Bio 131 Chapter 34 Plants
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/106
Last updated 9:51 PM on 2/5/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
107 Terms
1
New cards
2 basic systems to help plants get resources
root and shoot system
2
New cards
root+ shoot systems=
plant body
3
New cards
vascular tissue
connects the root and shoot system
h20 and nutrients are transported from roots to shoots
sugars go in both directions
h20 and nutrients are transported from roots to shoots
sugars go in both directions
4
New cards
importance of a large sa/vol ratio
more absorption area allows for more photosynthesis and uptake of nutrients
5
New cards
taproot
large vertical main root of plant’s root system
6
New cards
axis of a plant (from bottom to top)
basal to apical
7
New cards
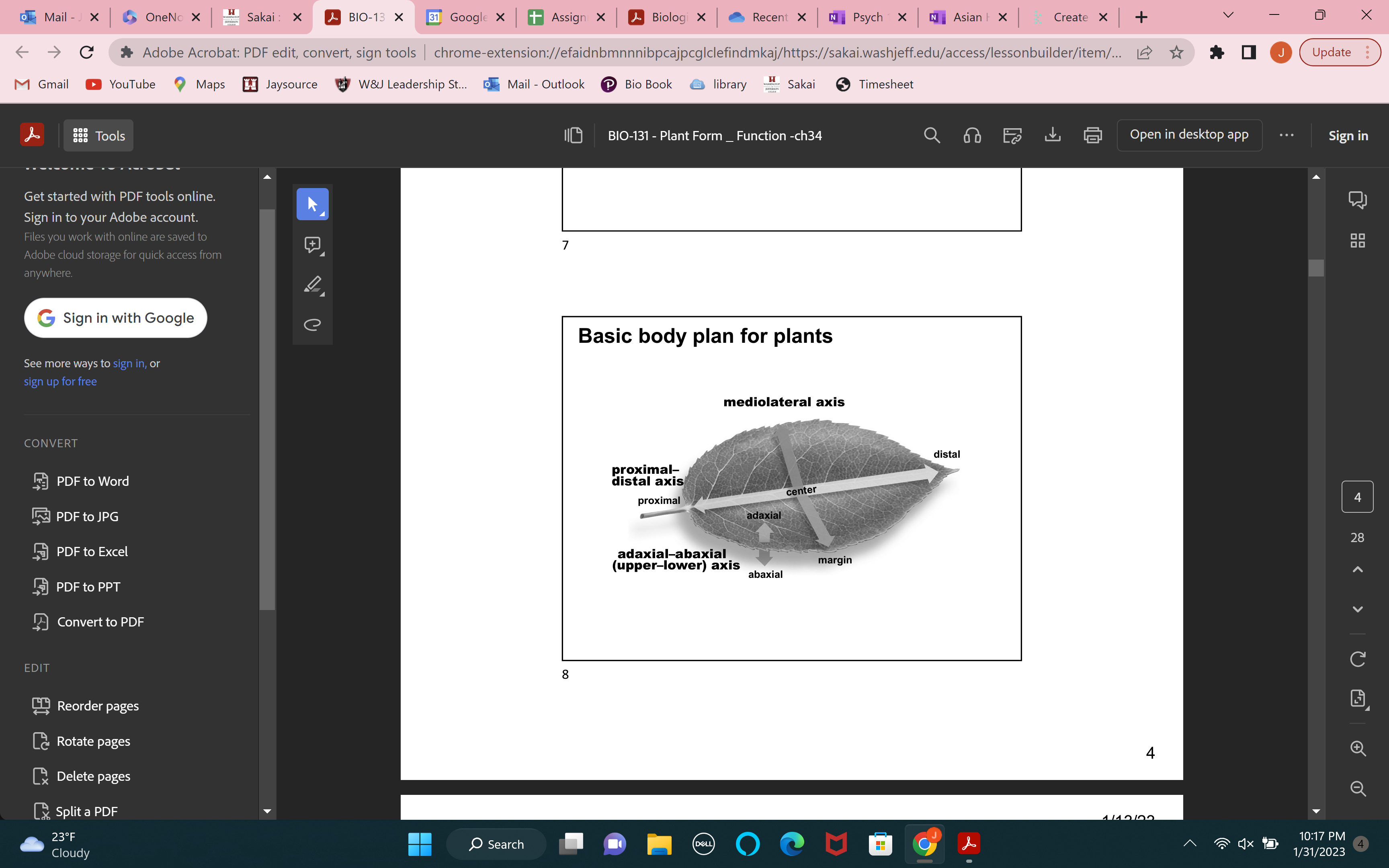
3 leaf axis
proximal-distal (stem to the tip of the leaf)
mediolateral axis (margin is on the other side)
adaxial-abaxial axis (adaxial-upper side abaxial- bottom side)
mediolateral axis (margin is on the other side)
adaxial-abaxial axis (adaxial-upper side abaxial- bottom side)
8
New cards
lateral roots
plant root that extends horizontally from another root
9
New cards
herbaceous plants
seed plants that lack woody tissue
10
New cards
perennial
live for many years
11
New cards
phenotypic plasticity
form changeable due to environmental conditions
12
New cards
adventitious
roots that develop from the shoot system instead of the root system
13
New cards
pneumatophores
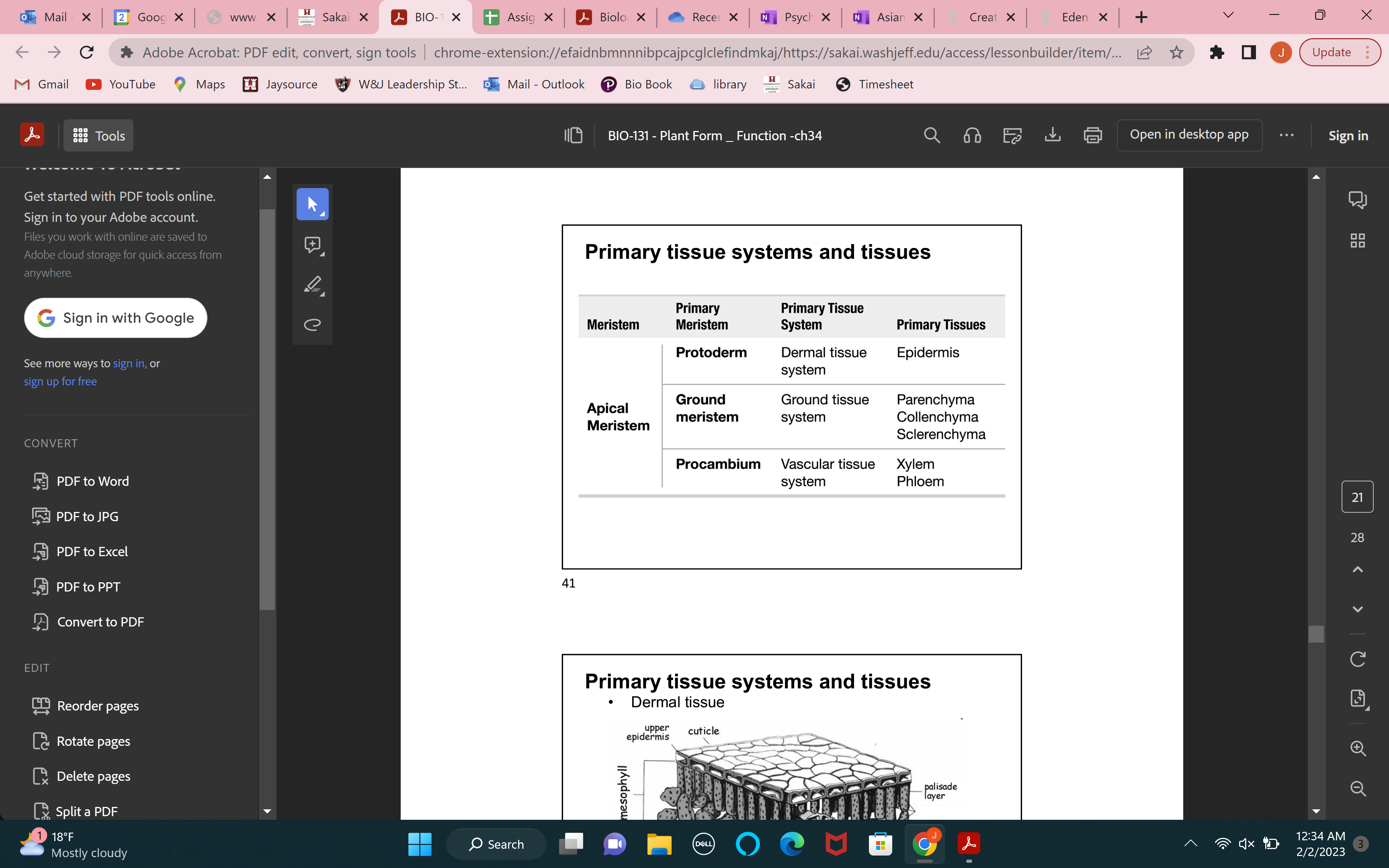
allow gas exchange between roots and atmosphere, lateral roots grow upward due to gravity
14
New cards
stem
vertical aboveground structure made up of nodes
15
New cards
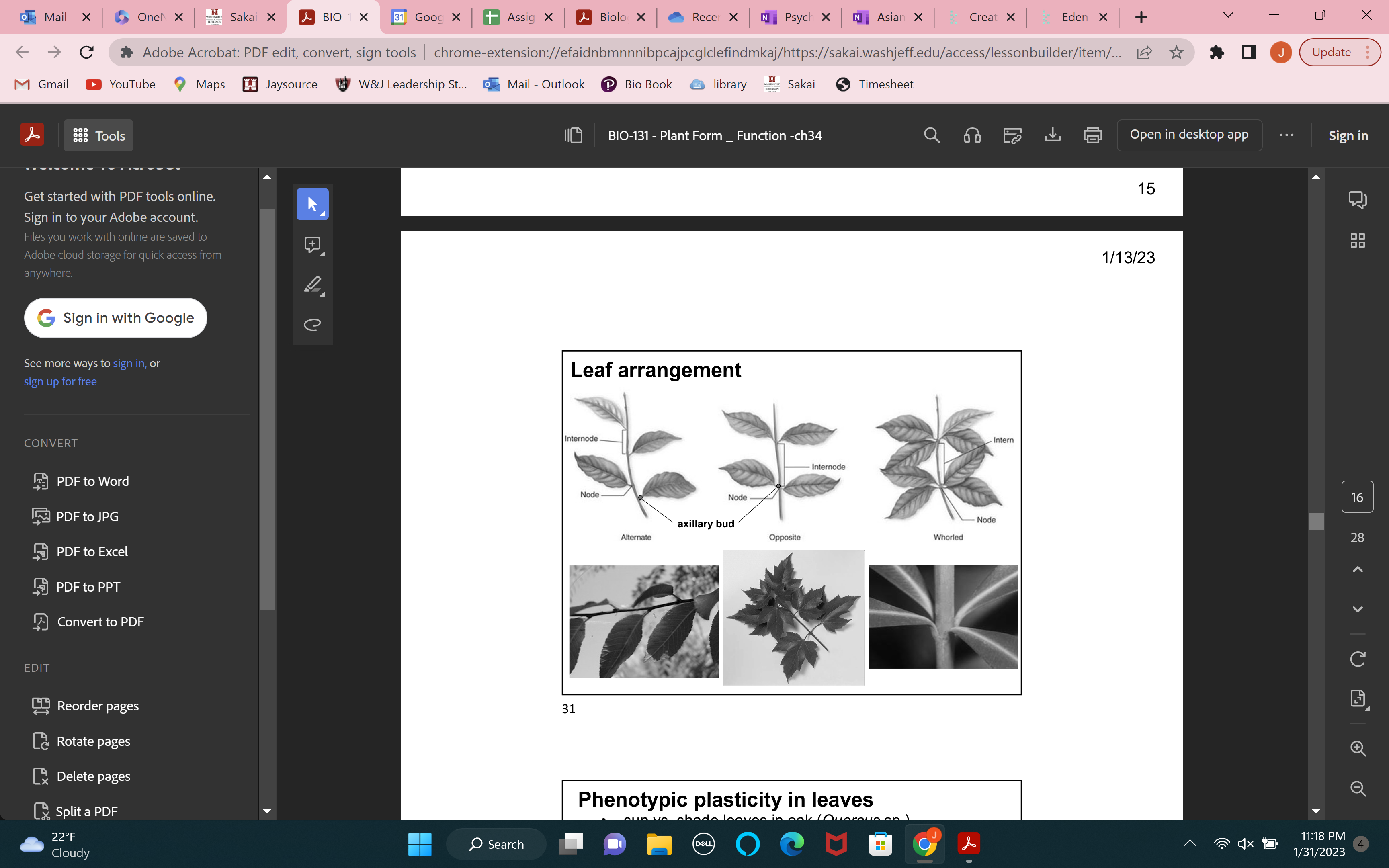
nodes
where leaves attached
16
New cards
internodes
spaces between the nodes
17
New cards
leaf
appendage that projects from a stem laterally and functions as a photosynthetic organ
18
New cards
axillary or lateral bud
nodes where leaves attach to the stem
site of leaf attachment
have dormant meristematic stems
site of leaf attachment
have dormant meristematic stems
19
New cards
branch
a lateral extension of a shoot system
if conditions right grow from axillary bud
if conditions right grow from axillary bud
20
New cards
apical bud
tip of each stem and branch contains this where growth occurs that extends the length of the stem or branch
21
New cards
flowers
reproductive structures that form at the apical or axillary buds if conditions are right
