Pediatric Skin Disorders
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
What is the largest organ in the body?
Skin
Why do infants have a greater risk of having topic meds absorbed systemically?
They have thin skin and a large body surface are
pH alkaline in the 1st week of life which puts infants at a greater risk of:
infections
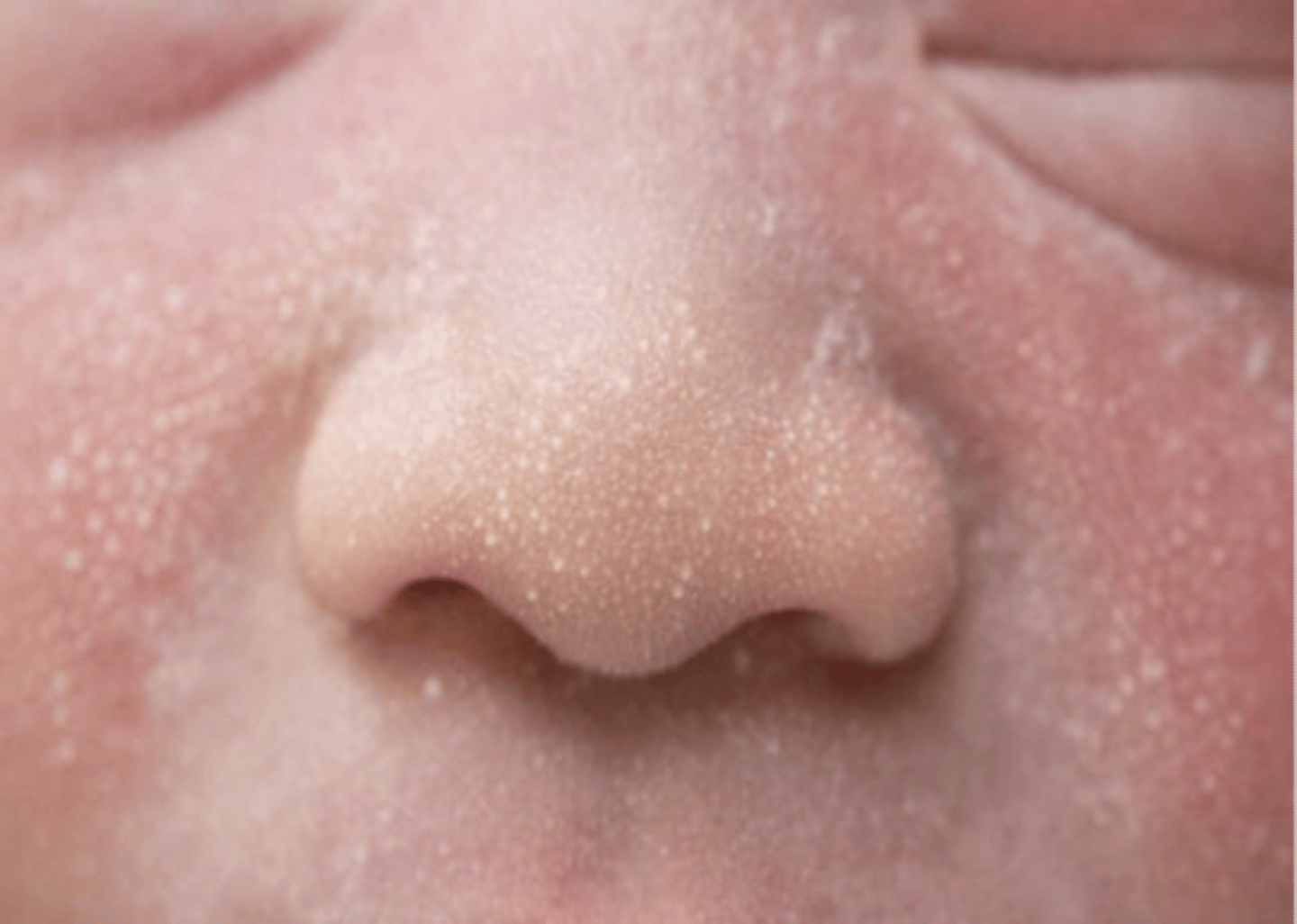
Active sebaceous glands due to maternal hormones put infants at a risk for developing:
Milia
Neonatal acne is due to:
An inflammatory reaction to yeast on the skin. Forms pustules that last 1-3 month
IgA is dimished until...
2-5 years which makes them more prone to infections when they are less athan 2 years. IgA also helps to establish normal gut flora
Eccrine gland matures by...
2-3 years old. This allows for perspiration and more effective thermoregulation
Aprocrine gland is function at...
8-10 years old. Sweat glands are concentration in axillae, scalp, face, abdomen, and genital area. They further mature during puberty
Darker pigmented skin has more...
melanin
Lighter pigmented skin is more prone to...
