Genetics Exam 3
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/175
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 9:07 PM on 11/17/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
176 Terms
1
New cards
Centric fragment
A piece of chromosome containing a centromere
2
New cards
Acentric fragment
A chromosomal piece without a centromere
3
New cards
dicentric chromosome
A chromosome with two centromeres
4
New cards
Inversion
The replacement of a section of a chromosome in the opposite orientation
5
New cards
deletion
the loss or absence of one or more nucleotides from a chromosome
6
New cards
Translocation
a part of the translation process in which the mRNA is shifted one codon in relation to the ribosome.
7
New cards
reciprocal translocation
A chromosomal configuration in which the ends of two nonhomologous are broken off and become attached to the non-homologs
8
New cards
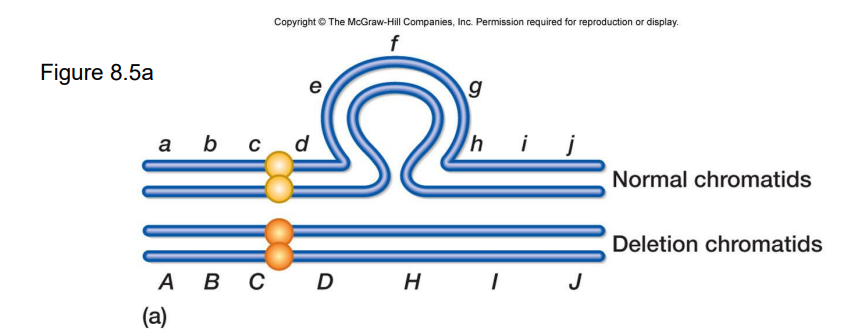
deletion loop
See image
9
New cards
pseudodominance
the phenomenon in which a recessive allele confers the phenotype when only one copy of the allele is present, as in hemizygous alleles or in deletion heterozygotes
10
New cards
Deletion mapping
a technique used to find out the mutation sites within a gene
11
New cards
genetic imbalance
unnatural ratio of gene expression
12
New cards
Haploinsufficiency
lethal phenotype due to expression of only a single wild type allele
13
New cards
pericentric inversion
A chromosomal inversion that includes the centromere within the inverted region
14
New cards
paracentric inversion
A chromosomal inversion that does not include the centromere in the inverted region
15
New cards
Suppression (of recombination)
The phenomenon where a mutation (suppressor) restores the wild-type phenotype to a different mutation. the suppressor mutation may be in the same gene as the original mutation (intragenic suppression) or may be in a different gene (intergenic suppression)
16
New cards
variegation
Patchiness; a type of position effect that results when particular loci are contiguous with heterochromatin
17
New cards
duplication
extra copies of a chromosomal region are formed
18
New cards
aneuploidy
the condition of a cell or of an organism that has addition or deletions of whole chromosomes
19
New cards
euploidy
the condition of a cell or organism that has one or more complete sets of chromosomes
20
New cards
polyploid
anything above diploid
21
New cards
tetraploid
organism with four homologous sets of chromosomes
22
New cards
triploidy
organism containing three homologous sets of chromosomes
23
New cards
monosomy
absence of one member of a chromosomal pair
24
New cards
disomy
normal state of chromosomes in a eukaryote cell
25
New cards
trisomy
chrosomal abnormality in which there is one more than the normal number of chromosomes in a cell
26
New cards
nullisomic
A diploid cell missing both copies wof the same chromosome
27
New cards
Down syndrome
Trisomy 21 (three chromosomes on chromosome 21)
28
New cards
nondisjunction
the failure of a pair of homologous chromosomes to separate properly during meiosis
29
New cards
mosaic
Individuals made up of two or more cell lines with different genotypes that originated in the same zygote
30
New cards
heterochromatin
Chromatin that remains tightly coiled ( and darkly staining) throughout the cell cycle (transcriptionally inactive)
31
New cards
Chromatin
The DNA-protein complex that composes the eukaryotic chromosome
32
New cards
ribose
a pentose sugar important as a component of ribonucleic acid
33
New cards
deoxyribose
a sugar that is a constituent of nucleic acids
34
New cards
phosphate
a salt of phosphoric acid
35
New cards
nitrogenous base
A molecule that contains nitrogen and has the chemical properties of a base
36
New cards
pentose sugar
5 carbon sugar
37
New cards
nucleotide
Basic structure of DNA and RNA that consists of a nitrogenous base, a sugar, and one or more phosphates
38
New cards
nucleoside
A sugar-base compound that is a nucleotide precursor. A 5-carbon sugar with a nitrogenous base attached
39
New cards
Purine
Double C and N rings, has Adenine and Guanine
40
New cards
Pyrimidine
Single C and N rings, has Thymine, and Cytosine, and Uracil
41
New cards
DNA base pairs
Adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine
42
New cards
RNA base pairs
Adenine, guanine, cytosine, uracil
43
New cards
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid, heritable molecule
44
New cards
RNA
Ribonucleic Acid, single helix, shorter than DNA
45
New cards
dsDNA
double-stranded DNA
46
New cards
ssDNA
single strand DNA
47
New cards
sugar-phosphate backbone
Forms the structural framework of nucleic acids, including DNA and RNA, joins together nucleotides in a DNA sequence
48
New cards
phosphodiester bond
a chemical bond of the kind joining successive sugar molecules in a polynucleotide
49
New cards
Chargaff's ratios
Amount of A = T, amount of G=C
50
New cards
double helix
the normal structure of DNA consisting of two helices rotating about the same axis
51
New cards
antiparallele
parallel but orientated oppositely
52
New cards
complementarity
the correspondence of DNA bases in the double helix so that adenine in one strand is opposite thymine in the other strand and cytosine in one strand is opposite guanine in the other. relationship explains Chargaff's rule
