ETECH Test 03 Lighting
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
What is the layered approach in lighting design and its advantages?
The layered approach in lighting design is a strategy that combines multiple types of lighting to create a balanced, flexible, and visually appealing environment. Types of lighting utilized are normally: ambient light, task lighting, accent lighting, decorative lighting.
1. Ambient luminescence 2. Focal glow 3. Brilliance
Considered aspects in determining the CU (coefficient of utilization) of a fixture:
1. Room cavity ratio 2. Surface reflectance 3. Lamp luminaire characteristics
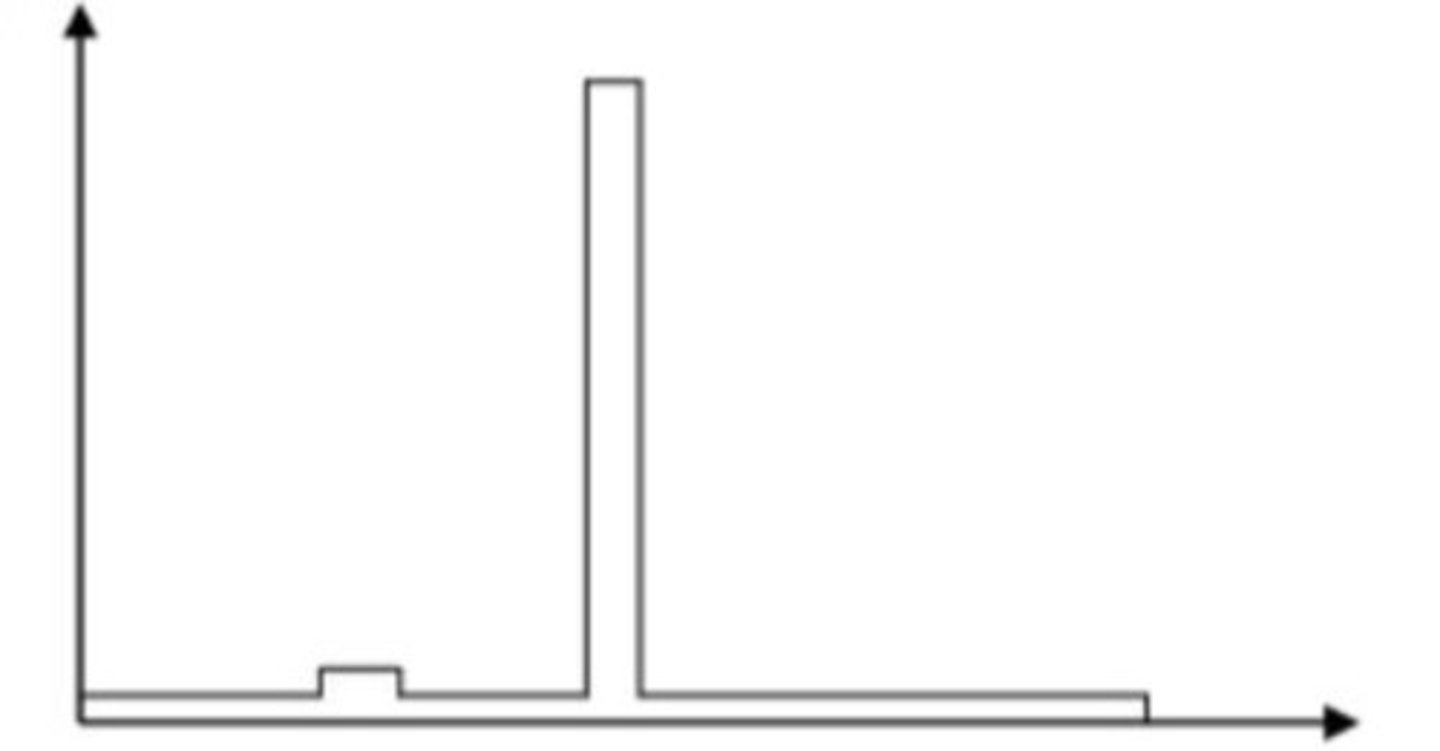
Which light source is most likely represented by this spectral distribution curve?
High Pressure Sodium
The visible portion of the electromagnetic wave spectrum lies between:
380-780 nanometers
The LED lamp is typically fitted with heat sink because:
b. the electric junction cannot be allowed to excessively overheat
Which of the three lamps has the highest luminous efficacy?
