3.3 - Vaginal DD
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
vaginal route local effect
used for vaginal infections, lubrication, contraception
vaginal route systemic effect
- not common route
- research ongoing
- good for highly metabolized drugs (no hepatic first pass effect)
vaginal dosage forms
liquids, semisolids, solids
liquid dosage form
douche
semisolid dosage form
creams, gels, ointments, foams
solid dosage forms
suppositories/compressed tablets (Pessary, Ovule, Insert), and film
film dosage form
- rapidly disintegrating polymer sheet
- drug uniformly dispersed and dissolved
gross anatomy of vagina
- fibromuscular tube (6-10 cm long in adult)
- extends from cervix
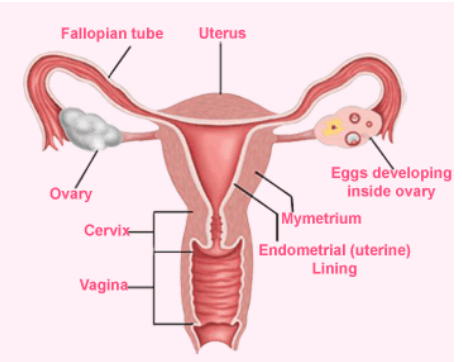
vaginal mucosa
- stratified squamous epithelium (skin-like)
- contains rugae (folds → increase SA/aid in retention)
- contains natural microflora (Lactobacilli)
vaginal epithelium
- SC has dead corneocytes
- intercellular lipids present
- does NOT form impermeable intercellular lipid envelope
- more permeable than skin SC
mucous layer of vagina
- limited amount, complex fluid
- source = cervical secretions
- contains transudates, exfoliated cells, leukocytes
pH of vagina
- generally low/acidic (due to lactic acid from Lactobacilli; bacteriostatic)
other features of the vagina
- presence of enzymes
- relatively limited SA (vs GI tract)
- venous drainage NOT to hepatic portal system (NO first pass)
Variations in Mucosa
- fluid amount/consistency varies (Menstrual cycles)
- pH is higher: age 4 wks to puberty or upon menopause
- epithelium thickness changes (thinner upon menopause)
systemic drug absroption
- good for some drugs (large molecules/peptides)
- limited for most current products
- significant interpatient variability
- affected by mucosal variations
dosage form considerations
product pH, microbial presence, attributes post-administration, administration aids
product pH
- consider natural vaginal pH (acidic)
- formulate low pH to match if possible
- important for drug solubility and stability
- avoid strong buffer capacity (allows fluids to control pH)
Microbial Prescence
- must be free of microorganisms, yeast, and molds
- do NOT disrupt natural microflora
Attributes post-administration
- retention → long enough for distribution
- liquefaction → solids must melt/dissolve rapidly
- distribution → should spread well
- spreading ranking: foams/liquids > suppositories > disintegrating tablets
- leakage → should NOT be excessive or too quick
administration aids
- applicators usually required
- supplied w/ drug product
- products often designed for high insertion
Imvexxy
- estradiol vaginal inserts
- used for moderate to severe dyspareunia
Clotrimazole Vaginal Cram and Vagistat Ointment
used in treatment of Candidasis
Cleocin Suppository and Metronidazole Vaginal Gel
used in treatment of bacterial vaginosis
Crinone gel
- used as a progesterone supplementation
- bioadhesive gel (polycarbophil)
VCF Film
- fast-dissolving polymer film (nonoxynol-9)
- used in contraception