KPER 1500 Chap 4
1/108
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
109 Terms
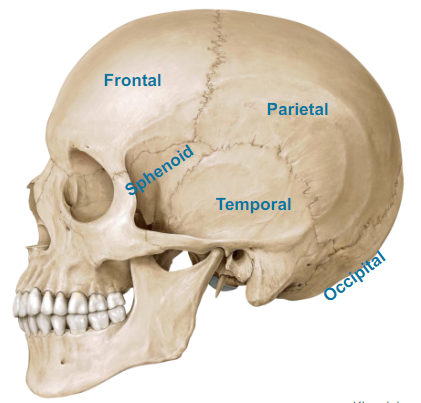
What are the Calvaria parts of the Skull?
Frontal (forehead, frontal bone)
Parietal (both back sides of the head, it’s a flat bone)
Sphenoid (dont worry)
Temporal (near the ears)
Occipital (very back of your head)
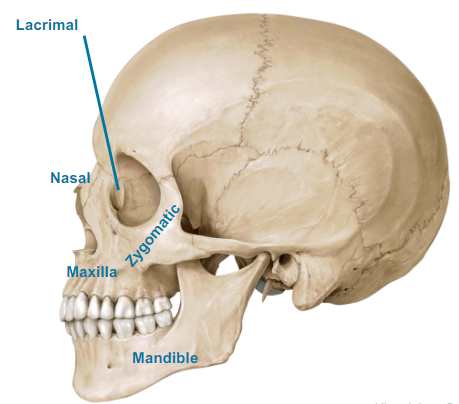
What are the Facial bones of the Skull?
Lacrimal (dont worry)
Nasal (nose bone)
Maxilla (bottom of your nose, mustache region)
Zygomatic (cheek bones, dont worry)
Mandible (jaw)
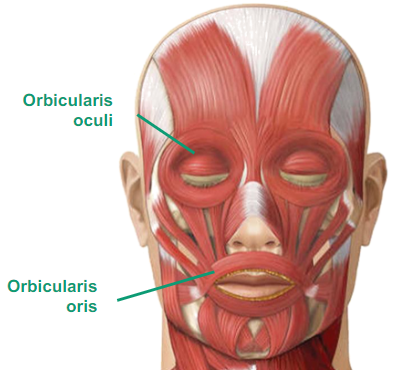
What are the Facial Muscles?
Orbicularis oculi (around the eye, of the eye, ability to blink, to wink, etc)
Orbicularis oris (oral, of the mouth, pucker our lips, keeping lips shut)
What are the parts in the Back Region?
Vertebral Column
Ribs and Sternum
Neck and Back muscles
Abdominal muscles
What is the Vertebral column made up of?
made up of 33 vertebrae
Describe the Vertebral Column
7 cervical vertebrae (neck)
of the neck
12 thoracic vertebrae (chest)
of the thorax, where the rib cage is, where ribs are attached to
5 lumbar vertebrae
L for low back, L1 to L5
1 sacrum
5 fused vertebrae (midline region of buttocks)
the dimples on your back
1 coccyx
3 or 4 fused vertebrae (tail bone)
What are Intervertebral discs?
absorb shock along the vertebral column
What’s the reason you hear C1 and T4 or L3
the letter means what part of vertebrae and the number means which one it is (each vertebrae has a number of them)
What does the Ribs and Sternum made up of?
12 pairs of ribs
Describe the Rib
1 to 7 = True ribs
all directly attached to the sternum
8-10 = False Ribs
aren’t attached to the sternum
attached to other True ribs to connect indirectly to the sternum
11-12 = Floating ribs
2 pairs of ribs that attach only to the vertebral column
chilling ribs
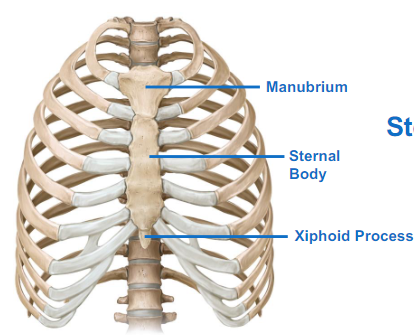
Describe the Sternum
= breastbone
Manubrium
Sternal body
Xiphoid process
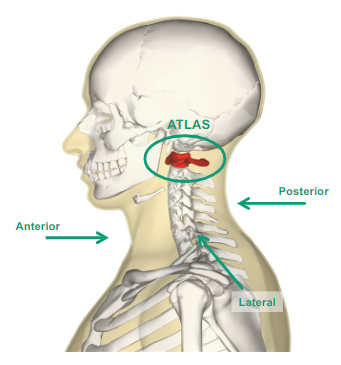
What does Atlas mean?
It’s the first vertebrae where the head sits on (C1)
What is Axis?
C2 portion of the cervical vertebra
How do we maintain our head looking straight ahead?
The muscles posterior, lateral, and anterior to the neck or cervical region
On the Anterior part of our Neck and Back muscles, what muscle is there?
Sternocleidomastoid
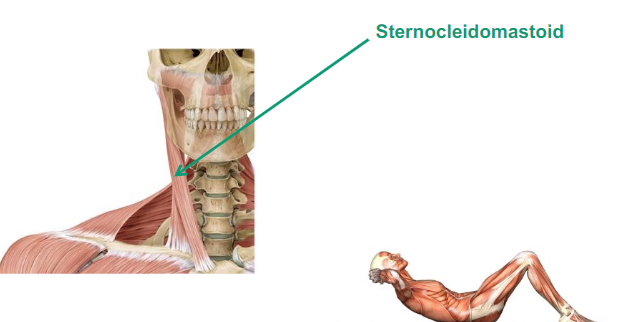
Describe Sternocleidomastoid
attached to your sternum (Sterno), clavicle (Cleido) and mastoid = behind ear
On the Posterior part of our Neck and back muscles, what muscle is there?
