Biology Chapter 8: Photosynthesis
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Photosynthesis
CO2 + H2O + Light —> C6H12O6 (glucose)+ O2
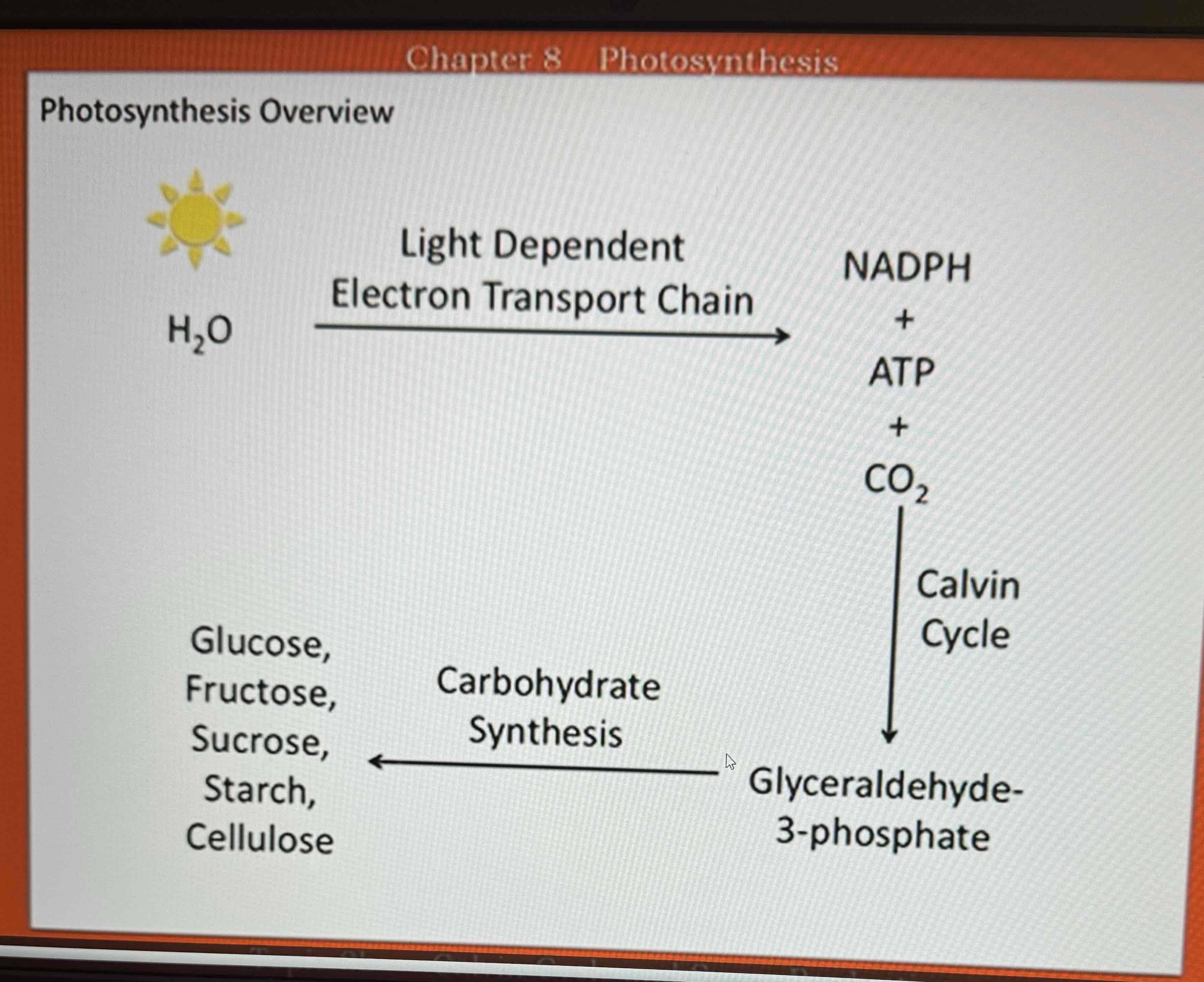
Process used by living things to capture light energy and convert it into useable chemical energy stored in the chemical bonds of a carbohydrate (Ex, glucose). In this process, CO2, light, and water are used to make sugar: 6CO2 + 6H2O + light —> C6H12O6 +6O2, oxygen is produced as a byproduct, photosynthesis occurs in plants, algae, and some bacteria (occurs in the chloroplast), 3 processes: Light Dependent Electron Transport Chain, Calvin Cycle, Sugar Production will produce carbs + oxygen: C6H12O6 + 6O2
Light is harvested by photosystem 1 and 2 by way of pigment (organic (carbon based) molecule that absorbs light of a specific range) molecules attached to the proteins, more pigments = different ranges of light that can be absorbed, plant pigments mainly absorb reds + blues, yellow + green is not absorbed, which is the reason plants appear green to us
Light Dependent Electron Transport Chain
