Plants and Humans Exam 2
1/134
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
135 Terms
Photosynthesis
How Plants use sunlight to produce their food
Use sunlight energy to change it into the energy stored in the bonds of glucose
Cellular Respiration
Take the energy stored in the bonds of glucose and BREAK IT DOWN to produce cellular energy
Photosynthesis Reactants
6CO2 + 6H2O + sunlight
Photosynthesis Products
C6H12O6 + 6O2
Where does photosynthesis occur?
Chloroplasts of Leaf Cells
Pigment
Substances that give off a color due to light absorbance and reflection.
Chlorophyll
Main pigment for photosynthesis; Mainly absorbs in the red and blue areas of the light spectrum
Chlorophyll B
Associated pigment for photosynthesis; absorbs in the red-orange and blue areas of the light spectrum
Carotenoids
Absorbs in the blue-green and violet areas of the light spectrum
Chloroplasts are
Double Membraned
Granum
stack of thylakoids
Thylakoid
Quarter-Shaped Disc
Stroma
Fluid inside the chloroplast
Stages of Photosynthesis
1) Light-Dependent Stage
2) Calvin Cycle/Light-Independent Stage
Light-Dependent Stage
Light Energy Splits water, resulting in oxygen
ATP is formed
Occurs in the thylakoids
Calvin Cycle/Light-Independent Stage
Carbon Dioxide enters the leaf
Produces sugars
Occurs in the stroma
ATP is
adenosine triphosphate, the cell's energy currency
Reactants of Cellular Respiration
C6H12O6 + 6O2
Products of Cellular Respiration
6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP
Where does MOST of cellular respiration occurs?
Mitochondria
Mitochondria has
Double Membranes
Cristae
Folds on the inner mitochondrial membrane
Mitochondrial Matrix
Innermost compartment of a mitochondrion (fluid)
aerobic respiration
requires oxygen
anaerobic respiration
Does not use oxygen
Steps of Cellular Respiration
1) Glycolysis
*Transition Step-
2) Citric Acid Cycle/Krebs Cycle
3) Electron Transport Chain
Glycolysis
Sugar Splitting
Glucose splits into 2 pyruvate molecules
Happens in the cytosol
Transition Step*
2 Pyruvate molecules are changed into 2 acetyl coenzyme A molecules
Citric Acid Cycle/Krebs Cycle
Occurs in the mitochondrial Matrix
Glucose is oxidized to carbon dioxide
Requires Oxygen
Electron Transport Chain (MOST IMPORTANT STEP)
Occurs on the inner mitochondrial membrane
Requires oxygen
Produces most of the ATP
1) Perception
A) External Environment
B) Internal Plant Body
2) Information Transfer
Hormones
3) Response
Action that is taken
Stimulus/Stimuli
Something that happens that causes an activity
Examples of Stimuli
Drought
Bugs
Not enough sunlight
