Keratinization, Hereditary, and Misc
1/124
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
125 Terms
What is feline acne a disorder of?
Follicular keratinization
What is the cause of feline acne?
Unknown
What are the C/S of feline acne?
Comedones on chin and lips
Papules and pustules if secondary bacterial infection is present
How do you diagnose feline acne?
Clinical presentation and cytology
How do you treat feline acne?
None if mild
Can use antiseborrheic shampoo, topical creams, fatty acids, systemic antibiotics if bacterial infection, clipping warm compresses
What are some antiseborrheic shampoos?
Sulfur/salicyclic acid
Benzoyl peroxide
What is canine tail gland hyperplasia?
Glandular hyperplasia due to androgen stimulation (caused if its intact)
What does canine tail gland hyperplasia look like?
Greasy, scaly, with alopecia on the affected area. Usually located on dorsal tail
How do you treat canine tail gland hyperplasia?
Antiseborrheic topical therapy and castration
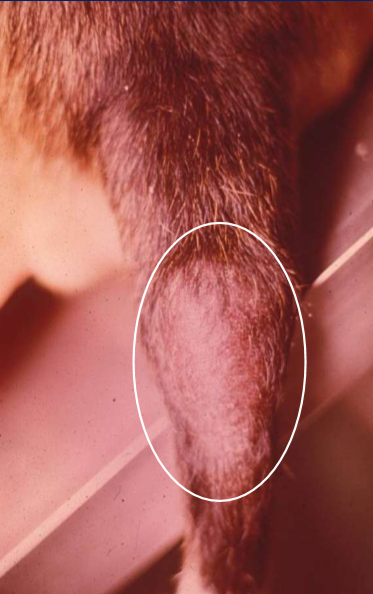
Canine tail gland hyperplasia
What is stud tail?
Feline tail gland hyperplasia
What is feline tail gland hyperplasia?
Same thing as dog feline tail gland hyperplasia
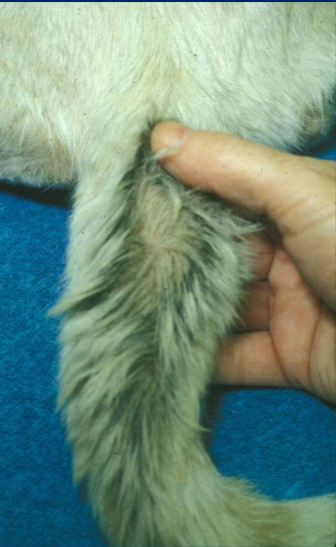
Feline tail gland hyperplasia
What is acquired pattern alopecia (pattern baldness)?
Follicular dysplasia due to color dilution alopecia or canine flank alopecia
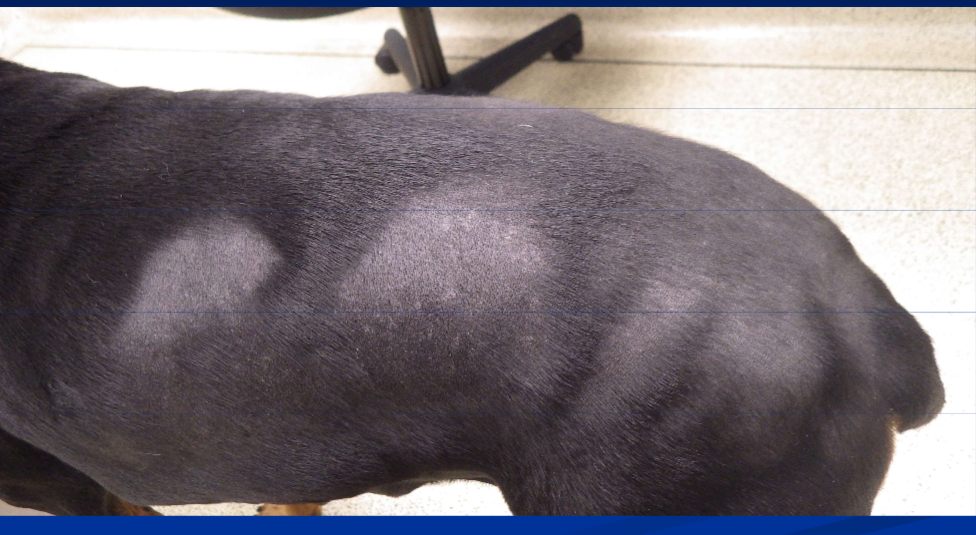
Pattern baldness (acquired pattern alopecia)
What breeds are predisposed to acquired pattern alopecia?
