Large Scale Tropical Weather Patterns and Oscillations
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
What is a hovmoller?
A time-longitude plot useful for seeing propagation of waves in the tropics. Typically plots outgoing longwave radiation (OLR) but can be other things.
What does lower OLR signify?
Colder cloudtops → convection
What is a Kelvin wave?
Move eastward and fast (15 m/s). Maximize near equator and rainfall hotspots. Equatorial trapped gravity wave with no meridional velocity, just zonal/vertical.
What is an Equatorial Rossby Wave? (ER)
Move westward and slow (5 m/s). Maximize off the equator (~12°) in the West Pacific. Restoring mechanism is the latitudinal gradient of the Coriolis parameter.
What is a Mixed Rossby-Gravity Wave? (MRG)
Either moves eastward and fast or westward and slow. Maximize off the equator, near the dateline. Combines restoring forces of buoyancy (gravity waves) and latitudinal gradient of the Coriolis parameter (ER).
What is the Gill Model?
Puts heat (Q) at the equator to realize an analytical response symmetric about the equator. Produces an idealized version of the Walker circulation:
Kelvin wave propagates rapidly east and generates easterly trades while Rossby wave propagates more slowly west and produces westerlies west of the heating.
What do the shallow water equations depict?
Inviscid flow of a thin layer of fluid in two directions. We use this when the horizontal scale is much larger than the vertical scale. Kelvin, ER, and MRG waves are in this flow, but Easterly Waves and the MJO are not.
What are the horizontal momentum shallow water equations?
\frac{\delta u}{\delta t}-\beta yv=-\frac{\delta p}{\delta x}
\frac{\delta v}{\delta t}+\beta yu=-\frac{\delta p}{\delta y}
Where Beta*y is equal to the coriolis parameter f.
What is the continuity shallow water equation?
\frac{\delta p}{\delta t}+\frac{\delta u}{\delta x}+\frac{\delta v}{\delta y}=-Q
Where Q is convective heating.
How do we assume solutions for the shallow water equations?
That u and v specify waves in (x,t) dimensions with an undetermined functional form in y.
v=e^{ikx-iwt} where k=wave number and w=frequency
Why do we care about equatorial trapped waves?
Powerful forecasting tools between 20° of the equator. Also cause wind perturbations at upper and lower levels (low-level easterlies in Kelvin wave, low-level westerlies in an ER wave) that can help trigger oscillations.
What is the MJO?
Madden-Julian Oscillation. A 30-60 day oscillation in the near-equatorial troposphere, and the dominant mode of intraseasonal variability in the tropics.
What are the three initiation theories for the MJO?
Convection and Environment
Different convective cloud type combinations by MJO phase
Ocean/air-sea processes
What are the three tracks MJOs typically take?
Directly east over the maritime continent
Northeast/southeast around the maritime continent
North to the Indian sub-continent
Where do MJO events typically start?
The Indian Ocean, but some are secondary events from a previous MJO that went all the way around the globe
What/where are the spectral peaks when trying to observe MJO?
Peaks in sea-level pressure for 40-50 days in the West Pacific, peaks in upper-level zonal winds for 30-60 days over the Central Pacific
Where does convection typically initiate and die within an MJO?
Convection can occur in the West Pacific, Maritime Continent, and the Indian Ocean, then dies off as the MJO propagates eastward into Central and West Pacific. The winds continue propagating and do not die off.
What is the Realtime Multivariate MJO Index (RMM)?
Pair of empirical orthogonal functions (EOFs) using OLR, 850 hPa zonal winds, and 200 hPa zonal winds. Useful real-time metric to determine location and strength of the MJO (strong MJOs outside unit circle).
How does convection move with the MJO?
Against the prevailing winds
How well can we predict the MJO?
Weather models and global climate models have trouble initiating the MJO but can predict it well once it starts
Which phases of the MJO are the hardest to predict?
Phase II (initation over the Indian Ocean) and Phase IV (complex maritime continent topography affecting different propagation paths)
What are the MJOs impact on tropical cyclogenesis?