LED (lm/watts)
Give 2 specific reasons that privilege the use of LED lamps in comparison to fluorescent lamps:
1. Energy efficiency 2. long life span 3. don't put off heat
The visual comfort probability is an index indicating the potential effect of glare. The threshold minimum value and acceptable VCP is:
70%
Explain the difference between maintained illuminance and initial illuminance in the use for the Lumen Method:
Initial illuminance is the illuminance of a new light source. Maintained illuminance is over time (dirt, aging, maintenance) with use (20-40%)
CT is:
b. a scale to measure color appearance of light expressed in degree Kelvin
In specifying a light source for clothing store display:
a. The CRI and the CCT of a lamp would be useful references
If a red car is parked under high pressure sodium lamps, the perceived color is:
brown
In designing a store dedicated to carpets displays at floor level, the height of the surface us considered equal to:
0 (work plane height)
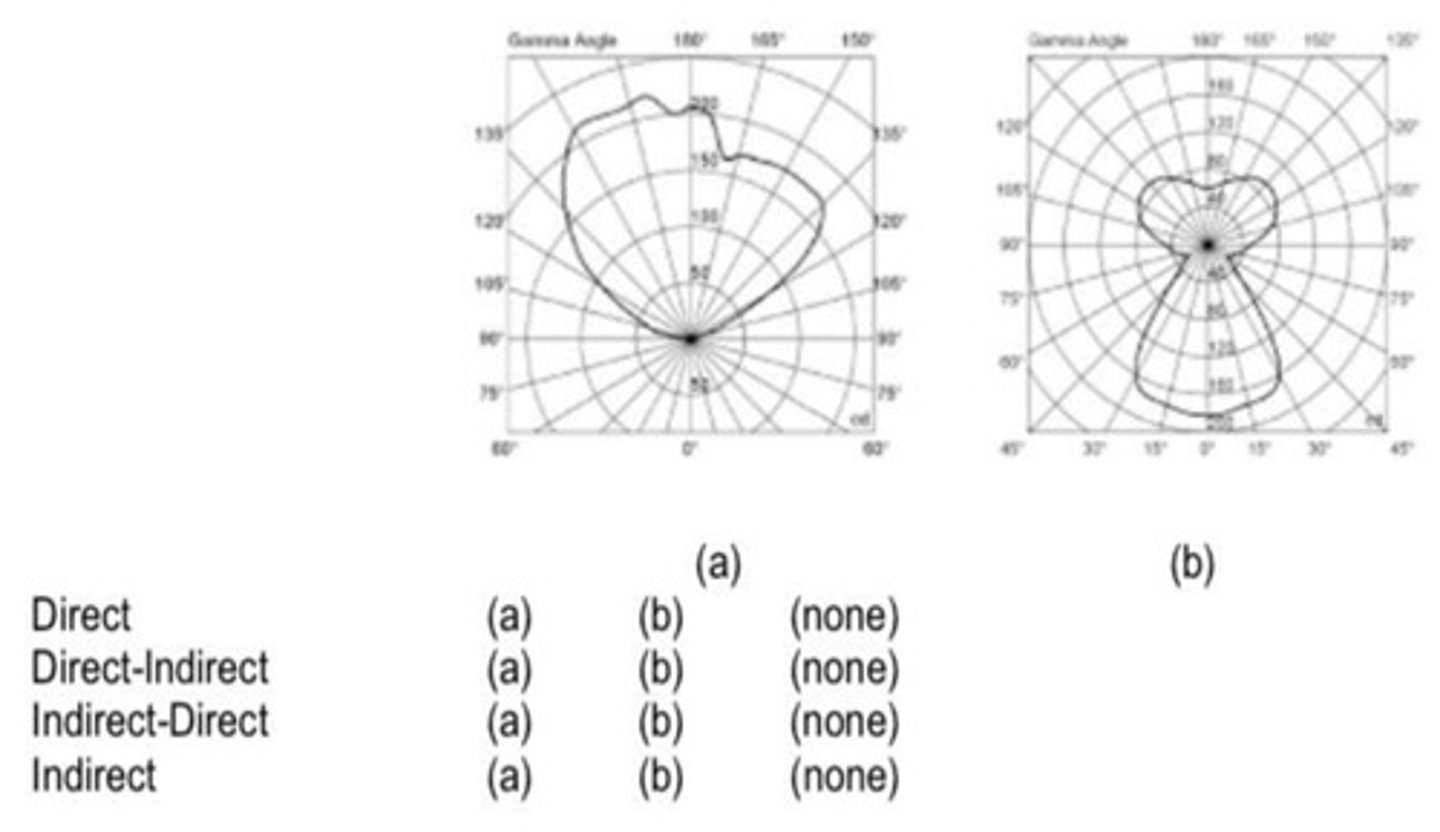
Examine the 2 photometric webs below and match them to the corresponding type:
a. indirect b. direct-indirect
The diameter of a lamp is represented in:
1/8ths of an inch
Which of the following lamps require a driver instead of a ballast?