22
New cards
the leaf 2 parts
the stalk- petiole
expanded portion-blade
expanded portion-blade
23
New cards
the leaf function
absorb photons and supports photosynthesis
24
New cards
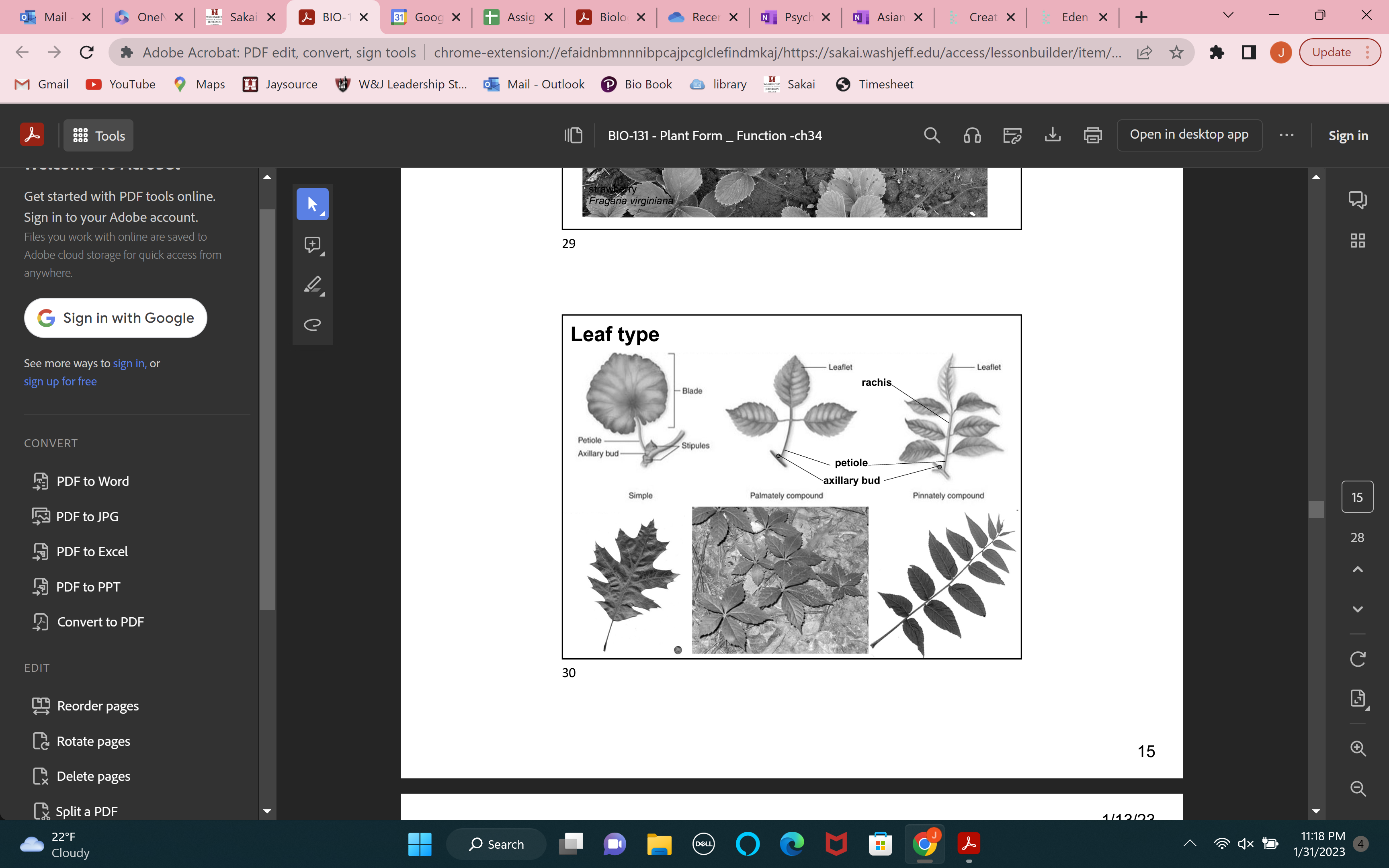
leaf type
25
New cards
leaf arrangement
26
New cards
compound leaves
blades divided into a series of leaflets
27
New cards
transpiration
loss of h2o vapor from above ground plants parts primarily through the stomata
28
New cards
sun leaves vs shade leaves in oak trees
sun leaves- thicker relatively smaller sa which reduces h2o loss in areas with lots of light
shade leaves- thin board high sa to get photons h20 loss less of a problem
shade leaves- thin board high sa to get photons h20 loss less of a problem
29
New cards
features common in all plants
primary cell wall some have a secondary cell wall
plasmodesmata
chloroplasts or plastids
vacuoles
plasmodesmata
chloroplasts or plastids
vacuoles
30
New cards
plasmodesmata
physical connections between 2 plant cells consisting of membrane lined gaps in the cell walls in which the cells plasma membrane’s cytoplasm and smooth er can directly connect
31
New cards
plastids
in almost all plants
precursor/related to chloroplasts
precursor/related to chloroplasts
32
New cards
tissue
group of cells that function as a unit
33
New cards
simple tissue
plant tissues that consist of a single cell type
34
New cards
complex tissues
tissues that contain several types of cells
35
New cards
tissue system
grouped based on structural features and location in the plant
36
New cards
the dermal tissue system
consists of dermal tissue also called the epidermis outermost layer of cells represents the interface between the organism and the external environment
function in shoots- protect the plant from h2o loss, disease causing agents, herbivores
function in roots- absorb h20 nutrients
epidermis made of several diff cell types complex tissue
function in shoots- protect the plant from h2o loss, disease causing agents, herbivores
function in roots- absorb h20 nutrients
epidermis made of several diff cell types complex tissue
37
New cards
how exactly do epidermal cells protect the surface and functions of this thing
secrete cuticle
cuticle-waxy layer that forms a continuous sheet on surface of stems and leaves
reduces h2o lose by evaporation
forms a barrier to protect plants from viruses bacteria spores and fungi
cuticle-waxy layer that forms a continuous sheet on surface of stems and leaves
