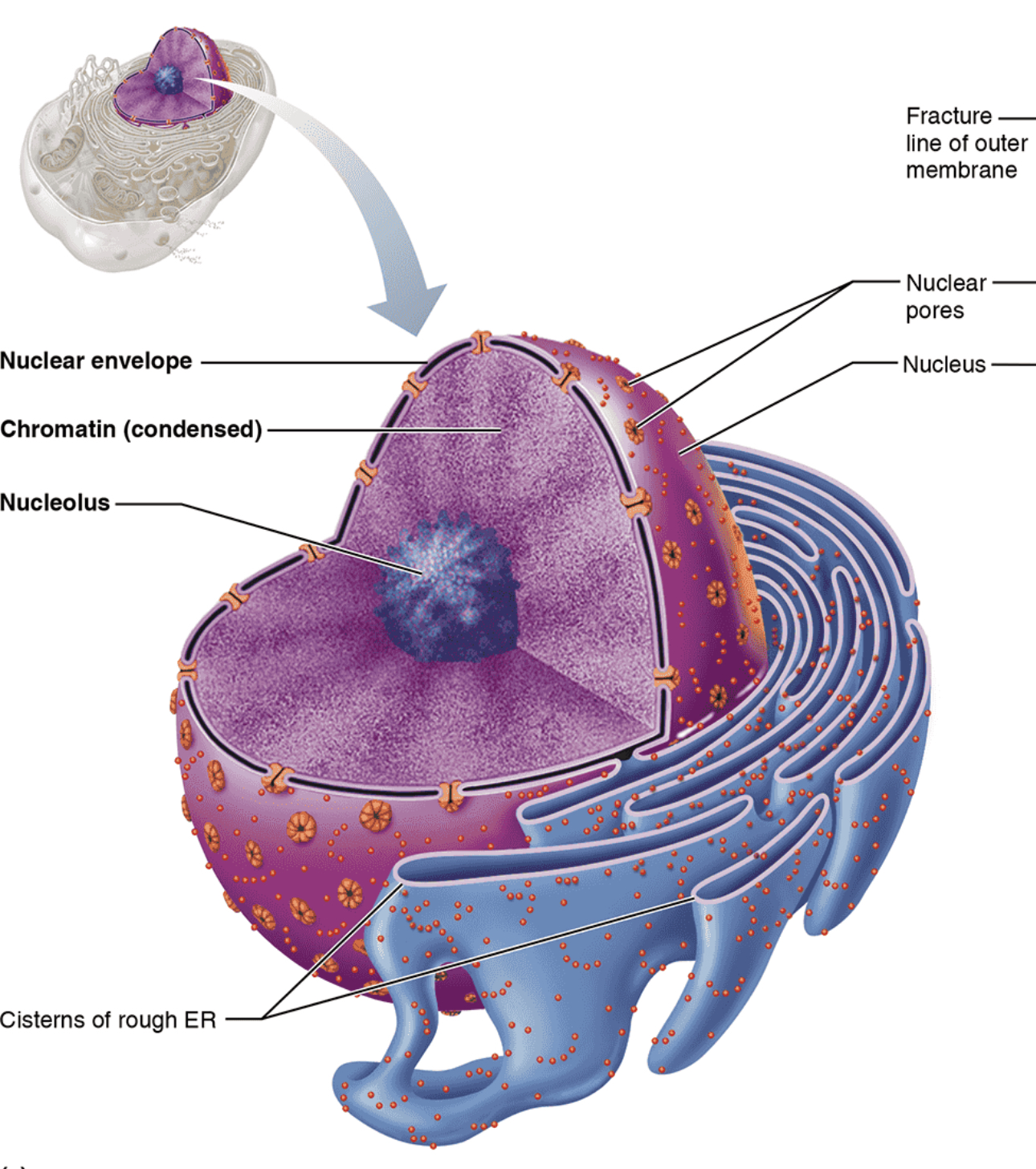
Nuclear Envelope
Structure: Double membrane barrier separated by fluid-filled space; outer membrane continuous with Rough ER and is also externally studded with ribosomes and punctured with nuclear pores
Function: Maintain shape of nucleus; separates nucleoplasm from cytoplasm; regulates passage of substances to and from the nuclei
