Alex Lopez AP Psychology Review
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Acetylcholine
Muscle movement, attention, and memory
Dopamine
Reward, pleasure, motivation, and movement
Serotonin
regulates mood, sleep, and appetite.
Norepinephrine
influences attention, response actions, and stress.
GABA
Primary inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain, reduces excitability and helps to regulate anxiety.
Glutamate
The primary excitatory neurotransmitter in the brain, involved in learning and memory.
Adrenaline
neurotransmitter that increases heart rate, muscle strength, and energy supply during stress.
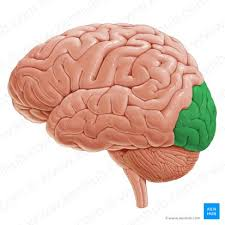
Occipital lobe; processes visual information and sight
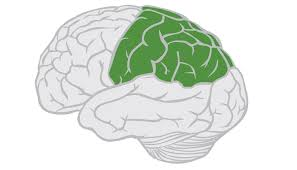
Parietal lobe; sensory processing
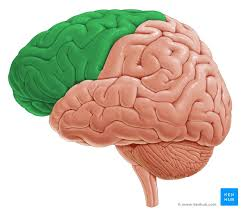
Frontal lobe; Planning, organizing, COGNITIVE, and emotional control. Broca’s area.
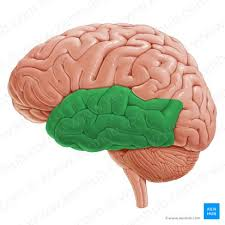
Temporal lobe; processes auditory information and memory. Wernicke’s area.
medulla
controls automatic functions like breathing heart rate etc
pons
voluntary movements/dreams
cerebellum
balance and coordination
amygdala
involved in processing emotions, particularly fear, and in forming emotional memories
EEG
a test that measures electrical activity in the brain, often used to diagnose conditions such as epilepsy or sleep disorders.
CT
uses cross sectional scans to create detailed images of internal organs and structures.
MRI
Uses magnetic fields to create detailed images of the brain and other soft tissues.
PET
Uses radioactive tracers to measure processes in the body.
fMRI
Uses magnetic fields and blood flow to create dynamic images of brain activity.
NREM Stage 1
Theta waves; Initial stage of sleep where you're easy to wake and in a dream like state
NREM Stage 2
Theta waves; A deeper sleep stage, where body temperature decreases and heart rate slows.
NREM Stage 3
Delta waves; The deepest stage of sleep, crucial for restorative processes in the body.
REM Sleep
Beta waves; A stage of sleep characterized by rapid eye movement, increased brain activity, and vivid dreams.
CNS
The central nervous system, consisting of the brain and spinal cord, responsible for processing and transmitting information throughout the body.
PNS
The peripheral nervous system, which includes all the nerves outside the central nervous system and connects the CNS to the limbs and organs.
sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system
Sympathetic is fight or flight. Parasympathetic is calming
Split brain research
Split brain research involves the study of patients who two hemispheres of the brain which cannot communicate.
Opponent-process theory
A psychological theory that suggests emotional responses to stimuli are followed by opposite emotional responses, helping to explain feelings of motivation and behavior.
Rods and cones in the eye
rods detect light and dark, while cones detect colors.
Retina
light-sensitive layer at the back of the eye that contains rods and cones responsible for converting light into neural signals.
Transduction
The process by which sensory receptors convert stimuli from the environment into neural impulses that can be interpreted by the brain.
James-Lange
Stimulus-Response-Emotion
Cannon-Bard
Emotion and Physiological response happens at the same time
Schacter-Singer
Physiological response and then cognitive interpretation leads to emotion.
Kohlberg
Preconventional, conventional
Avoid punishment, social reciprocity,take punishment if its the right thing to do,
Piaget’s
Sensorimotor, preconven, concrete op, formal
object permanence, egotism, learn conservation, abstract thinking
Erikson
Big question for each part of your life.