reduces h2o lose by evaporation
forms a barrier to protect plants from viruses bacteria spores and fungi
38
New cards
problem with the cuticle
waxes in cuticles can be bad by reducing gas exchange needed for photosynthesis solved by stomata
39
New cards
stomata
typically found on leaves pores that allow co2 to enter o2 to exit
40
New cards
guard cells
change shape to open or close the stomata
dermal tissue
dermal tissue
41
New cards
trichomes
hairlike appendages made up of specialized epidermal cells
found in shoot systems and come in a wide range of shapes size abundance
\
found in shoot systems and come in a wide range of shapes size abundance
\
42
New cards
trichomes function
1 keep the leaf surface cool by reflecting sunlight
2 reduce h20 loss by forming a dense mat that limits transcription
3 provide barbs or store toxic compounds that thwart herbivores
4 trap or digest insects
2 reduce h20 loss by forming a dense mat that limits transcription
3 provide barbs or store toxic compounds that thwart herbivores
4 trap or digest insects
43
New cards
the ground tissue system
responsible for most of the synthesis and storage of specialized products such as colorful pigments hormones and toxins required for defense
play a large role in structural support of the shoot system
3 diff. types parenchyma collenchyma sclerenchyma
play a large role in structural support of the shoot system
3 diff. types parenchyma collenchyma sclerenchyma
44
New cards
parenchyma tissue
composed of parenchyma cells have relatively thin primary cell walls most common and versatile
alive and totipotent (can divide
has to do most of the work so it has chloroplasts
important in healing wounds and reproducing asexually
alive and totipotent (can divide
has to do most of the work so it has chloroplasts
important in healing wounds and reproducing asexually
45
New cards
callus
mass of undifferentiated cells
46
New cards
collenchyma
characterized by an unevenly thickened primary cell wall longer and thinner than parenchyma cells
simple tissue
resilient support alive thickened primary cell wall totipotent
not rigid allows it to flex in the wind
provide flexible structural support for shoots
simple tissue
resilient support alive thickened primary cell wall totipotent
not rigid allows it to flex in the wind
provide flexible structural support for shoots
47
New cards
sclerenchyma
tissue characterized by the presence of the thick rigid secondary cell wall in addition to relatively thin primary cell wall