Dachshunds, whippets, italian greyhounds, boston terriers, chihuahuas
When does acquired pattern alopecia start?
6-9 months of age
What does acquired pattern alopecia look like?
Slowly progressive noninflammatory thinning of the hair coat on ventrum, caudomedial thighs and pinnae
No pruritus
Where do male dachshunds get acquired pattern alopecia
Pinnae
How do you diagnose acquired pattern allopecia?
C/S rule out other causes
How do you treat acquired pattern alopecia?
Irreversible
What is color dilution alopecia?
Color linked follicular dysplasia due to hereditary predisposition of a mutation with melanophilin gene related to coat color
What is happening during color dilution alopecia?
Abnormal clumping of melanin in hair shafts causing distortion and breakage of hair
What dogs get color dilution alopecia?
Dogs with diluted coat colors like blue or fawn Doberman pinschers, silver labs
What is the timeline of color dilution alopecia?
Starts as a puppy or young adult causing progressive hypotrichosis affecting the diluted regions
Secondary folliculitis and comedones can occur
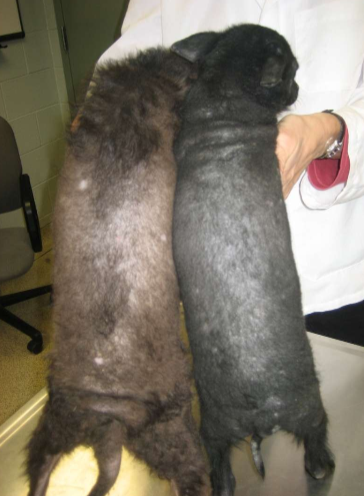
Color dilution alopecia
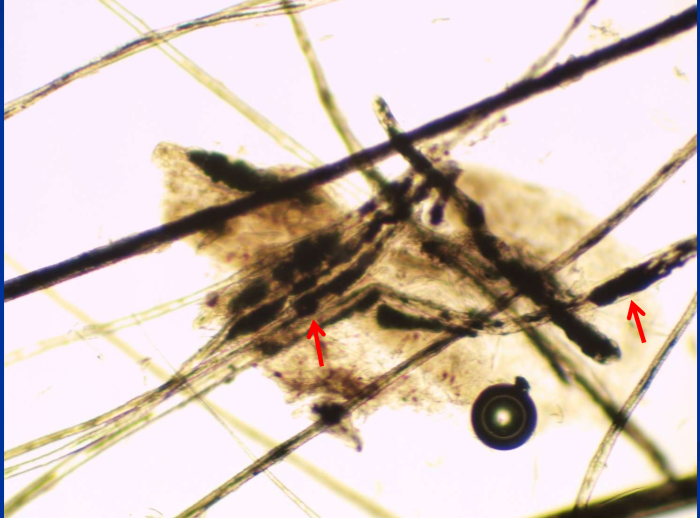
Melanin clumps in hair shafts (color dilution alopecia)
How do you diagnose color dilution alopecia?
C/S
Melanin clumping on trichogram
Biopsy to confirm
How do you treat color dilution alopecia?
Incurable so control secondary infections
What is the cause of canine flank alopecia?
Hereditary predisposition
What is the pathogenesis of canine flank alopecia?
Photoperiod (hair loss in fall and winter and can regrow 3-6 months later)
What is the signalment for seasonal flank alopecia?
Boxers, english bulldogs
What are the C/S of seasonal flank alopecia?
