A&P Chapter 1
1/45
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
What is Anatomy
The study of the structure of the body
What is Physiology
the function of the body (explains how the parts work and function)
What is the weight reference for a healthy male
155lbs
What is the weight reference for a healthy female
125lbs
What is the female sign for sex
XX
What is the male sign for sex
XY
What is Gross anatomy
study of parts of the body seen with the naked eye
What is another term for Gross Anatomy
Macroscopic anatomy
What is surface anatomy
the study of internal structures as they relate to the overlying skin surface (ex: locating veins)
What does Microscopic anatomy emphasize
cell organization and tissue
What is histology
the study of tissues
What is Developmental anatomy
changes in body structure from fertilization through old age.
What is Renal Physiology
the function of the kidneys and urine
What is the Principle of complementary of structure and function
The function of a certain body structure depends on its form
What is the organization of the body from smallest to largest?
organelles, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, and organism
Are body cells dependent or interdependent? Why?
Interdependent → they are each specialized to perform certain specific, limited functions rather than life-sustaining tasks
What is contractility
the muscle cell’s ability to move by shortening
What is excitability
the ability to sense & respond to stimuli
What is Metabolism
includes all chemical reactions that occur within body cells
What is anabolism
synthesizing more complex substances from simpler building blocks
What is catabolism
breaking down substances into simpler building blocks
What is Cellular Respiration
using nutrients & O2 to produce ATP
What is ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate)
enery-rich molecules that power cellular activities
What is excretion
the processing of removing wastes from the body
What is the rule for Growth
constructive activities must happen faster than destructive ones
What are the main survival needs of cell systems
Nutrients, Oxygen, Water, and Body temp/ atmospheric pressure control
What percentage of weight is water
50-60%
What is a normal body temp in C
37o C
What is the Law of Mass Balance
in order to ensure that the total amount of a substance in the body remains constant, any gain of that substance in the body must be offset by an equal loss.
What are the 3 steps of cell communication
Receptor, Control Center, and Effector
In Homeostatic Communication, what is the Receptor
(the first component)- a sensor that monitors the environment and responds to stimuli by sending the message to the control center
In Homeostatic Communication, what is the Control Center
determines the set point- analyzes input by comparing with set point.
What is the Set point
the level (or range) at which a variable is to be maintained
In Homeostatic Communication, what is the Effector