stiff support
dead at maturity
rigid support and secondary cell wall
once they are functional they are dead
stiff support
dead at maturity
rigid support and secondary cell wall
once they are functional they are dead
48
New cards
what does sclerenchyma secondary cell wall contain
lignin and cellulose
49
New cards
2 types of sclerenchyma cells
fibers and sclereids
50
New cards
fibers
extremely elongated important for paper and fabric production
51
New cards
sclereids
relatively short have variable shapes and often function in protection why pears are gritty
52
New cards
the vascular tissue system
vascular tissue system functions in support and in long distance transport of h20 and dissolved nutrients in vascular plants moves the products of photosynthesis that are made and stored in ground tissue
53
New cards
vascular system made of 2 types of complex tissues
xylem and phloem
54
New cards
xylem
conducts h20 and dissolved nutrients in 1 direction from the root system to the shoot system
55
New cards
phloem
conducts sugar amino acids hormones and other substances in 2 directions
roots to shoots and shoots to roots
roots to shoots and shoots to roots
56
New cards
vascular bundle
in a plant stem a cluster of xylem and phloem strands that run the length of the stem
57
New cards
xylem structure
includes h20 conducting cells as well as parenchyma cells and fibers
2 types of h20 conducting cells in xylem
2 types of h20 conducting cells in xylem
58
New cards
2 types of h20 conducting cells in xylem
tracheid and vessel elements
59
New cards
tracheid
in a vascular plant a long thin h20 conducting cell that has pits where its lignin (containing secondary cell wall) is absent allowing h20 movement between adjacent
sides and ends have pits- gaps in secondary cell wall where only the primary cell wall in present moves from cell to cell both vertically and laterally through pits bc resistance flow lowest
long slender cells w/tapered ends
sides and ends have pits- gaps in secondary cell wall where only the primary cell wall in present moves from cell to cell both vertically and laterally through pits bc resistance flow lowest
long slender cells w/tapered ends
60
New cards
vessel elements
in vascular plants a short wide h20 conducting cell that has gaps through both the primary and secondary cell walls allowing unimpeded passage of h20 between adjacent cells
shorter and wider