Bilaterally symmetric well-demarcated areas of alopecia, areas are hyperpigmented on lateral thorax and flank regions
Nonpruritic
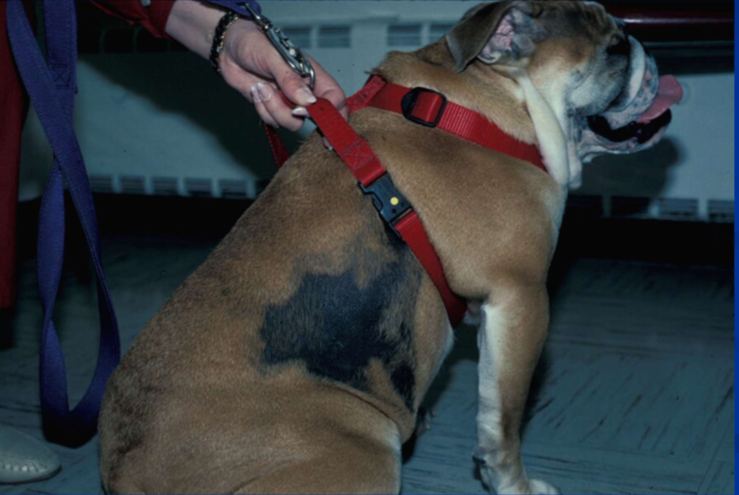
Canine flank alopecia
How do you diagnose canine flank alopecia?
C/S and history
Biopsy of dysplastic follicles
How do you treat canine flank alopecia?
Unpredictable course but melatonin can help
What is melatonin?
Hormone secreted by pineal gland involved in photoperiod-related hair growth
When do melatonin levels increase?
Winter
What does melatonin decrease?
Adrenal sex hormone levels
T/F melatonin is an antioxidant?
True
What is ichthyosis?
Rare congenital condition due to inherited defect in keratin synthesis or defects in stratum corneum
What breeds are predisposed to ichthyosis?
Goldens, WHWT, Jack russels, Cav King Charles, bulldog
What are the C/S of ichthyosis?
Scaly skin, hyperkeratosis of nasal planum and footpads
How do you diagnose ichthyosis?
C/S and history, biopsy, genetic testin
How do you manage ichthyosis?
Topical therapy
Oral fatty acids
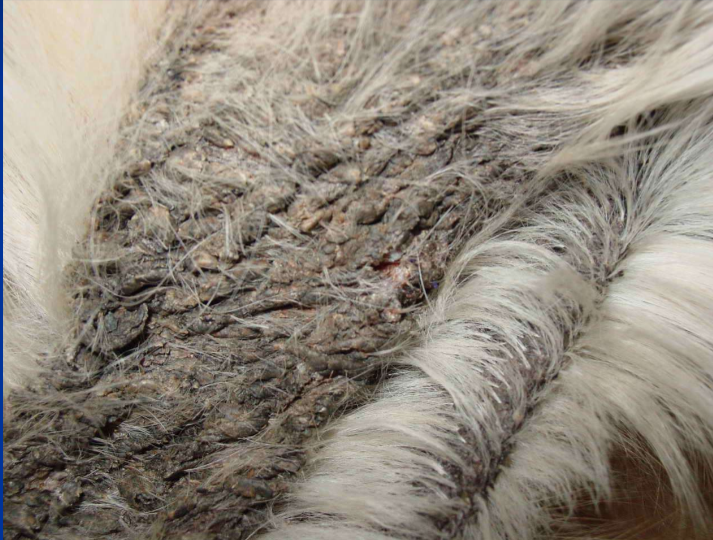

Ichthyosis
What is familial canine dermatomyositis?
Inherited inflammatory condition of skin and muscles that causes ischemic dermatopathy
What is the etiology of familial canine dermatomyositis?
Immune-mediated
What breeds are predisposed to familial canine dermatomyositis?
Collies, shelties, belgian tervuren
When does familial canine dermatomyositis onset?
Young with variable clinical course
What are the C/S of dermatomyositis?
Erythema, scale, alopecia, crusts, scarring
Ulceration if severe
What areas get dermatomyositis?
Face, pinnae, legs, digits, tip of tail (areas subject to friction
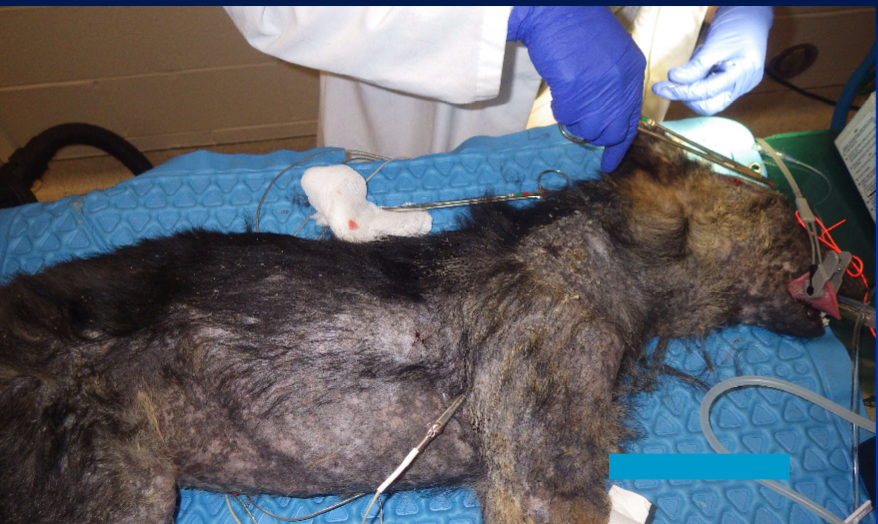
Dermatomyositis
how do you treat dermatomyositis?
