chapter 14: autonomic nervous system
1/49
Earn XP
Description and Tags
meltzer
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
central nervous system (CNS)
brain and spinal cord
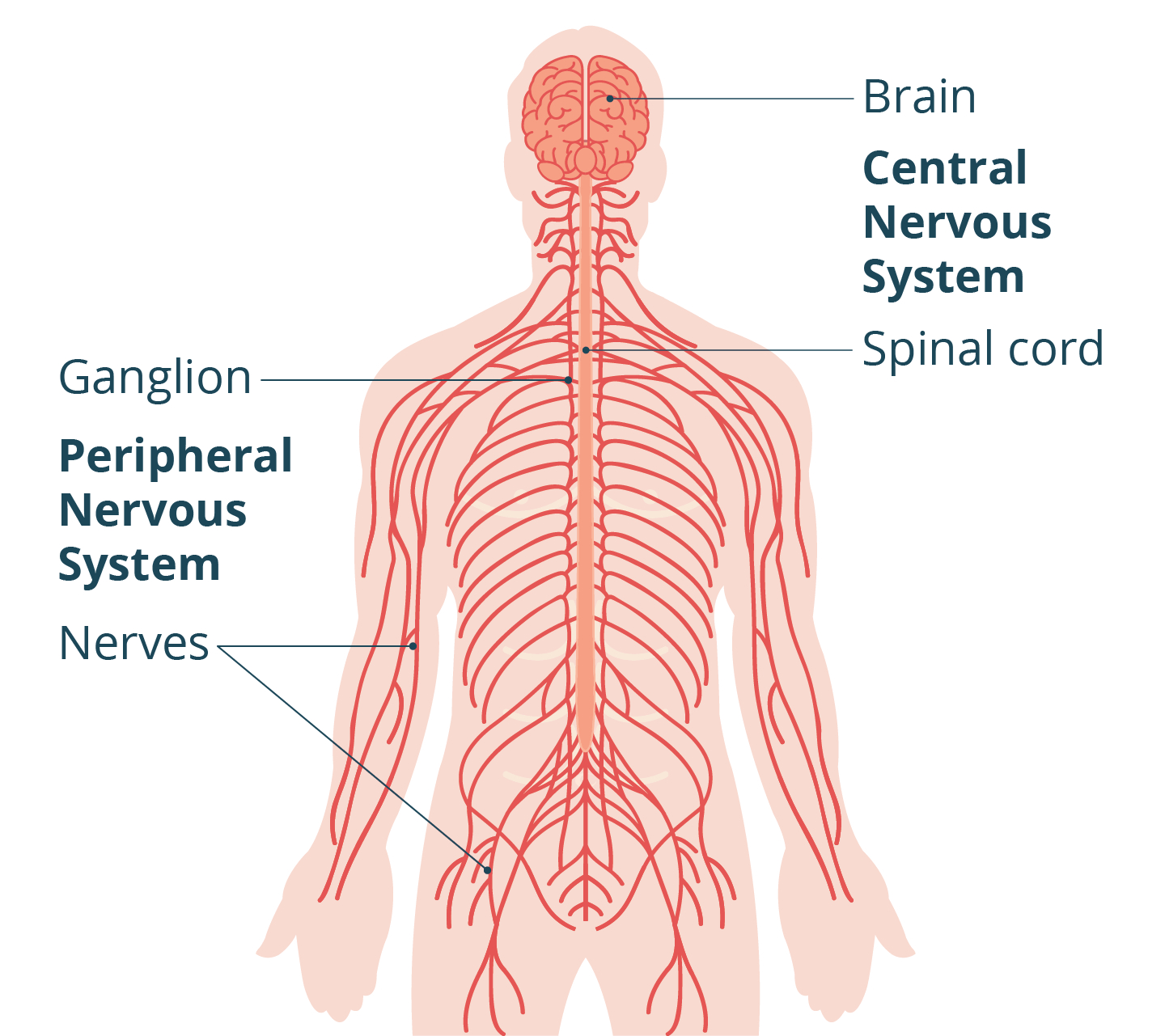
peripheral nervous system (PNS)
nerves and ganglia located outside of the brain and spinal cord
autonomic nervous system (ANS)
involuntarily controls smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands to maintain homeostasis (part of PNS)
2 divisions
somatic nervous system
cell body of motor neurons that enter CNS to ventral horn and exits through ventral root will NOT synapse and go straight to target organ
acetylcholine (ACh)
transmitter released by neurons
autonomic nervous system: sympathetic division
two-neuron system
pre-ganglionic sympathetic neuron exciting CNS is SHORT
makes ACh and goes onto post-ganglionic sympathetic neuron
post-ganglionic sympathetic neuron is very LONG & goes all the way to target organ
makes NE and goes onto target organ
NE (norepinephrine)
also known as adrenaline, neurotransmitter released by neurons
autonomic nervous system: sympathetic exception
only one neuron
pre-ganglionic sympathetic neuron that goes to adrenal gland
releases ACh on specialized cells in middle of gland (adrenal medulla)
modified cells then release epinephrine & norepinephrine (neurohormones) into blood
very fast and widespread response is based on..
