MCAT Psych/Soc: Memory and Learning
1/119
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
120 Terms
Limbic system
The neural system located below the cerebral hemispheres; associated with emotions and drives. Comprised of the hippocampus, thalamus, hypothalamus, and amygdala.
hippocampus
A neural center located in the limbic system that helps process explicit memories for storage. Important for memory and learning
amygdala
A limbic system structure involved in memory and emotion, particularly fear and aggression. Communicates with the hypothalamus to produce the endocrine response to emotions
visual sensory perception
First, sensory information arrives at the thalamus. If there is no need to process further, the thalamus filters out the sensory input
structural techniques of neuroscience
measures what the brain looks like: MRI and CT scan
functional techniques of neurosceince
measure what brain regions are doing: PET, fMRI, EEG
neural plasticity
cortical reorganization in the brain that occurs in response to learning and experience, as well as behavior, emotions, etc. Change can occur from the cellular level to the anatomical level.
long-term potentiation
Connections between neurons strengthen the more you use them. Physical methods are not completely understood
basic steps of memory
encoding, storage, retrieval
encoding memory
transfer of sensation into our memory system
storage of memory
retaining information in short-term or long-term memory
retrieval of memory
extracting information that has been stored
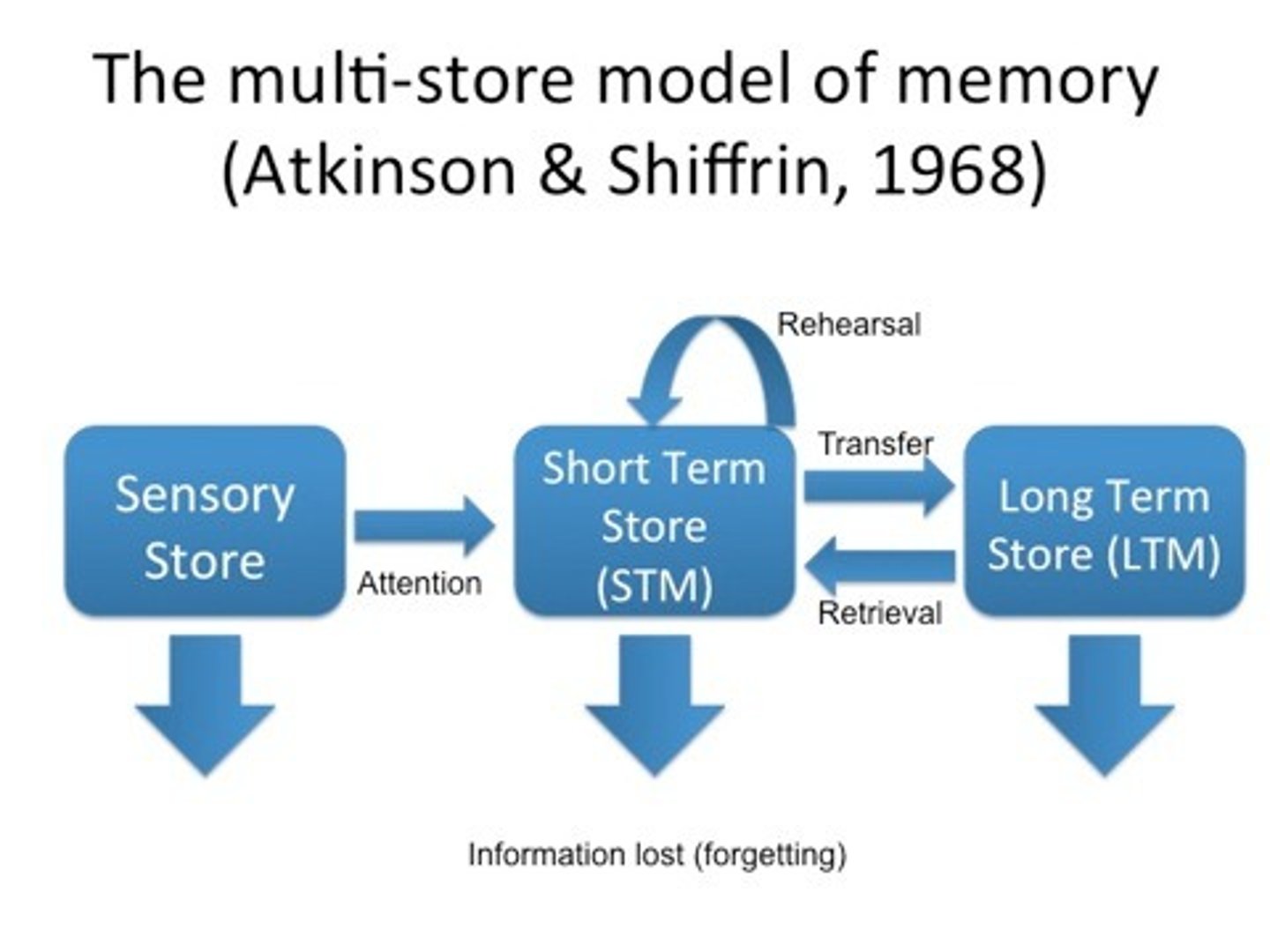
multi-store model of memory
Sensory input enters sensory memory, and unattended information is quickly lost. Attention to the stimulus causes short-term memory, unrehearsed information is lost. Encoding consolidation of short-term memory causes long-term memory, which can be retrieved into short-term memory. Over time, some information may be lost from long-term memory.