Supportive care and treat skin
Pentoxifylline, vitamin E, fatty acids, steroids initially, cyclosporine
What is the etiology of feline eosinophilic granuloma complex?
Underlying hypersensitivity sometimes unknown
What syndromes does feline eosinophilic granuloma complex make?
Indolent ulcer
Eosinophilic plaque
Eosinophilic granuloma
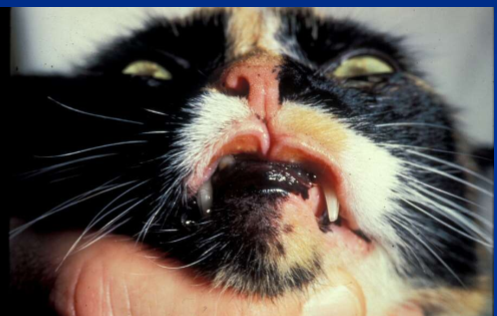
Indolent ulcer
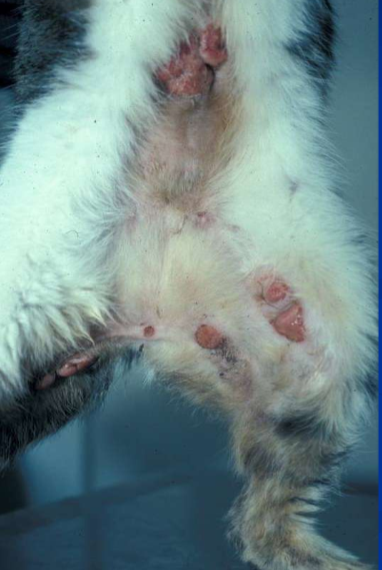
Eosinophilic plaque
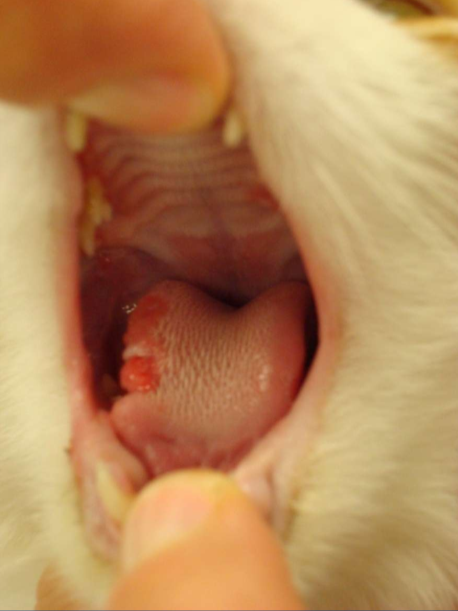
Eosinophilic granuloma
Where are indolent ulcers located?
Lip usually
Where are eosinophilic plaques located?
Body
How do you dx eosinophilic granuloma complex?
C/S
Eosinophilia
Cytology with lots of eosinophils and maybe basophils
Biopsy
How do you treat eosinophilic granuloma complex?
Steroids initially
Atopica (cyclosporine can help)
Antibiotics for any secondary infection
What do you need to do to prevent eosinophilic granuloma complex from recurring?
Assess underlying hypersensitivity
Diet trial
Testing for environmental allergy
Trails with drugs to manage atopy
Flea control
What is canine juvenile cellulitis?
Young puppies with sterile pus usually
Secondary bacterial infection can occur
What is the etiology of canine juvenile cellultis?
Unknown
What are C/S of juvenile cellulitis?