Westerly wind anomalies aloft assist in Atlantic tropical cyclogenesis. Enhanced upper-level divergence in all basins assist in tropical cyclogenesis, but especially so in the West and East Pacific
What are the impacts over the United States due to the MJO?
Temperature anomalies can be predicted. Also, more rain can occur over the West Coast during certain MJO phases, often linked with atmospheric rivers.
How long was DYNAMO in the field? Why?
3.5-6 months because they wanted to sample multiple MJOs/multiple MJO phases
What kind of equipment did DYNAMO use?
Radars, soundings, aircraft, and ships
What was DYNAMO’s goal?
To identify and explore the different MJO theories
What is a monsoon and how does it occur?
A large-scale seasonal shift in low-level winds between land and ocean that is associated with dry winters and wet summers.
Land heats compared to the ocean in the summer forming low pressure and convection. Vice versa in the winter
What was Ramage (1971)’s criteria for monsoons?
Prevailing wind direction shift
Be a fairly continuous shift through the season
Mean wind > 3 m/s
Low synoptic pressure system (cyclone/anticyclone) occurrence
What are the different monsoon regions and their seasonality?
India/SW Asia
June-September
West Africa
May-July
Northern Austrailia
January-Feburary
SE Asia
SW United States
What are the typical rainfall patterns for the SW Monsoon?
20-200 inches (500-5000 mm). Regional variability due to topography (temperature difference enhancement). Highest totals are near the mountains and just offshore
What is the typical progression of the SW Monsoon?
Starts June 1st at the southern tip of India and reaches Pakistan by July 15th. Retreat starts in September and ends by mid-October
What are the five ingredients in Webster’s Elementary Monsoon?
Strong differential heating between the NH and SH
Coriolis (weak at EQ, flow typically cross-equatorial)
Land/sea temperature contrast and differing heat capacities (ocean 2 months behind land)
Surface Evaporation (monsoon reaps solar energy stored in tropical oceans)
Moist processes overland (latent heat mixed release)
What is the interseasonal variability of the monsoon?
Onset is driven by annual march of solar radiation, but year-to-year linked to the MJO. Also, active break period can occur during monsoons often about 2 weeks long due to synoptic-scale features the MJO
What is the interannual variability of the monsoon?
Droughts more likely to occur during El Nino years and during the negative phase of the Indian Ocean Dipole (occur biennially)
What are some impacts of monsoons?
The SW monsoon is vital to India’s agriculture and economy. If the monsoon withdraws early, late-planted crops are impacted. Lower than normal seasonal rainfall heavily impacts their economy
What model types would we use for monsoon forecasting?
Dependant on timescales
Seasonal → statistical
subseasonal → statistical/dynamical
5 days → numericla weather prediction
6 hours → observational network
What is the El Nino Southern Oscillation (ENSO)?
Coupled ocean-atmosphere phenomenon regarding SSTs in the eastern Pacific and sea-level pressure, affecting global weather and climate patterns.
What is the Southern Oscillation aspect of ENSO?
Low-latitude seesaw in sea level pressure between the eastern Pacific and the western Pacific. It is the atmospheric-based aspect
How does ENSO affect the Walker Cell?
La Nina enhances the walker circulation. El Nino weakens and disrupts it, even occasionally producing westerlies.
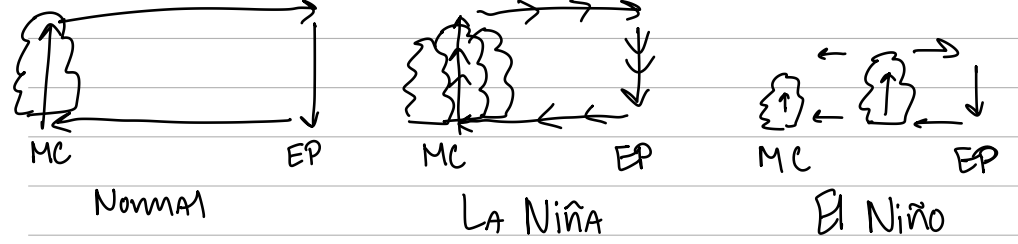
How does ENSO affect the upper ocean?