has pits and perforations openings in the end walls that lack both primary and secondary cell walls
conduct h20 more effiecntly than tracheids bc their width preformation offer less resistance to flow
shorter and wider
has pits and perforations openings in the end walls that lack both primary and secondary cell walls
conduct h20 more effiecntly than tracheids bc their width preformation offer less resistance to flow
61
New cards
are vessel elements and tracheids both alive or dead at maturity
dead
62
New cards
phloem structure
2 specialized types of cells
both are alive at maturity and lacks secondary cell walls
sieve and companion cells
both are alive at maturity and lacks secondary cell walls
sieve and companion cells
63
New cards
sieve tube elements
long thin cells that have perforated ends
lack nuclei and most other organelles and connected to adjacent companion cells by plasmodesmata
lack nuclei and most other organelles and connected to adjacent companion cells by plasmodesmata
64
New cards
sieve plates
responsible for transporting sugars and other nutrients
65
New cards
companion cells
not conducting cells but instead provide materials to maintain the cytoplasm and plasma membrane of sieve tube elements
contain most of the organelles normally found in plant cells and support the metabolic activity of sieve tube elements
contain most of the organelles normally found in plant cells and support the metabolic activity of sieve tube elements
66
New cards
meristems
populations of undifferentiated cells that retain the ability to undergo mitosis
\
\
67
New cards
apical meristem
located at each root and shoot where growth occurs from
68
New cards
primary plant body
all cells and tissues that are derived directly from apical meristems
69
New cards
apical meristems give rise to 3 meristems which are
protoderm ground meristem and procambium
70
New cards
protoderm
gives rise to the dermal tissue system which includes the epidermis
71
New cards
ground meristem
gives rise to the ground tissue system makes up the bulk of the primary plant body
includes the parenchyma collenchyma and sclerenchyma
includes the parenchyma collenchyma and sclerenchyma
72
New cards
procambium
gives rise to the vascular tissue system which includes the xylem and phloem
73
New cards
components of primary growth chart
74
New cards
root cap
protects the root apical meristem
necessary to protect and allow for outward growth
synthesizes and secretes a polysaccharide which lubricates it and reduces friction and protects the apical meristem