53
New cards
histones
Arginine- and lysine- rich basic proteins making up a substantial portion of eukaryotic nucleoprotein
54
New cards
nucleosome
the basic structure of eukaryotic chromatin that is composed of approximately 165 base pairs of DNA wrapped around a histone structure that consists of two molecules each of H2a, H2b, H3, and H4
55
New cards
solenoid
contains six nucleosome per turn
56
New cards
2nm fiber
short region of DNA double helix
57
New cards
11nm fiber
1st level packaging (nucleosome) "beads- on- a- string" form of chromatin
58
New cards
30nm fiber
2nd level (solenoid)
59
New cards
240nm fiber
3rd level (chromosome scaffold)
60
New cards
700nm fiber
4th level condensed scaffold
61
New cards
1400nm fiber
metaphase chromosome
62
New cards
chromosome banding
Characteristic banding pattern in chemically stained chromosomes
63
New cards
euchromatin
Eukaryotic chromosomal regions that are diffuse during interphase and presumably are the regions that are actively transcribed. (transcriptionally active)
64
New cards
Facultative heterochromatin
can shift between transcriptionally active and inactive states
65
New cards
centromeres
constrictions in eukaryotic chromosomes on which the kinetochore lies. Also, the DNA sequence within the constriction that is responsible for binding the kinetochore
66
New cards
telomere
the ends of linear eukaryotic chromosomes
67
New cards
C-value
genome size
68
New cards
C-value paradox
Genome size does not correlate with complexity of organism
69
New cards
transposon
repetitive DNA sequences that have the capability to move (transpose) from one location to another in genome
70
New cards
junk DNA
Eukaryotic DNA that lacks genes and has no known purpose
71
New cards
semiconservative replication
the mode by which DNA replicates, where each strands acts as a template for a new double helix.
72
New cards
theta structure
an intermediate structure formed during the replication of a circular DNA molecule
73
New cards
replication fork
The point at which the two strands of DNA are separated to allow replication of each strand
74
New cards
replication bubble
an unwound open region of the DNA helix from where the replication of DNA occurs
75
New cards
origin of replication
a sequence of DNA at which replication is initiated on a chromosome, plasmid or virus
76
New cards
DNA polymerase 1
removes RNA primers and replaces with DNA
77
New cards
DNA polymerase 3
Builds leading strand and Okazaki fragments
78
New cards
Primer
In DNA replication, a length of DNA or RNA, which is base paired to a single- stranded DNA template, that provides a 3' end for the addition of another nucleotide
79
New cards
leading strand
Strand of DNA being replicated continuously towards the replication fork
80
New cards
lagging strand
The DNA strand that is replicated discontinuously away from the replication fork
81
New cards
continuous replication
uninterrupted DNA replication in the 5' to 3' direction that is moving in the same directions the replication fork
82
New cards
discontinuous replication
DNA replication in short 5' to 3' segments that are moving away from the replication fork
83
New cards
Okazaki Fragments
Segments of newly replicated DNA produced during discontinous DNA replication on the lagging strand a
84
New cards
RNA Primase
A RNA polymerase that creates the short RNA primer for initiation of okazaki fragment synthesis during DNA replication. (places RNA primers)
85
New cards
Proofreading
the DNA pol reads the newly added base before adding the next one, so a correction can be made
86
New cards
3’ to 5’ exonuclease activity
Removes mismatched base pairs (proofreading)
87
New cards
Ligase
Joins Okazaki fragments into continuous daughter strand
88
New cards
helicase
unzips DNA
89
New cards
Single- strand binding (ssb) protein
maintains ssDNA
90
New cards
initiator proteins
(dnaA) bind to origin and separate
91
New cards
topoisomerase
relaxes supercoiling
92
New cards
template strand
The DNA strand that serves as the DNA template for transcription, which will be complementary to the RNA sequence; also the DNA strand that is used by DNA polymerase in a DNA sequencing reaction.
93
New cards
Exonuclease
exo- external
nucl - nucleous/ nucleic acid
ase - enzyme
nucl - nucleous/ nucleic acid
ase - enzyme
94
New cards
gene expression
The process of producing a functional gene product
95
New cards
central dogma
the original postulate that information can be transferred from DNA to RNA and then to protein, barring any transfer originating from the protein
96
New cards
transcription
the process whereby RNA is synthesized from DNA template
97
New cards
translation
the process of protein synthesis wherein the nucleotide sequence of the mRNA determines the amino acid sequence of the protein
98
New cards
initiation (transcription)
RNA polymerase (RNAP) binds to promoter, DNA strand unwind, RNA polymerase builds RNA
99
New cards
elongation (transcription)
RNAP moves downstream elongating RNA transcript from 5' to 3', DNA strand rewinds after RNAP passes
100
New cards
termination (transcription)
RNA transcript (mRNA) is released and polymerase detaches from DNA