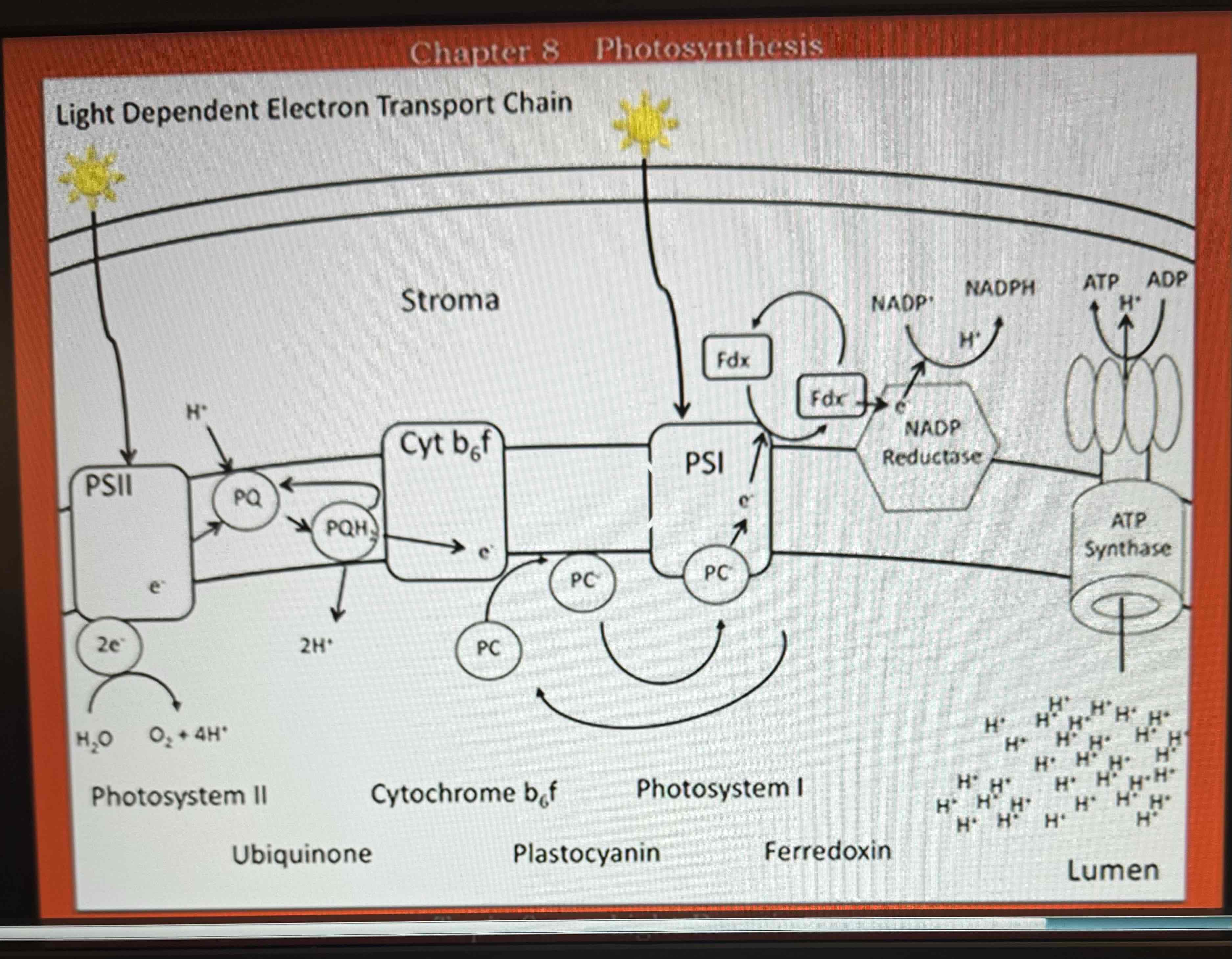
Begins with Light + Water, Ends with NADPH + ATP, occurs across the thylakoid membrane of the chloroplast: Photosystem 2 harvests a photon of light and uses it to break down a water molecule into O2 that can diffuse throughout the chloroplasts, H+ remains in the lumen and cannot diffuse, e- become energized with the remaining energy from the light, plastoquinone picks up H+ from stroma and e- from PS2. It deposits H+ into the lumen and passes e- to Cy+b6f, Cy+b6f passes the e- to plastocyanin which takes the e- to PS1. PS1 re-energizes the e-, PS1 passes the re-energized e- to Ferridoxin which takes it to NADP reductase, NADP reductase uses the energy to produce NADPH, protons have accumulated in the Lumen pass through a transmembrane protein channel/enzyme called ATP synthase. The energy produced by diffusion i used to produce ATP, ATP is cellular energy currency
Calvin Cycle
Input: NADPH, ATP, CO2, Product: Glyceraldehyde 3 phosphate, utilizes the NADPH + ATP to from the e-transport chain to “fix” CO2 from the atmosphere and build carbon molecules in 3 stages:
Fixation of CO2
Reduction
Regeneration
Begins with CO2, uses the NADPH + ATP produced by the electron transport chain to make a 3-carbon molecule called Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate, these reactions occur in the stroma of the chloroplast, can be split into 3 phases: Fixation of CO2, Reduction, Regeneration
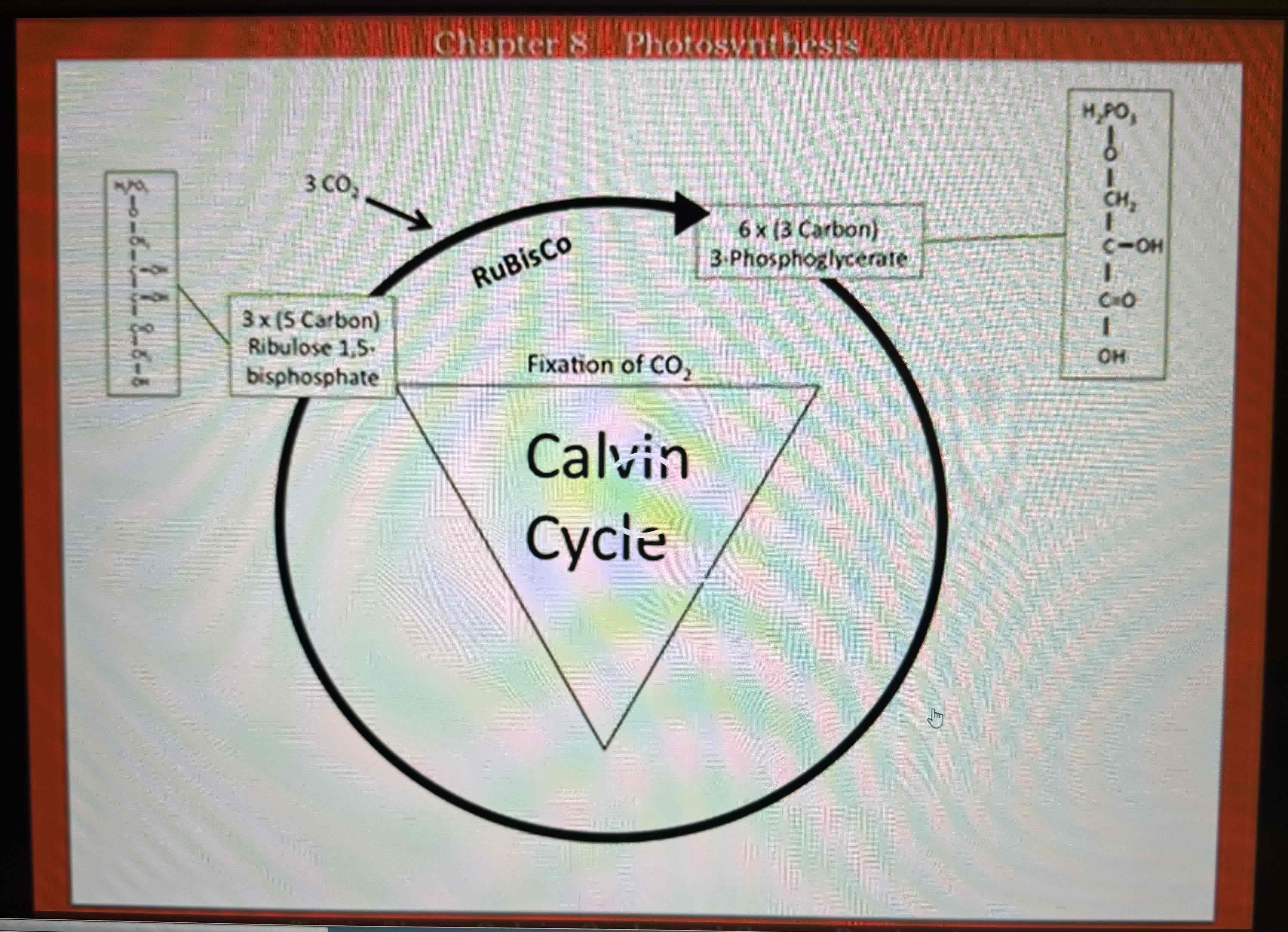
Fixation of CO2
carbon dioxide is fixed by the enzyme RuBisCO - Ribulose Biphosphate Carboxylase/Oxygenase, CO2 is added to an existing molecule called ribulose 1,5 biphosphate
the enzyme RuBisCO adds CO2 to Ribulose 1,5 biphosphate to make 3-phosphoglycerate
3 CO2 molecules are attached to 3 (x5 carbon ribulose 1,5 biphosphate) molecules by the enzyme RuBisCo: produces 6 (x3 carbon molecules of 3-phospoglycerate)
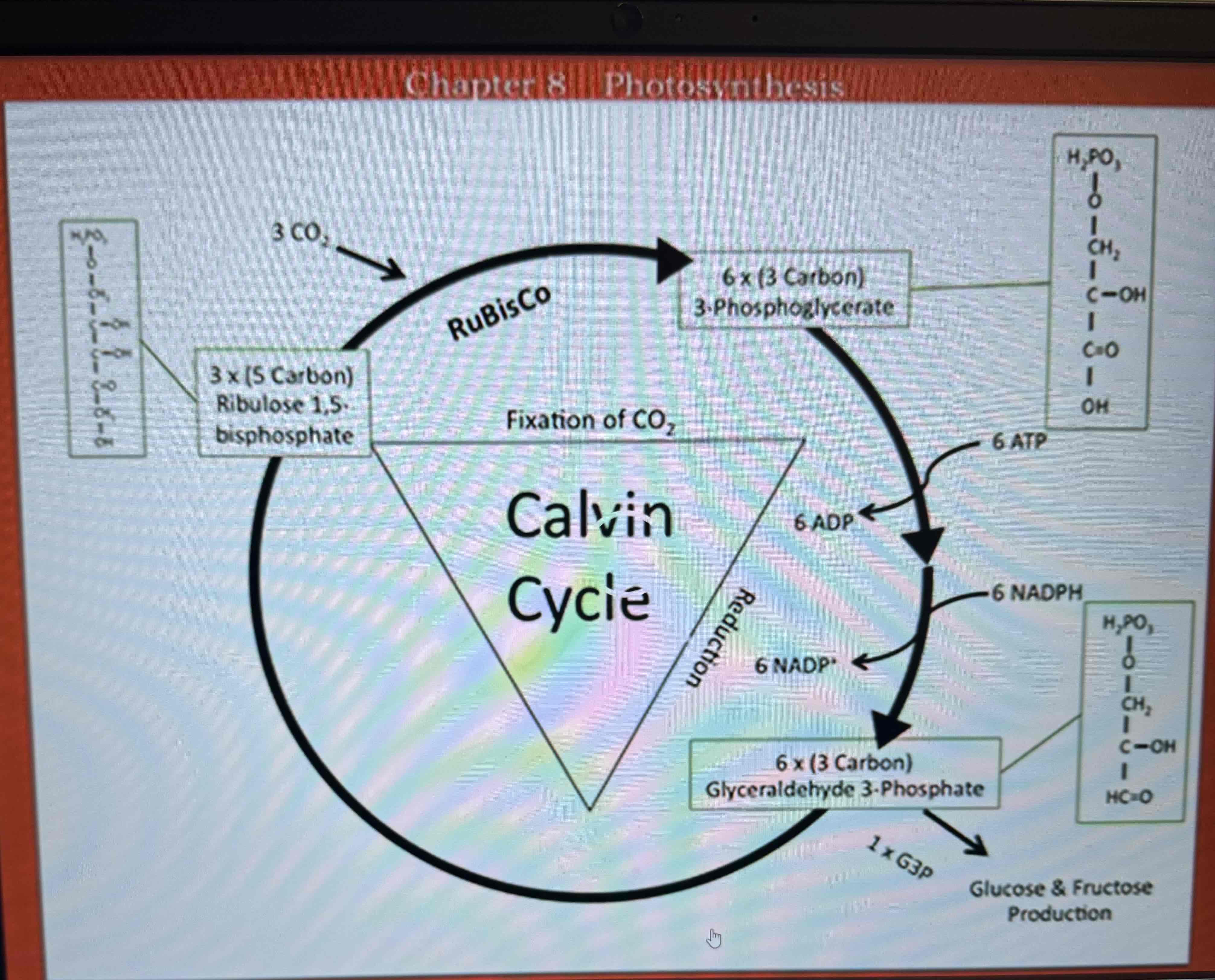
Reduction phase
ATP + NADPH are consumed to produce Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate or G-3-P
ATP and NADPH are utilized to convert 3-phosphoglycerate to G-3-P