Erector Spinae
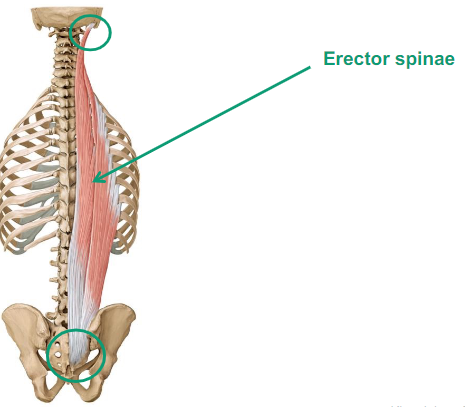
Describe Erector spinae
group of muscles
keep us upright
muscle mass that helps you maintain your upright posture
they do spinal extension
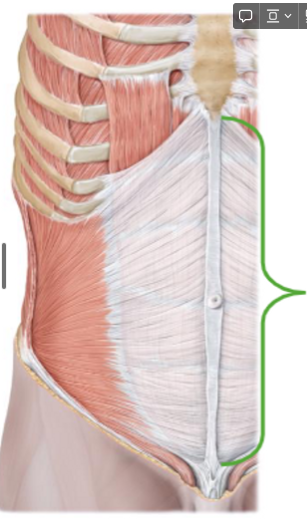
Describe the Abdominal Muscle
Attach
Posteriorly: vertebral column, ribs, and hip bone
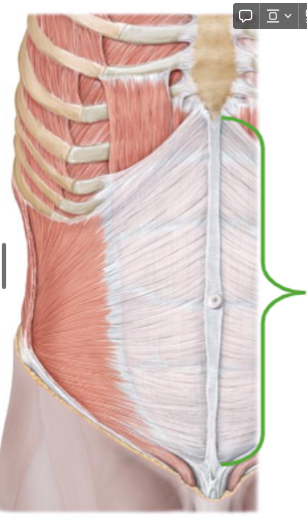
What is this?
Linea alba (anteriorly)
a thin band of connective tissue that runs down the front of your abdomen.
It separates the left and right sides of your rectus abdominis
What are the different parts of the Abdominal muscles
External oblique
Internal oblique
Rectus Abdominis, Transversus abdominis
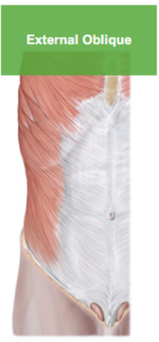
Describe the External Oblique
fibers come down on an angle (fingers in your pocket)
helps with rotation, lateral bending, flex spine forward
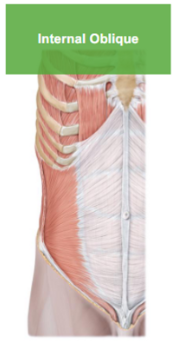
Describe the Internal Oblique
helps external oblique,
underneath the external oblique,
important to keep our rib cage down
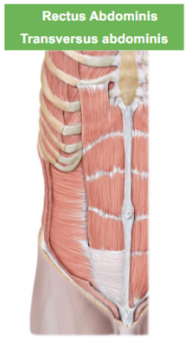
Describe the Rectus Abdominis
cube looking muscle,
our abs,
attaches to zyphoid to the pubic bone to cause flexion
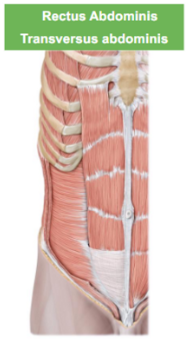
Describe the Transversus Abdominis
it hold our guts in
What does Abdominis mean?
it’s to lock our stability (our score)
What is in the Appendicular Skeleton?
Pectoral Girdle
Scapulohumeral Region
Upper Limb
Pelvic Girdle
Lower Limb
Describe the Pectoral Girdle
Suspends the upper limb away from the chest wall
Enables a great range of movement
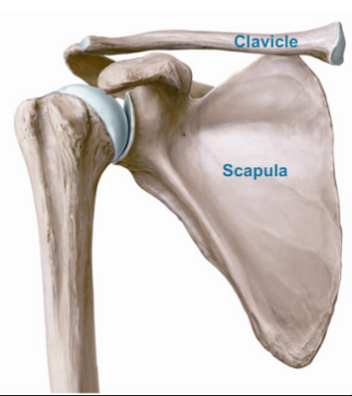
What are the Bones of the Pectoral Girdle?
Clavicle (Collar bone)
Scapula (Shoulder blade)
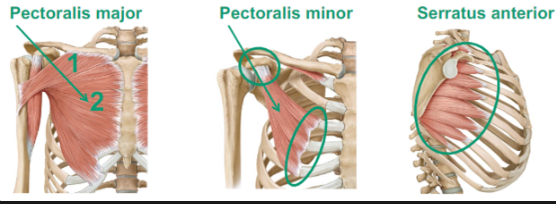
What are the Anterior Muscles of the Pectoral Girdle?
Pectoralis major
Pectoralis minor
Serratus anterior
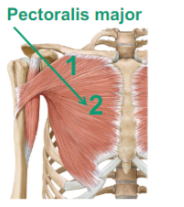
Describe the Pectoralis Major
(attaching to the clavicle, sternum and the ribs, comes out and gets attached to your humerus (arm bone))
will do shoulder flexion
adduct (adduction) to the midline (chest fly workout)
will do medial rotation
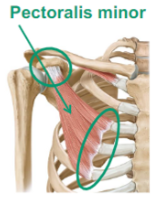
Describe the Pectoralis Minor
goes from the scapula, pulls it forward
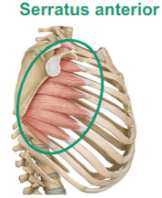
Describe the Serratus Anterior
serratus (sawlike) attaches from your scapula to your rib cage
Word for pulling your scapula forward is?