LED
The intensity of light in a particular direction is expressed in units called:
a. candelas
In general, ceiling are bright surfaces. Identify one space scenario for which a dark ceiling surface is desirable:
A theater:
-Dark ceilings minimize light reflection and glare, which is crucial for maintaining optimal visual contrast on the screen.
-They help create an immersive environment by absorbing ambient light, allowing the audience to focus on the performance or projection.
-This also improves the overall atmosphere and mood, supporting the intended dramatic or visual experience.
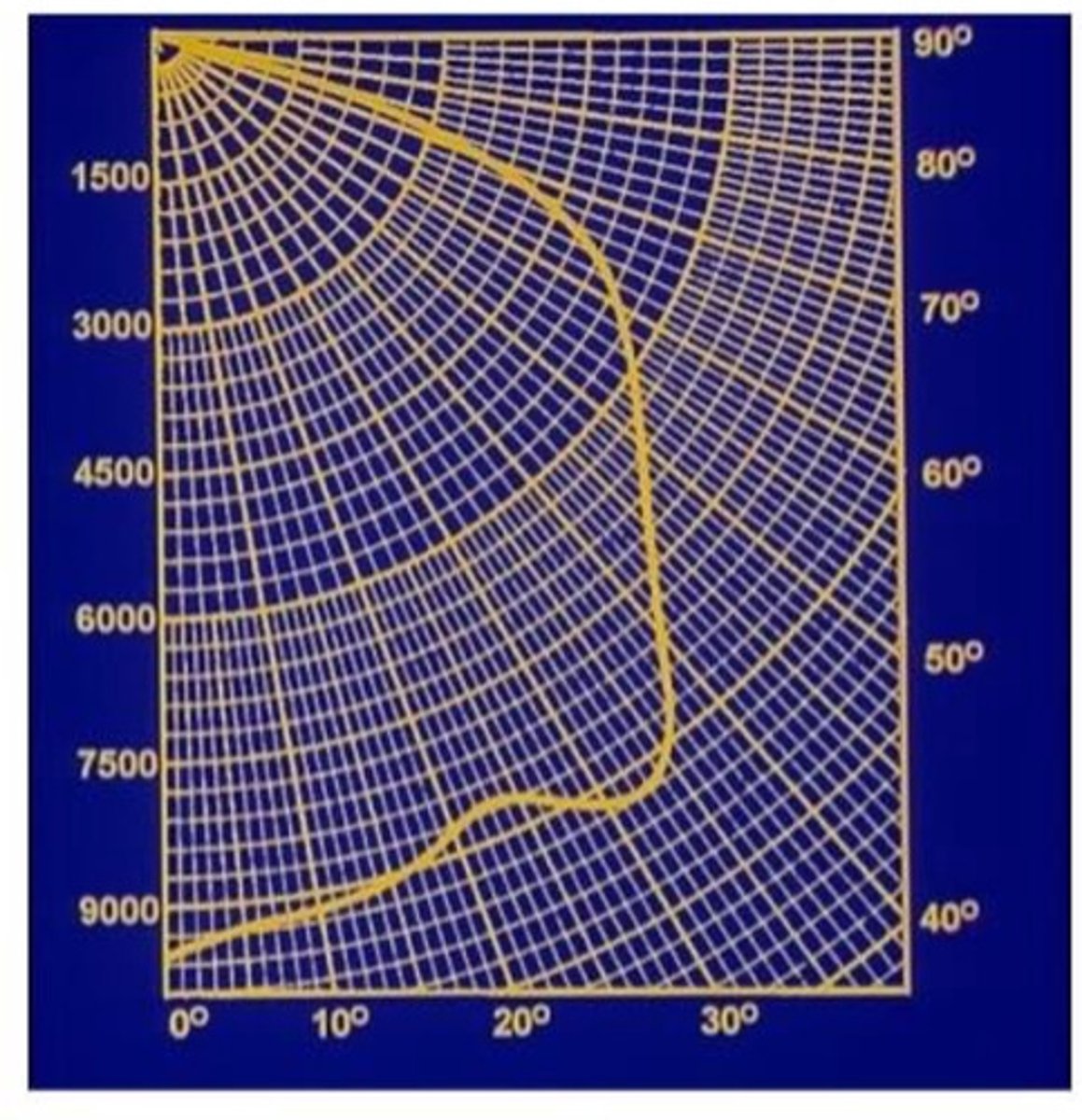
From the photometric web below give the luminous intensity of light at 15 degrees from the vertical line:
~9,000
Efficacy
How efficiently a light source produces visible light in lumens/watt
Driver
LEDs use these in place of ballasts to regulate and convert power
What unit is luminance measured in?
candela per square meter cd/m2
What unit is illuminance measured in?
