AQA physics a level - electricity
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
electric current
the rate of flow of charge around a circuit
potential difference
energy transferred per unit charge between two points.
resistance
the ratio of potential difference across a component to current flowing through it
ohms law
the current through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the voltage across the two points and inversely proportional to the resistance where physical conditions such as temperature remains constant
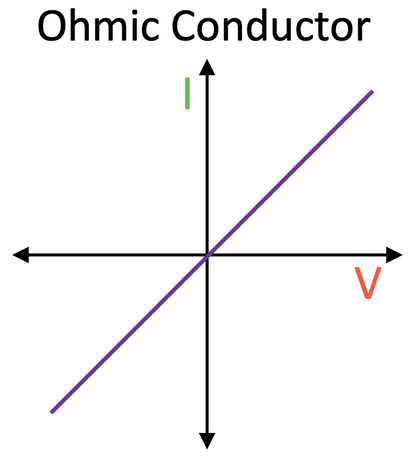
graph for an ohmic conductor
linear graph through the origin
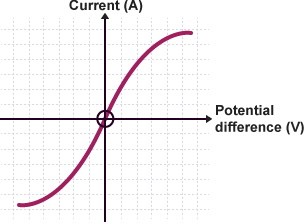
graph of a filament lamp
when the filament gets hot as the current increases causing a higher resistance. the increased collisions of the electrons with the metal ions causes more kinetic energy to be transferred to the metal and therefore will vibrate more vigorously, so it is harder for a current to flow.
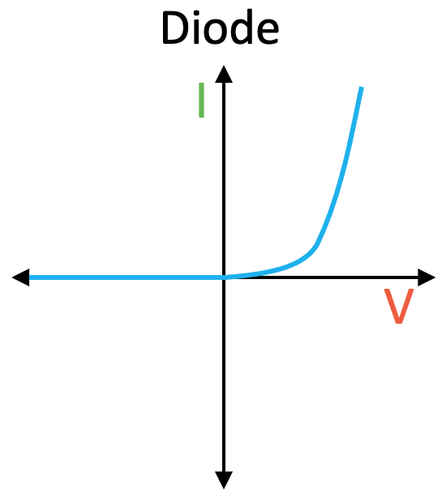
graph of a semiconductor diode
current only flows in the forward bias after surpassing a threshold voltage.
resistivity
how easily a metal conducts electricity (resistance of a material 1m³)
semiconduction
loosely bound electrons released after a threshold voltage is applied
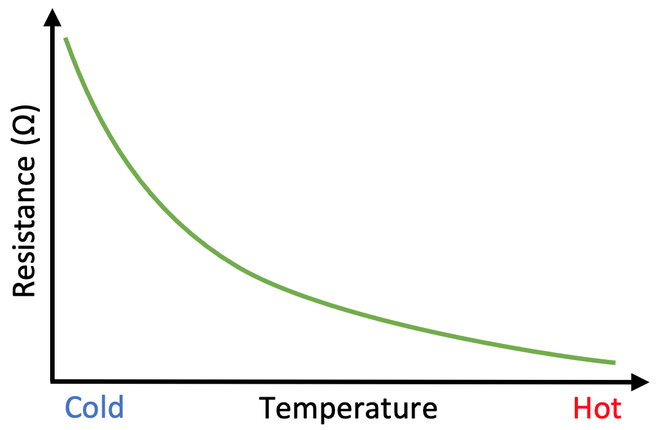
how does a thermistor work
as temperature ↑ the resistance ↓ due to atoms within the thermistor releasing electrons, and increase in charge carriers increases current meaning the resistance decreases V=IR
what is application of a thermistor
temperature sensor (to turn of heating in a home)
what is a superconductor
a material that when cooled below a critical temperature has zero resistance
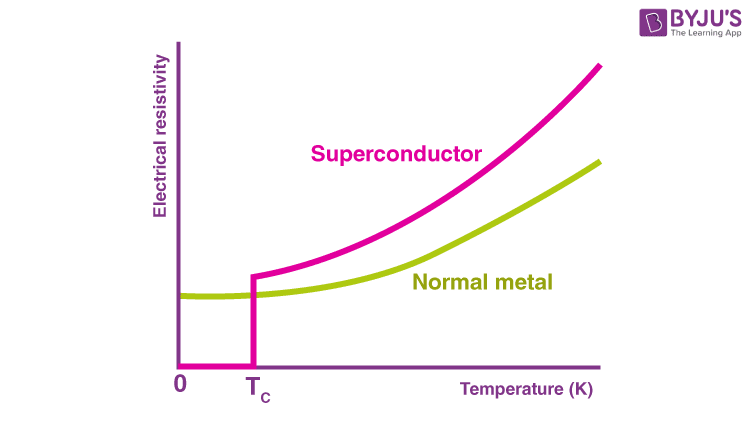
what are the two uses of super conductors
power cables - reduce the energy loss to zero during transmission, however this is expensive to keep the cables cold enough
strong magnetic fields without need of a constant power source
characteristics of series circuits
current is the same everywhere
voltage is shared across components
total resistance is the sum of all resistances within the circuit
characteristics of parallel circuits
current is shared
voltage is the same across branches
1/Rtotal=1/R1+1/R2+…
kirchoffs first law
total current flowing in must flow out
kirchoffs second law
sum of voltages in series must equal battery voltage
what is potential divider circuit
a circuits with several resistors that have a required fraction of the potenial difference source