Protract
What are the Posterior Muscles of the Appendicular Skeleton?
Trapezius
Latissimus Dorsi
Levator Scapulae
Rhomboid Major and Minor
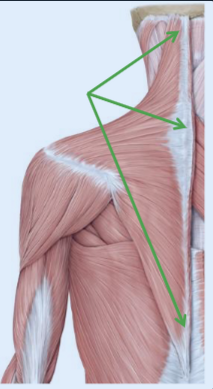
Describe Trapezius
runs from your spine to your clavicle and then scapula
upper ___, upper fibers shorten, it will cause us to shrug our shoulders (elevates the shoulders)
middle ____, retract, pull backwards
lower ___, depress the scapula, pull the scapula down
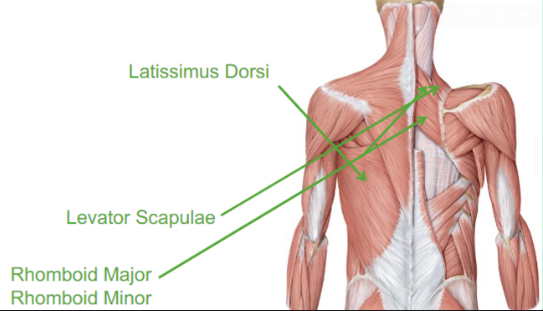
Describe the Latissimus Dorsi
lat pull down
seating row
will extend, adduct and medial rotates
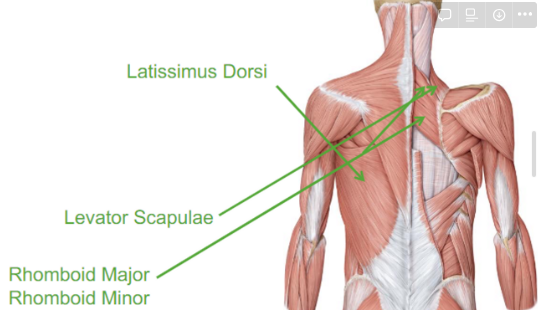
Describe the Levator Scapulae
elevates our scapula
scapula to our vertebrae
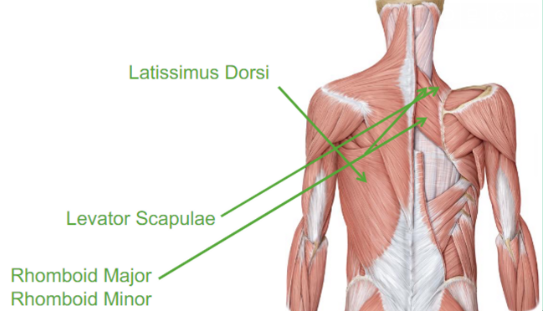
Describe the Rhomboid Major and Minor
they both do similar retraction
What are the Joints in the Appendicular Skeleton
Sternoclavicular
between our sternum to our clavicle
Acromioclavicular Joint
a joint in the shoulder where two bones meet
Describe the Scapulohumeral Region
Rotator cuff muscles (also known as SITS muscles)
What are the SITS muscles in the Scapulohumeral Region
Supraspinatus (Ab = abduction)
Infraspinatus (Ex = externally rotate)
Teres Minor (Ex = externally rotate)
Subscapularis (In = internally rotate)
Which muscles are in the Superior and Posterior part of the Scapulohumeral Region?
Supraspinatus
Infraspinatus
Teres minor
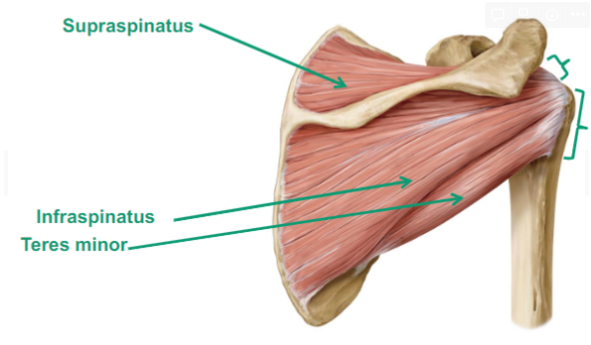
What are the Anterior muscles of the Scapulohumeral Region?
Subscapularis
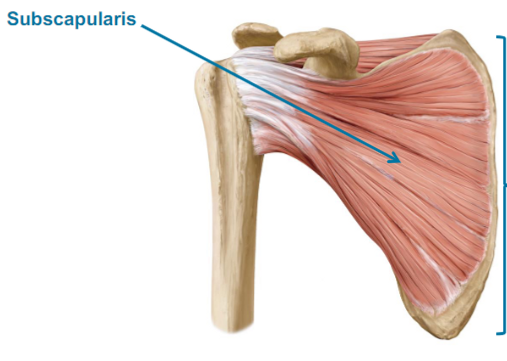
What are the Lateral muscles of the Scapulohumeral Region?
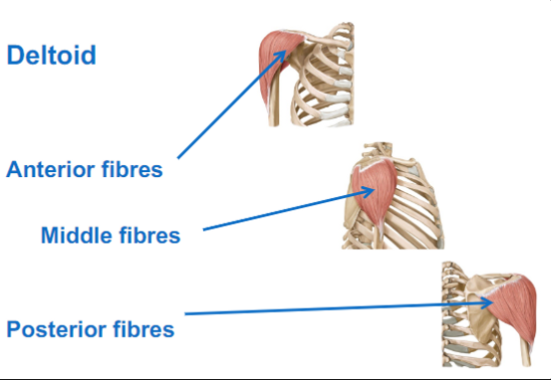
Deltoid
Anterior fibres: does shoulder flexion, internal rotation
Middle fibres: does abduction, supraspinatus initiates the movement
Posterior fibres: shoulder extension, external rotation
What are the Upper Limbs?
