practical 4 microbiology
1/123
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
124 Terms
what are the distinguishing characteristics of Saccharomyces cervisiae?
budding only
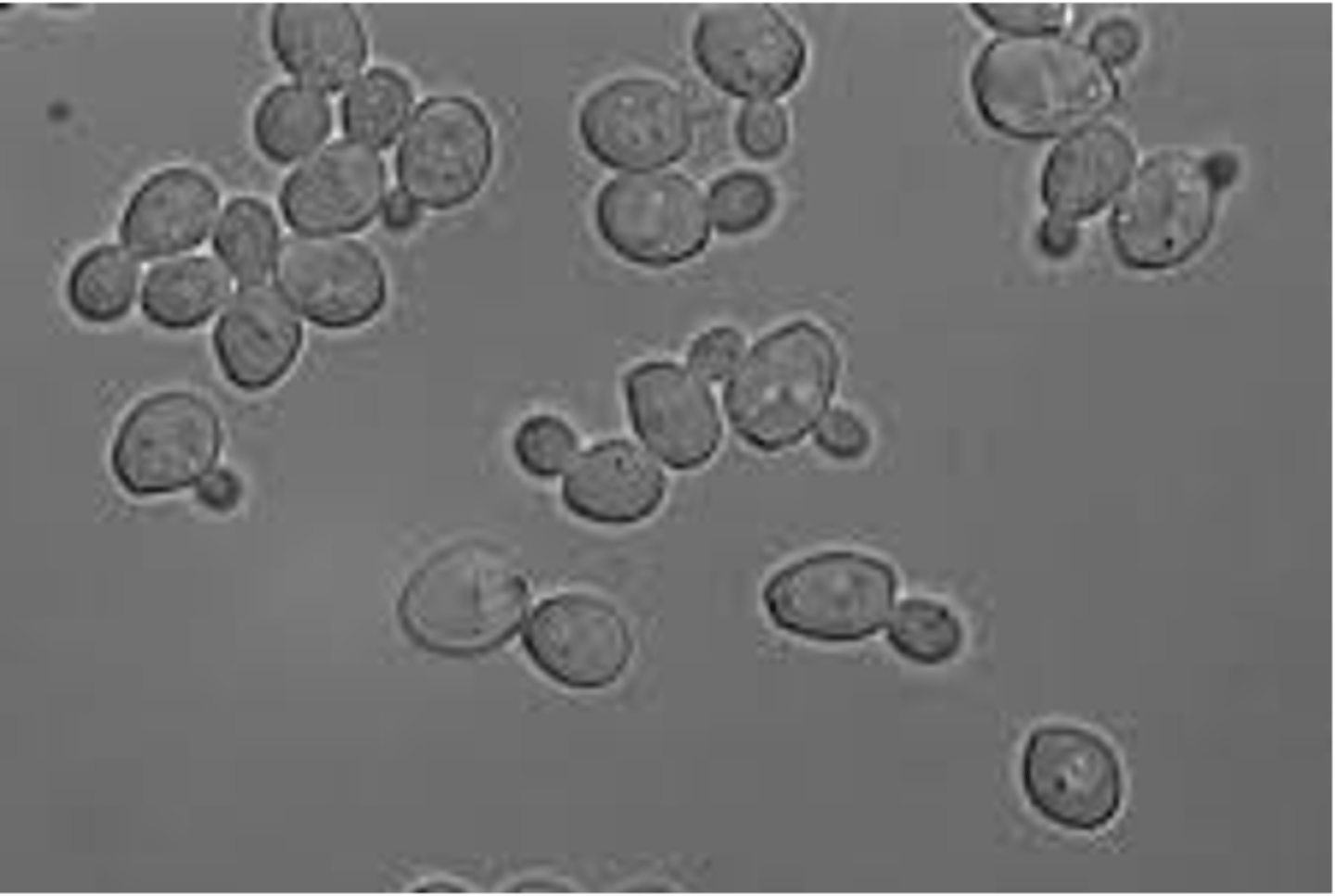
how do you differentiate Candida albicans form other yeast?
pseudohyphae and budding
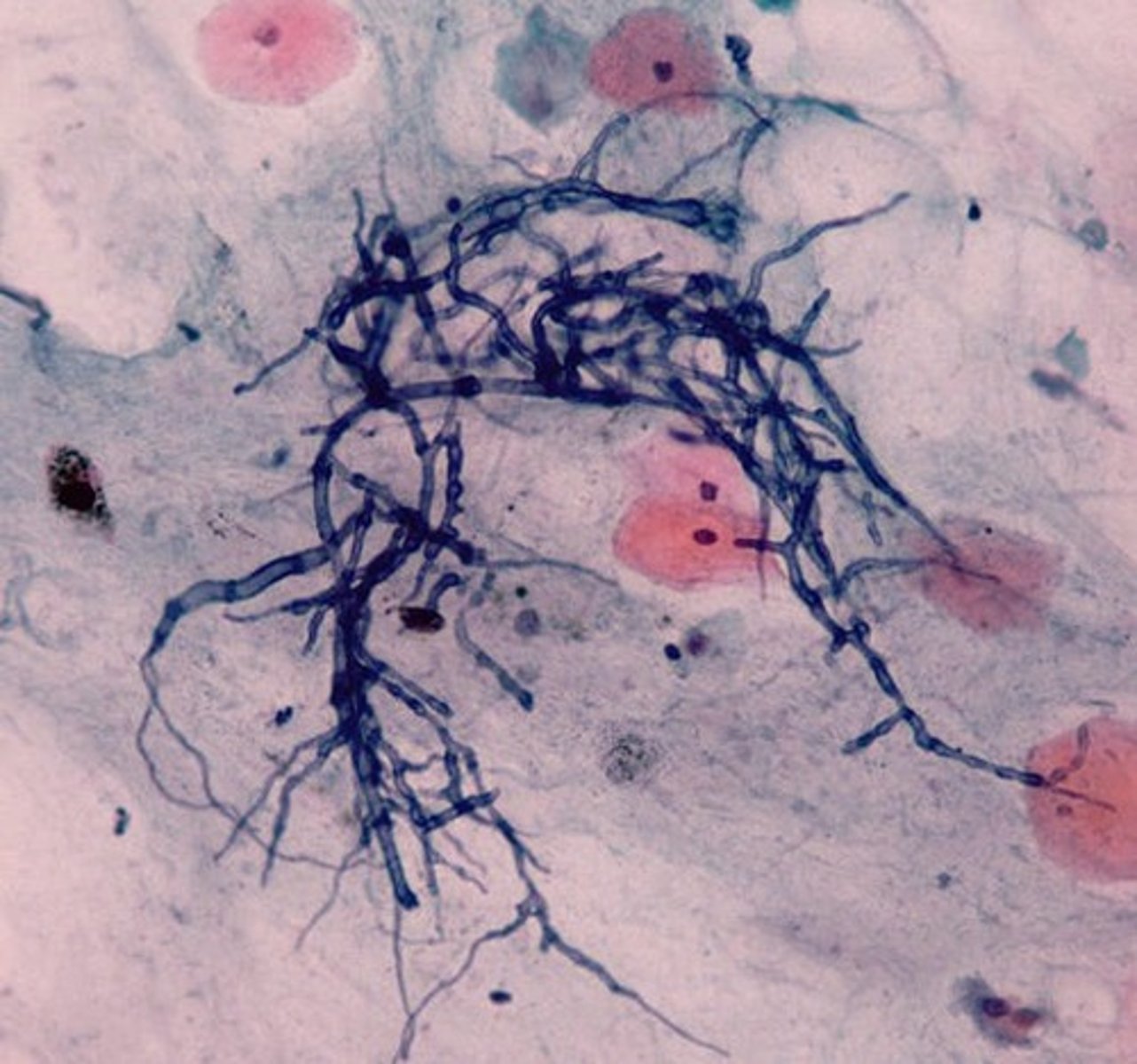
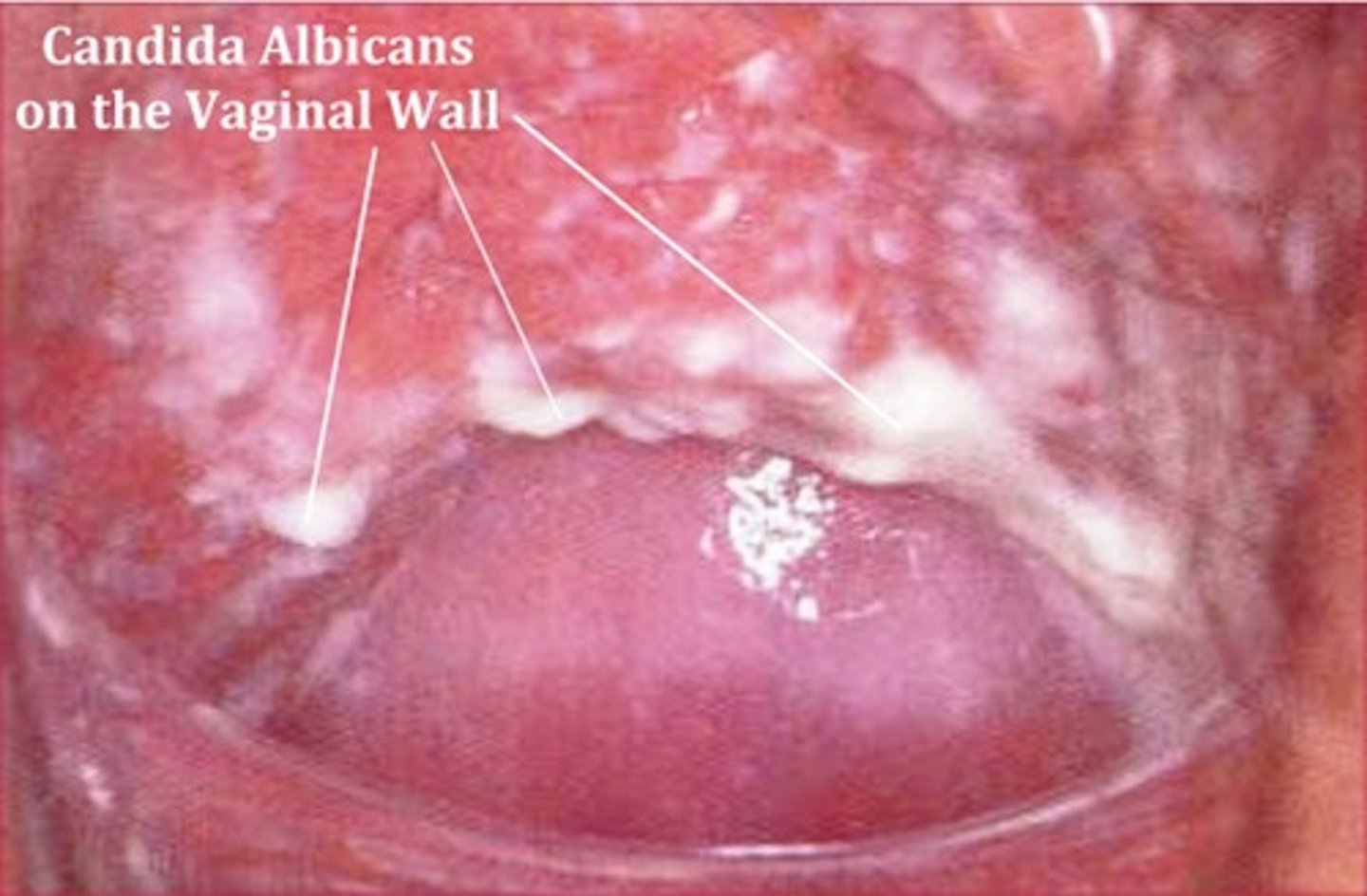
what is the clinical relevance of Candida albicans?
causes thrush, vaginitis
how to differentiate rhizopus stolonifer from other zygmycota?
spores inside vesicle and have root like apendages at base (rhizoids)
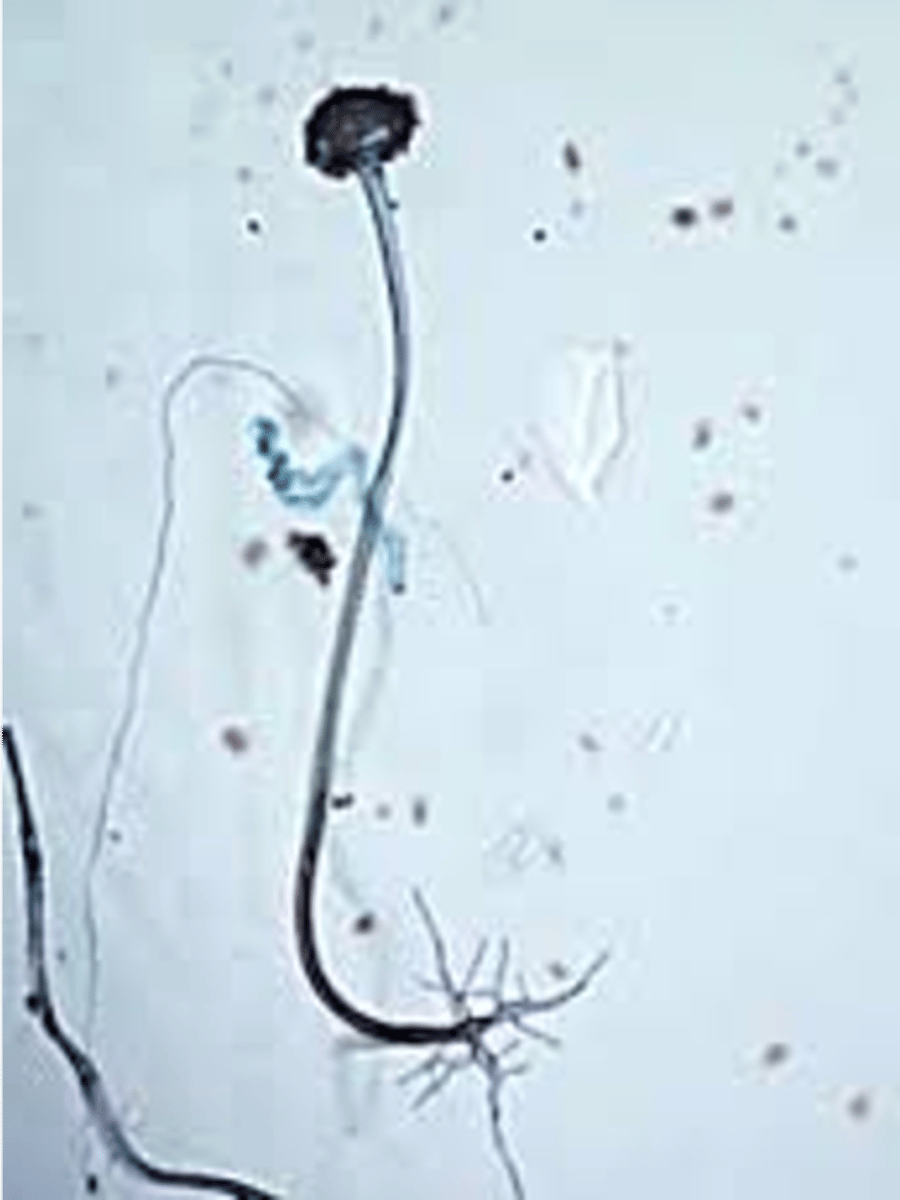
what is the clinical significance of rhizopus stolonifer?
causes problems for immunocompromised people especially in the skin and other places with high oxygen
what are rhizoids or the root like appedages of rhizopus stolonifer used for?