La Niña deepens the thermoclines in the West Pacific and causes extreme upwelling in the East Pacific. El Nino flattens the thermocline across the Pacific and suppresses upwelling the East Pacific.
What is the typical timeline of ENSO?
La Nina/El Nino lasts only about 1-2 years, with 2-7 years between successive events
What is the Southern Oscillation Index?
Measure of Tahiti → Darwin sea-level pressure changes. Normal is slightly positive
What is Nino indices in ENSO?
The numbers in the Nino indices represent different sectors of the tropical pacific, each focusing on the changes that typically occur in their respective sectors. Nino3.4 is the most common and measures both SST changes and convection signals
What is the Random Trigger theory in relation to ENSO?
ENSO onset theory. Proposes that a strong westerly wind anomaly weakens the easterly trades and starts an El Nino (such a wind anomaly can be caused by the MJO).
What is the Delayed Oscillator theory in relation to ENSO?
ENSO Onset Theory. Describes propagation and reflection of oceanic equatorial waves. Starts with a westerly wind burst that either:
Produces a downwelling Kelvin wave (warms upper ocean) that travels east.
Produces an upwelling Rossby wave (cools upper ocean) that travels west.
Takes 2-5 months to traverse the Pacific. They then hit a boundary and reflect as the other type:
A downwelling Rossby wave in the East Pacific, reinforcing warming from the Kelvin wave (2-5 month timeframe) → El Nino conditions.
An upwelling Kelvin wave in the West Pacific at the 5+ month mark that propagates east → La Nina conditions (in a year)
How well can we predict ENSO?
Limited by climate noise (weather), imperfect model physics, and imperfect data for initialization. However, Rossby waves can be observed for months before they reflect making seasonal climate forecasts with 3-9 months of lead time possible
What kind of teleconnections do we get from ENSO affecting TCs?
El Nino is assosciated with more TCs in the East Pacific and fewer in the Atlantic (mostly due to shear changes).
What kind of teleconnections do we get from ENSO affecting Texas?
In El Niño, the Pacific jet stream shifts eastward and equatorward into SW United States, causing Texas to have a cooler and wetter winter.
In La Niña, blocking is common over the North Pacific and Pacific NW, often causing drought over the winter in Texas.
What is the Modoki/Central Pacific El Niño?
Seperate from ENSO with different teleconnections/impacts. Creates warm Central Pacific SSTs and cool East Pacific SSTs. Can affect ENSO phase and impacts
What is the Quasi-Biennial Oscillation (QBO)?
Oscillation of lower stratospheric zonal winds, propagating alternating zonal wind directions downward about 1km/month over 26-30 months. Strongest about the equator with a half-width about 12° latitude.
What is the theory for QBO?
Convection generates waves that propagate in the vertical, dissipate in the stratosphere, and deposit momentum below the wind maximum. Easterly momentum is deposited by Rossby-gravity waves and westerly momentum is deposited by Kelvin waves. Wind maximum descends with time until a new wave can break through and travel higher in the stratosphere.
What impacts does the QBO have on the troposphere?
Upper-level shear, tropospheric depth, and deep convective properties are most common.
Westerly QBO increases Atlantic TC activity, Indian monsoon rain, and La Nina. Easterly QBO is linked to stronger MJO activity.
What is the Pacific Decadal Oscillation (PDO)?
Long-lived El Nino-like pattern of Pacific climate variability that lasts about 20 years. Signal is strongest poleward of 20°N, PDO can enhance the similar ENSO phase (e.g. warm PDO + El Nino) and impacts.
How was PDO discovered?
Comparing salmon catch in the Gulf of Alaska vs. the Oregon coast in the 1990s
How does PDO help with forecasts?
Improves long term outlooks as it appears to be an oceanic response to atmospheric forcing
What is the overall outlook for climate change in the tropics?
Wet regions (ITCZ, Indian Monsoon, etc.) will experience more extreme rainfall totals. Marginal-dry regions (trade-wind regimes, Sahel, etc.) will experience less rainfall totals.