going to the blood or
the type of receptor on organ for the neurotransmitter
receptor type
determines weather the muscles of cardiac and smooth will be excitatory or inhibitory
skeletal muscle
is excitatory only
autonomic nervous system; parasympathetic division
two-neuron system
pre-ganglionic parasympathetic neuron that exits spinal cord is very very LONG
releases ACh onto post-ganglionic neuron
ganglion oftentimes on surface of target organ
post-ganglionic parasympathetic neuron is very SHORT
releases ACh onto target organ
three D’s of parasympathetic division
body processes that happen at rest:
Digestion
Defecation
Diuresis (urine)
sympathetic
flight vs. flight
mobilizes energy stores
parasympathetic anatomy: craniosacaral division
goes to target organs by the cranial region/lower brain stem or sacral region/sacral nerves
parasympathetic anatomy of cranial region
ACh released onto…
eyes → pupillary constriction
salivary glands → boosts saliva production
vagus nerve → decreases (heart) rate
→ slight bronchial constriction (lungs)
→ increases contraction, mobility, production of digestive juices (stomach)
→ boosts digestive enzyme production and releases (pancreas)
→ boosts production of bile (liver)
→ contracts & expels bile into GI tract & relaxation if sphincters (gall bladder)
→ inhibit blood flow to labia, penis, clit and addition mucous and lube (genitalia)
parasympathetic anatomy of sacral region
Ach released onto…
bladder → increase contractile activity
genitalia → sexual arousal: increases production of mucus/lubricants, vasodilation of blood vessels to engorge penis, clit, labia, etc
sympathetic anatomy (thoracolumbar division)
travel to organs by blood vessels, exits spinal cord through thoracic regions or upper lumbar regions
sympathetic anatomy of neurons
all pre-ganglion neurons are SHORT, then immediately synapse in sympathetic ganglion chain
sympathetic ganglion chain
sense of ganglion that are adjacent on either side of spinal cord that allow for communications up & down
sympathetic anatomy thoracic region
T1 pre-ganglionic neuron exits, then synapses
post-ganglionic neuron could go to lungs or ride sympathetic ganglion chain with blood vessels to the eyes or skin
long post-ganglionic sympathetic neuron to salivary glands
sympathetic anatomy lumbar region
NE released onto…
eyes → pupillary dialation
skin → sweating & hair rising (ACh released by SNS onto sweat glands)
heart → increase heart rate
lungs → bronchodilation
stomach →inhibits digestion
blood → to everything!
liver → inhibits
bladder → bladder contraction & keep sphincter closed
genitalia → inhibit blood flow
adrenal glands → causes release of more catecholamines
salivary glands → inhibit (dry mouth)
kidney → stop making urine
catecholamines
norepinephrine and epinephrine
arrector pilae
muscles on base on each hair of skin (caused goosebumps)
parasympathetic cranial nerves
CN III. 3. oculomotor: pupillary construction
CN VII. 7. facial: PS info to lining of nasal cavity to keep moist of mucous, maintence of eye protection by lacrimal gland, and salivary glands
CN IX. 9. glossopharyngeal: goes to parotid gland for saliva in mouth while chewing
CN X. 10. vagus: stomach, pancreas, GI tract turns on, intestines get increased mobility, physical contractions, peristalsis, moving things along + mixing things up, boosts production of digestive juices
vertebral level of L1 and L2
PS info exits spinal cord into sacral region of nerves: S2, S3, S4 nerves
pelvic splanchnic nerves
goes to rest of the organs of pelvis
S2, S3, S4
menstruation
parasympathetic nervous system
defecation
parasympathetic
adrenic receptors
recognize catecholamines (Ne and epinephrine)
on surface of all organs controlled by sympathetic NS
sympathetic nervous system anatomy
spinal cord located behind thoracic vertebrae
two new rami
white ramus communicates
gray ramus communicants
two new rami in sympathetic nervous system that only carry sympathetic axons to sympathetic chain/trunk
3 different pathways
Spinal nerve pathway
Sympathetic nerve pathway
Splanchnic nerve pathway
Spinal nerve pathway
Synapse at the same level
Preganglionic fiber enters the sympathetic chain
Synapses in a ganglion at the same spinal level
Postganglionic fiber exits via gray ramus communicans
Goes to body wall structures (sweat glands, arrector pili muscles, blood vessels)
ex. arrector pili muscles & sweat glands of skin
Sympathetic nerve pathway
Ascend or descend, then synapse
Preganglionic fiber enters the sympathetic chain
Travels up or down the chain
Synapses at a different level
Postganglionic fiber exits to target
ex. smooth muscle of blood vessels
Splanchnic nerve pathway
Pass through without synapsing (splanchnic pathway)
Preganglionic fiber passes through sympathetic chain
Forms splanchnic nerves
Synapses in prevertebral (collateral) ganglia
Targets abdominal and pelvic organs
ex. gi tract
medullary chromosphere cells
postganglionic neurons modified by ACh
make norepinephrine & epinephrine
pheochromocytoma
tumor of medullary chromophere cells
visceral reflexes
receptor in viscera
visceral sensory neuron
integration center: preganglionic neuron, dorsal horn
motor neuron: both post & pre
visceral effector
cholinergic & adrenergic receptors
receptors that recognize chemicals
cholinergic receptors
receptors that recognize acetylcholine (ACh)
nicotinic
muscarinies
nicotinic receptors
type of cholinergic receptors that are located in skeletal muscles and cell bodies of postganglionic neurons on ANS
muscarinies receptors
everywhere else in ANS, all PS organs, some sympathetic organs
adrenergic receptors
receptors that recognize norepinephrine and epinephrine released by adrenal medulla
Beta 1 (B1)
heart → increases heart rate
Beta 2 (B2)
lungs
Beta 3 (B3)
fat → breakdown of adipose/fat cells
Alpha 1 (a1)
blood vessels → constricts except skeletal muscles, heart, & brain
Alpha 2 (a2)
moderates how much NE release there is (moderator of sympathetic activity)
how ANS is controlled
brain:
hypothalamus: communicates up and down w limbic system and cerebral cortex involved, and communicates down and controls ANS and endocrine system
brain stem: hypothalamus controls primatial functions like pupil size, heart, blood pressure etc by nuclei and neurons
spinal cord: reflexes for urinarion, defecation, erection, and ejaculation