attachment
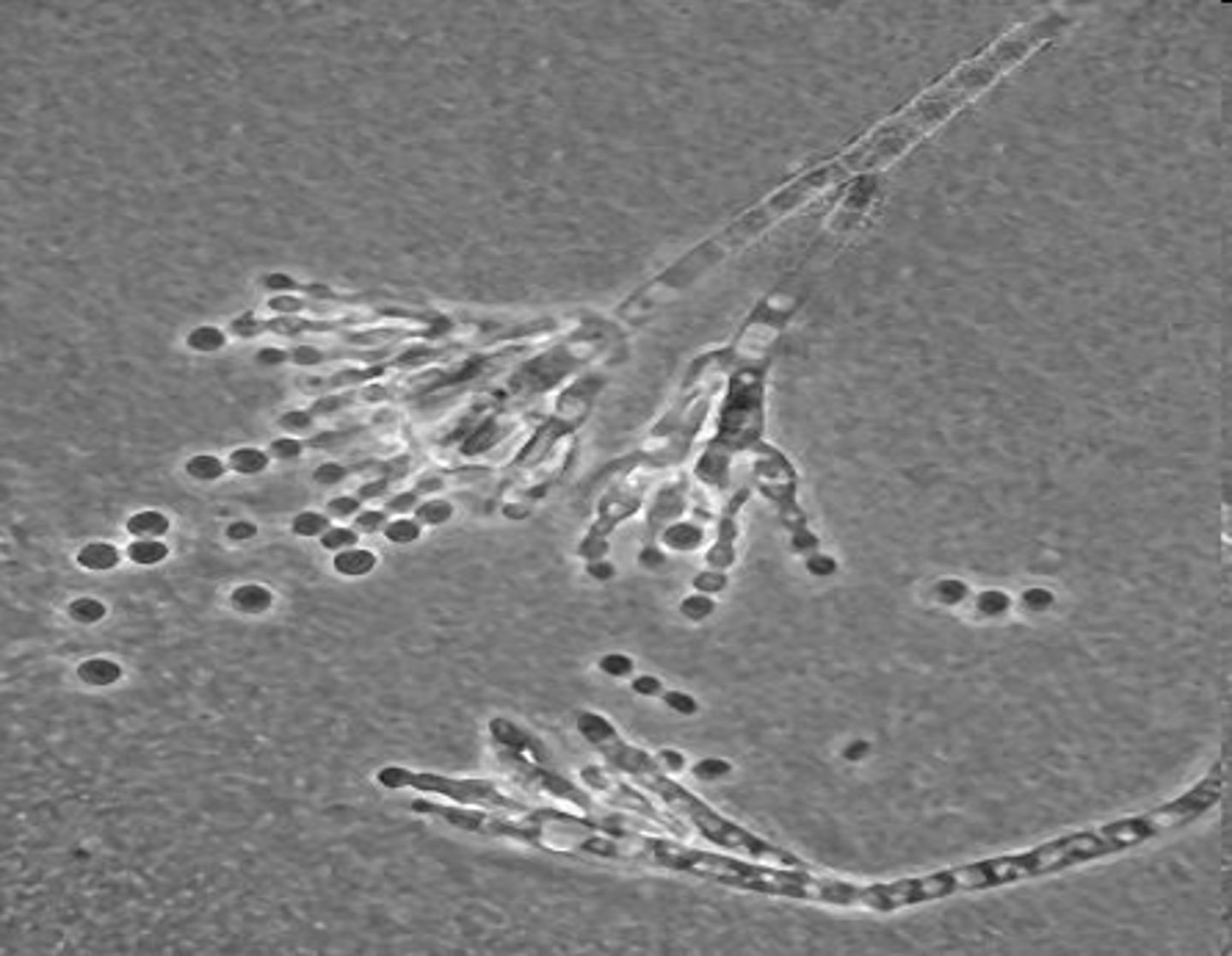
how can you differentiate pencillium notatum from other ascomycota?
looks like a brush (structures arise from each/ branching), not overly broad
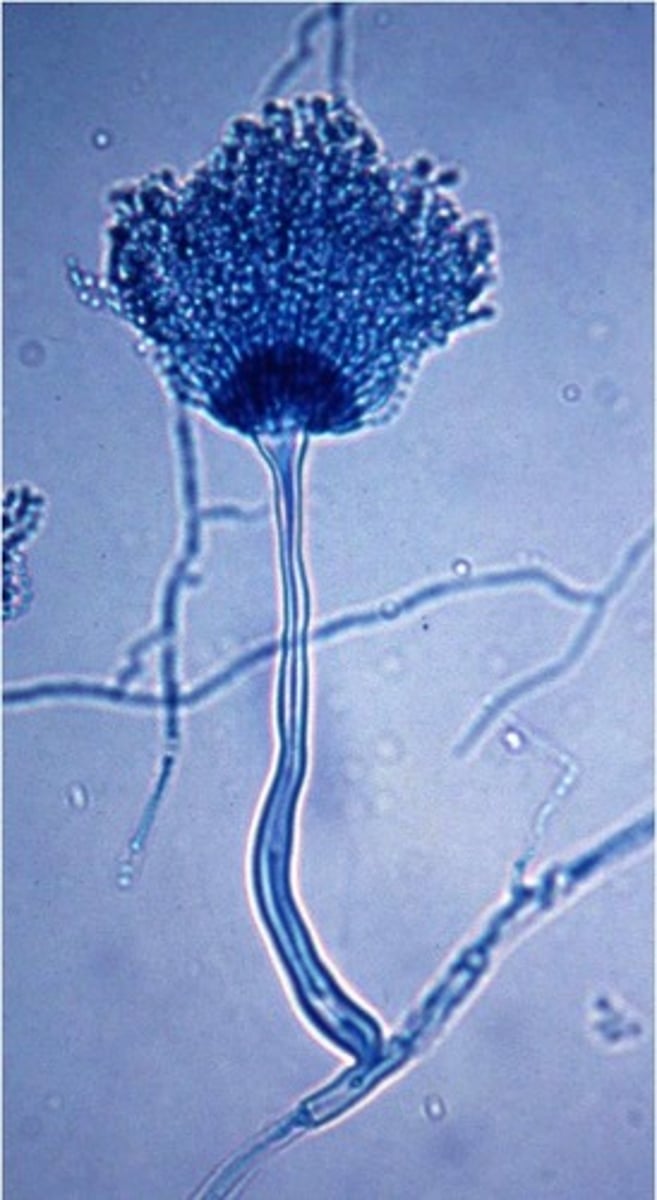
how to differentiate aspergillum niger from other ascomycota?
looks like feather duster (all structures stem from one area) and posses a foot cell at its base
how to differentiate microsporium canis from other ascomycota?
large terminal conidia spore, spore looks like leaf
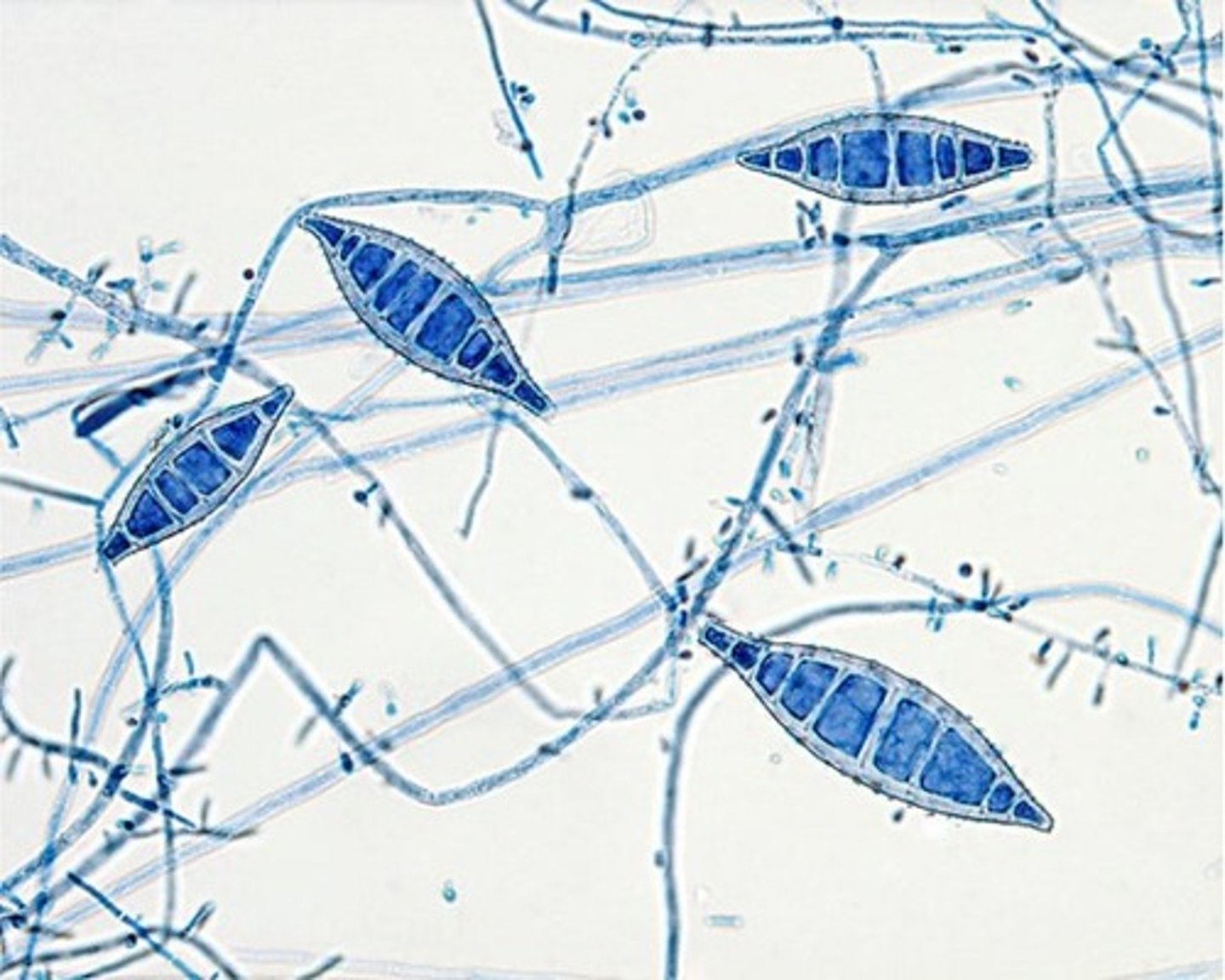
what is the clinical significance of microsporium canis?
causes ring worm or tinea
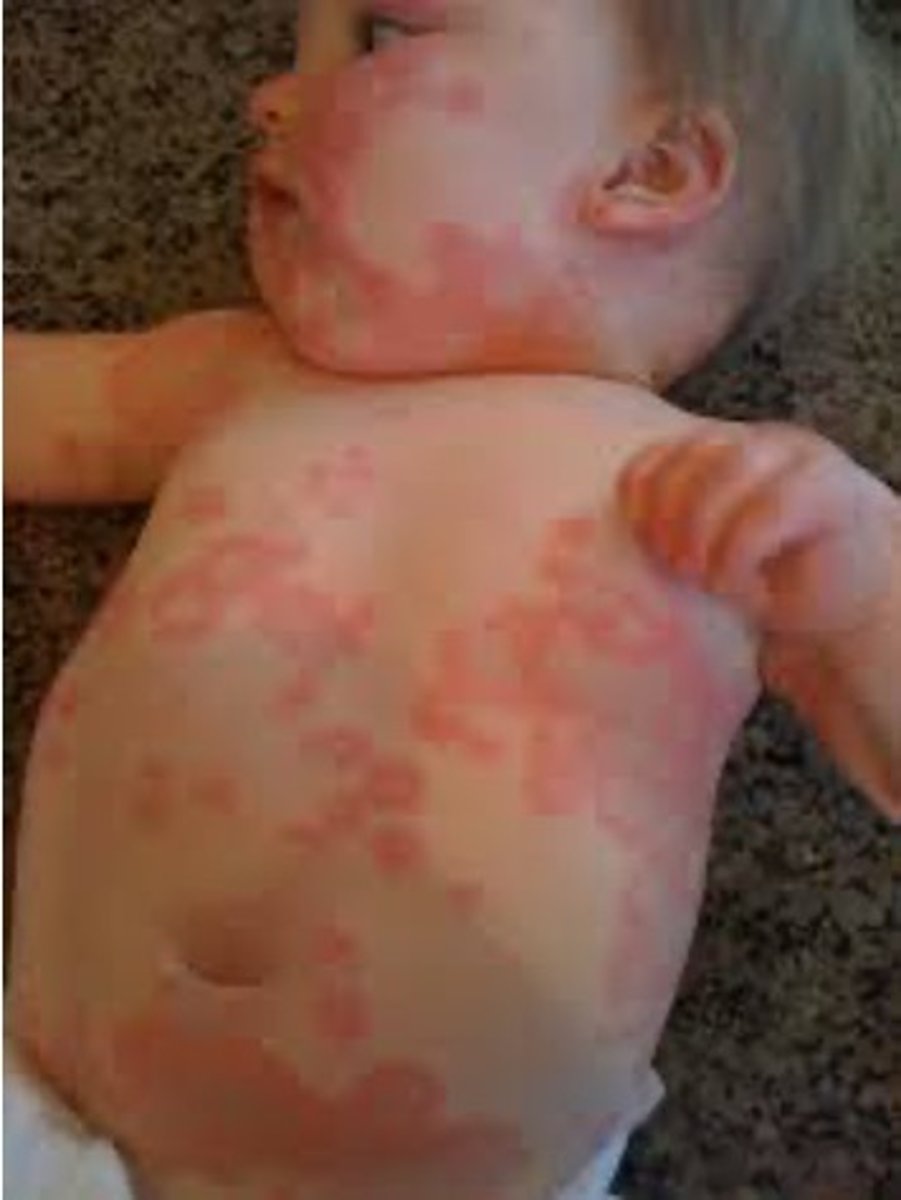
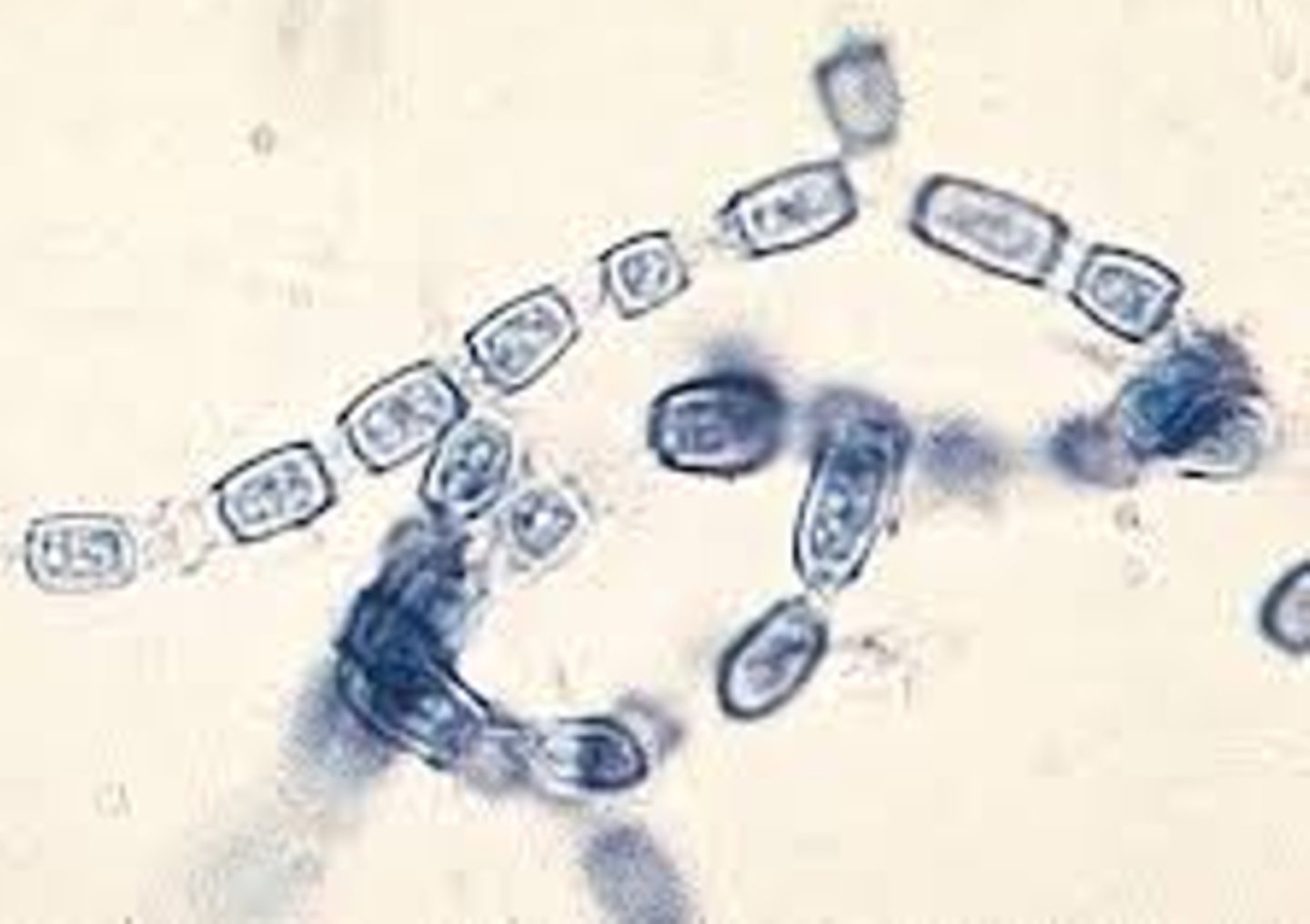
how to differentiate coccidiodies immitis from other ascomycota?