necessary to protect and allow for outward growth
synthesizes and secretes a polysaccharide which lubricates it and reduces friction and protects the apical meristem
75
New cards
3 zones behind the root cap
zone of cellular division
zone of elongation
zone of cellular matuartion
zone of elongation
zone of cellular matuartion
76
New cards
root hairs
increase sa of dermal tissue and allows for increased absorption
77
New cards
shoot system includes vascular tissue that runs through it and it’s divided into 2 major regions
pith and cortex
78
New cards
pith
ground tissue towards the center of the stem
79
New cards
cortex
the ground tissue that is between the vascular bundles and the epidermis
80
New cards
what does primary growth do
increases the length of the roots and shoots and increases the plants ability to absorb h20 co2 and nutrients
81
New cards
secondary growth
in trees and other woody plants increases the width of roots and shoots
82
New cards
wood
xylem resulting from secondary growth forms strong supporting material
83
New cards
cambium
special type of meristem (lateral meristem) that differs from an apical meristem in 2 ways
1. made up of a single layer of meristematic cells apical meristem are clusters of cells localized at root and shoot tips
1. cambium cells divide in a way that increases the width of root trunks and branches apical meristems increase the length
1. made up of a single layer of meristematic cells apical meristem are clusters of cells localized at root and shoot tips
1. cambium cells divide in a way that increases the width of root trunks and branches apical meristems increase the length
84
New cards
2 types of cambium
vascular cambium and cork cambium
85
New cards
vascular cambium
a cylinder of meristematic cells located between the secondary xylem and phloem in roots and trunks and branches
generates new layers of cells toward both the interior and exterior (more toward the inside tho) new cells formed to the inside push all of the other cells outside increase girth
generates new layers of cells toward both the interior and exterior (more toward the inside tho) new cells formed to the inside push all of the other cells outside increase girth
86
New cards
cork cambium
cylinder of meristematic cells located near the outer perimeter of roots trunks and branches
produces new cells primarily toward the exterior
produces new cells primarily toward the exterior
87