Swollen muzzle, submandibular lymphadenopathy
Pustules, papules
Purulent otitis
Lethargy
Lameness
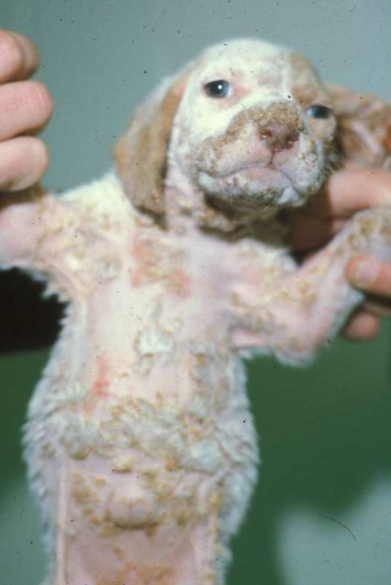
Juvenile cellulitis
How do you dx juvenile cellulitis?
Puppy and pyogranulomatous inflammation on cytology with no bacteria
How do you treat juvenile cellulitis?
Short course of prednisone or dexamethasone
Antibiotics if secondary infection is present
What is the signalment for acral lick dermatitis?
Large breed dogs, associated with allergic dermatitis, infection, and localized pain
Can be psychogenic
What are the C/S of acral lick dermatitis?
Single lesion where dog licks usually on carpal/metacarpal area
How do you diagnose acral lick dermatitis?
C/S are suggestive but can biopsy
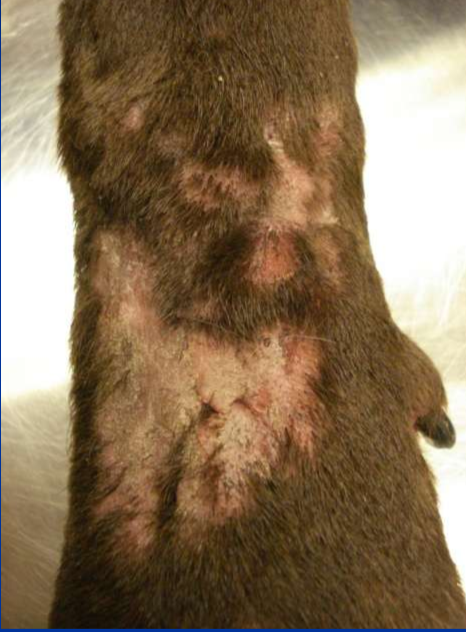
Lick granuloma
How do you treat acral lick dermatitis?
Treat with antibiotics if bacterial infection is there
Treat lesion itself with steroids, topicals, cryosurgery
Eliminate boredom and stress
Psychological drugs might be needed
What is the prognosis of acral lick dermatitis?
Very difficult to resolve
Alopecia and a focal area of thickened/fibrotic skin can persist is lesion becomes chronic
What is feline psychogenic alopecia?
Self-induced alopecia due to overgrooming and stress
Where is feline psychogenic alopecia found?
Ventrum, medial thighs, forelegs, sides
What is on biopsy for feline psychogenic alopecia?
Normal skin
How do you tx feline psychogenic alopecia?
Reduce stress and add enrichment
Can use SSRIs
When feline psychogenic alopecia is misdiagnosed what is missed?
An allergic cause
What is syndrome 1 of zinc-responsive dermatosis?
Decreased absorption of zinc in puppies causes dermatosis
What breeds are predisposed to canine zinc-responsive dermatosis?
Siberian huskies
Alaskan malamutes
What is syndrome 2 of canine zinc-responsive dermatosis?
Transiently affecting growing puppies with a diet that is high in calcium and phytates
What are C/S of canine zinc-response dermatosis?
Young adults with adherent scale (hyperkeratosis), erythema, crusts on face and footpads
How do you diagnose canine-zinc responsive dermatosis?