oidia, disarticulation of the hyphae of mycelia, looks like train cars being pulled apart
why is coccidiodies immitis the most dangerous fungi amoung the ones discussed?
is dimorphic can change from mold to yeast (which are facultative anaerobic)
what is the clinical importance of coccidiodies immitis?
causes lung infections, valley fever and infections of the skin
what Is the function of a cyst (protozoan)?
environmentally resistant, enables transmission
what is a trophozoite?
active motile and damaging form of a protozoan (fragile in environment)
how do archaezoa move? do they have mitochondria?
flagella, no
how do euglenozoa move? do they have mitochondria?
flagella, yes
how do amoebozoa move?
pseudopodia
how do ciliophora move?
cilia
how do apicomplexa move?
non motile, require fluid matrix
does trichomonas vaginalis have a cyst?
no
why does trichomonas vaginalis lack a cyst?
moves penis to vagina and back and forth, hospitable places
what is the clinical significance of trichomonas vaginalis?
causes vaginitis
what is indicative of trichomonas vaginal, in regards to symptomology'?
strawberry cervix
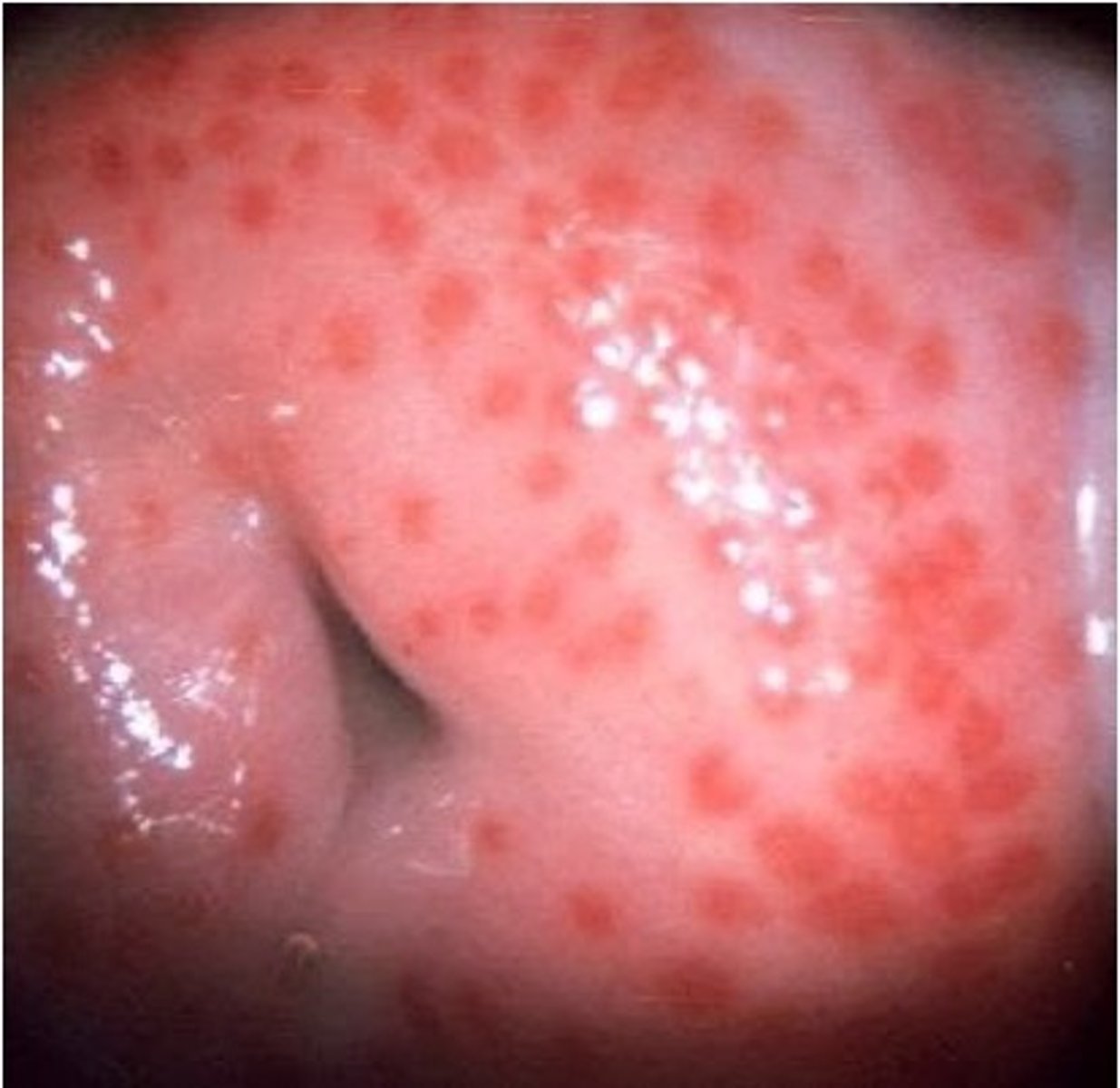
what are the distinguishing features of trichomonas vaginalis?
looks like computer mouse and looks as if it has a stinger (IMO)
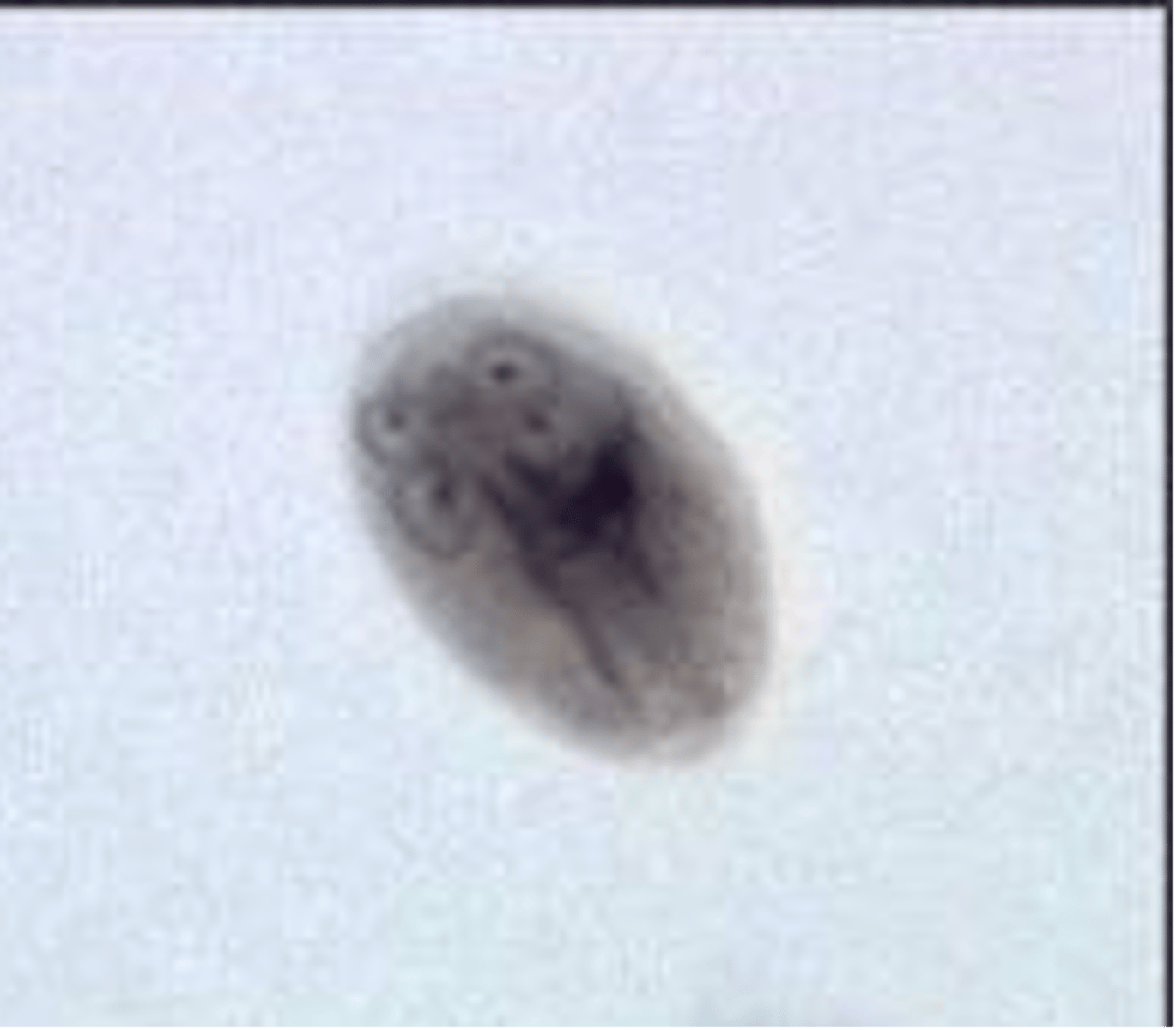
how can you distinguish the cyst stage of Giardia lamblia?
oval shaped, with four nuclei
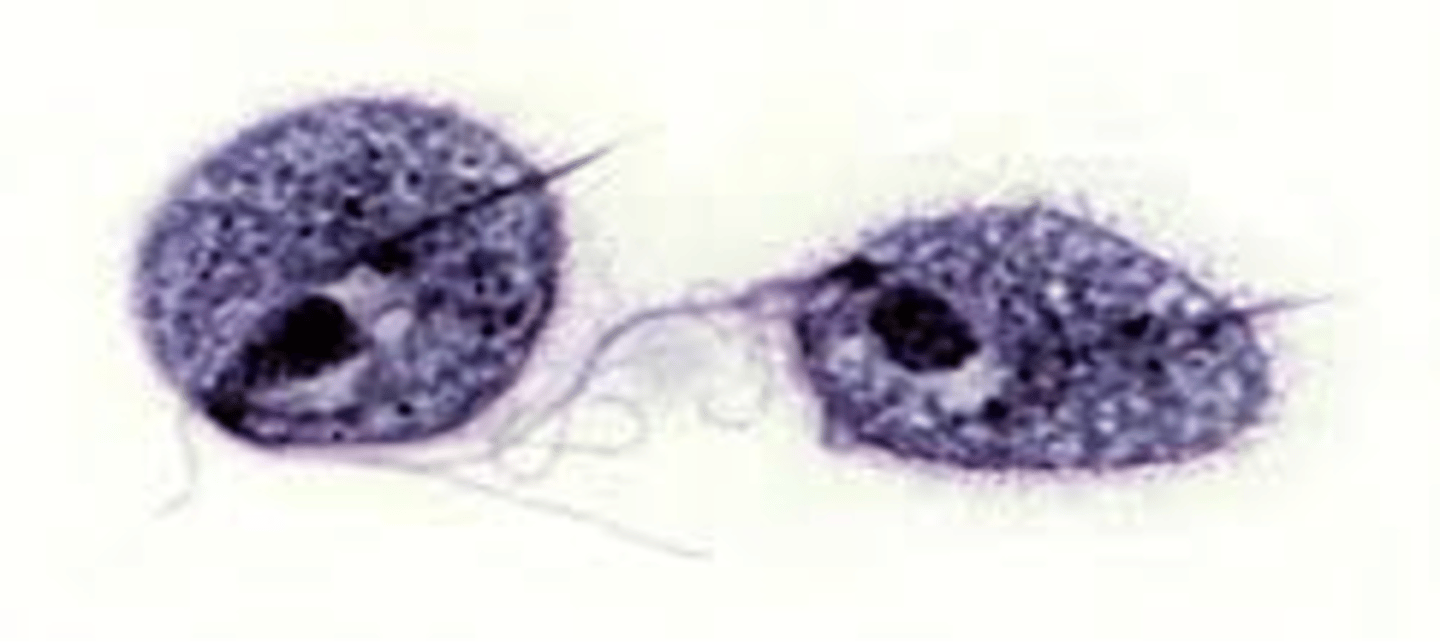
how can you distinguish the trophozoite stage giardia lambda
looks like tear drop or balloon with two sucking discs
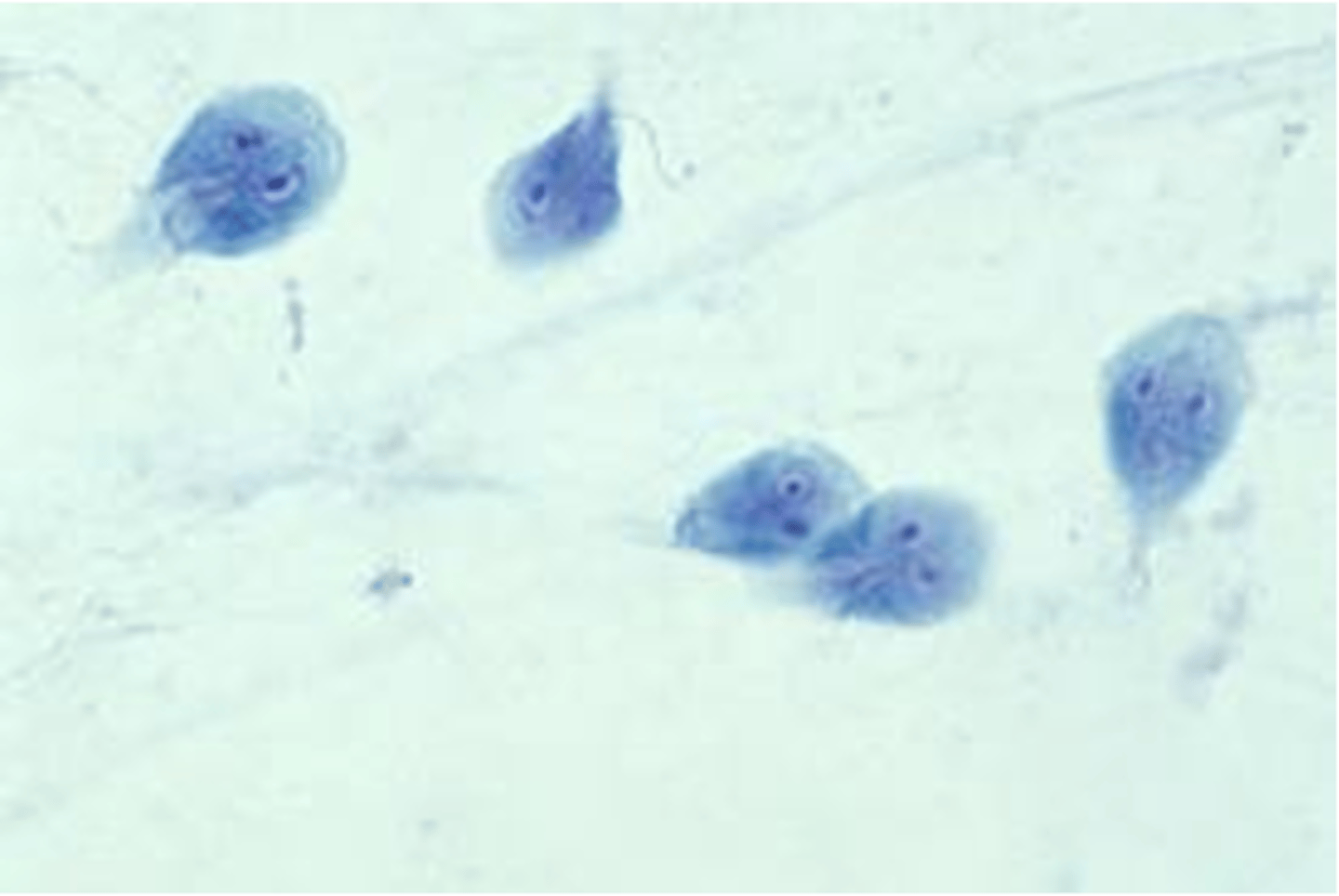
what is the clinical significance of giardia lamblia?