New cards
cork cambium mature tissue direction of growth mature cell comp and mature tissue function
cork
produced to the outside
cork cells
protection
produced to the outside
cork cells
protection
88
New cards
vascular cambium (2 types) mature tissue direction of growth mature cell comp and mature tissue function
secondary phloem
produced to the outside
sieve tube elements companion cells sclerenchyma cells (fibers)
transport of sugars amino acids hormones etc
\
secondary xylem
produced to the inside
tracheid’s vessels parenchyma cells (arranged in rays) sclerenchyma cells (fiber)
transport of h20 and ions structural support
produced to the outside
sieve tube elements companion cells sclerenchyma cells (fibers)
transport of sugars amino acids hormones etc
\
secondary xylem
produced to the inside
tracheid’s vessels parenchyma cells (arranged in rays) sclerenchyma cells (fiber)
transport of h20 and ions structural support
89
New cards
structurally primary and secondary xylem and phloem are
complex tissues
90
New cards
functionally primary and secondary phloem function in
sugar transport
91
New cards
functionally primary and secondary xylem function in
h20 transport and structural support
92
New cards
secondary xylem makes up
wood
93
New cards
secondary phloem makes up
inner part of tree’s bark
94
New cards
rays
rows of cells and form a living conduit through which h20 and nutrients are transported laterally across the trunk
95
New cards
results of cell division in vascular cambium are
highly asymmetrical
96
New cards
cork cells
a cell in the protective outermost layer of a woody stem and roots that produces and accumulates waxes that make cells less permeable to gases
97
New cards
bark=
and function
and function
cork cambium+ cork cells
provides a particularly tough barrier in species whose cork cells secrete a strong secondary cell wall containing lignin
helps prevent h20 loss bc cork cells make a layer of wax
protects from damage from pathogens
some can protect from fire damage
provides a particularly tough barrier in species whose cork cells secrete a strong secondary cell wall containing lignin
helps prevent h20 loss bc cork cells make a layer of wax
protects from damage from pathogens
some can protect from fire damage
98
New cards
how can gas exchange still occur through the bark
by way of lenticels
99
New cards
lenticels
small spongy openings in the bark allow for gas exchange
100
New cards
perennial
plants that live for many years