TOPIC 2 - Energy and voltage in circuits (Current - voltage practical and graphs in experiment notebook) (Resistor graphs in experiment notebook)
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Explain why a parallel circuit is more appropriate for domestic lighting
- If one bulb breaks, current will still be able to reach the bulbs on other branches, so the rest of the lights stay on.
- Components may be switched on/off independently.
- Bulbs maintain a similar brightness, because the potential difference is the same across all branches of a parallel circuit.
Describe the qualitative effect of changing resistance on the current in a circuit
- The current flowing through a component depends on both the resistance of the component, and the potential difference across the component.
- GREATER RESISTANCE = LOWER CURRENT for a given potential difference across the component (and vice versa.)
- This is because of the equation V=IR
Describe the qualitative variation of resistance on light - dependent resistors with illumination
The resistance of an LDR changes depending on the light intensity on it.
- As the light intensity INCREASES, the resistance of an LDR decreases (and vice versa.)
Why is current conserved at a junction in a circuit?
Current flowing into the junction is equal to the amount of current flowing out of it.
- This is because charge is CONSERVED.
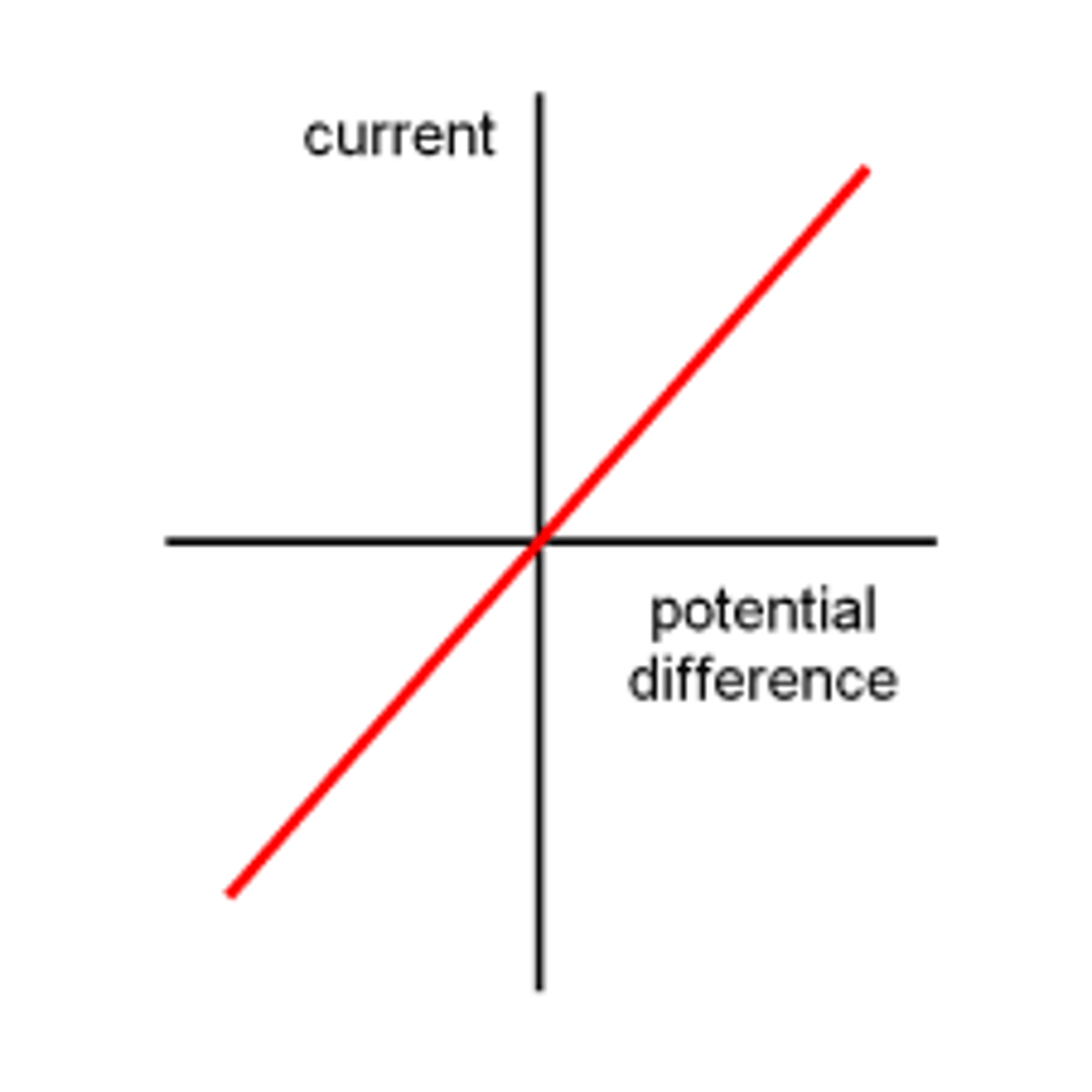
Describe how current varies with voltage in wires and resistors
At a constant temperature, current is PROPORTIONAL to voltage.