causes dysentery (poop smells bad, malodorous feces)
what organism on this practical are archaezoa?
1. trichomonas vaginalis
2. giardia lamblia
where is trypanosoma Spp. found in the body?
blood
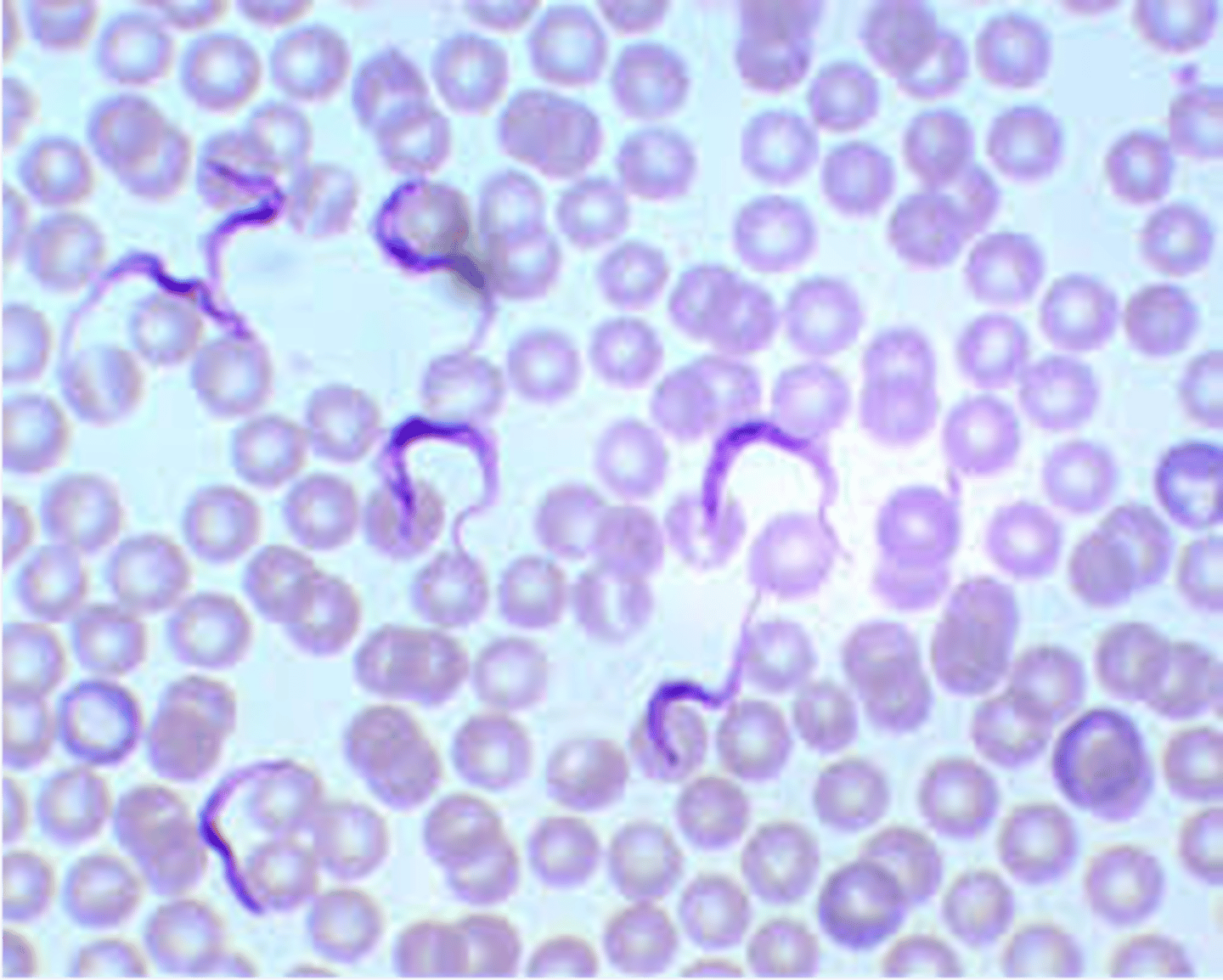
what is the vector of Trypanosoma Brucei or African sleeping sickness?
tsetse
what is the vector of trypanosoma cruzi or chagas disease?
reduviid (triatomine) bug, or assassin bug or kissing bug
what are the distinguishable features of trypanosoma spp.?
found outside of cell (red blood cels), resembles ribbon, 2-3 blood cells long
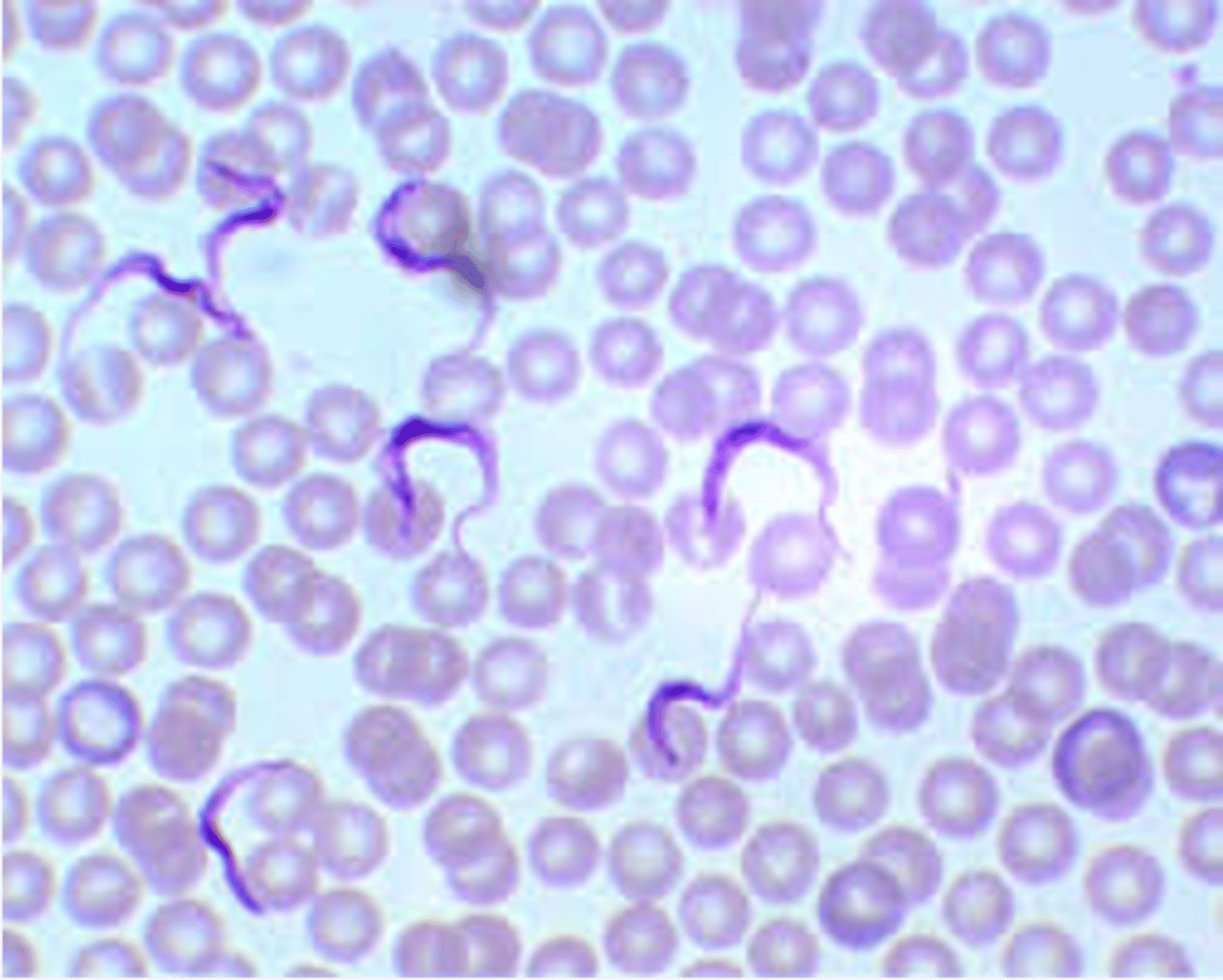
what to species on this practical are euglenozoa?
1. Trypansoma cruzi
2. Trypanosoma brucei
what is the clinical significance of of Trypanosoma cruzi?
causes chagas disease, cardiomyopathy
what is the clinical significance of of Trypanosoma Bruce?
causes African sleeping sickness
what continent is associated with trypanosoma cruzi?
South America
what continent is associated with trypanosoma brucei?
Africa
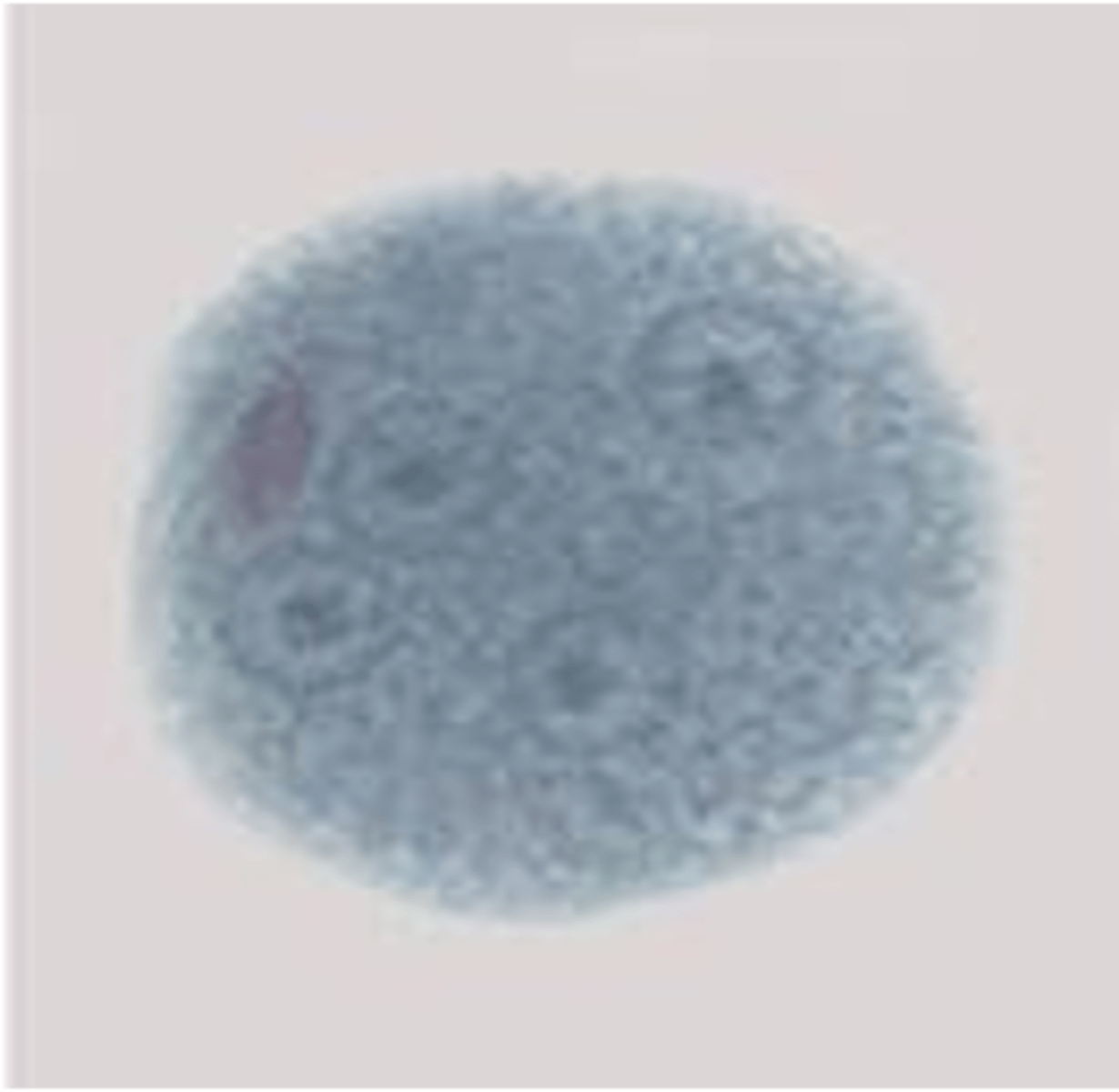
what are the distinguishing features of Entamoeba histolytica's cyst?
round and has atleast four nuclei
what are the distinguishing features of Entamoeba histolytica's trophozoite?