serial position effects
primacy effect and recency effect, hard to remember things in the middle
primacy effect
tendency to remember information at the beginning of a body of information better than the information that follows
recency effect
tendency to remember recent information better than earlier information
Working memory
short-term memory
Baddeley's model of working memory
Consists of the central executive, which acts as a supervisory system and controls the flow of information from and to its slave systems: the phonological loop, the visuo-spatial sketchpad, and the episodic buffer
phonological loop
short-term phonological store with auditory rehearsal. Can be encoded into long-term semantic verbal memory.
visuospatial sketchpad
A component of working memory where we create mental images to remember visual information. Can be encoded into long-term semantic visual memory
episodic buffer
A component of working memory where information in working memory interacts with information in long-term memory. Can be encoded into long-term episodic memory
encoding
The process of transforming information into a form that is more easily stored in our brains. Four basic kinds: semantic, acoustic, visual, and elaborative.
elaborative encoding
the process of actively relating new information to knowledge that is already in memory
Rehearsal
an encoding strategy where reptition of information leads to increased retention.
chunking
An encoding strategy that groups related information into chunks (phone numbers)
elaboration
an encoding strategy that intertwines information to be remembered with well-entrenched pre-existing long term spatial, visual, acoustic, or semantic memories
self-reference
An encoding strategy that makes information to be remembered personally relevant
spacing
an encoding strategy that states that memory works better when reviewed material is spaced out over time
mnemonics
Any encoding strategy that improves the retention of information
sensory memory
iconic and acoustic/echoic memory, which decays quickly (iconic in less than a second, acoustic in 2-4 seconds)
Short-term memory
is separated by a rehearsal buffer capacity of 7+/-2 items at a time. Decays in 15-30 seconds and is primarily acoustic
long-term memory
permanent storage with an unknown upper limit to capacity. Encoding is primarily semantic (meaning-making)
Explicit memory
long-term memory of facts and experiences that one can consciously know and "declare"
episodic memory
long-term explicit memory of events you have personally experienced
semantic memory
long-term explicit memory of general knowledge of facts and information
implicit memory
long-term Memories we don't deliberately remember or reflect on consciously
procedural memory
The long-term implicit memory of motor skills and actions that have been learned previously
classical conditioning
long-term implicit memory through association of stimuli.
priming
occurs when exposure to one stimulus influences the response to another stimulus
semantic networks
Organization of information in networks of meaningfully related memories, storage of semantic memory
spreading activation
Occurs when one item brought into working memory triggers an activation of related semantic memory
retrieval cue
any stimulus that assists in memory retrival
positive priming
speeds up processing caused by simply experiencing the stimulus
negative priming
An implicit memory effect in which prior exposure to a stimulus unfavorably influences the response to the same stimulus

context-dependent memory
We are better at retrieving information in the same environmental context in which the information was learned. "Context effect"
state-dependent memory
We are better at remembering when we are in the same internal state that we were in when the information was encoded; "state-dependency effect"
retrieval
the process of finding information stored in memory
free recall
a testing condition in which a person is asked to retreive information without explicit retrieval cues
cued recall
A test of long-term memory that involves remembering an item of information in response to a retrieval cue.
