Acid Base Equilibrium
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
CHEM 14BL
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
volumetric analysis is an experimental technique because
it is commonly used to determine the concentration of an unknown solution by measuring the volumes required to react completely with an unknown by using a standard solution
standard solution
a solution with a precisely known concentration
volumetric analysis is an
analytical technique
titrant
the solution inside the buret in a titration
acid base titration is a
volumetric analysis
titration graph
volume of titrant v. pH
strong acid
essentially 100% disassociated in water to produce H3O+ (ka = 10^6)
weak acid
disassociates very slightly in water (ka around 10^-6)
strong base
100% disassociated in water to produce OH-
weak base
disassociates very slightly in water (Kb around 10^-5)
terms “strong” and “weak” are
not related to the concentration of an acid or a base, related to the magnitude of ka or kb (disassociation in water)
strong acids have
large ka or small pka
weak acids have
small ka or large pka
strong bases have
large kb or small kb
weak bases have
small kb or large pkb
how to properly collect the experimental data in lab when performing volumetric analysis
use the pH meter as your reference, record buret volume when the pH readings change
approaching the equivalence point
very little NaOH is needed to increase the pH of the solution
equivalence point region
when the pH jumps up
equivalence point region on graph
around mid-point of the “vertical region
titration between a strong acid and a strong base
equivalence point pH = 7
titration between a weak acid and a strong base
pH > 7 (basic)
titration between a weak base and a strong acid
pH < 7 (acidic)
equilibrium exists
at every single point on a titration graph
buffer solution
consist of a weak acid and its conjugate base (or a weak base with its conjugate acid) to resist a change in pH when a strong acid or strong base is added to the buffer solution
if a buffer solution contains both HA and A- and is reacted with a strong base solution
stabilization of the base occurs when HA (weak acid) is in excess so it can neutralize all the base so it can produce the conjugate base
if a buffer solution contains both HA and A- and is reacted with a strong acid solution
stabilization of the strong acid occurs when the conjugate base neutralizes it and produces the conjugate acid to stabilize the pH
buffer pH equatio
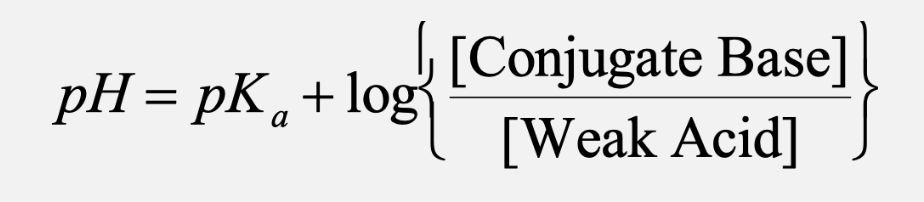
what is special about the half-equivalence point
half equivalence point (added half of the titrant) is still within the buffer region
at half equivalence point
[conjugate base] = [weak acid] for the best general purpose buffer
limitations of the henderson-hasselbach equation
ka for the weak acid in buffer < 10^-5 and applies only to buffer solutions
half equivalence point
pH = pka