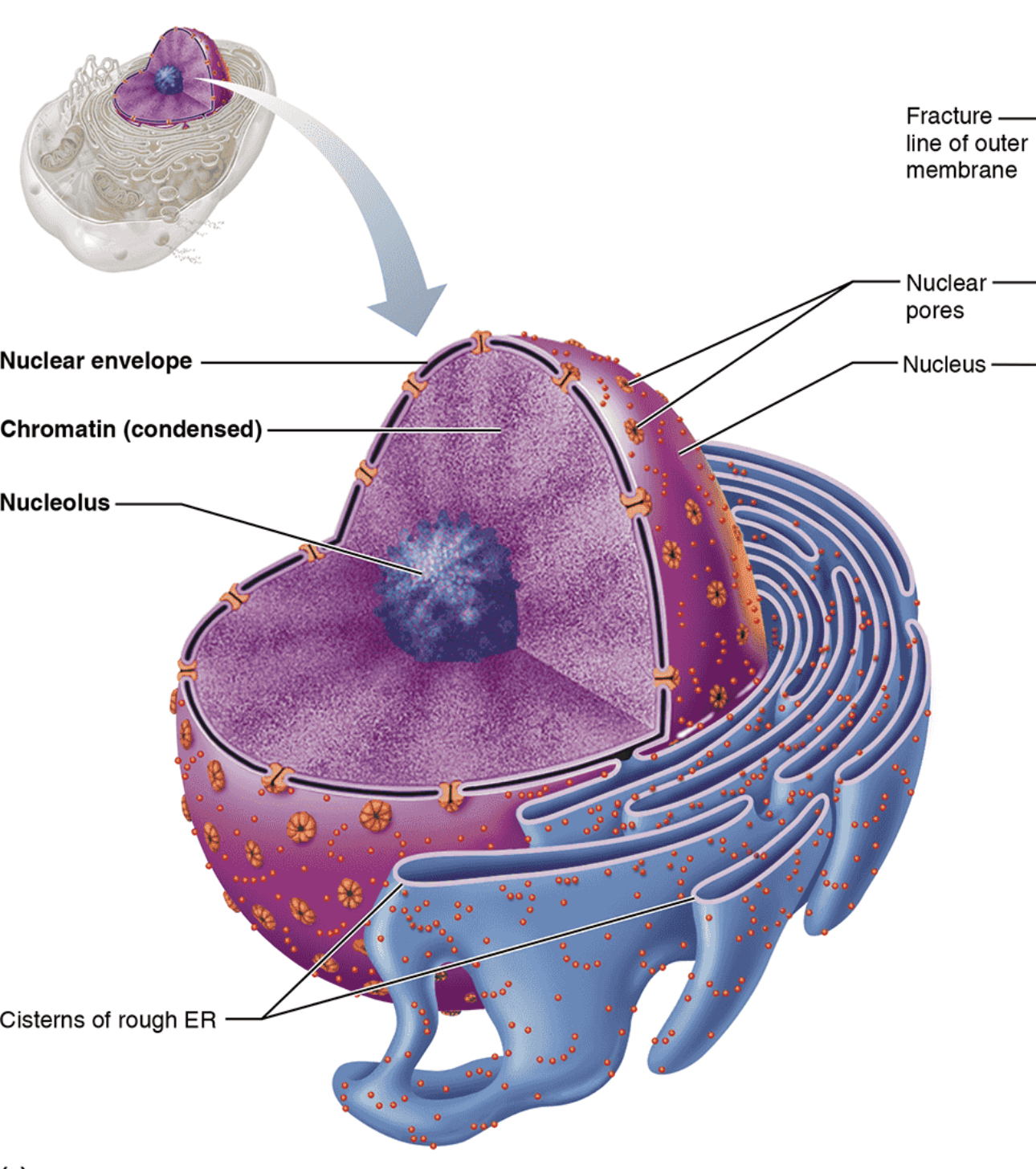
Nucleolus
Structure: Dark-staining spherical bodies found within nucleus, but is not bounded to membrane
Function: Site of rRNA synthesis and ribosomal subunit assembly
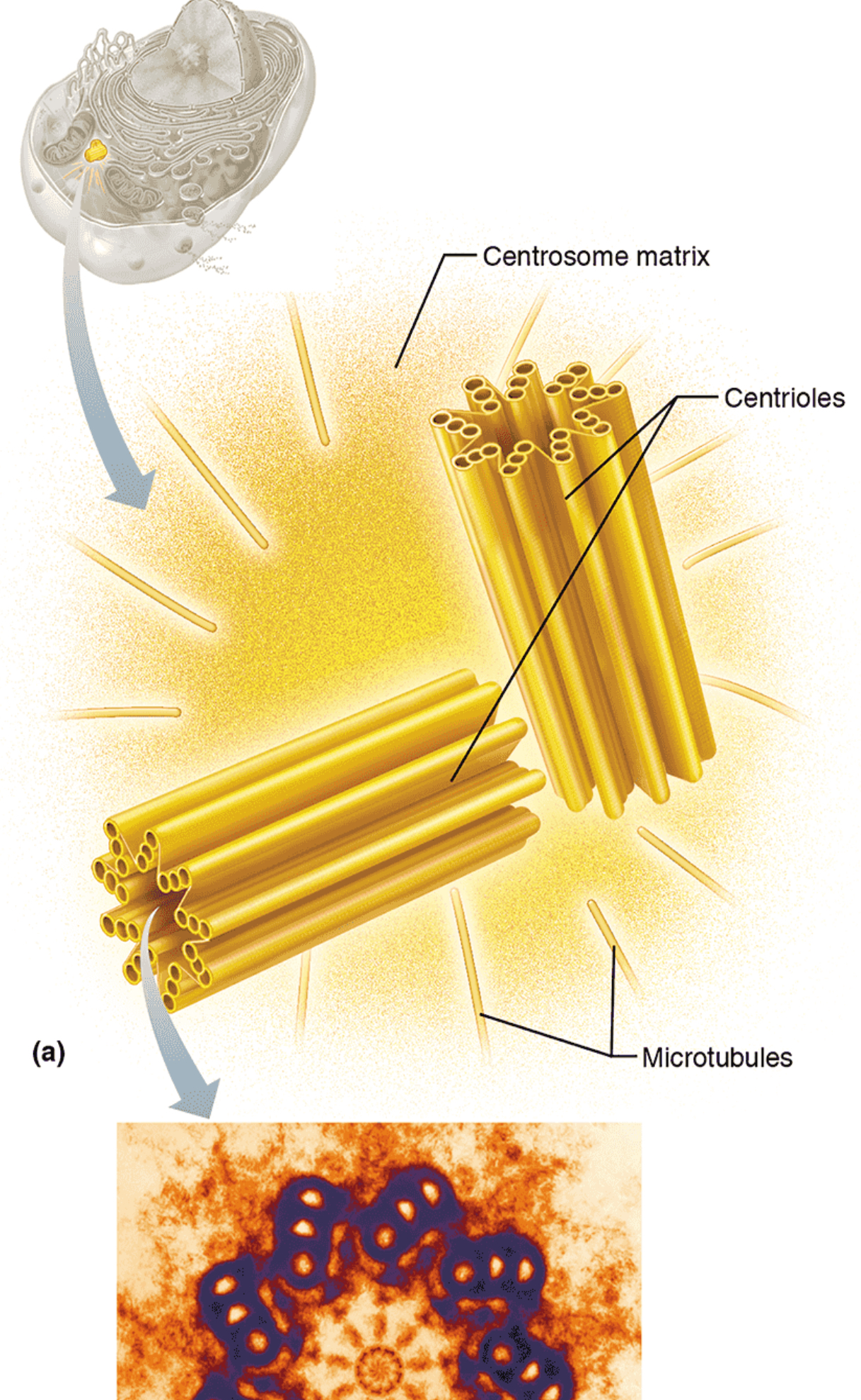
Centrioles