amorphous (no definite shape), and may have pseudopodia (rare, less numerous), debris in background due to being found in stool
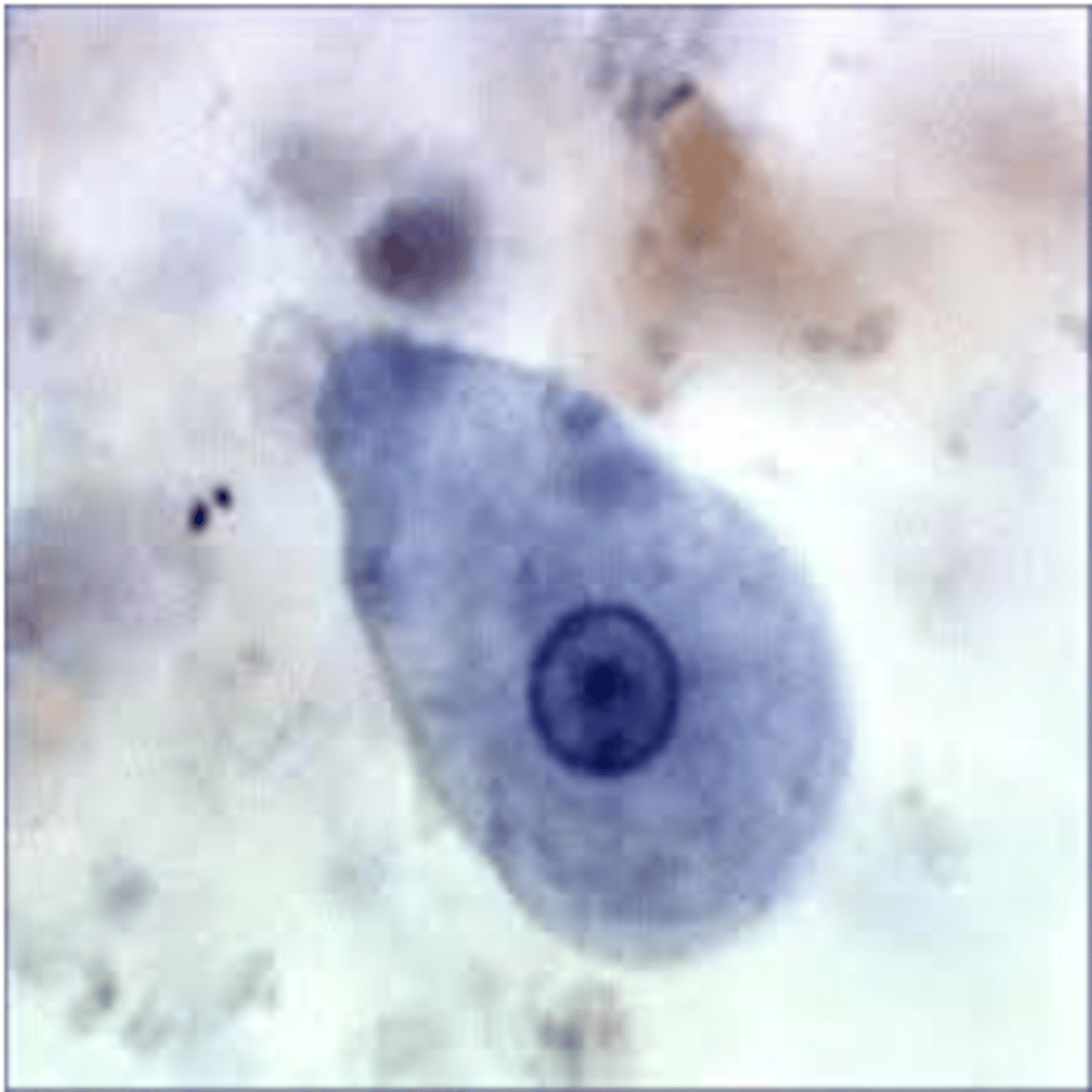
what is the clinical significance of Entamoeba histolytica?
causes amoebic dysentery, liver abscesses and other extra intestinal infections
what is the distinguishing characteristics of amoeba proteus (trophozoite)?
amorphous and has pseudopodia
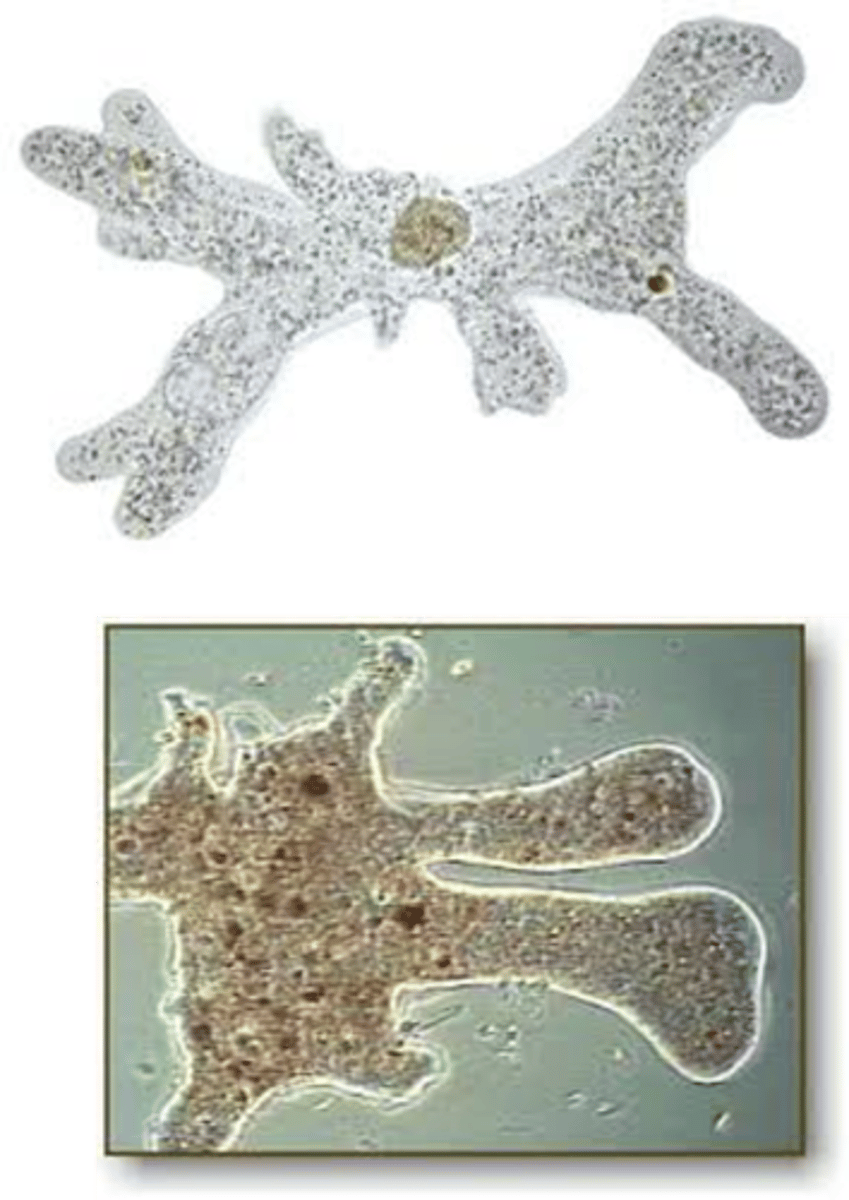
what is the clinical significance of amoeba proteus?
none, doesn't cause disease
what organisms on this practical are amoebozoa
1. Entamoeba histolytica
2. Amoeba proteus
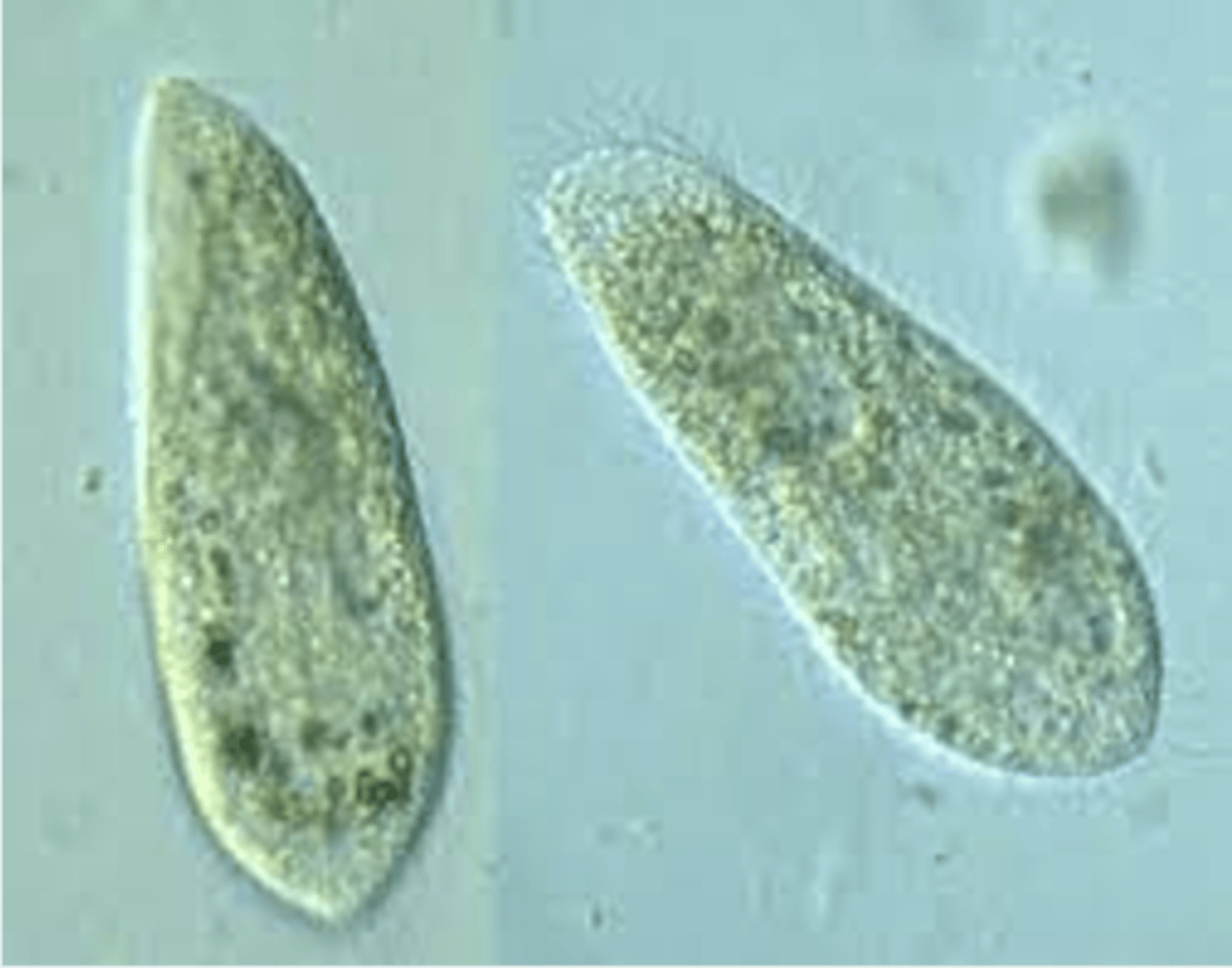
what is are the distinguishing characteristics of paramecium caudatum (trophozoite)?
has cilia
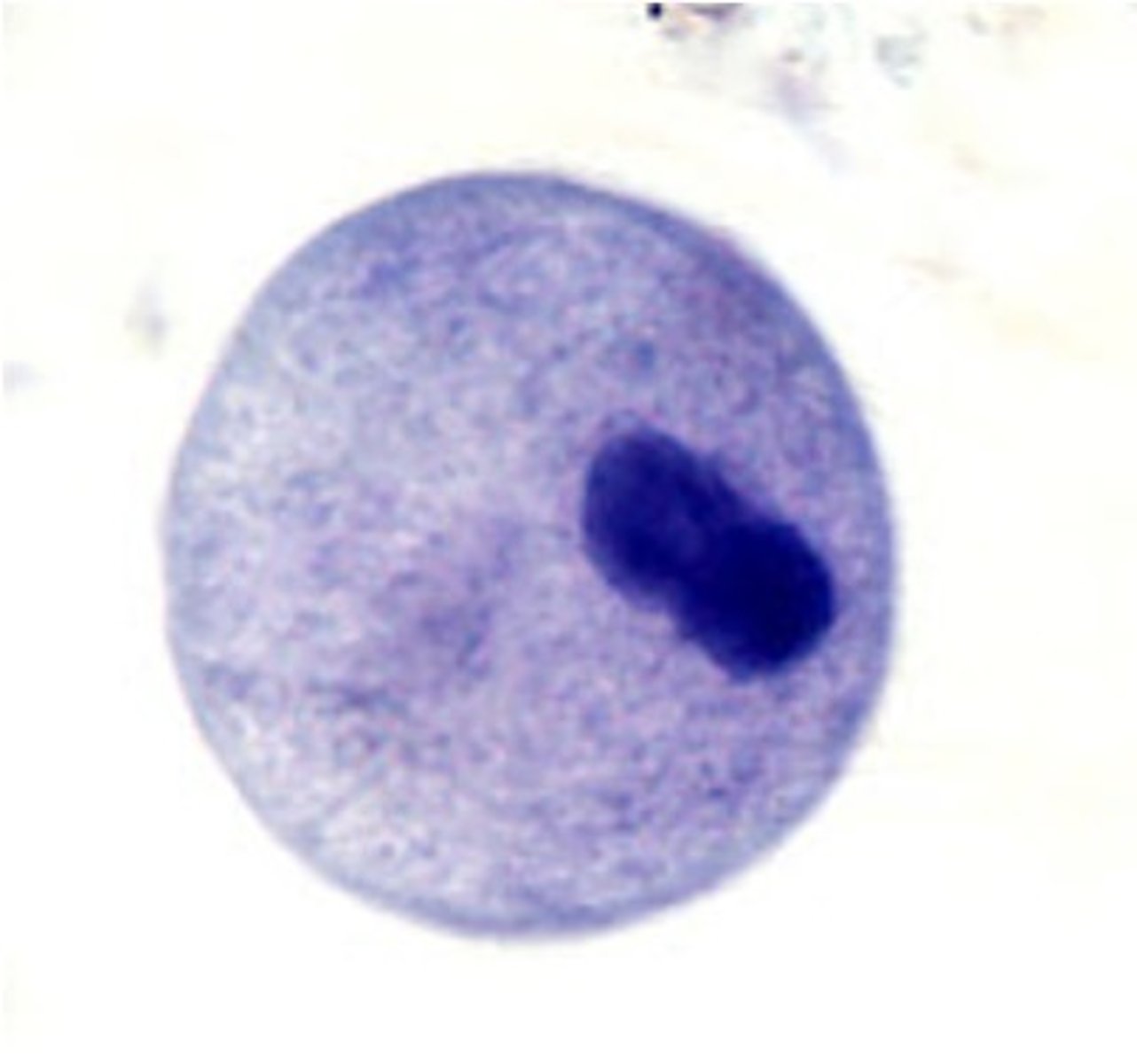
what is are the distinguishing characteristics of Balantidium coli (cyst)?