Arm: shoulder to elbow
+
Forearm: elbow to wrist
+
Wrist
+
Hand
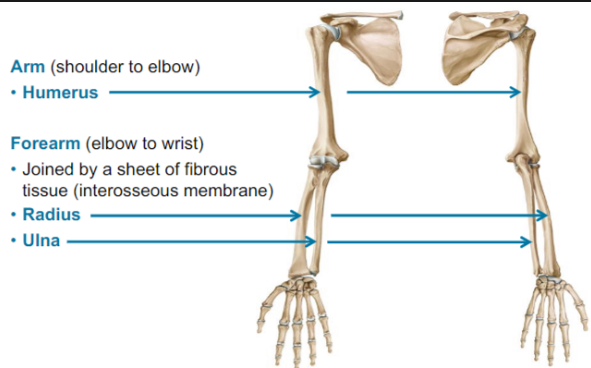
What are the Bones in the Upper Limb
Arm (shoulder to elbow)
Humerus
Forearm elbow to wrist)
Jointed by a sheet of fibrous tissue (interosseous membrane)
Radius: side of the thumb
Ulna: towards the midline
What are the Bones after the forearm?
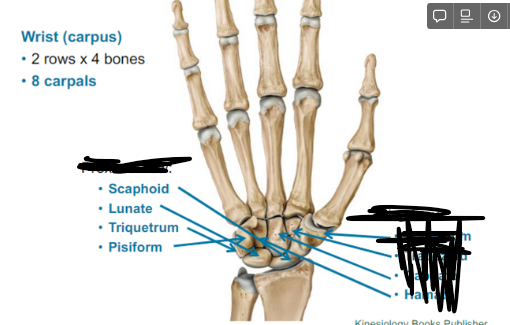
Wrist (carpus)
2 rows x 4 bones
8 carpals
What is in the Proximal row of the wrist?
Scaphoid
Lunate
Triquetrum
Pisiform
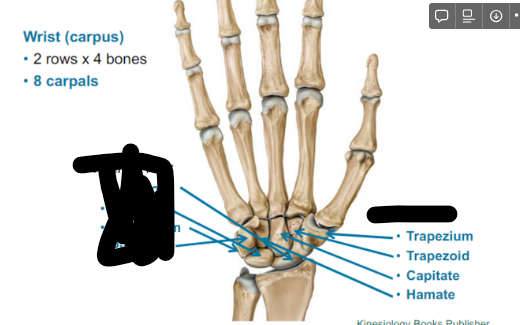
What are the Distal row of the wrist?
Trapezium (by the thumb)
Trapezoid
Capitate
Hamate
What is a good way to remember the Wrist bones?
Lateral to Medial
She - Scaphoid
Likes - Lunate
To - Triquetrum
Play - Pisiform
Try - Trapezium
To - Trapezoid
Catch - Capitate
Her - Hamate
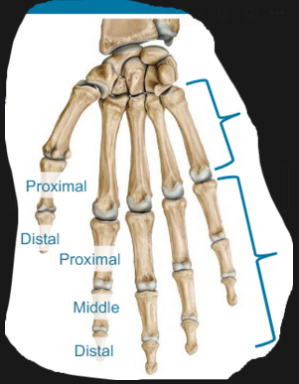
What are the Bones in the hands?
5 metacarpals join distal wrist row (meta = beyond)
14 phalanges (i.e., digits) join metacarpals
3 phalanges per finger (proximal, middle, distal)
2 phalanges per thumb (proximal, distal)
What are the muscles of the Upper limb
primarily flexors or extensors
Flexors = anterior
Extensors = posterior
What are the Anterior Arm muscles?
Coracobrachialis
Biceps brachii
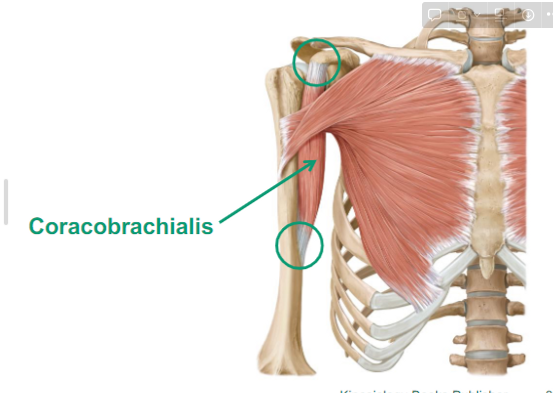
Describe the Coracobrachialis
muscle that goes from the scapula to the mid humerus
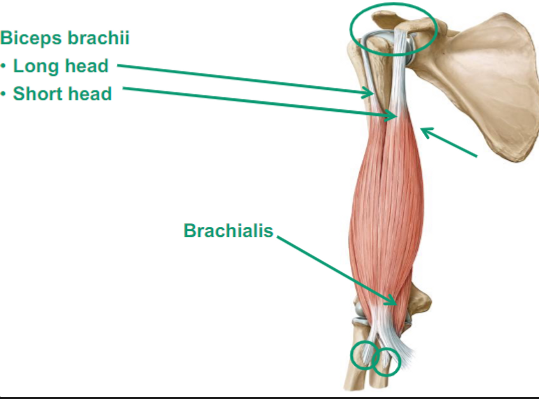
Describe the Biceps Brachii
Biceps go down the radius
it will supinate the forearm
causes flexion at the elbow and shoulder
What are the different parts in the Biceps brachii
Long head
Short head
Brachialis
(goes from your humerus to your ulna)
causes elbow flexion
What are the Posterior Arm muscles?
