ECO 202 Module 3: Interaction of Supply and Demand
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
perfectly competitive market (model)
market with:
many buyers and sellers
all firms selling identical products
no barriers to new firms entering the market
market demand
the demand by all consumers of a given good or service
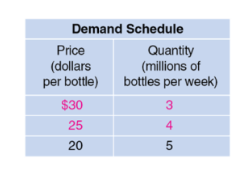
demand schedule
table that shows the relationship between the price of a product and the quantity of the product demanded
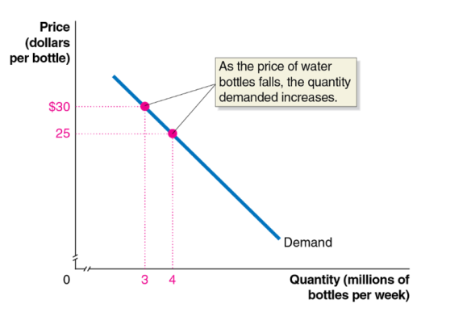
demand curve
a curve that shows the relationship between the price of a product and the quantity of the product demanded
affected by factors other than price
quantity demanded
amount of a good or service that a consumer is willing and able to purchase at a given price
affected by changes in price
law of demand
a rule that states, holding everything else constant, when the price of a product falls, the quantity demanded of the product will increase, and when the price of a product rises, the quantity demanded of the product will decrease
when the price of a good falls…
1) consumers substitute toward the good whose price has fallen
2) consumers have more purchasing power, which is like an increase in income
substitution effect
the change in the quantity demanded of a good that results from a change in price, making the good more or less expensive relative to other goods, holidng constant the effect of the price change on consumer purchasing power
income effect
the change in the quantity demanded of a good that results from the change in the good’s price on a consumer’s purchasing power, holding all other factors constant
purchasing power
the quantity of goods a consumer can buy with a fixed amount of income
ceteris paribus (“all else equal'“) condition
the requirement that when analyzing the relationship between two variables - such as price and quanitity demanded - other variables must be held constant
shifting the demand curve
a change in something other than price that affects demand causes the entire demand curve to shift
shift to the right is an increase in demand, shift to the left is a decrease in demand
when the demand curve shifts, quantity demanded will change, even if the price doesn’t change
quantity demanded changes at every possible price
variables that shift market demand
income: an increase in income increases demand if the product is normal, and decreases demand if the product is inferior
prices of related goods: an increase in the price of related goods increases demand if products are substitutes, and decreases demand if products are complements
tastes
population and demographics
expected future prices
natural disasters and pandemics
normal good
a good for which the demand increases as income rises and decreases as income falls
ex) new clothes, resaurant meals, vacations
inferior good
a good for which the demand increases as income falls and decreases as income rises
ex) second-hand clothes, instant noodles
substitutes
goods and services that can be used for the same purpose
ex) Big Mac and Whopper, Ford F150 and Dodge Ram, reusable water bottles and bottle spring water
complements
goods and services that are used together
ex) Big Mac and McDonald’s fries, left shoes and right shoes, resuable water bottles and gym memberships
changes in tastes
if consumers’ tastes change, they may buy more or less of the product
ex) influencers successfully advertise reusable water bottles, changing tastes, and increasing demand
changes in demographics
demographics are the characteristics of a population with respect to age, race, and gender
ex) an increase in the elderly population increases the demand for medical care
changes in expectations about future prices
consumers decide which products to buy and when to buy them
future products are substitutes for current products
an expected increase in the price tomorrow increases demand today
an expected decrease in the price tomorrow decreases demand today
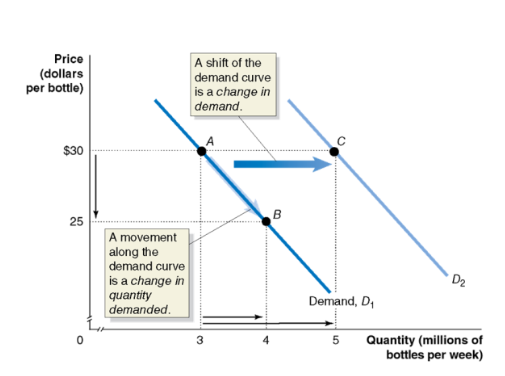
change in demand vs change in quantity demanded
a change in the price of the product being examined causes a movement along the demand curve — this is a change in quantity demanded
any other change affecting demand causes the entire demand curve to shift — this is a change in demand
market supply
the decisions of (generally) firms about how much of a product to provide at various prices
supply schedule
a table that shows the relationship between the price of a product and the quantity of a product supplied
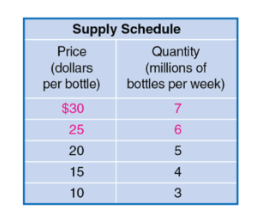
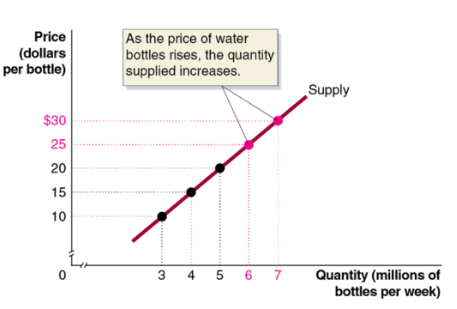
supply curve