oval in shape, has macronucleus (one big nucleus)
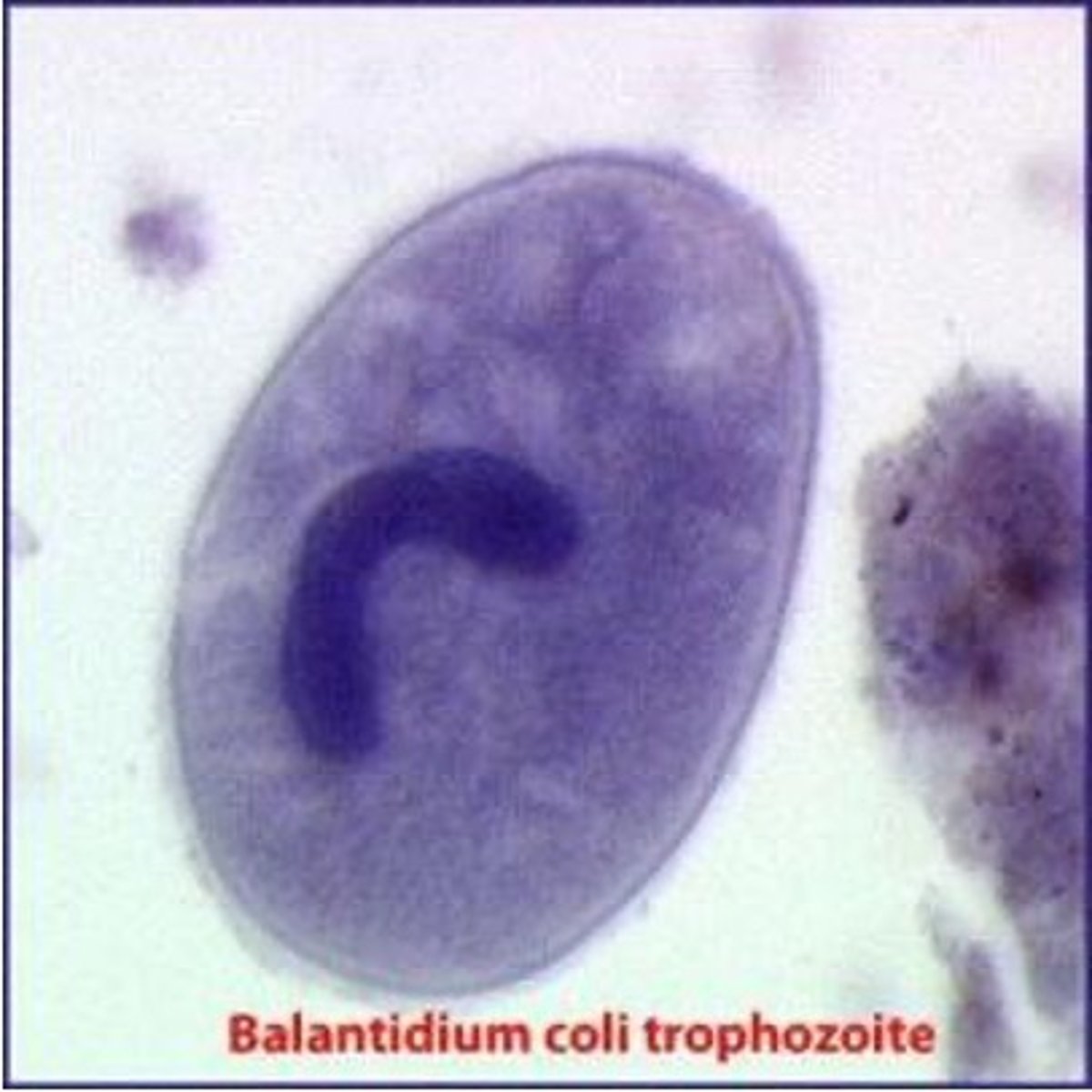
what is are the distinguishing characteristics of Balantidium coli (trophozoite)?
has cilia, peritrichous (all around), is round and has horseshoe shaped nucleus
what is the clinical significance of Balantidium coli?
causes dystentery, can infect other parts of the body, liver abscesses and other extra intestinal infections
what species on the practical are ciliophora?
1. Balantidium coli
2. Paramecium caudatum
what are the distinguishing characteristics of plasmodium Spp. or falciparum (trophozoites)?
has ring like structure (merozoite), and is intracellular parasite of blood cells
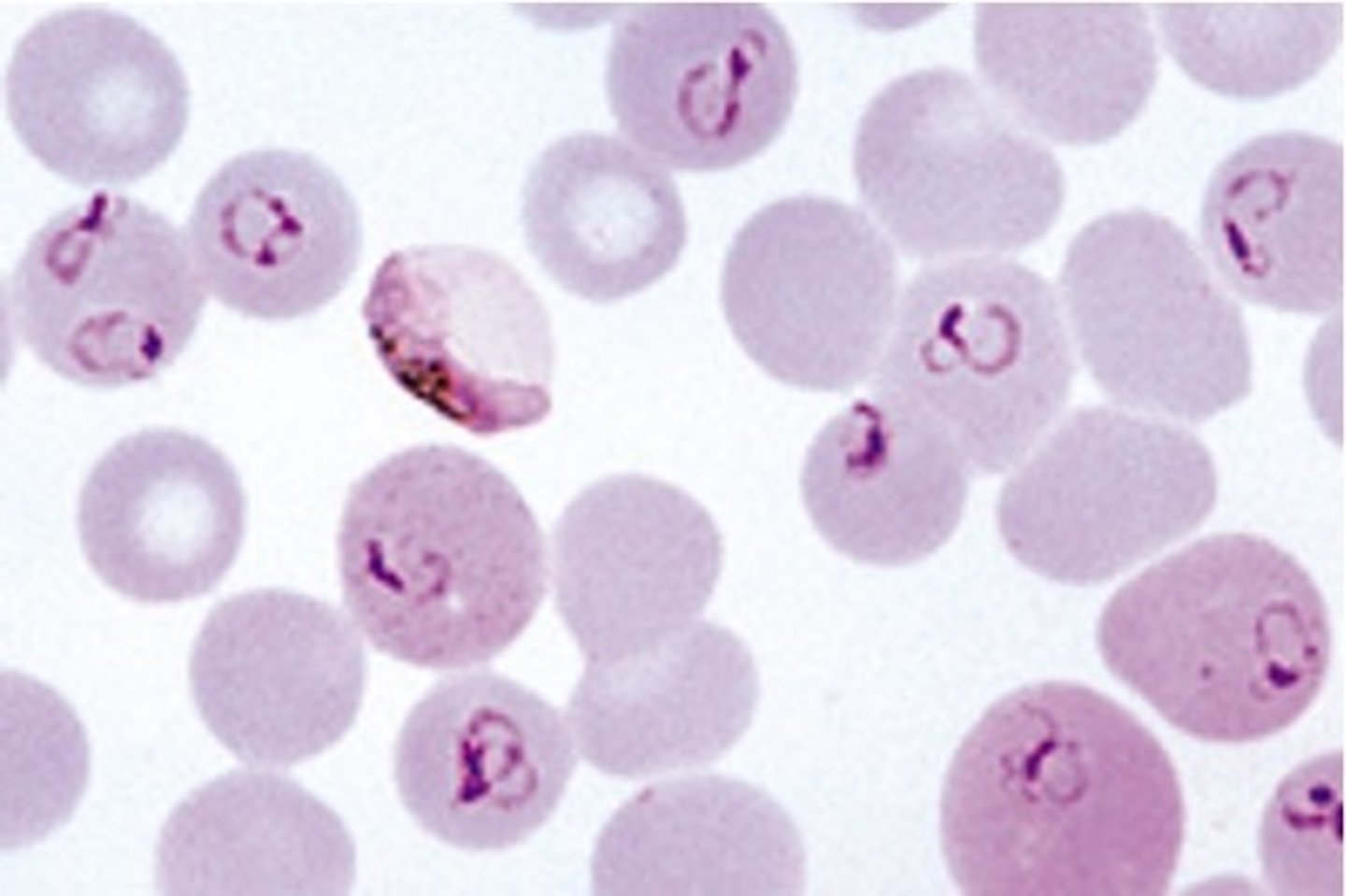
what is the clinical significance of plasmodium spp.?
causes parasitemia and or malaria
what are the distinguishing characteristics of toxoplasma gondii (trophozoites)?
crescent shaped
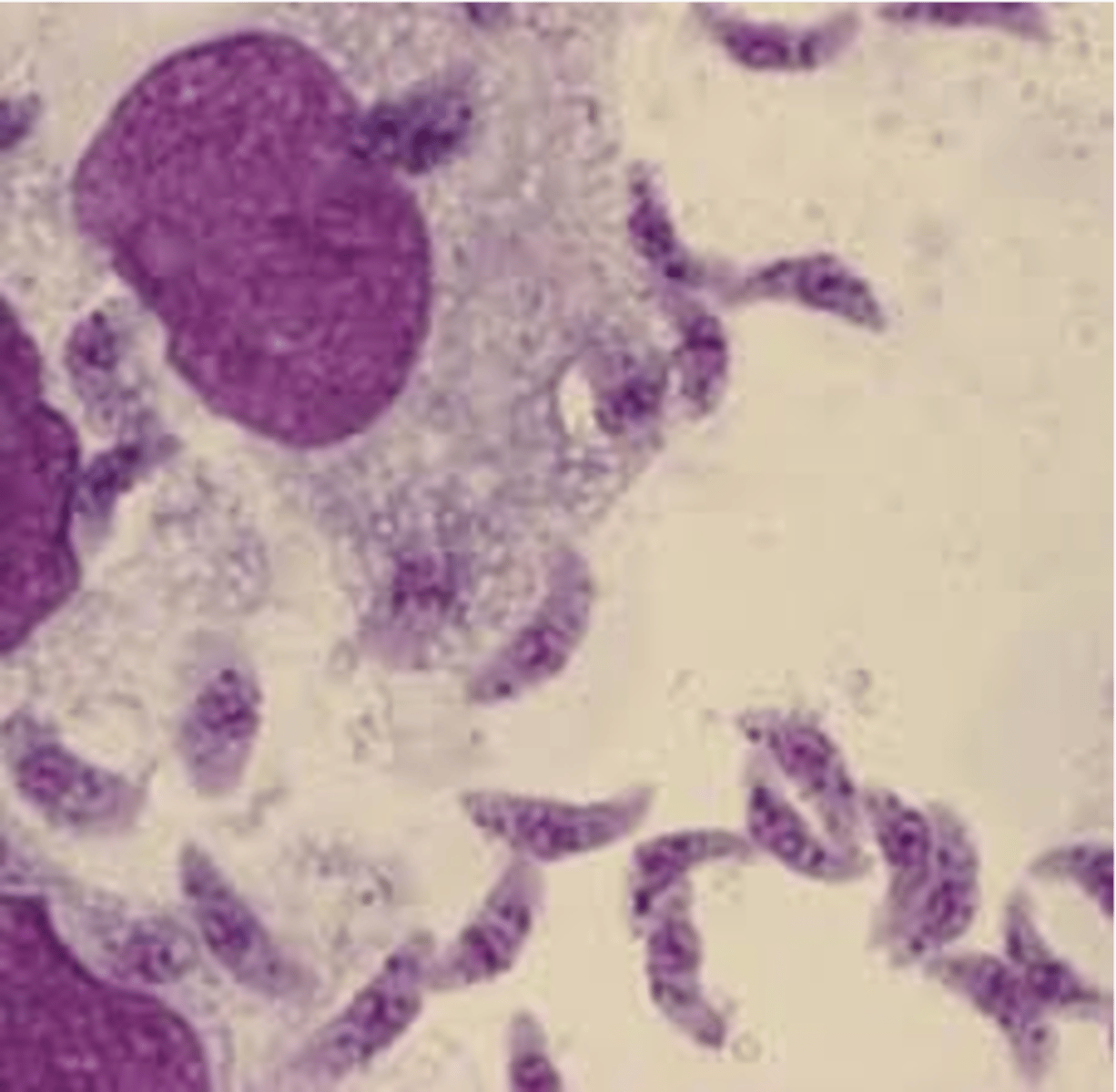
what are the distinguishing characteristics of toxoplasma gondii (cyst)?
perfectly round, with mainy dots within
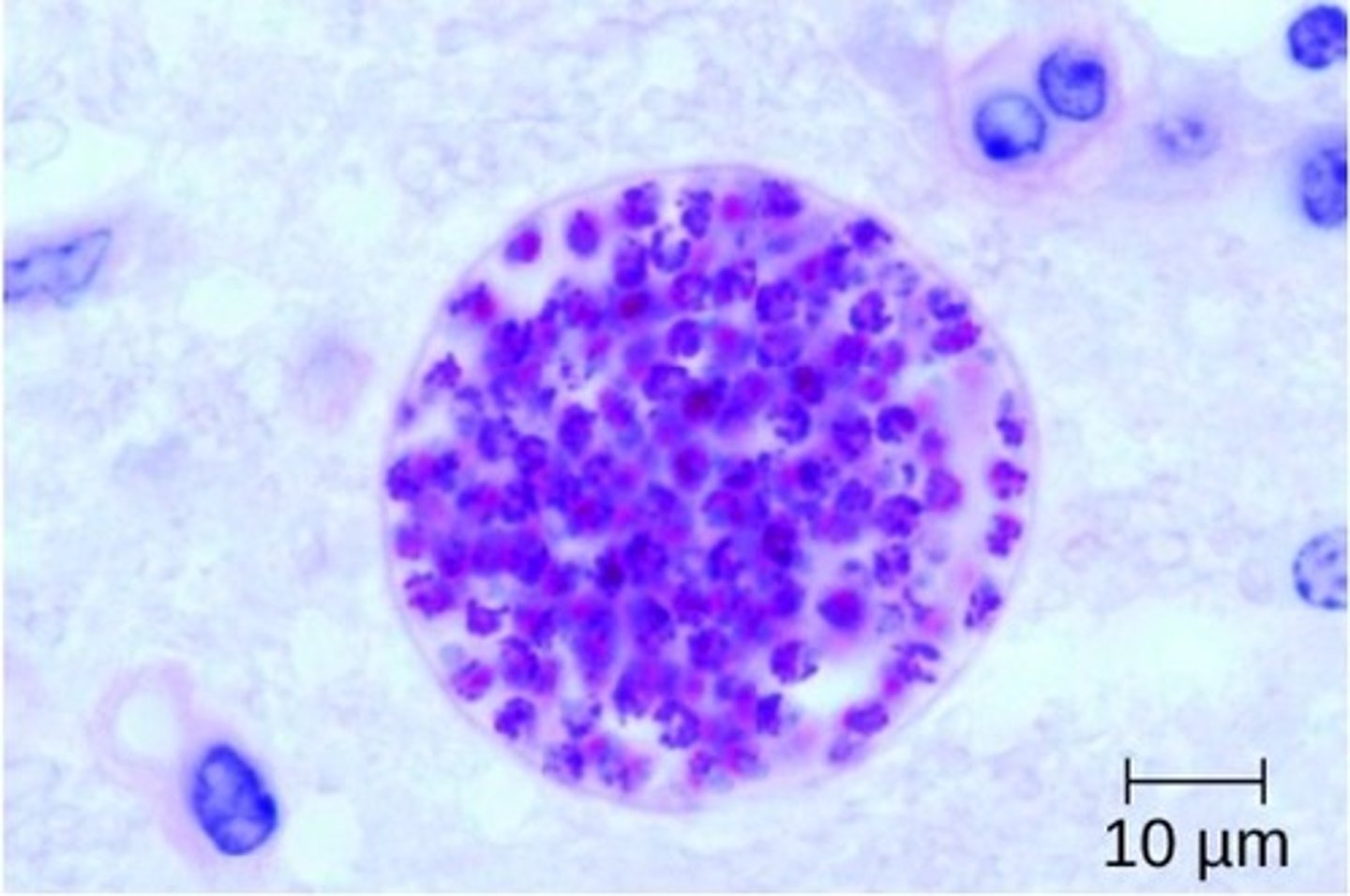
what is the clinical significance of toxoplasma gondii
can infect every tissue in the body (eye of immunocompromised, can cause abortion of fetus
what are the two reservoirs of toxoplasma gondii?