Lux (lux) or lumen per m2 (lm/m2)
luminous intensity unit
candela (cd)
luminous flux unit
lumen (lm)
VCP
Visual comfort probability - a metric used in evaluating the issue of direct glare. Higher number is less glare
Cones vs rods
Cones are color perception. Rods are value
Color Temperature
Measured in kelvin, describes the warmth or coolness of light. Higher is cooler lower is warmer
CCT
More general perceived color of light source not specific to black body radiators
CRI
Color rendering index measures how accurately a light source displays the color of an object compared to natural light measured from 1-100. Where anything 80 and above is acceptable.
Primary colors in white light
red, green, blue
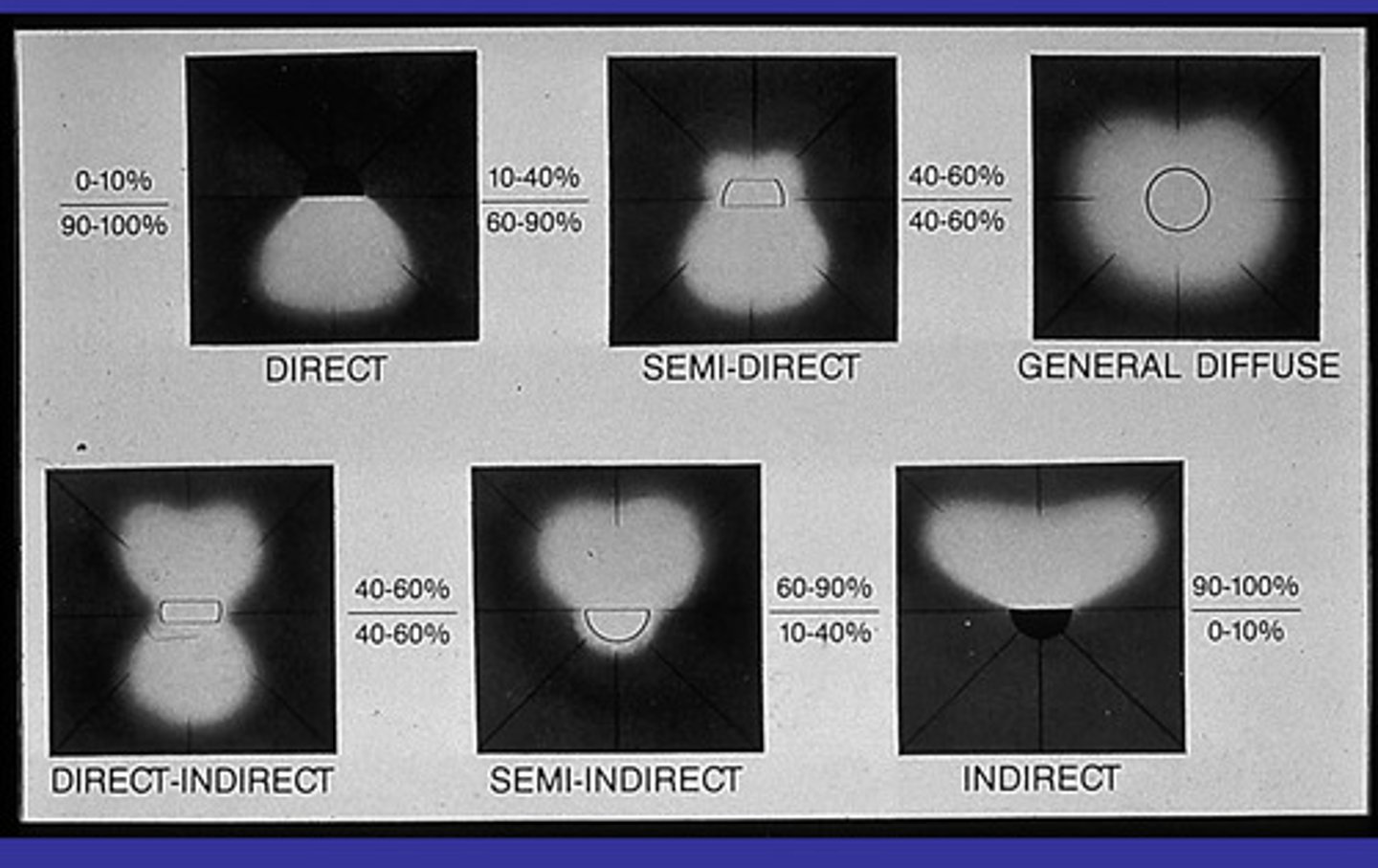
What percentages of light distribution are direct, direct indirect, semi direct, and semi indirect.
10%-90%
60%-40%
40-60%
60-90%-40-10%
A19 lamp diameter
19/8=2.375
LLF
Light loss factor - quantifies the reduction in illuminance (light output) of a lighting system over time due to various factors like lamp lumen depreciation, luminaire dirt buildup, and room surface depreciation