carries out control center’s response to the stimulus; causes shift for homeostasis
What are Negative Feedback Mechanisms
most common control mechanism; net effect is that the output of the system shuts off the original stimulus or reduces its intensity (opposite direction)
What is the Positive Feedback Mechanism
Feedback that tends to cause the level of a variable to change in the same direction as the initial change. (childbirth or blood clotting)
What is the Feedforward Response
maintains homeostasis by taking action in anticipation of a change to the internal environment (smelling food prompts saliva production and hunger)
What is the Afferent pathway
enters the control center from the receptor
What is the Efferent pathway
leaves the control center to the effector
What is the Hypothalamus
homeostatic control center
what are the basic body functions
integumentary, skeletal, muscular, endocrine, cardiovascular, urinary, and nervous systems
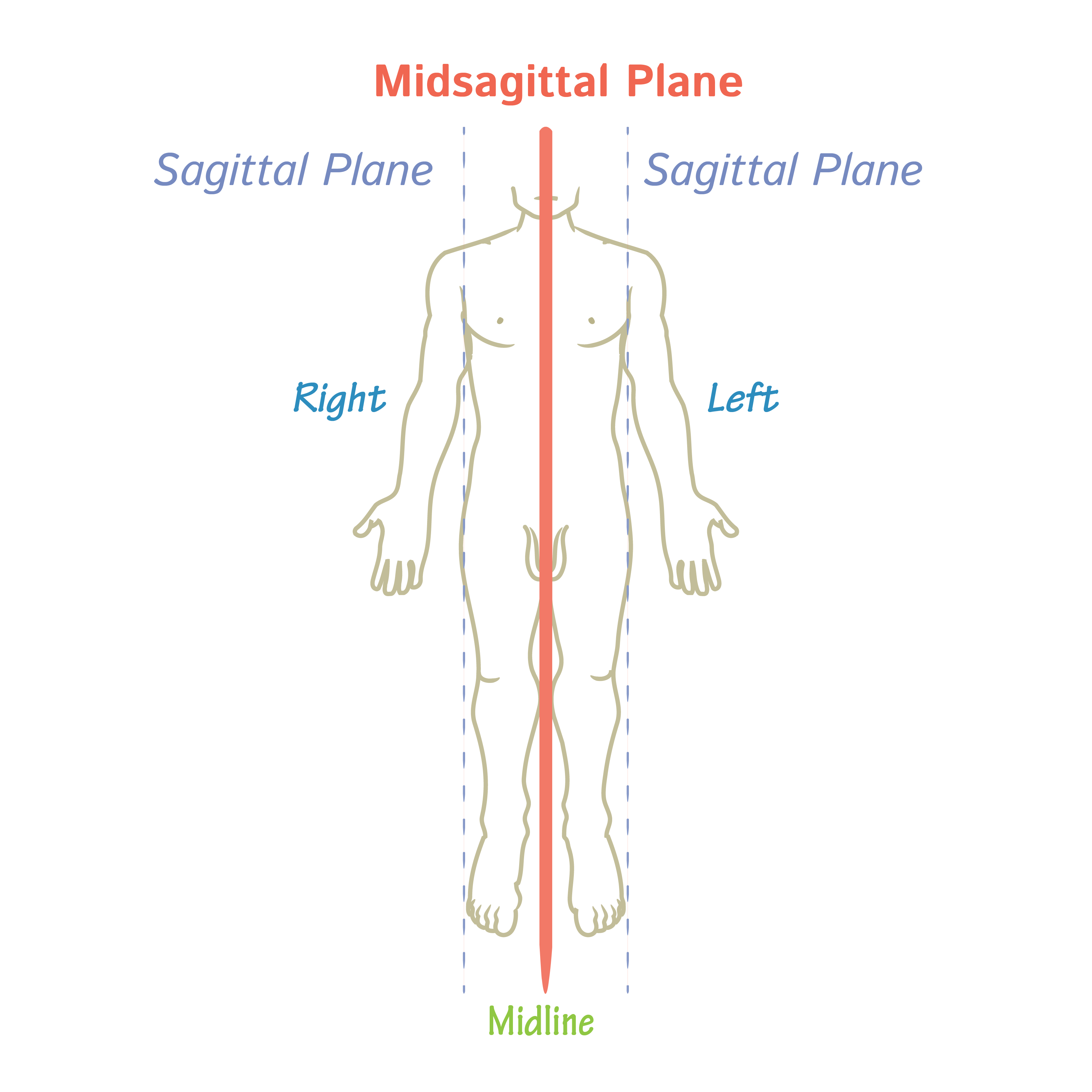
What is the Midsagittal plane
divides body into equal right and left parts
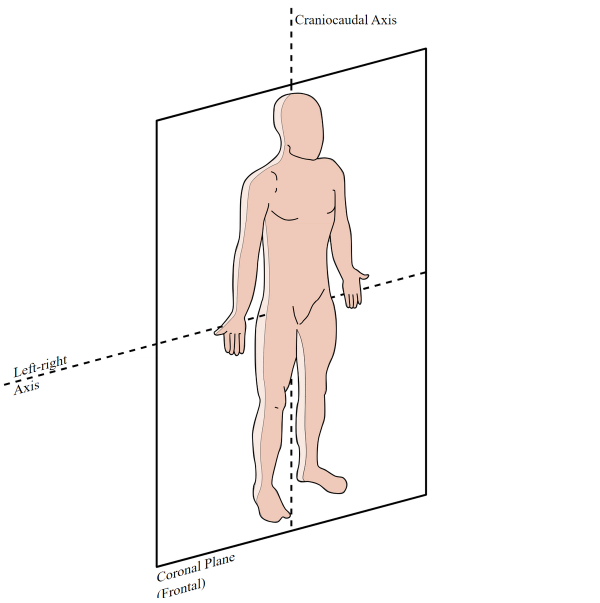
What is the Frontal plane
made parallel to body’s longitudinal axis
(anterior and posterior)
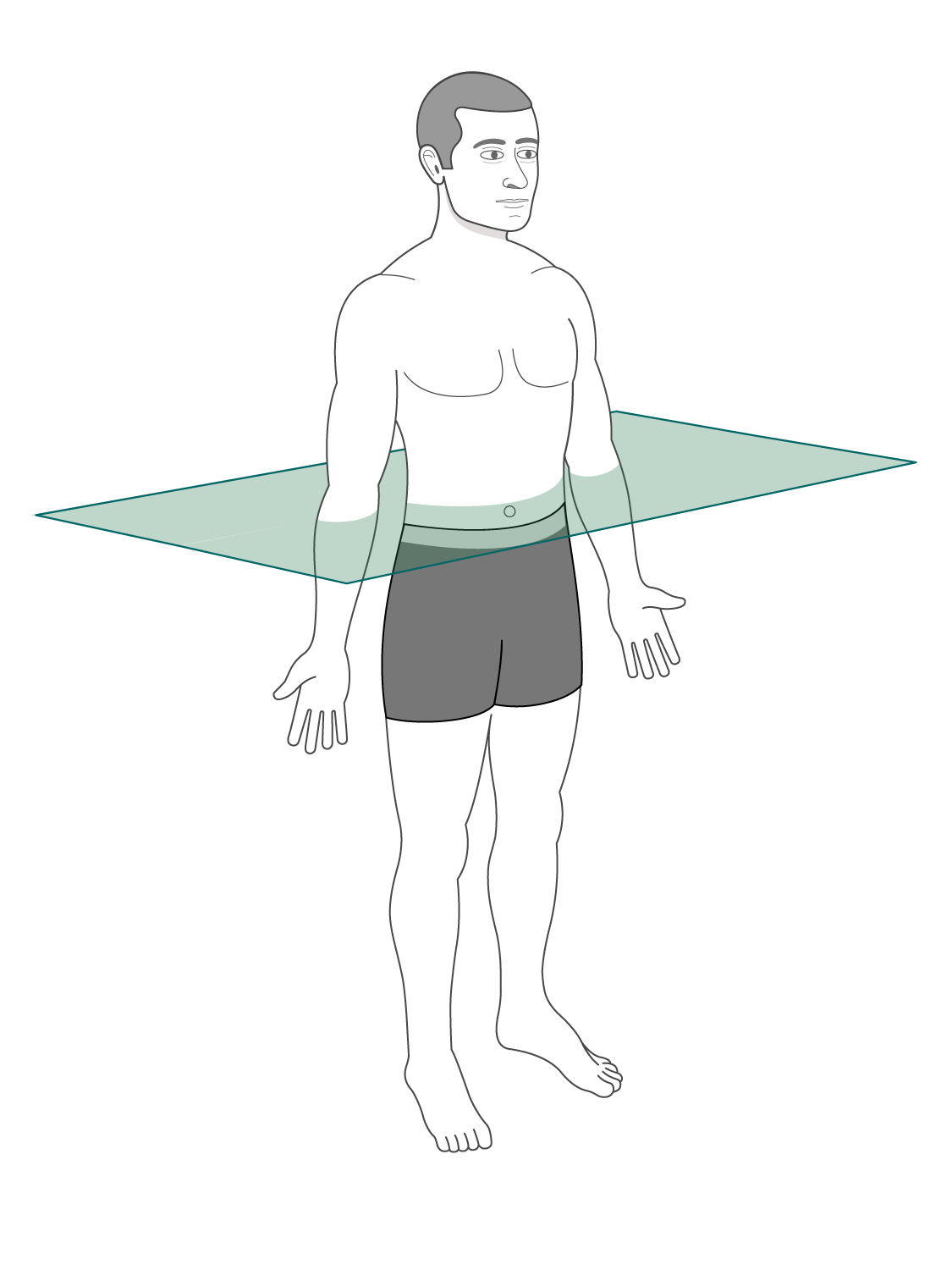
What is the transverse plane
perpendicular to the body’s longitudinal axis
(superior and inferior)
What is the Axial region of the body
the head, neck, and trunk
What is the appendicular region of the body
appendages or limbs attached to the body’s axis