recognition memory
an ability to correctly identify previously learned information given different retrieval cues
relearning
a measure of memory that assesses the amount of time saved when learning material for a second time
flashbulb memory
people can remember great detail about their episodic memories of particularly emotionally arousing events; however, this is not entirely dependable
eidetic memory
the ability to vivdly recall images from memory after only a few instances of exposure with high precision for a brief time after exposure without using mnemonic devices
reproductive memory
accurate retrieval of information from memory, without significant alteration
prospective memory
remembering to perform a planned action or recall a planned intention at some future point in time, such as remembering to do your next assignment
dual coding theory
a theory that holds that the combination of words with visuals provides us with two different channels for later recall, which assists in memory retrieval. Thus, learning works better when words are presented with relevant images or such images are imagined by the learner.
levels of processing model
focuses on the depth of processing involved in memory; predicts the deeper information is processed, the longer a memory trace will last
reminiscence bump
older adults generally remember events they experienced from 10-30 years old better than any other time period, includng more recent time periods
practice effects
The improvement that would be expected to occur simply from repeated exposure to a specific memory test.
method of loci
a method of memory retention in which the individual uses visualized spatial information (like their house) to recall lists of words to be memorized. Also called: memory journey, memory palace, or mind palace
peg words
a memory technique in which an individual connects words to numbers and creates an association to improve retention. The item-number pairs also rhyme to assist in recollection
intrusion errors
Substitution of an often semantically meaningful word during free and serial recall of word lists. Can also occur in episodic ememories when information that is consistent but did not actually occur is appended during memory retrieval
Memory as a reconstructive process
each time a memory is retrieved, the memory trace is strengthed, but also potentially altered
displacement of memory
occurs in short term memory when one item in the list of words to be remembered bumps out another as most people can only store 7+/-2 items in STM
interference
when competing material makes it more difficult to encode or retrieve information
Proactive interference
Prior learning interferes with new learning (PRior, PRoactive)
Retroactive interference
recent learning interferes with old learning (REtroactive, REcent)
Memory that improves with aging
semantic memory, emotional intelligence
Memory that is stable with aging
implicit memory, crystallized intelligence (ability to retrieve general info)
Memory that declines with aging
episodic, source memory, divided attention, operation span in working memory, processing speed
source memory
recall of when, where, and how information was acquired
Operational span
measures working memory capacity
source monitoring errors
Misidentifying the origins of our knowledge
false memories
An invented or distorted recollection of an episodic event that did not actually happen.
misinformation effect
when episodic memories become less accurate because post-event information works backwards in time to distort the memory of the original even through retroactive interference
anterograde amnesia
a loss of the ability to create new memories after the event that caused the amnesia, leading to an inability to recall the recent past while long-term memories remain. (50 1st dates)
retrograde amnesia
a loss of access to retrograde memories before the onset of a disease
Korsakoff's Syndrome
Chronic memory disorder caused by severe defiency of thiamine most commonly caused by alchohol misuse.
nonassociative learning
a change in the magnitude of a response due to the repeated exposure to a stimulus
habituation
occurs when the response diminishes as the organism becomes accustomed to a repeated stimulus, nonassociative learning
dishabiuation
occurs when an organism that had become habituated to a stimulus recovers its responsiveness because of the removal of the stimulus and/or the experience of a different stimulus, nonassociative learning
sensitization
occurs when instead of exhibiting habituation, the organism demonstrates increasing responsiveness to a repeated stimulus associated with increased arousal.
associative learning
Classical conditioning, a process in which two stimuli are paired in such a way that the response to one of the stimuli changes
Pavlov Experiment and Classical Conditioning
The most famous example of classical conditioning was Pavlov's experiment with dogs, who salivated in response to a bell tone. Pavlov showed that when a bell was sounded each time the dog was fed, the dog learned to associate the sound with the presentation of the food.
unconditioned stimulus
A stimulus that evokes an unconditioned response without previous conditioning
unconditioned response
in classical conditioning, an unlearned, naturally occurring response to an unconditioned stimulus without previous conditioning
neutral stimulus
in classical conditioning, a stimulus that elicits no response before conditioning
conditioned stimulus
In classical conditioning, an originally irrelevant stimulus that, after association with an unconditioned stimulus, comes to trigger a conditioned response
conditioned response
in classical conditioning, the learned response to a previously neutral (but now conditioned) stimulus
Acquisition phase of learning
The process of classical conditioning from the original unconditioned stimulus to the conditioned response.