UV damage
Pallor and cyanosis is more easily detected in...
mucus membranes and nail beds
Darker pigmented skin is more prone to...
keloid formation
Impetigo
Honey crusted lesions that are causes by streptococcus or staphylcoccus from nose picking or scratching
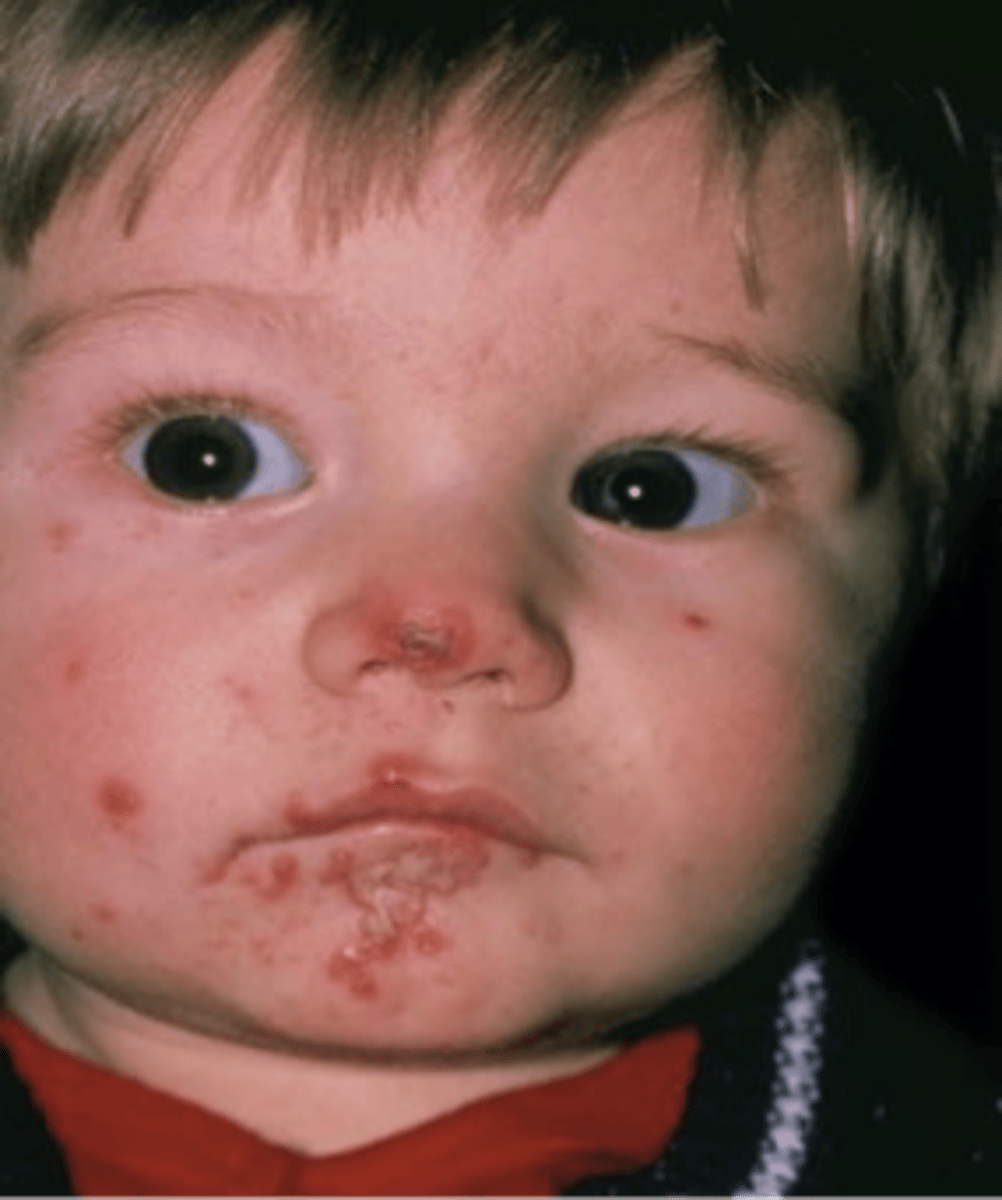
What is the treatment for impetigo?
Topical mupirocin within 24 hours, trim nails, good hygiene, out of school for 24-48 hours, scab and heal
Seborrheic dermatitis
Cradle cap, thick whitish yellow scaly oily patches on the scalp, forehead, and eyebrows that is commonly present in the first 3 months of life. This is due to a dysfunction of sebaceous glands and hormones
What is the treatment for seborrheic dermatitis?