- Current increases as voltage increases.
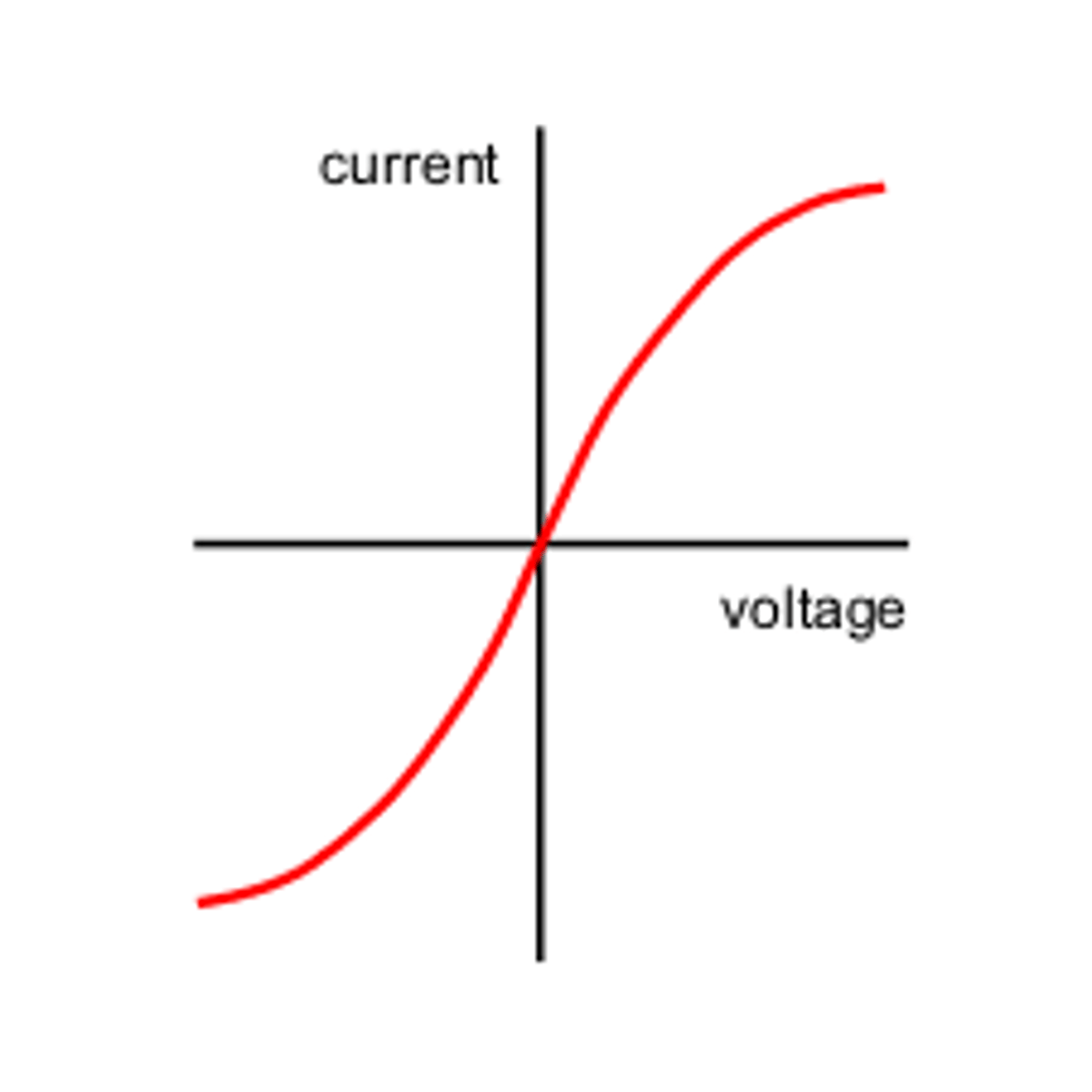
Describe how current varies with voltage in metal filament lamps
As the TEMPERATURE of the metal filament lamp INCREASES, the RESISTANCE INCREASES.