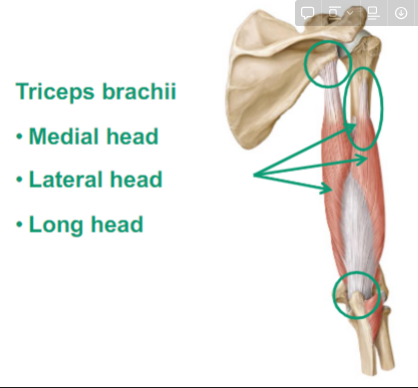
Triceps Brachii
Describe the Triceps Brachii
Medial head
attaches to the humerus
Lateral head
attahces to the humerus
Long head
Attaches to the scapula
goes down to the ulna called the
does elbow extension and shoulder extension
Describe the Forearm muscles
Flexor-pronator group
Extension-supinator group
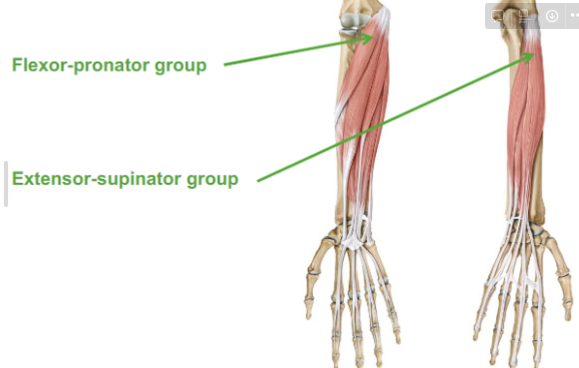
Describe the Hand muscles
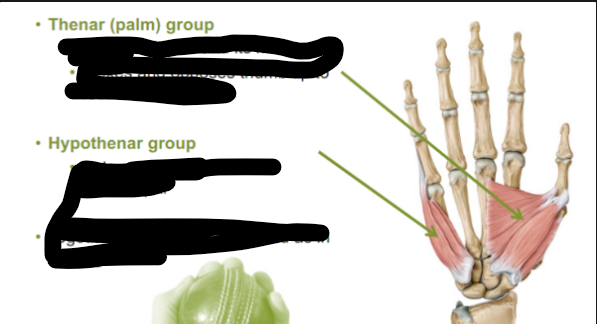
Thenar (palm) group
Abducts thumb and its metacarpal
Flexes and opposes thumb tip to four remaining digits
Hypothenar group
Acts on little finger and its metacarpal
Together they allow to cup hand as in holding a ball
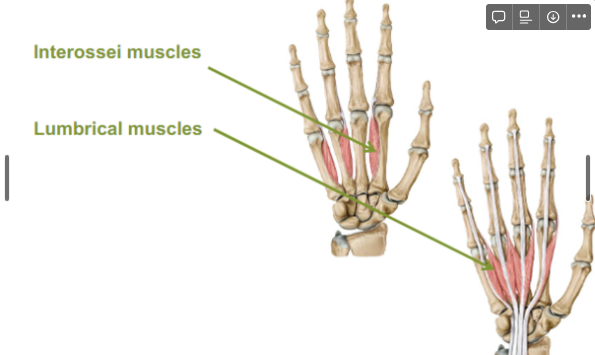
What are the muscles between the fingers?
Interossei muscles
Lumbrical muscles
What are the Different Joints of the Upper limb?
Shoulder joint
Elbow joint
Wrist joints
Hands joints
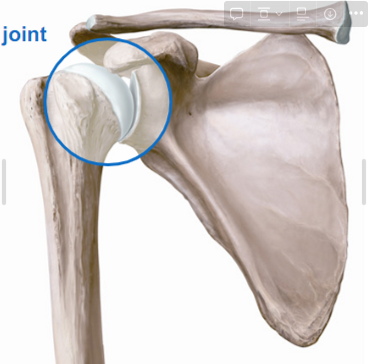
Describe the Shoulder joint
Glenohumeral
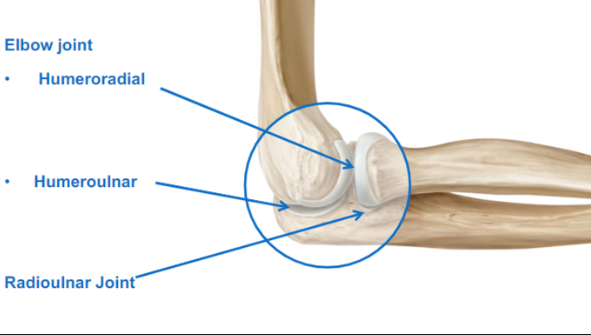
Describe the Elbow joint
Humeroradial (humeros to radius)
Humeroulnar (humeros to ulna)
Radioulnar Joint (radius and ulna)
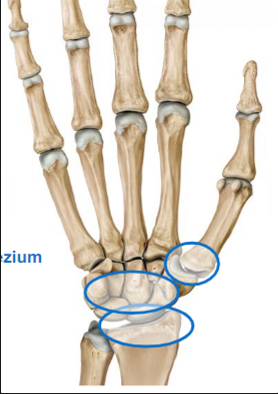
Describe the Wrist joints
Radiocarpal (radius and carpal)
Intercarpal, carpometacarpal, and intermetacarpal
1st carpometacarpal joint between trapezium and thumb metacarpal
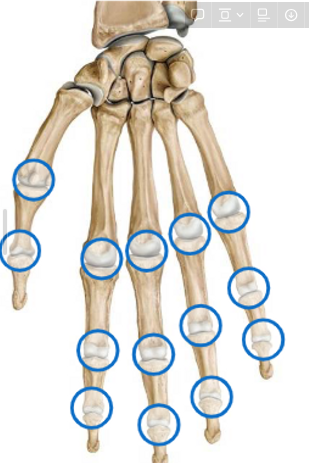
Describe the Hand Joints
Metacarpophalangeal (MCP) = our knuckles
Interphalangeal joints = between 2 phalanges
Describe the Pelvic Girdle
Weight bearer
Supports bladder and abdominal contents
Sacrifices mobility for stability and strength
What are the bones of the Pelvic Girdle
Paired hip bones
2 Innominate bones (on your hips)
Each made up of:
Ilium: side
Pubis: front
Ischium: back
Acetabulum: all 3 bones that make up
Makes a cup
Describe the muscles of the Pelvic Girdle
Permit a wide range of movement in the lower limb
Hip = ball and socket joint
Prime focus = stability and transfer of weight for walking
More limited than at the shoulder joint
What are the Anterior muscles of the Pelvic girdle
Iliopsoas (hip flexors)
Formed by:
Psoas major
Iliacus
What are the Posterior and Lateral muscles of the Pelvic girdle?