Structure: Paired cylindrical bodies, each composed of 9 triplets of microtubules
Function: Organize the microtubule network as part of centrosome; forms spindle and asters during mitosis; forms basis of cilia and flagella as basal bodies
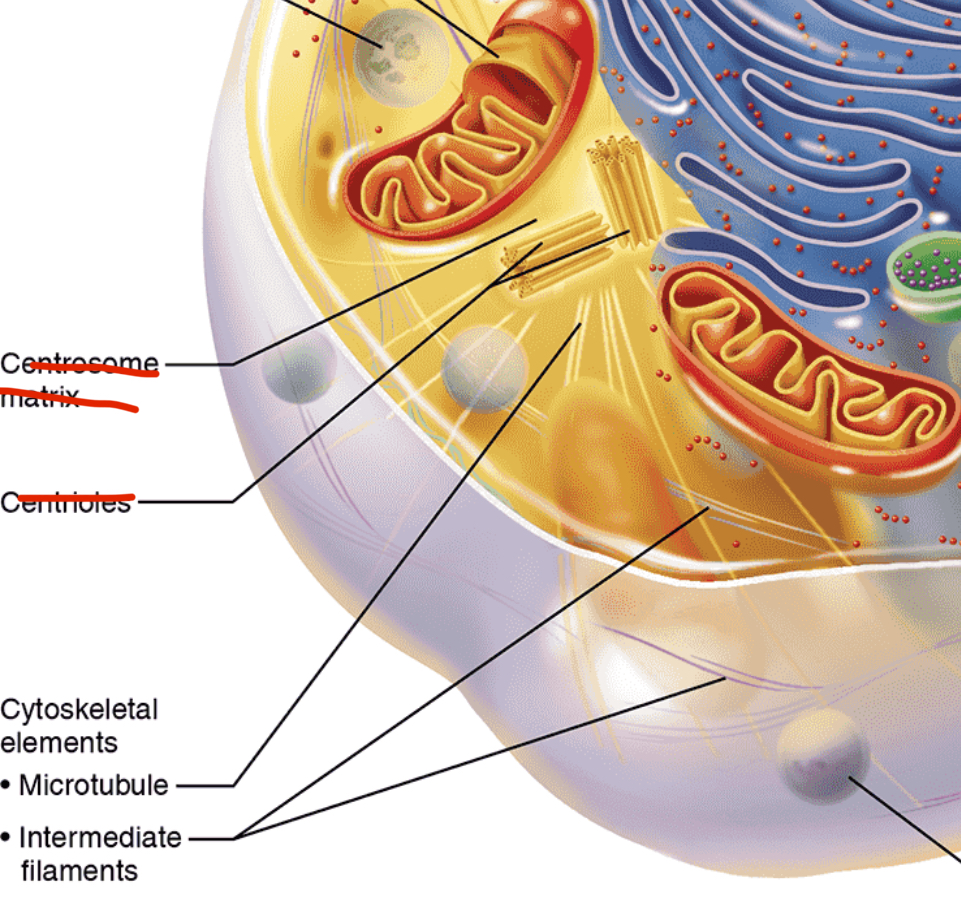
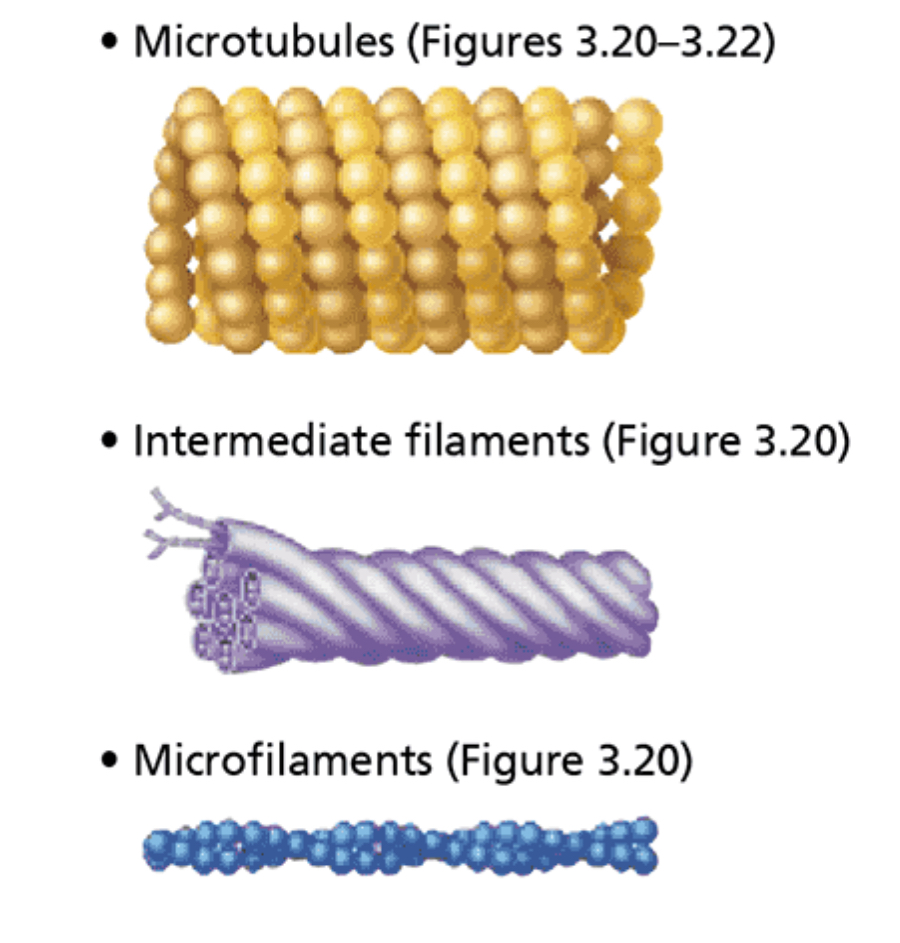
Cytoskeleton
Structure: Elaborate network of rods (microfilaments, intermediate filaments, and microtubules) running through cytosol and hundreds of accessory proteins that link these rods to other cell structures
Function: Acts as cell’s “bones,” “muscles,” and “ligaments” by supporting cell structure and providing machinery to generate various cell movements.