C/S or biopsy
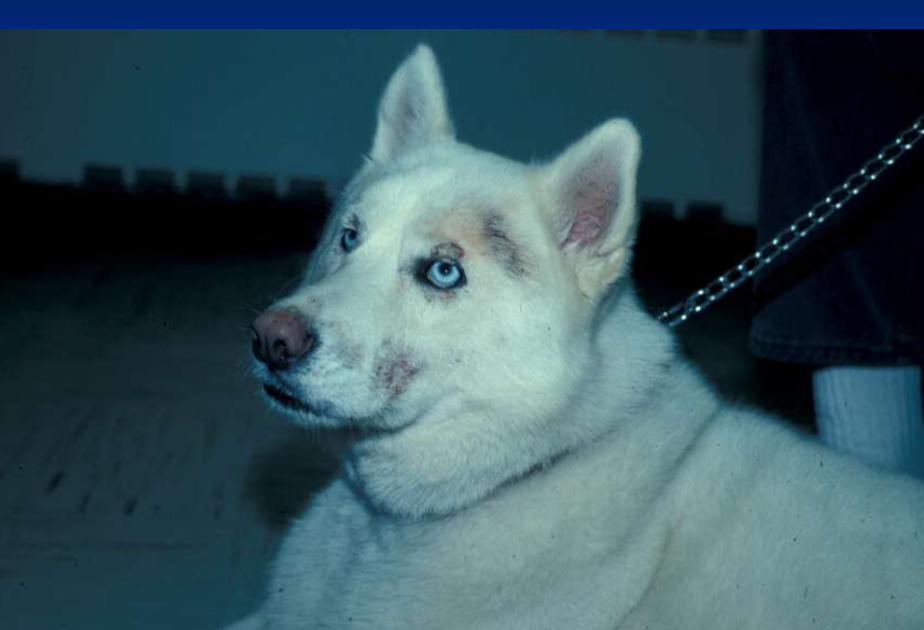

Zinc-responsive dermatosis
How do you treat canine zinc-responsive dermatosis syndrome 1?
Zinc supplementation for syndrome 1 starting with low end doses
What can enhance zinc absorption with canine zinc-responsive dermatosis tx?
Prednisone or fatty acids
How do you treat syndrome 2 canine zinc-responsive dermatosis?
Correct diet
How do you get granulomatous sebaceous adenitis?
Inherited in dogs
What is granulomatous sebaceous adenitis?
Sebaceous gland destruction due to granulomatous inflammatory response targeting sebaceous glands eventually they are destroyed
What does granulomatous sebaceous adenitis cause?
Scaly skin and poor hair coat due to destroyed sebaceous glands
What breeds are predisposed to granulomatous sebaceous adenitis?
Standard poodle, akitas, samoyeds, vizslas, german shepherds, havanese,
What are C/S of granulomatous sebaceous adenitis?
Scale, follicular casts, hypotrichosis, alopecia on face, pinnae and trunk
How do you dx granulomatous sebaceous adenitis?
C/S are suggestive
Definitively with biopsy
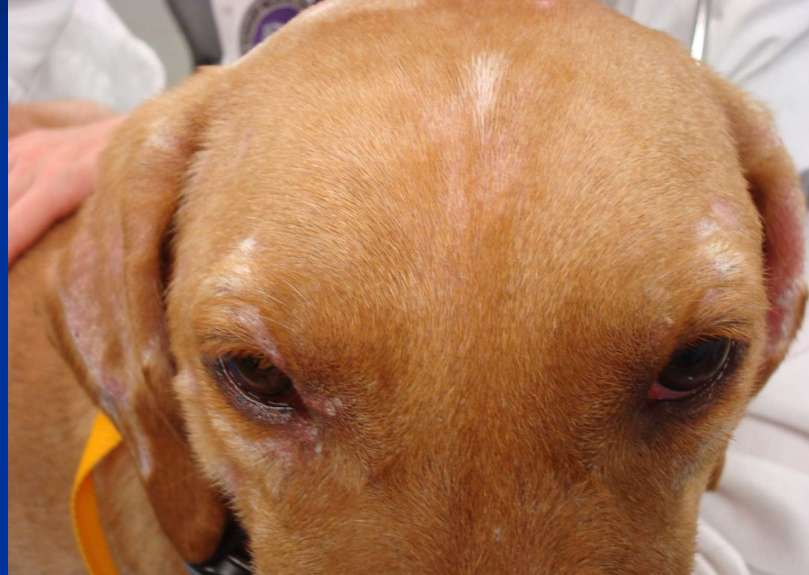
Sebaceous adenitis
How do you tx granulomatous sebaceous adenitis?
Keratolytic shampoos and moisturizers
Baby oil soaks then shampoo
Fatty acids
Cyclosporine
What is the goal when tx granulomatous sebaceous adenitis?
Decrease scale and improve skin quality but can be difficult to manage
What is hair cycle arrest (alopecia X)?
Disorder that causes progressive truncal alopecia. Includes many different disorders