Gluteal muscles (hip abductors)
Gluteus maximus (powerful hip extensor)
goes down to your iliotibial band
Gluteus medius (on top) and minimus (bottom)
What are the Joints of the Pelvic Girdle?
Pubic Symphysis (where the 2 pubic bones come together)
cardilagenous joint
Sacroiliac (between sacrum and ilium)
compound joint: part fibrous joint, part synovial joint
Describe the Lower limb
Thigh: hip to knee
+
Leg: knee to ankle
+
Ankle
+
Foot
What are the bones in the Lower limb
Thigh
Leg
Ankle
Foot
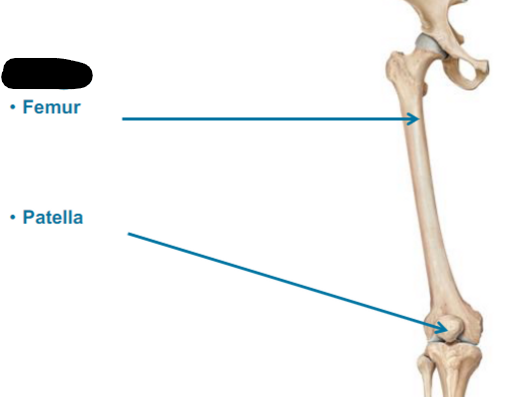
Describe the Thigh Bones
Femur
Patella is the knee cap
What are the Leg bones
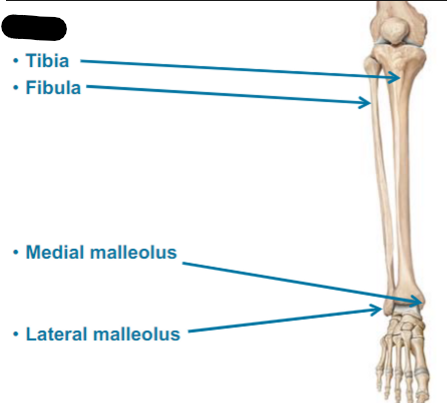
TIbia (shin bone)
Fibula
Medial malleolus
Lateral malleolus
Describe the Ankle bones
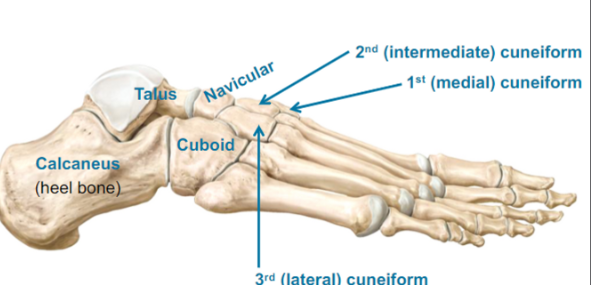
Tarsus (tarsal bones)
Talus (top)
Cuboid (lateral side of your foot)
Navicular (in front of talus)
3rd (lateral) cuneiform
2nd (intermediate) cuneiform
1st (medial) cuneiform
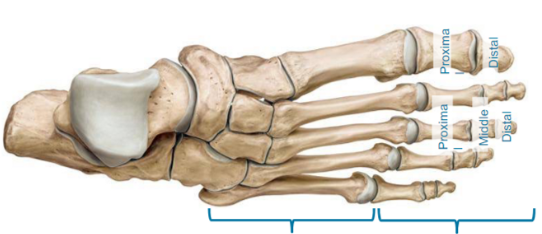
Describe the Foot bones
5 metatarsals (middle of our foot)
14 phalanges (toes)
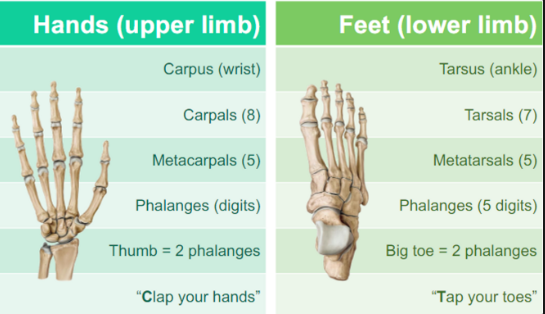
REVIEW THIS PHOTO
ANSWER FOR PHOTO
What are the Anterior Thigh Muscles?