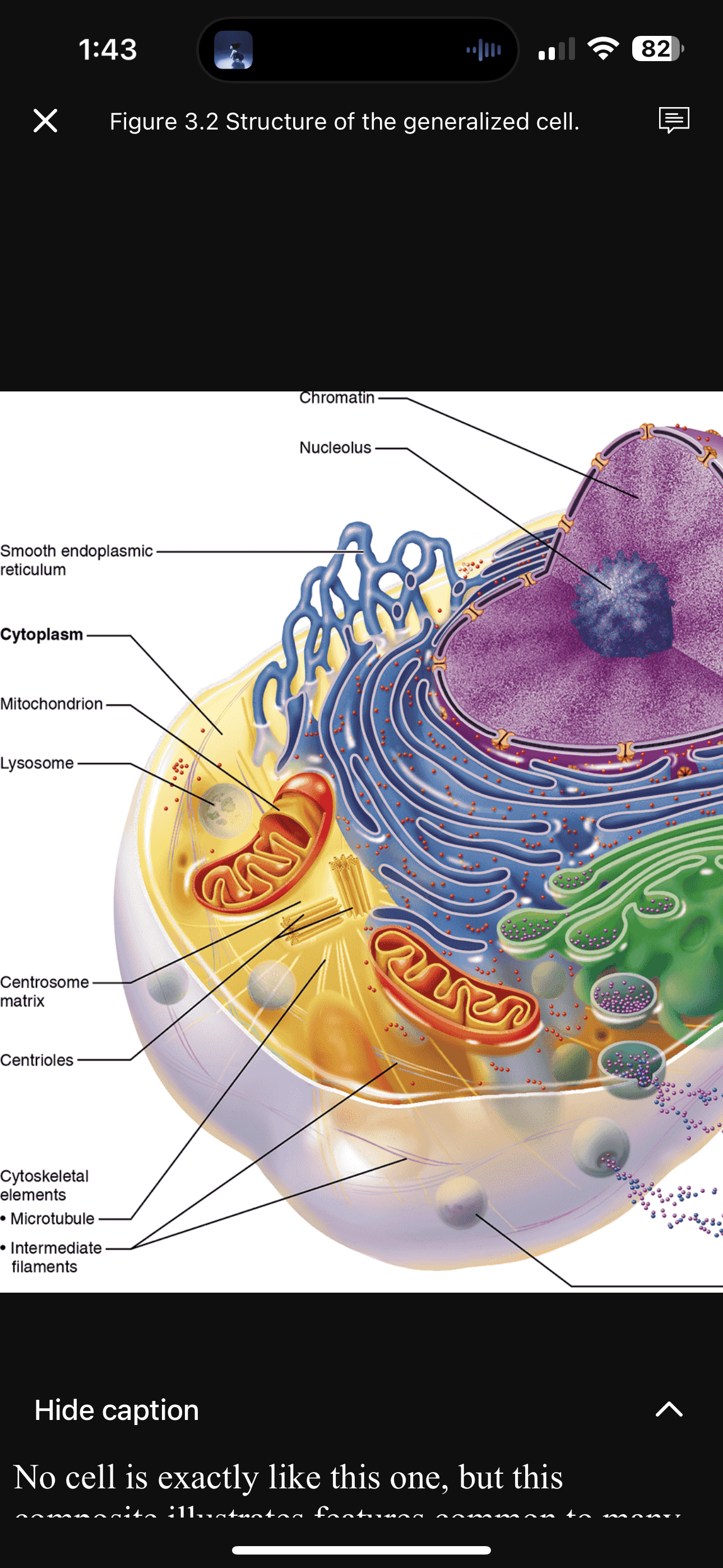
Cytoplasm
Structure: Cellular material between plasma membrane and nucleus containing cytosol, inclusions, and organelles
Function: Site of most cellular activities
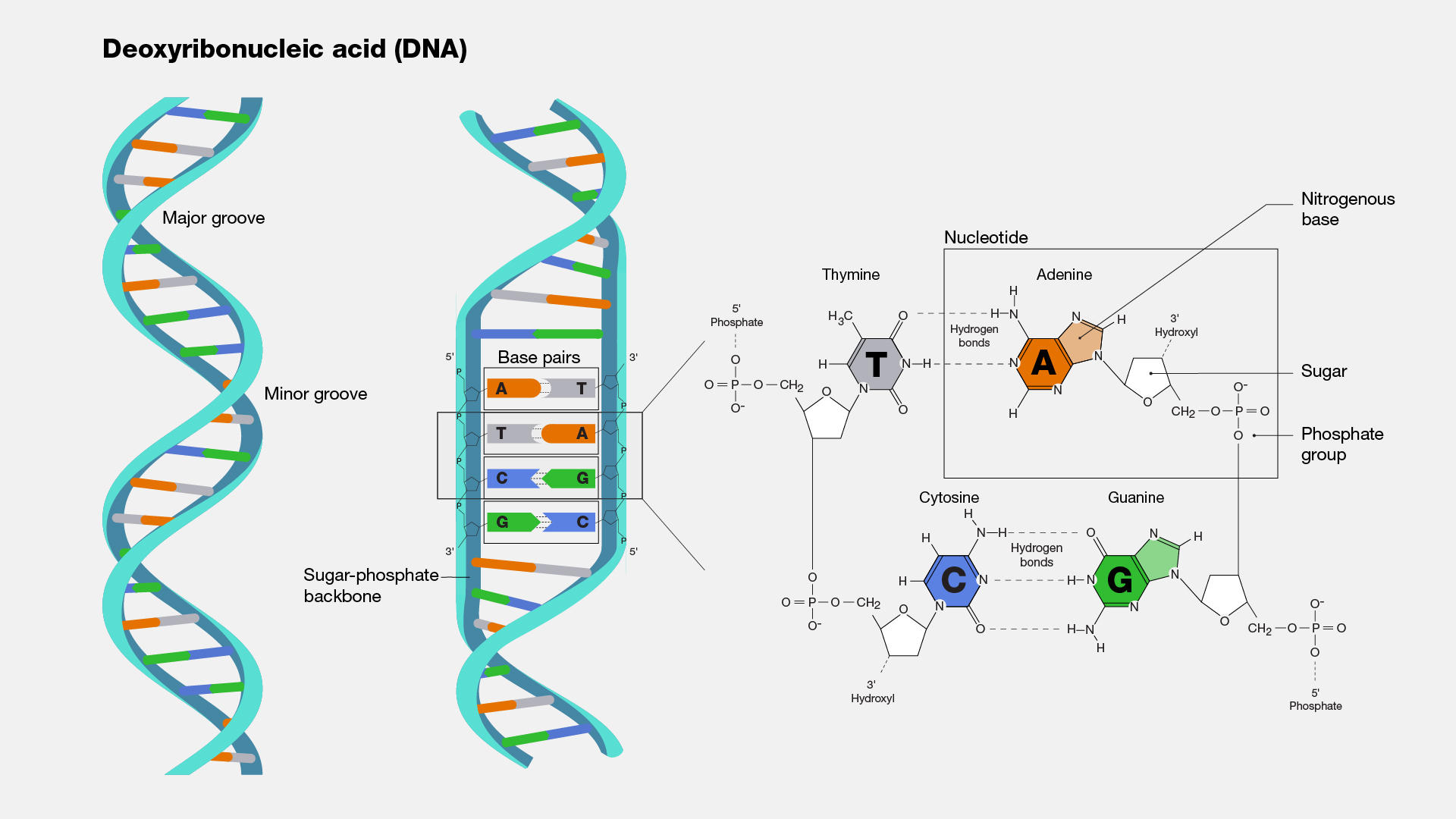
DNA
Structure: Double-helix strand made up of sugar-phosphate backbone and nucleotide base pairs, which connect the helix via hydrogen bonds to its complementary base pair
Function: Contains the instructions for protein synthesis; contains cell’s genetic information