Weather
Touch
More nutritious soil
Statocytes
Gravity-sensing cells in the root
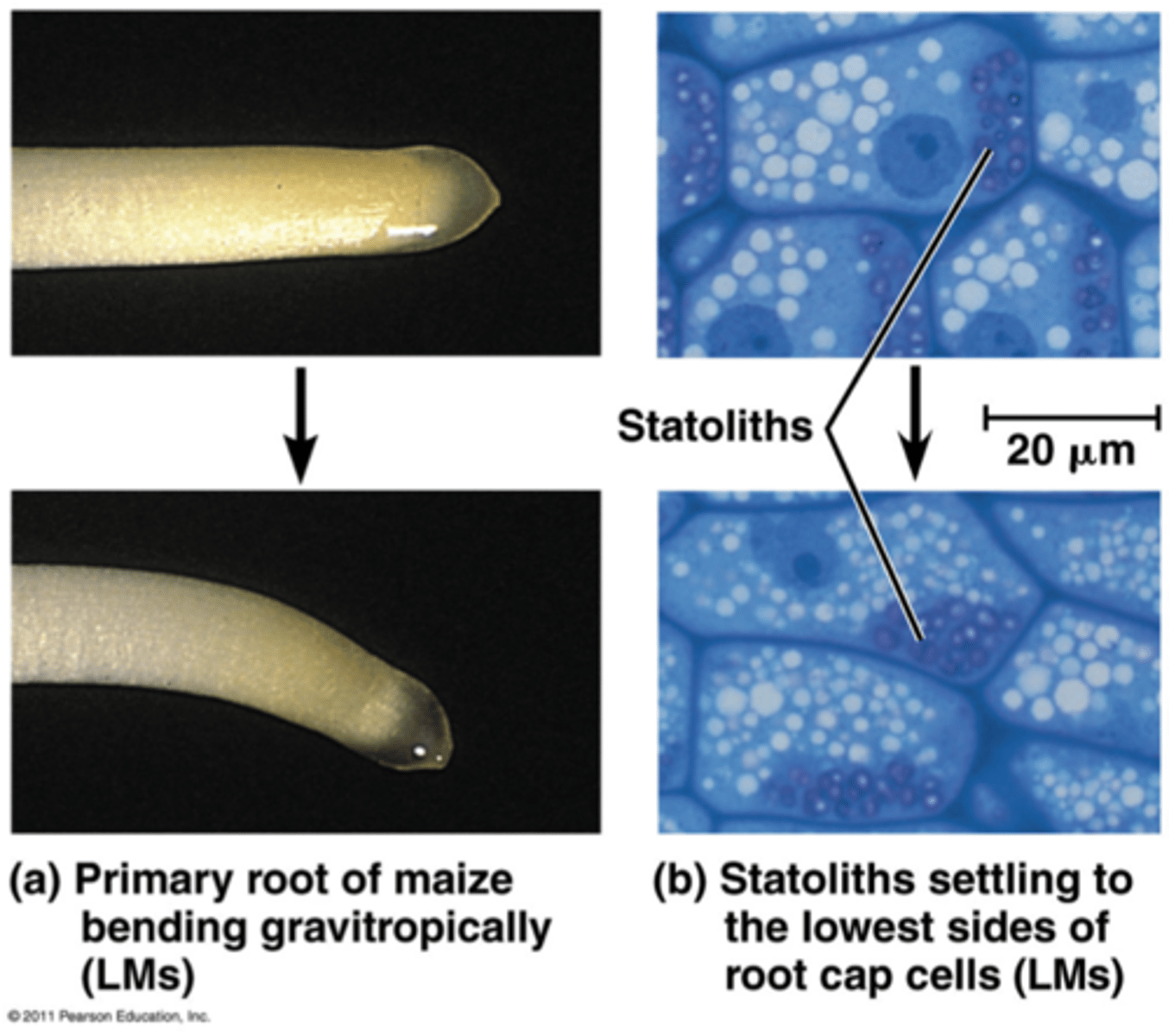
Statoliths
Starch grains within statocytes
Hormones
Chemical Messengers
-Made in small amounts, but have big effects
5 Basic Plants Hormones
Auxin
Cytokinin
Abscisic Acid
Gibberellin
Ethylene
1) Auxin (most important)
Apical Dominance, Cell elongation, cell suppression
2) Cytokinin
Activation cell division, dormant buds, "antagonist to Auxin"
3) Abscisic Acid
Involved in stress responses
4) Gibberellin
Involved in seed germination
5) Ethylene
Fruit Ripening
Seed Germination
A) The embryo takes in water and swells
B) The embryo secretes gibberellin into the aleurone layer, and enzymes produced
C) The enzymes move into the endosperm
D) The enzymes digest the endosperm to provide nutrients for the embryo
Tropic Response
Permanent, growth associated with a stimulus (toward-positive, away-negative, at an angle)
Nastic Response
Temporary, non-growth associated with a stimulus
Morphogenic Response
Change in the development or quality of a plant
All-or-None Response
A response is only present after a threshold is met
Ex. Venus Fly Trap
Dosage-Dependent Response
Response depends on the dose
Etiolation
Differences in development when seedlings are grown in the dark
-Less complex-looking
-Not green/tan-beige-yellow
-Leaves are not developed
Phototropism
Plants bending toward the light
-First studied in oat tips
Gravitropism
Roots bending down towards gravity
Apical Dominance
Terminal bud produces auxin that suppresses the growth of axillary buds
Climacteric Fruits
Ethylene involved in ripening
- Tomatoes, bananas, apples
Non-Climacteric Fruits
Ethylene NOT involved in ripening
- Cherries, Grapes, Oranges
Fruit Ripening Process
-Color Changes
-Texture Changes
-Size Changes
-Smell Changes
-Taste Changes
2 Basic Types of Reproduction
Sexual and Asexual
Advantages of Both Sexual and Asexual reproduction
Genetically Different (Sexual) and 1 Parent Involved (Asexual)
Disadvantages of Both Sexual and Asexual reproduction
2 Parents involved (Sexual) and No Genetic Diversity (Asexual)
Vegetative Propagation
Plant sends out a runner along the ground that can form a new plant
Asexual reproduction
Cell Cycle
Life cycle of the cells from one division to the next
Interphase
Cell growth, copies DNA
Cell Division/Nuclear Division
Division (divide) the DNA
Cytokinesis
Divide the cytoplasm
Uses a cell plate
Interphase Process
Longest Part of the Cell Cycle
G1, Synthesis, and G2
G1 (Gap 1)
Cell Grows, make proteins
S (Synthesis)
DNA is copied
G2 (Gap 2)