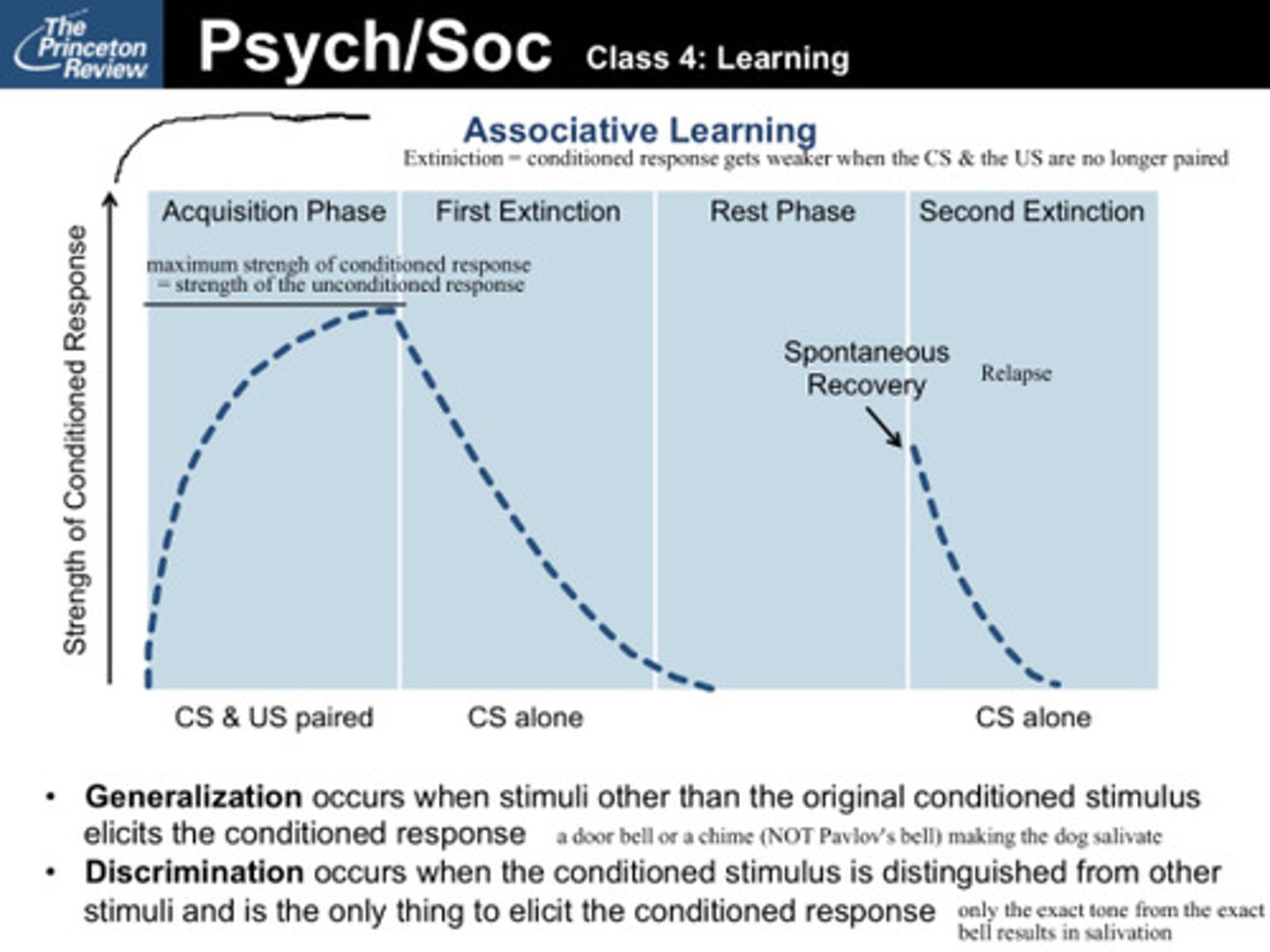
first extinction
Decreasing the strength of the conditioned response with the conditioned stimulus alone
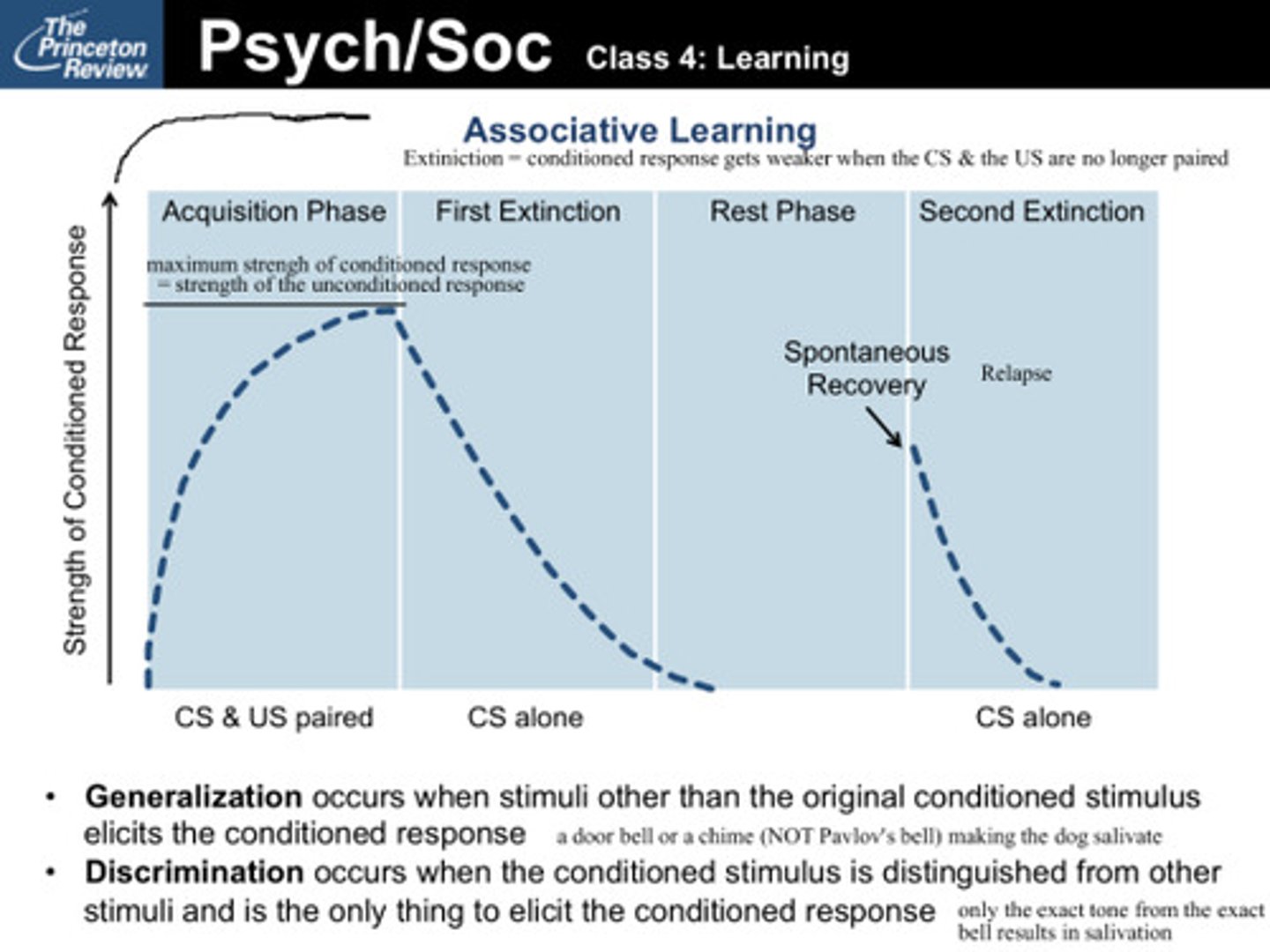
spontaneous recovery
the tendency of a learned behavior to recover from extinction after a rest period followed by a second extinction
generalization
occurs when stimuli other than the original conditioned stimulus elicit the conditioned response
discrimination
occurs when the conditioned stimulus is distinguished from other similar stimuli and is the only thing that elicts the conditioned response
BF skinner
A behaviorist who developed the theory of operant conditioning by training pigeons and rats
positive reinforcement
adds something desirable to increase the likelihood of the behavior happening again
positive punishment
adds something undesirable to decrease the likelihood of the behavior happening again
negative reinforcement
takes away something undesirable to increase the likelihood of the behavior happening again
negative punishment
takes away something desirable to decrease likelihood of behavior happening again
dopamine reward pathway
The reward pathway begins in the ventral tegmental area and connects to the nucleus accumbens to release dopamine