3-phosphoglycerate molecules are converted into glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate, ATP + NADPH are consumed during this phase, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate is the molecule that will be used to build other carbohydrates
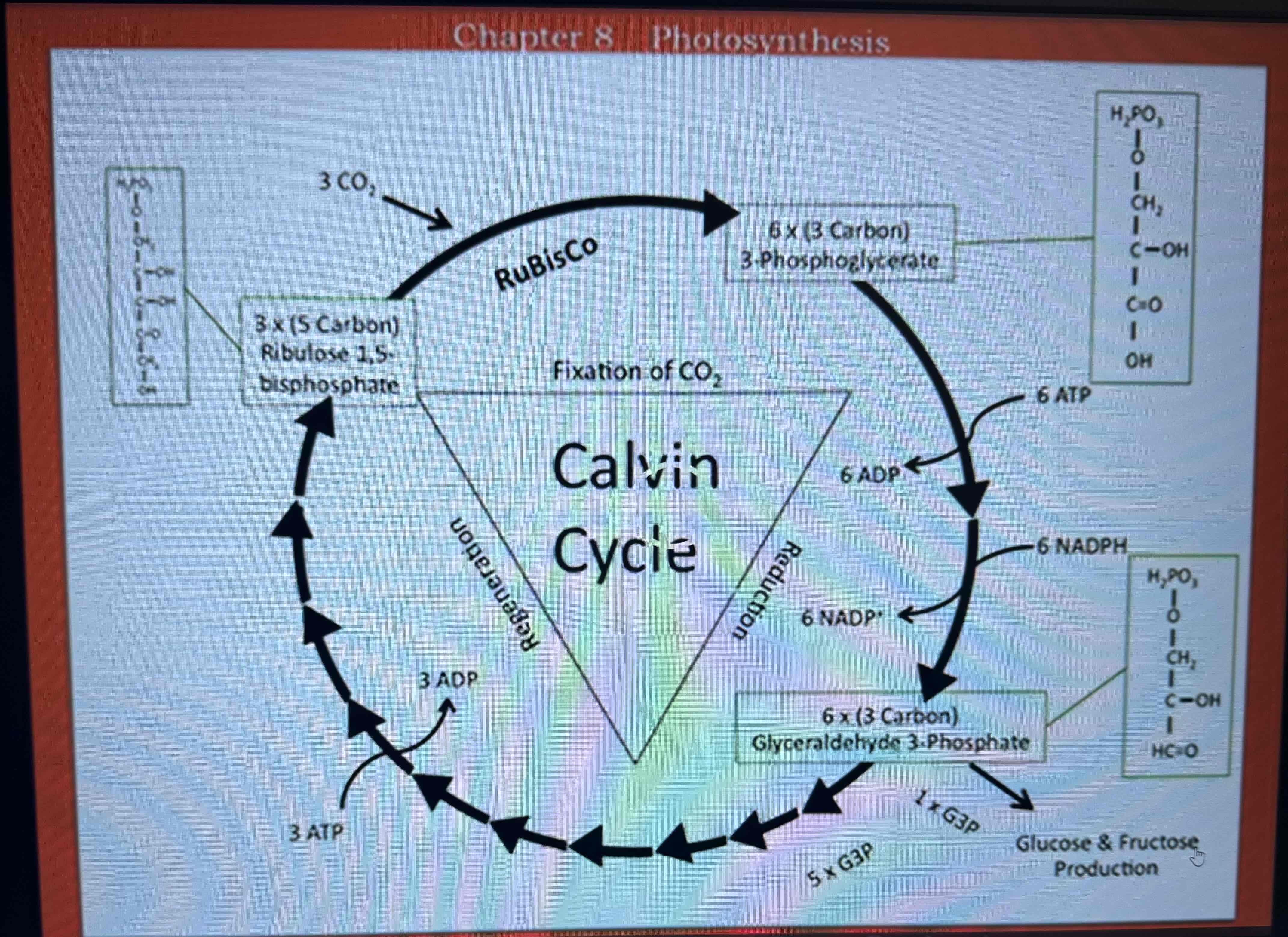
Regeneration
some G-3-P is used to produce ribulose 1,5 biphosphate, more ATP is consumed
For every 6 glyceraldehyde-3-phosphates produced, 1 goes to carbohydrate production and 5 are used to continue the Calvin cycle, so more ATP is consumed to regenerate ribulose 1,5 bisphosphate from the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
Photosynthetic Eukaryotic cells
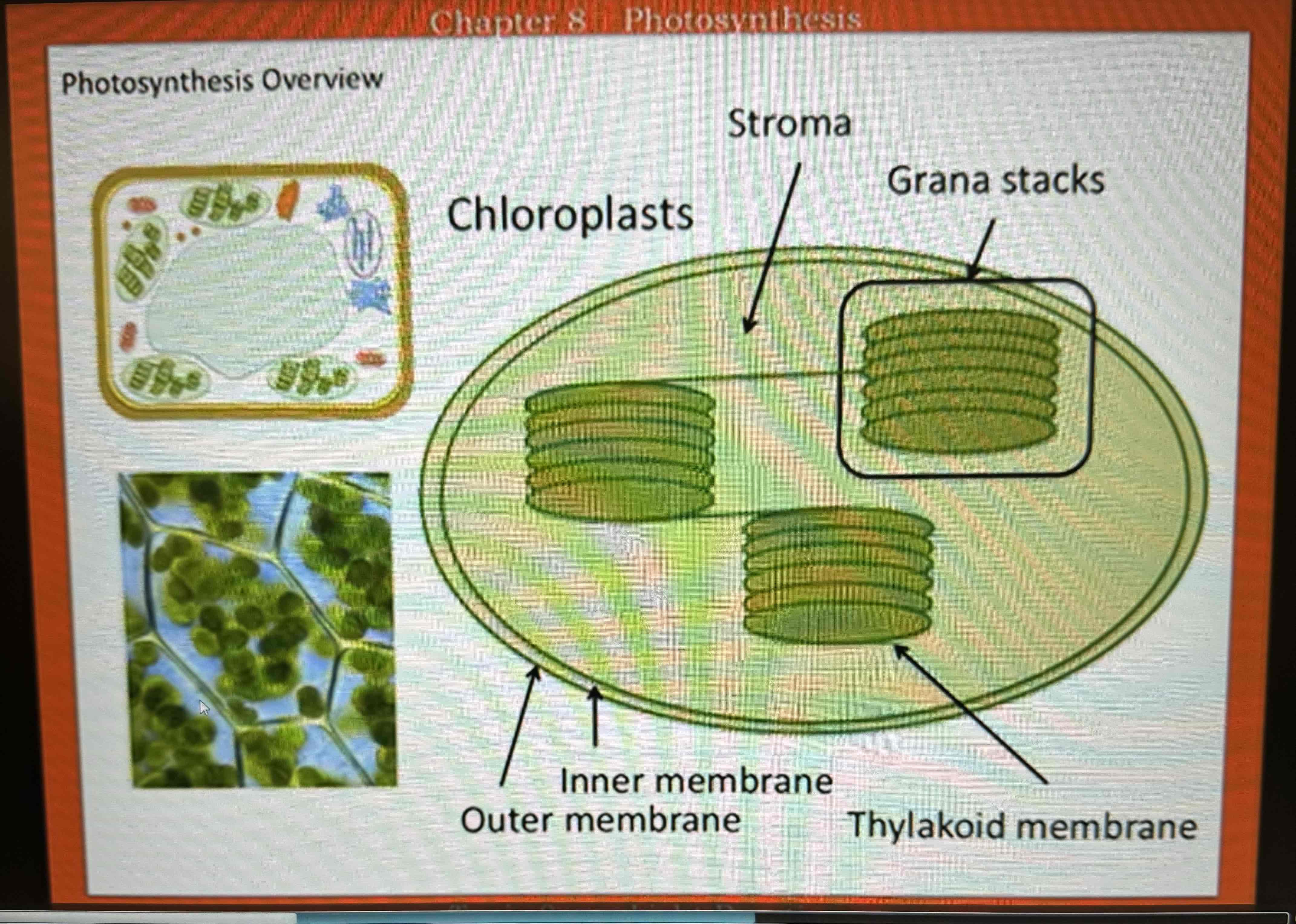
both processes occur in the chloroplast (chloroplast has 3 membrane systems). 1st stage of photosynthesis: Light Dependent electron transport chain - occurs in the thylakoid membranes, space between thylakoid membrane and inner membrane is called the stroma, thylakoid membranes form vesicle like sacks - interior of sack is called the lumen, begins with: Light + H2O, ends with: NADPH + ATP —> these reactions occur