Quadriceps femoris (knee extensors)
Rectus femoris
Vastus lateralis
Vastus intermedius
Vastus medialis
Sartorius
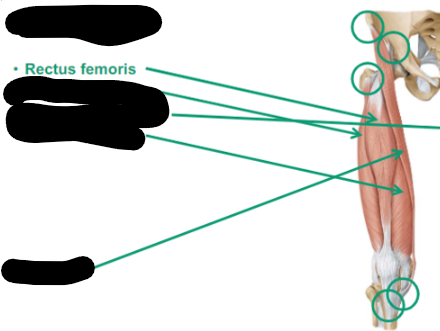
Describe the Rectus Femoris thigh muscle
anterior
attached to the pelvic bone
flexion of the hip (hip flexion)
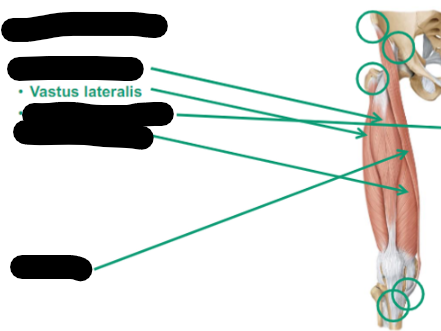
Describe Vastus Lateralis thigh muscle
anterior
Laterally located on the quads (facing away)
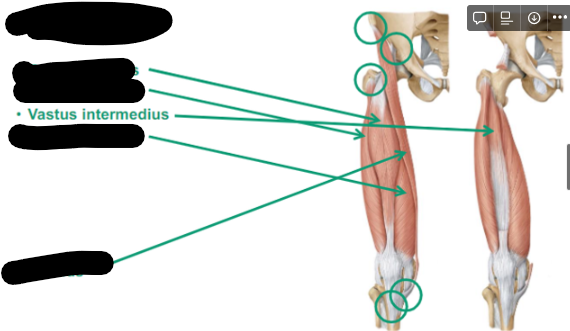
Describe Vastus Intermedius thigh muscle
anterior
In between lateralis and medialis
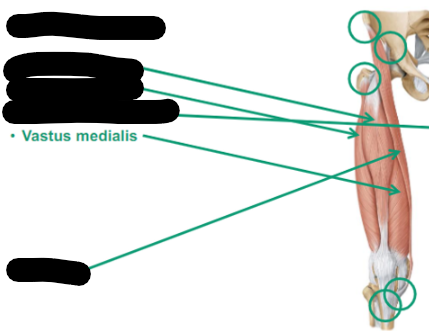
Describe Vastus medialis thigh muscle
anterior
medially located on the thigh (facing towards the middle)
Describe Sartorius thigh muscle
FABER: does flexion at the knee
Flexion
ABducts
External Rotation
hip bone to our tibia
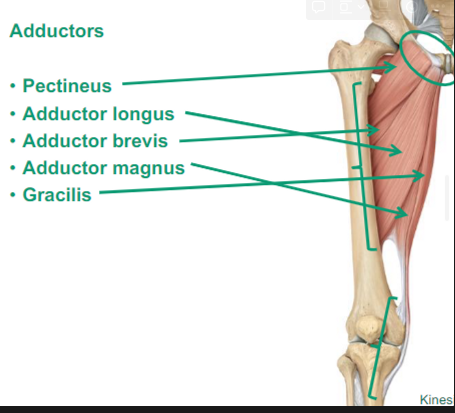
What are the Medial Thigh muscles?
Adductors: they bring the thigh to the midline
Pectineus
Adductor longus: long, adducts the thighs
Adductor brevis: short, adducts the thighs
Adductor magnus: biggest, adducts the thighs
Gracilis
What are the Posterior Thigh muscles?
Hamstrings
Biceps femoris
Semitendinosus
Semimembranosus
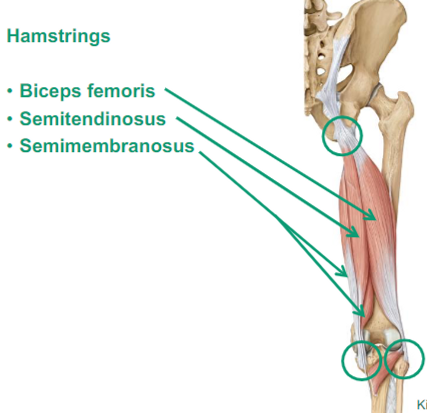
Describe Hamstrings thigh muscles
posterior
Does knee flexion, does hip extension
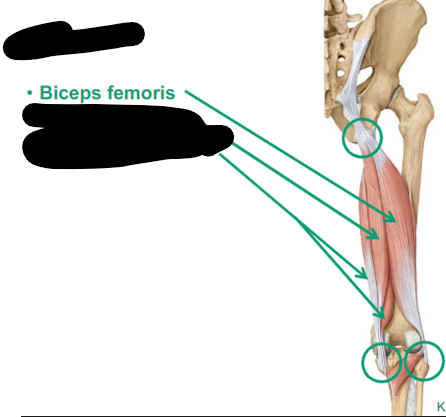
Describe Biceps femoris thigh muscle
posterior
lateral
goes to the head of the fibula
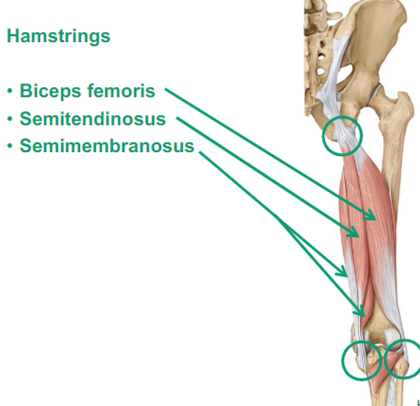
Describe Semitendinosus thigh muscle
posterior
both go together on the medial side
attached to the tibia
What are the Anterior Leg muscles?