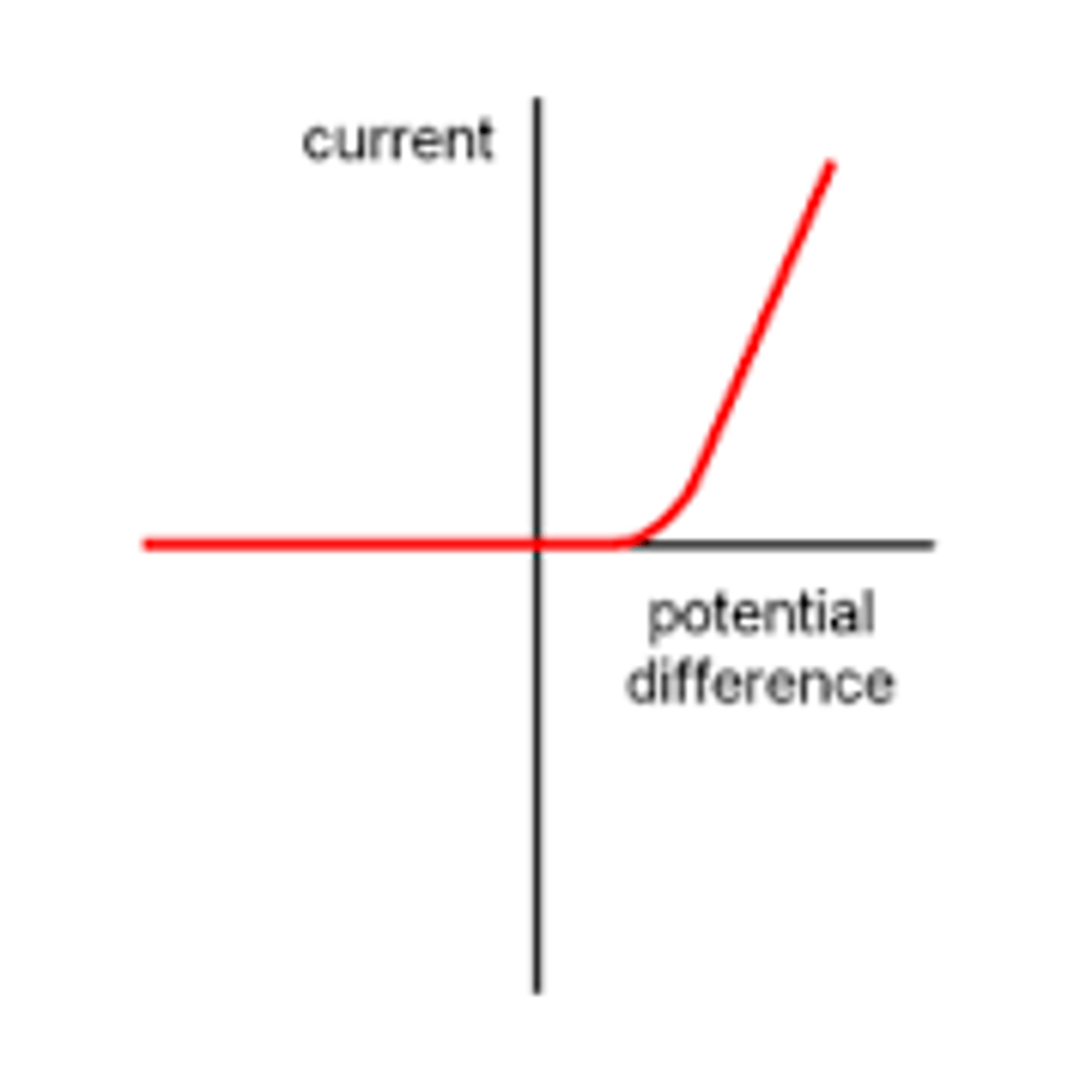
Describe how current varies with diodes
- A diode allows current to flow in only one direction (forward bias.)
- In the reverse direction, the diode has very high resistance, and therefore no current flows.
- FORWARD BIAS: Sharp increase in potential difference and current on the RIGHT side of the graph.
- REVERSE BIAS: Zero reading of current and voltage on the LEFT side of the graph.
Describe the qualitative variation of resistance on thermistors with temperature
The resistance of a thermistor changes depending on its temperature.
- As the temperature INCREASES, the resistance of a thermistor decreases (and vice versa.)
Components can be used to indicate the presence of current, such as... (2)
lamps and LED's
Equation linking voltage, current, and resistance
voltage = current x resistance
(V = I x R)
Definition of current
Current is the rate of flow of charge.
Equation linking charge, current, and time
charge = current x time
(Q = I x T)
Electric current in solid metallic conductors is a...
Flow of negatively charged electrons.
The voltage across two components in parallel is...
the SAME
Definition of voltage
- Voltage is the energy transferred per unit charge passed.
- The volt is a joule per coulomb.
Equation linking energy transferred, charge, and voltage
Energy transferred = charge x voltage
(E = Q x V)
describe how current varies with voltage in metal filament lamps
as current increases, voltage increases