Cell growth, final preparations for cell/nuclear division
Cell/Nuclear Division Process
2 options: mitosis and meiosis
Mitosis
Occurs in body cells
Associated with asexual reproduction
4 phases; PMAT
Cytokinesis Process
Division of the cytoplasm
Chromatin
DNA and protein
Chromosome
Condensed chromatin (easily visible)
Sister Chromatids
Duplicated Chromosome
Diploid
2 Complete sets of chromosomes
Haploid
1 Complete set of chromosomes
Prophase (Mitosis)
1) Chromatin condenses so x-shaped sister chromatids are easily seen
2) Nuclear envelope begins to break down
3) Nucleolus Degrades
4) The spindle begins to form
Metaphase (Mitosis)
Sister chromatids attached to the spindle and line up in the MIDDLE of the cell
Anaphase (Mitosis)
Sister Chromatids are separated and are now called chromosomes
Telophase (Mitosis)
1) Chromosomes unravel into chromatin
2) Nuclear envelope reappear
3) Nucleoli reappear
4) The spindle breaks down
Meiosis
Occurs in reproductive cells
Reduce the number of chromosomes by half
Associated with sexual reproduction
Meiosis I and Meiosis II
Meiosis I
separates homologous chromosomes
Meiosis II
Separate x-shaped structures
Prophase I (Meiosis I)
Homologous chromosomes pair up
Crossing-Over occurs
Metaphase I (Meiosis I)
Homologous chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell
Anaphase I (Meiosis I)
Homologous chromosomes separate
Telephase I (Meiosis I)
The amount of DNA is halved
Cytokinesis I (Meiosis I0
Division of the cytoplasm
2 Daughter cells are formed
Prophase II (Meiosis II)
Spindle starts forming
Nuclear envelopes break down
Nucleoli degrade
DNA condenses in the form of x-shaped structures
Metaphase II (Meiosis II)
DNA lines up in the middle of the cell
Anaphase II (Meiosis II)
DNA is separated (no longer x-shaped)
Telephase II (Meiosis II)
Spindle breaks down
DNA unravels into chromatin
Nucleoli reappear
Nuclear envelopes reappear
Cytokinesis II (Meiosis II)
Division of the cytoplasm
4 cells with half the amount of DNA from the starting point (genetically different)
Mitosis Characteristics
Asexual Reproduction
Same amount of DNA
1x through Interphase
1x through PMAT
2 cells produced
Genetically identical
Body/Somatic Cells
Meiosis Characteristics
Sexual Reproductions
Half the amount of DNA
1x through interphase
2x through PMAT
4 cells produced
Genetically different
Reproductive Cells
Alternation of Generations
Flip between the sporophyte generation and the gametophyte generation
Sporophyte
Diploid (produces spores)
Gametophyte
Haploid (produces gametes)
Gametophyte (Haploid) Makes
Gametes (sex cells) (haploid)