cats and birds
what are the distinguishing characteristics of cryptosporidium parvum (cysts)?
only one distinguishable by color, is hot pink or are acid fast
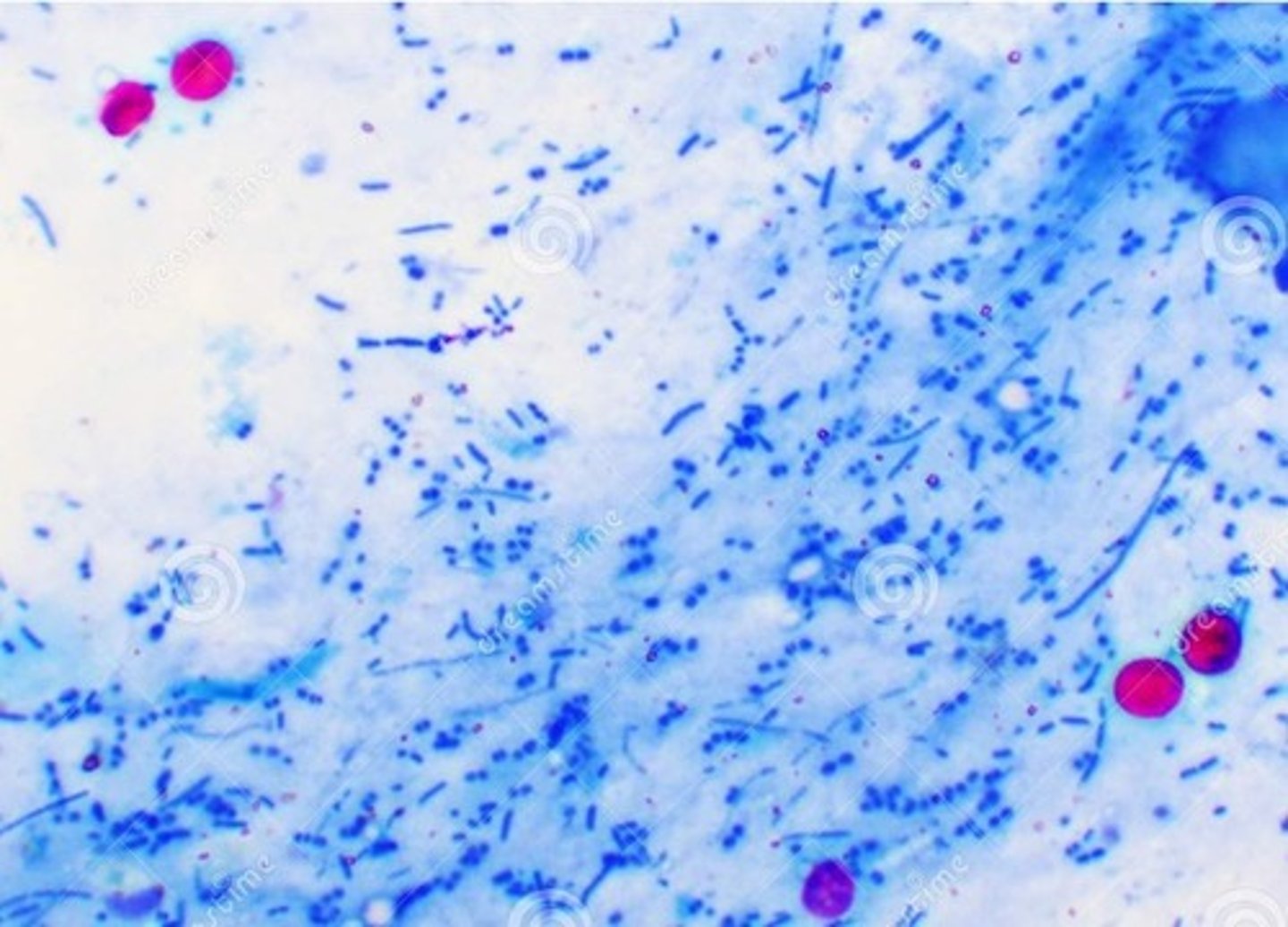
what is the clinical significance of Cryptosporidium parvum?
causes diarrhea that is non-bloody
what species on the practical are apicomplexa?
1. Plasmodium falciparum or spp.
2. Toxoplasma gondii
3. Cryptosporidium parvum
if the organism is on the outside it causes a _______? if it on the inside?
infestation, infection
how are exoparasites classified?
by number of legs
what species on this practical are insecta or insects?
1. Pediculus humanus
2. Pthirus pubis
3. Cimex lectularius
what are the distinguishing characteristics of pediculus humanus?
have six legs, have claws and are found in head hair
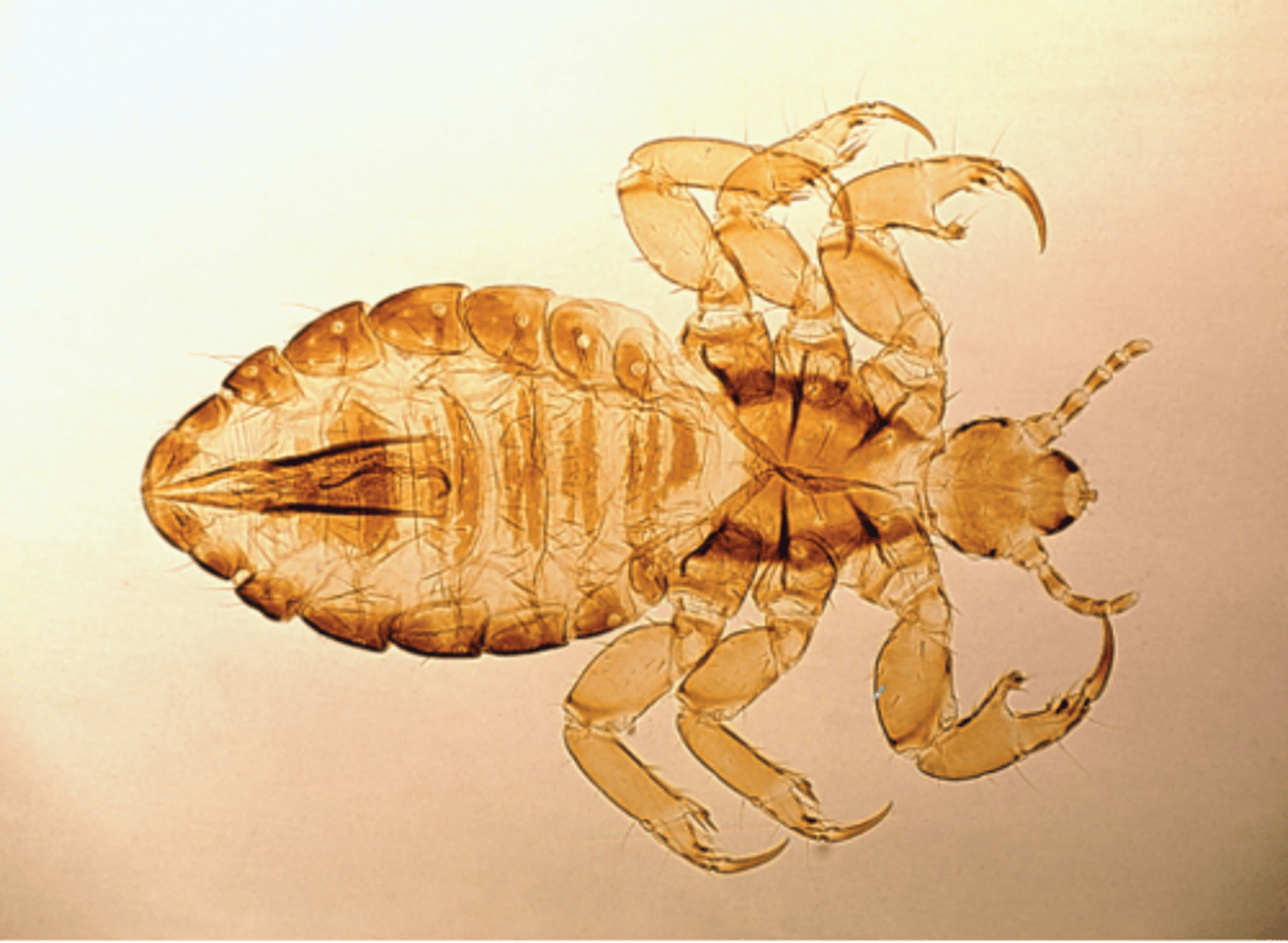
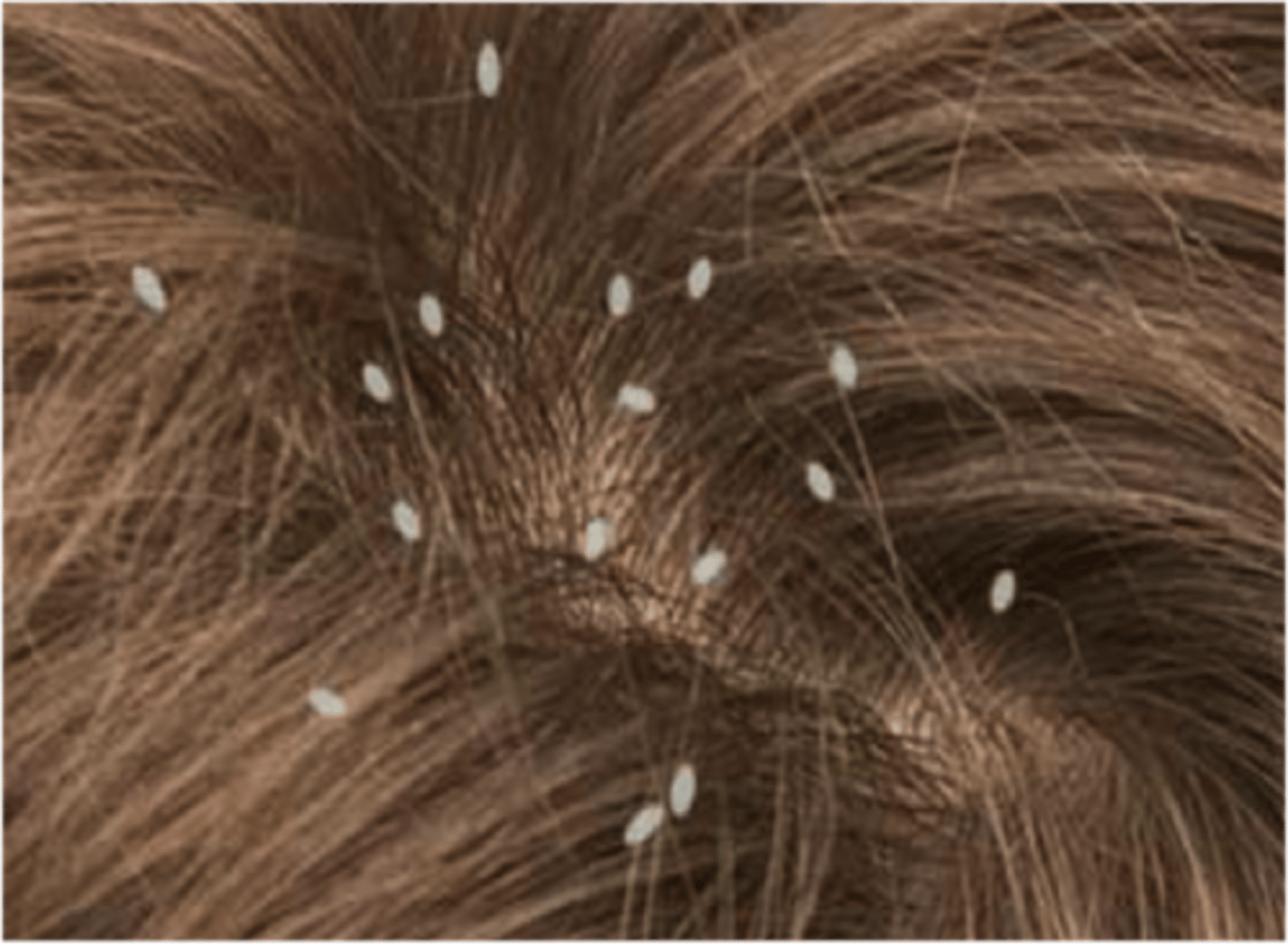
what its the clinical significance of pediculus humanus?
cause pediculosis or infestation with lice

what are the distinguishing characteristics of Pthirus pubis?
6 legs, have hooks, look like crabs, found in pubic hair, eyebrows , eyelashes, is sexually transmitted
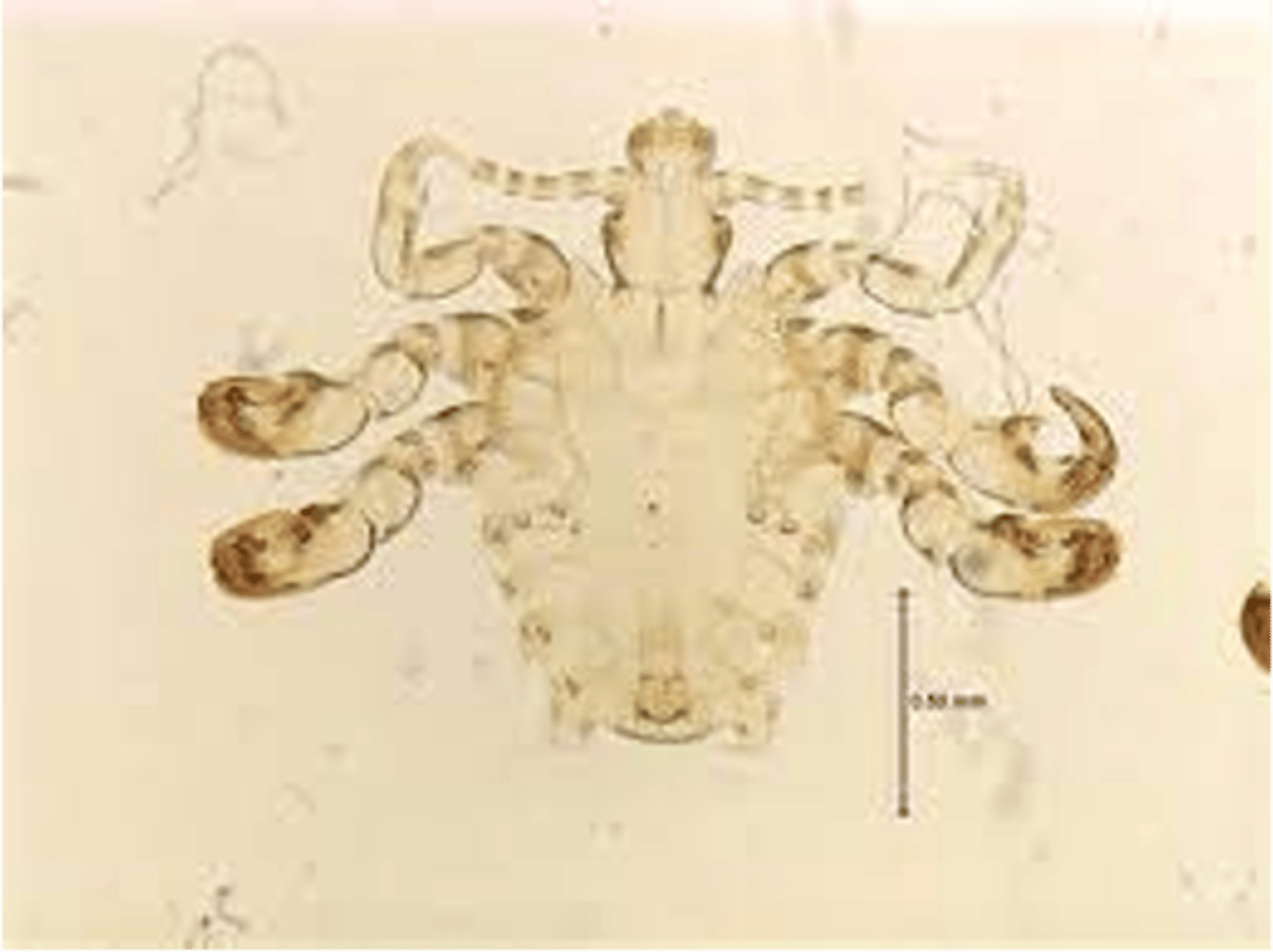
what its the clinical significance of Pthirus pubis?
