6) Chlorination vs. Bromination radical halogenation
1/10
Earn XP
Description and Tags
page 7
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
What is chlorination?
A chemical reaction where one or more chlorine atoms (Cl) are added to a molecule.
What is bromination?
A chemical reaction where bromine atoms (Br) are added to a molecule.
Chlorination occurs..?
faster than bromination but is unselective (a mixture of products is made)
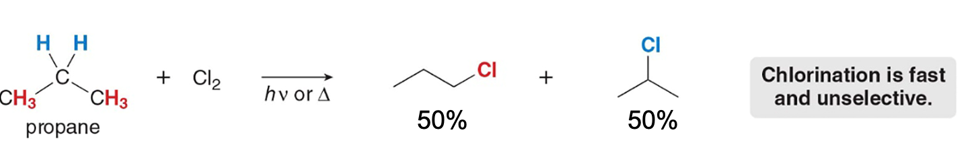
Bromination occurs
more slowly but is more selective (a single product is made).
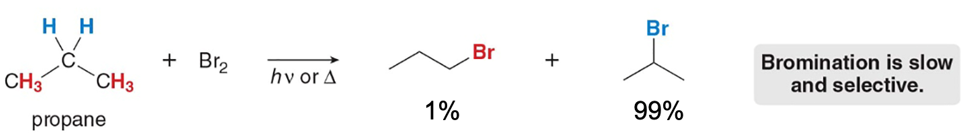
Why is bromination more selective than chlorination?
Bromine prioritizes radical stability; this lowers the Ea, which is important since the reaction is ENDOTHERMIC
When reacting with Br2, what will be the major product?
The carbocation with the more stable radical
What is the major product for Cl2?
usually an unstable radical; the hydrogens are easier to pick off
The ratio of Hydrogens matter for?
chlorination, MP is usually the radical with more hydrogens to grab
You can grab 3 H’s from?
methyl, CH3
You can grab 2 H’s from?
CH2
You can grab 1 H from?
CH, more stable due to lower Ea