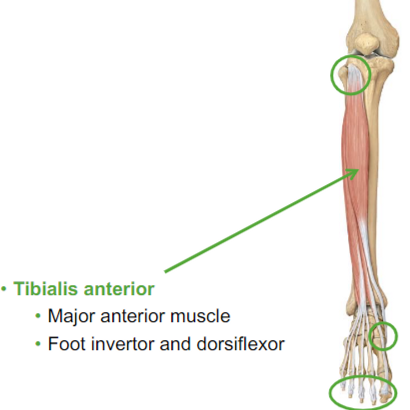
Tibialis anterior:
dorsiflexor of the ankle
found in the anterior part of your tibia
Major anterior muscle
Foot inventor and dorsiflexor
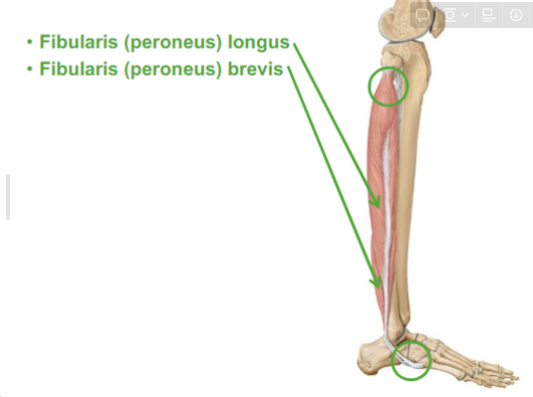
What are the Lateral Leg muscles
Fibularis (peroneus) longus
Fibularis (peroneus) brevis
will turn the foot away (eversion)
What are the Posterior Leg muscles?
Superficial
Gastrocnemius
Soleus
Plantaris
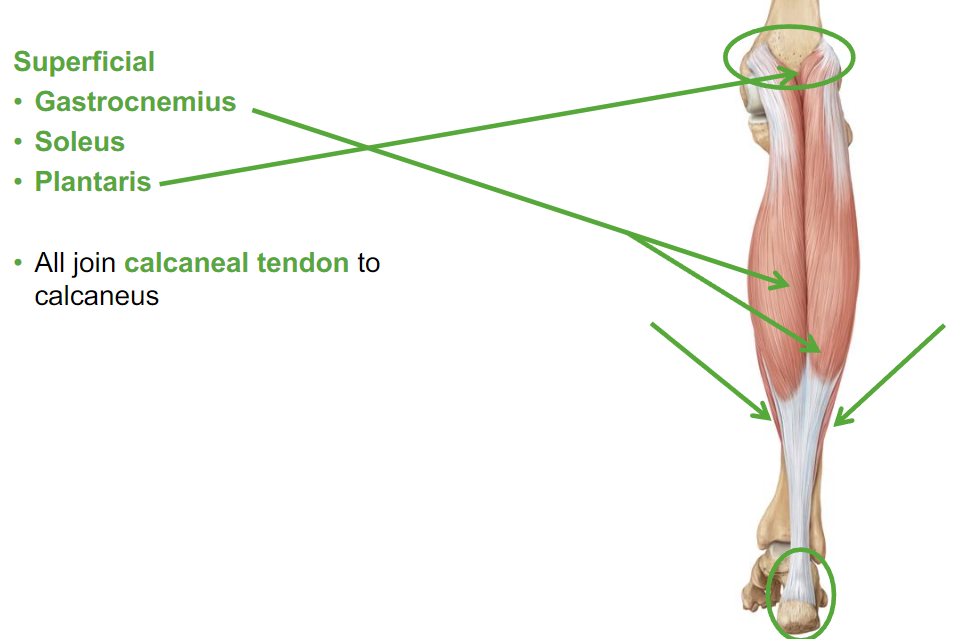
Describe Gastrocnemius leg muscle
posterior
attaches to our femur
crosses our ankle joint
help with knee flexion
Describe Soleus leg muscle
cross just the ankle joint
cause plantar flexion
All the muscles in the leg muscle join what?
The calcaneal tendon to calcaneus
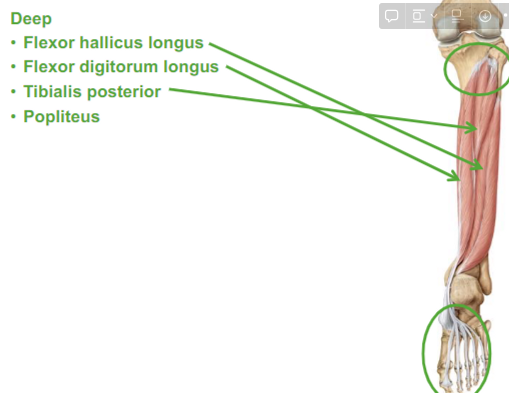
What are the Deep Posterior muscles?
Flexor hallicus longus
Flexor digitorum longus
Tibialis posterior
Popliteus
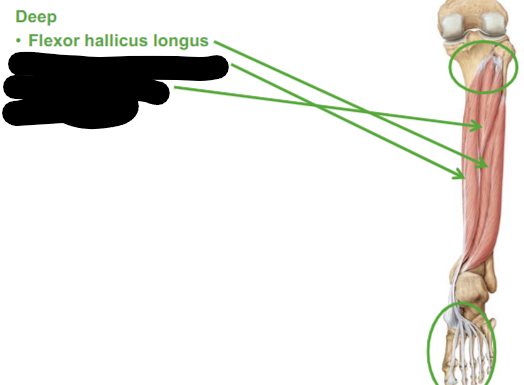
Describe the Flexor hallicus longus
causes flexion to our first toe
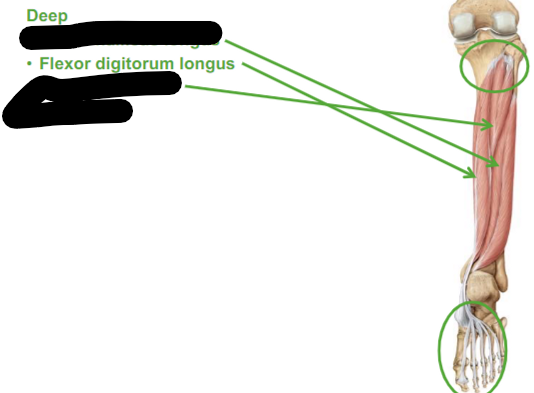
Describe Flexor Digitorum longus
flexes our digits (our toes)