a curve that shows the relationship between the price of a product and the quantity of a product supplied
quantity supplied
the amount of a good or service that a firm is willing and able to supply at a given price
law of supply
a rule that states that, holding everything else constant, increases in price cause increases in the quantity supplied, and decreases in price cause decreases in the quantity supplied
shifting the supply curve
a change in something other than price that affects supply causes the entire supply curve to shift
a shift to the right is an increase in supply and a shift to the left is a decrease in supply
as the supply curve shifts, the quantity supplied will change, even if the price doesn’t change
the quantity supplied changes at every possible price
variable that shift market supply
price of inputs
technological change
prices of related goods in production
number of firms in the market
expected future prices
natural disasters and pandemics
inputs
anything used in the production of a good or service
an increase in the price of an input decreases the profitability of selling the good, causing a decrease in supply
a decrease in the price of an input increases the profitability of selling the good, causing an increase in supply
technological change
positive or negative change in the ability of a firm to produce a given level of output with a given quantity of inputs
a new, more efficient way of producing water bottles would increase their supply
governmental restrictions on how much workers are allowed to work might decrease the supply of water bottles
prices of related goods in production
many firms can produce and sell alternative products: substitutes in productions
ex) farmer can plant either corn or soybeans. if the price of soybeans rises, that farmer will plant (supply) less corn
sometimes two products are necessarily produced together: complements in production
ex) cattle provide both beef and leather. an increase in the price of beef encourages cattle farming, which increases the supply of leather
number of firms and expected future prices
more firms in the market will result in more products available at a given price (greater supply). fewer firms mean supply decreases
if a firm anticipates that the price of its product will be higher in the future, it might decrease its supply today in order to increase it later
change in supply vs change in quantity supplied
a change in the price of the product being examined causes movement along the supply curve — this is a change in quantity supplied
any other change affecting supply causes the entire supply curve to shift — this is a change in supply
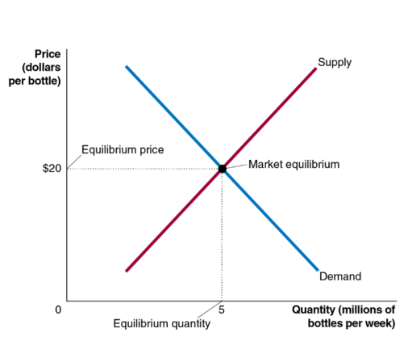
market equilibrium
situation in which quantity demanded equals quantity supplied
at a price of $20, consumers want to buy 5 million water bottles per week and producers want to sell 5 million water bottles per week
equilibrium price is $20 and equilibrium quantity is 5 million, we do not expect the price to change
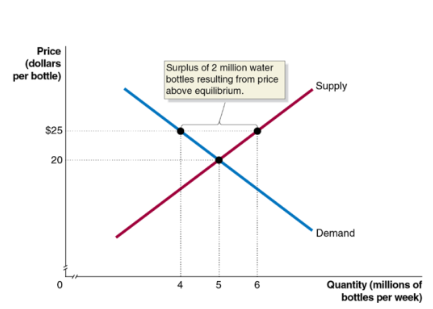
surplus
a situation where quantity supplied is greater than quantity demanded
at a price of $25, consumers want to buy 4 million water bottls and producers want to sell 6 million water bottles
this gives us a surplus of 2 million water bottles
prediction: sellers will compete among themselves, driving the price down
shortage
a situation in which the quantity demanded is greater than the quantity supplied
at a price of $10, consumers want to buy 7 million water bottles and producers want to sell 3 million
this gives us a shortage of 4 million water bottles
prediction: sellers will realize they can increase the price and still sell as many water bottles, so the price will rise
demand and supply both count
price is determined by the interaction of buyers and sellers
neither group can dictate price in a competitive market
however, changes in supply and/or demand will affect the price and quantity traded
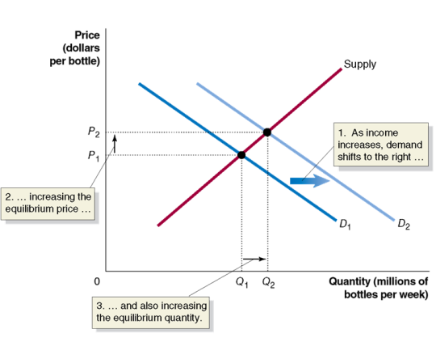
effect of an increase in demand on equilibrium
suppose income increases, water bottles are a normal good, so as income rises:
demand shifs to the right
equilibrium price rises
equilibrium quantity rises
effect of an increase in supply on equilbirum
suppose a new producer enters the market, so more water bottles can be supplied at any given price
supply increases - shifts to the right
equilibrium price falls
equilibrium quantity rises

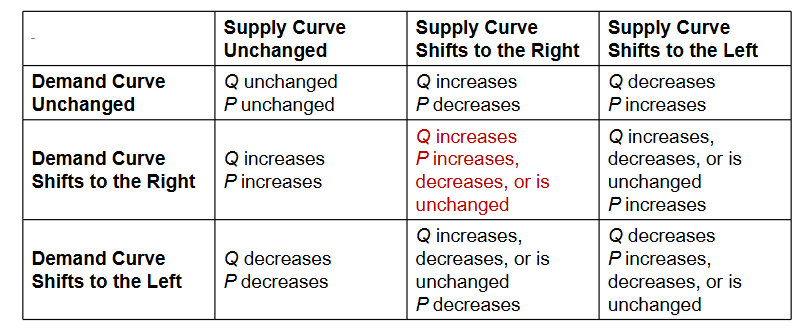
how shifts in demand and supply affect equilibirum price and quantity
when both curves move, we need to know the relative size of the changes to know the effects on equilibirum price and quantity