on the thylakoid membrane of the chloroplast (basically what you need to know is that Light Dependent Electron Transport converts light energy and water into ATP and NADPH)
Light absorbed by complex of protons called photosystem 2 (PS2)
Energy is then used to break a water molecule + collect an electron: electron passed to proton is called plastoquinone + grabs protons from the stroma
Plastoquinone will pass electrons to the cytochrome b6f complex and pass 2 protons into the lumen
Electrons will be passed to the protein plastocyanin, plastocyanin passes the electron to photosystem 1
Photosystem 1 (PS1) absorbs more light + uses it to re-energize the electron, Electron then passed to ferredoxin, which then passes it to the enzyme NADP reductase which produces NADPH
Enzyme ATP synthase uses the proton gradient to produce ATP
Process moves protons from the stroma to the lumen, creating a proton gradient
Sugar Synthesis
Begin with Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (G-3-P), will be converted to simple sugars, ends with glucose and fructose, this will occur in the cytosol, G-3-P is produced in the stroma of a chloroplast to produce carbohydrates, it will be exported to the cytosol, once there 2 of these molecules can be used to build a 6 carbon fructose molecule, fructose can be converted to glucose - these 2 monomers can be combined to make sucrose or the glucose will be used to produce starch and cellulose
G-3-P is used to produce fructose, glucose, starch, cellulose, and all other carbon compounds in the plant cell
Where is the chloroplast in the photosynthetic electron transport chain located?
thylakoid membrane
Photosystem 2 uses light energy to disassemble a water molecule at the start of the photosynthetic electron transport chain, what is produced from the water molecule?
Electron: Travel through the electron transport chain, the energy they carry is used to transport protons into the thylakoid lumen and eventually produce NADPH
Protons: accumulate in the thylakoid lumen, they are used by ATP synthase to produce ATP
Oxygen: By-product that has no role in photosynthesis
What is the role of the enzyme RuBisCO?
to fix carbon dioxide from the atmosphere
What is carbon dioxide initially attached to?
Ribulose-1,5 biphosphate
what is the primary product of the calvin cycle?
glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
Which product(s) of the photosynthetic electron transport chain are used by the Calvin cycle?
ATP, NADPH
Where does the photosynthetic electron transport chain occur?
thylakoid membrane
How many photosystems occur in the photosynthetic electron transport chain?
2
How do photosystems absorb light?
pigment
What is the source of the electron that is used by the photosynthetic electron transport chain?
water
The photosynthetic electron transport chain uses these things as substrates and enzymatic co-factors (i.e. inputs)
light and water
The photosynthetic electron transport chain produces these products
ATP, NADPH, oxygen
The Calvin cycle uses these things as inputs
Carbon Dioxide, NADPH, and ATP
The Calvin Cycle produces this product
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
Sugar production makes this compound from glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
fructose