Removing the crusts, mineral oil to scalp, cleanse daily with mild shampoo
Diaper dermatitis
Inflammatory reaction from prolonged exposure to urine and feces. Increases pH and activates fecal enzymes. Sin maceration in area that diaper covers
Treatment for diaper dermatitis
Barriers, open to air, frequent diaper changes. May progress to fungal diaper dermatitis
Diaper candiasis
Erythematous base with bumpy rash, red papules with peeling skin in the folds with satellite lesions outward
Treatment for diaper candiasis
Nystatin cream/ointment. If there is thrush, add oral nystatin
Atopic dermatitis (eczema)
Type 1 IgE mediated, on face elbows and back of knees, before 2 years of age, response to food/environmental allergies and sweating. Intense itching. Rash developed with subsequent pruiritus, interferes with sleep. Eczema and rhinitis are risk factors for asthma
Treatment for atopic dermatitis (eczema)
Hydrations, moisturizers, topical steroids such as hydrocortisone and triamcinolone, antihistamines, avoid triggers, trim nails, antibiotic for secondary bacterial infections, and immune modulators
Causes of contact dermatitis
Detergents, jewelry, perfumes rubber, latex, and poison ivy. Most common is from nickel
Treatment for contact dermatitis
Avoidance of triggers, topical steroidal cream
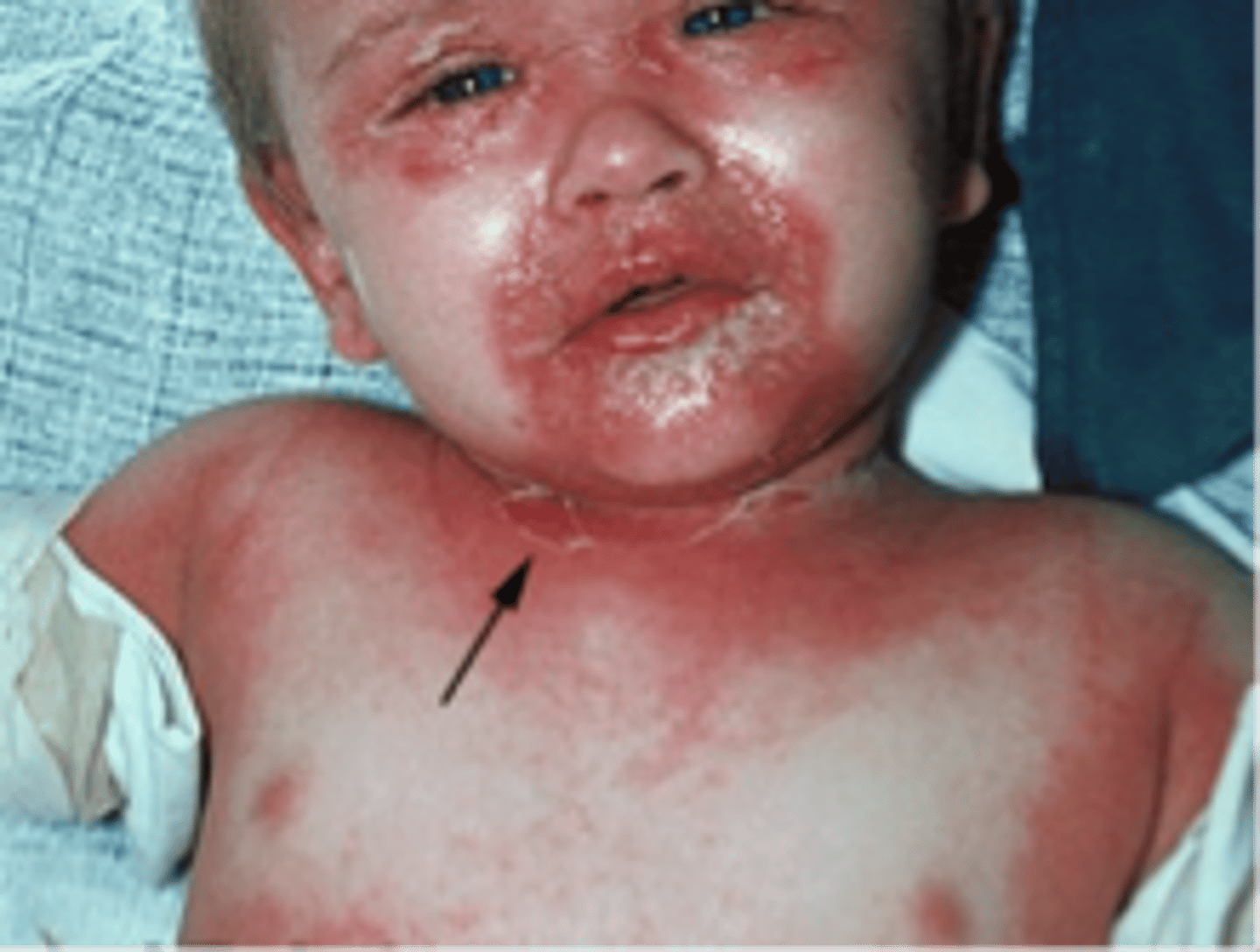
Staphylococcal scalded skin
Caused by toxin secreting staph, MSSA, MRSA. Under the age of 5, most common in infancy, low grade fever, fussiness for 24-48 hours, followed by peeling and blistering of the skin, very painful, may progress to blod stream infection if not identified quickly, hospitalization is necessary
Treatment for staphylococcal scalded skin
It is dependent on the organism. IV clindamycin, Clindamycin and cefazolin or nafcillin or clindamycin and vancomycin, acetaminophen
Periorbital cellulitis causes
From strep/staph infection, fungal. From insect bites, scratch or an abrasion, extension of impetigo, extension of poison ivy, extension of sinus infection
Treatment for periorbital cellulitis
Hospitalization. ENT/opthalmology consults, CT or head and sinuses, IV antibiotics and anaerobic coverage such as vancomycin, ceftriaxone, and metronidazole, NSAIDS or acetaminophen