cause pediculosis or infestation with lice
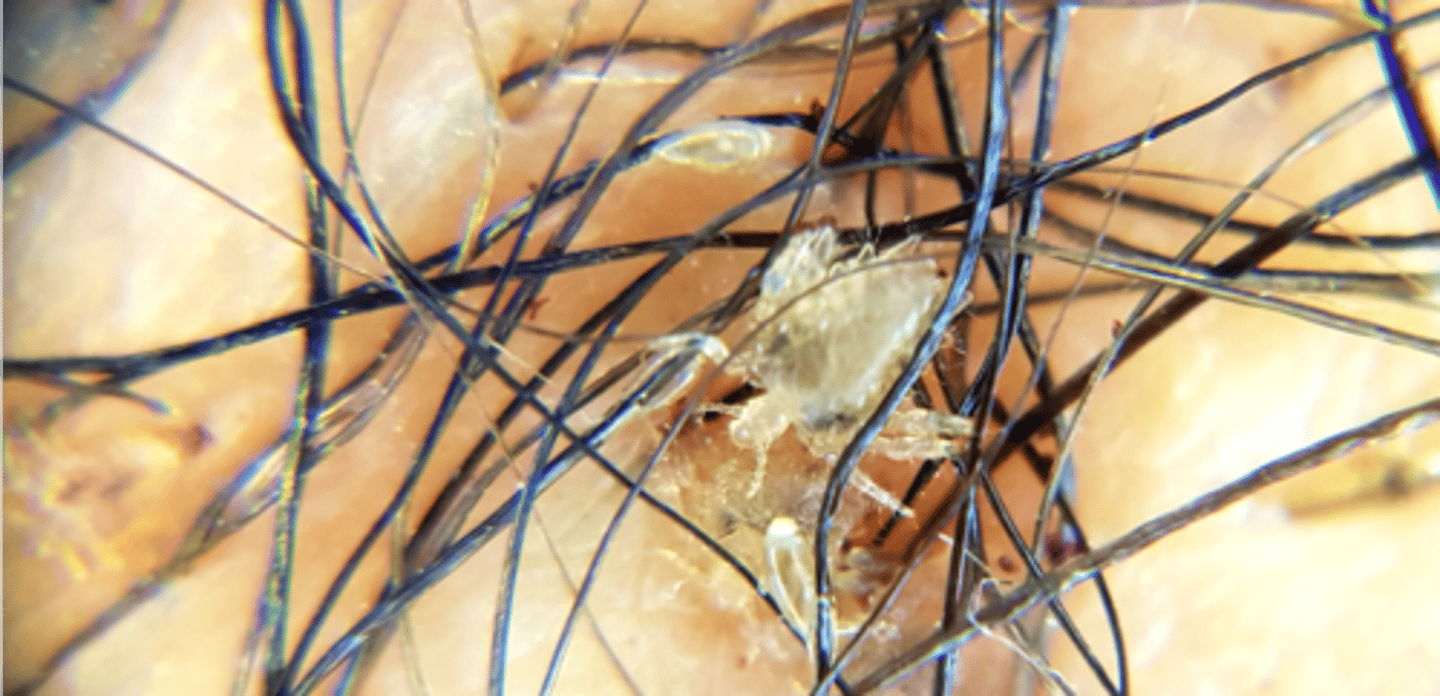

what are the distinguishing characteristics of Cimex lectularius?
feed on entire body at night, puke blood on bed, hide in crevices of bed, look like average bug
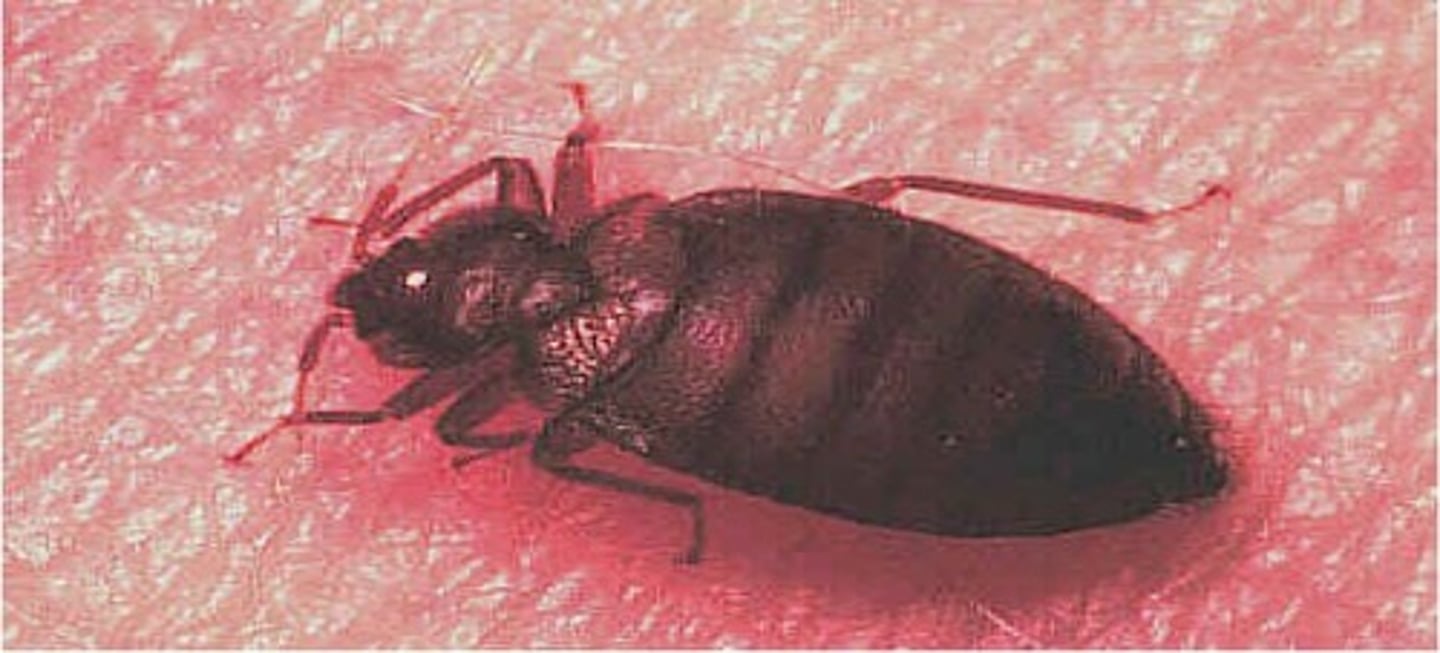

what is the clinical significance of Cimex lectularius?
blood feeding parasites, dont transmit disease
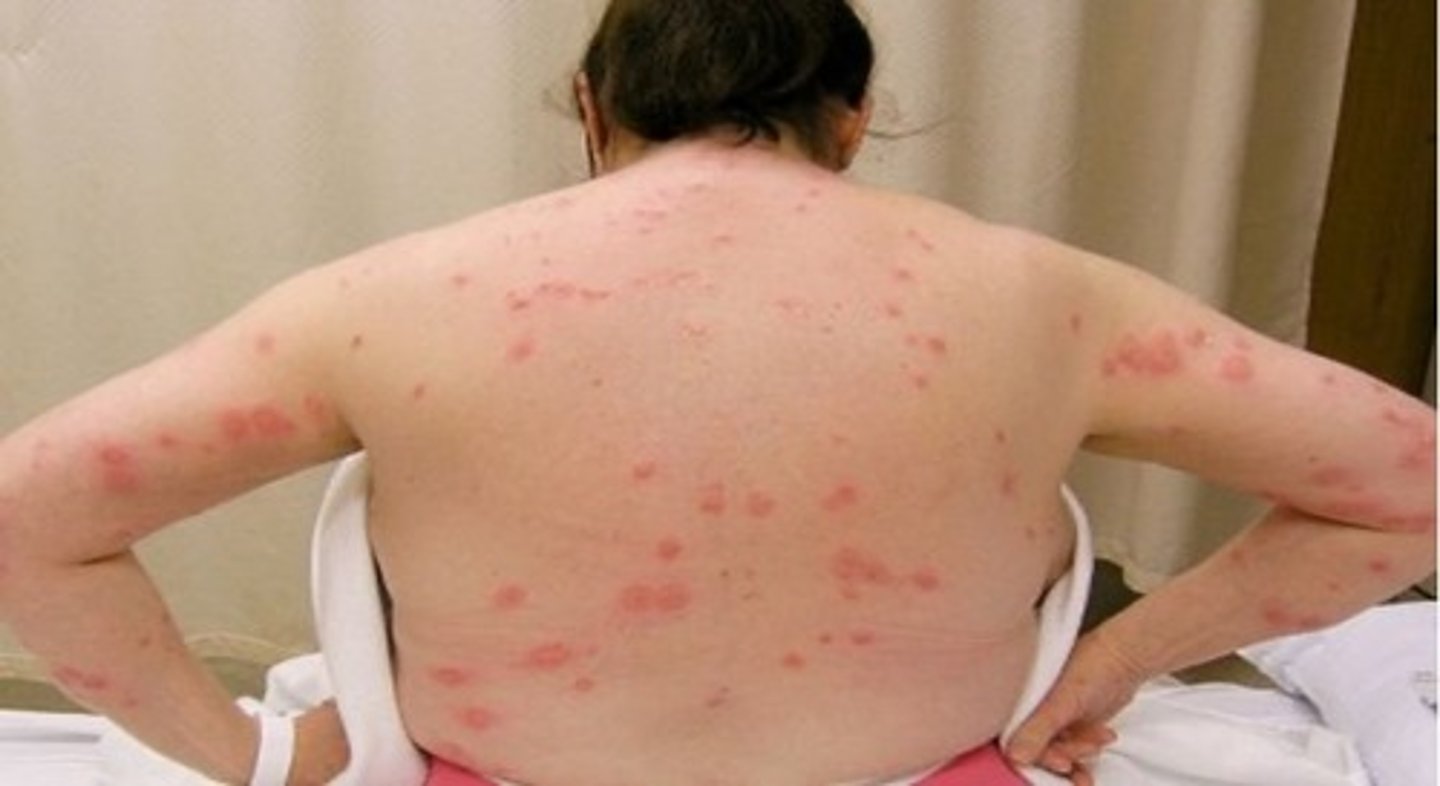
what species on this practical are archnidia or arachnids?
1. Amblyomma americanum (lone star tick)
2. Sacrcoptes scabiei (scabies)
3. Eutrombicula alfreddugesi (chigger)
what are the distinguishing characteristics of Amblyomma americanum or lone star ticks?
white dot on back, eight legs, do not burrow into skin, hyptosome (feeding tube) has recurved teeth or barbs
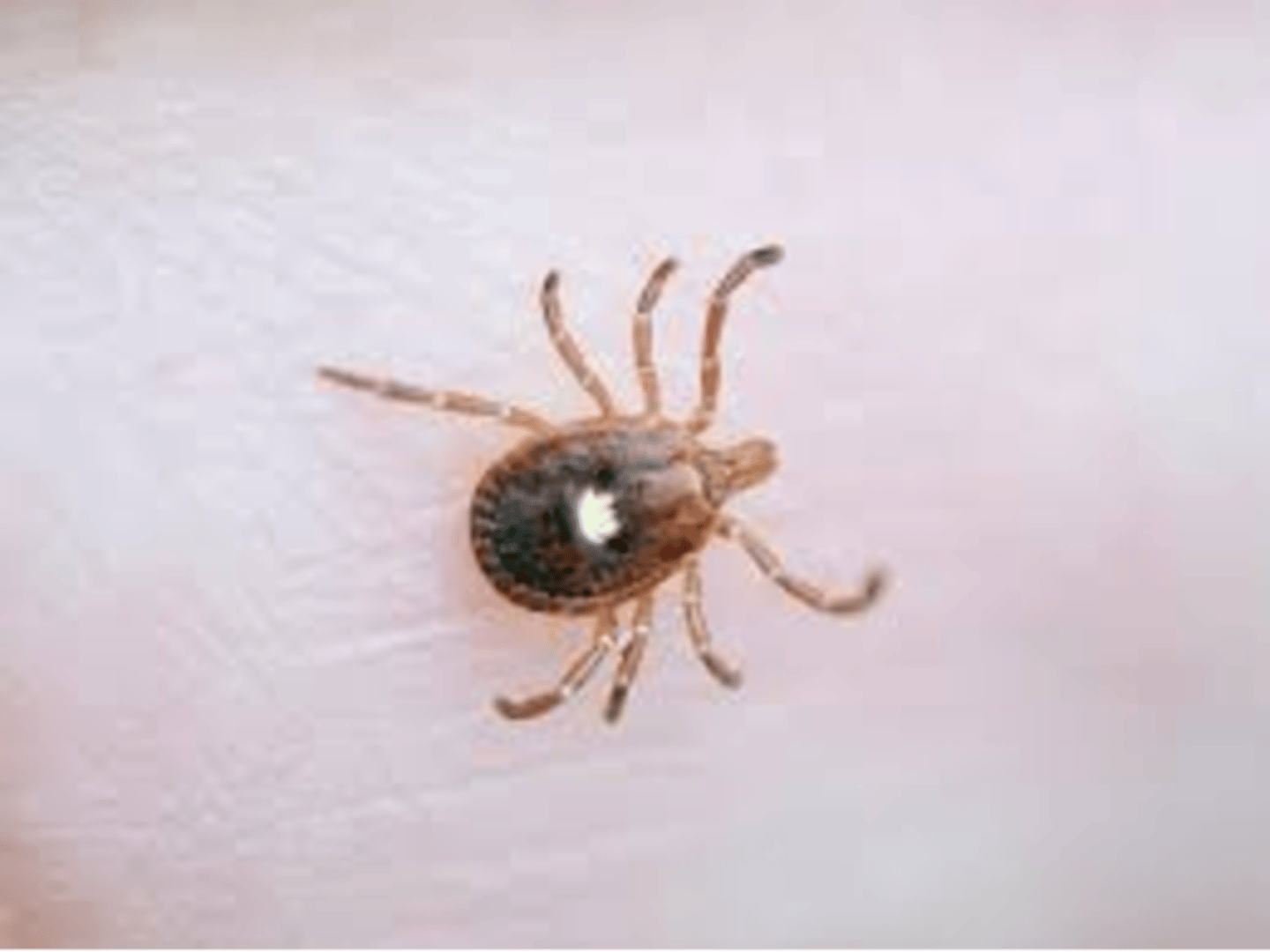

what is the clinical significance of amblyomma americanum?
can spread disease (Lyme disease)
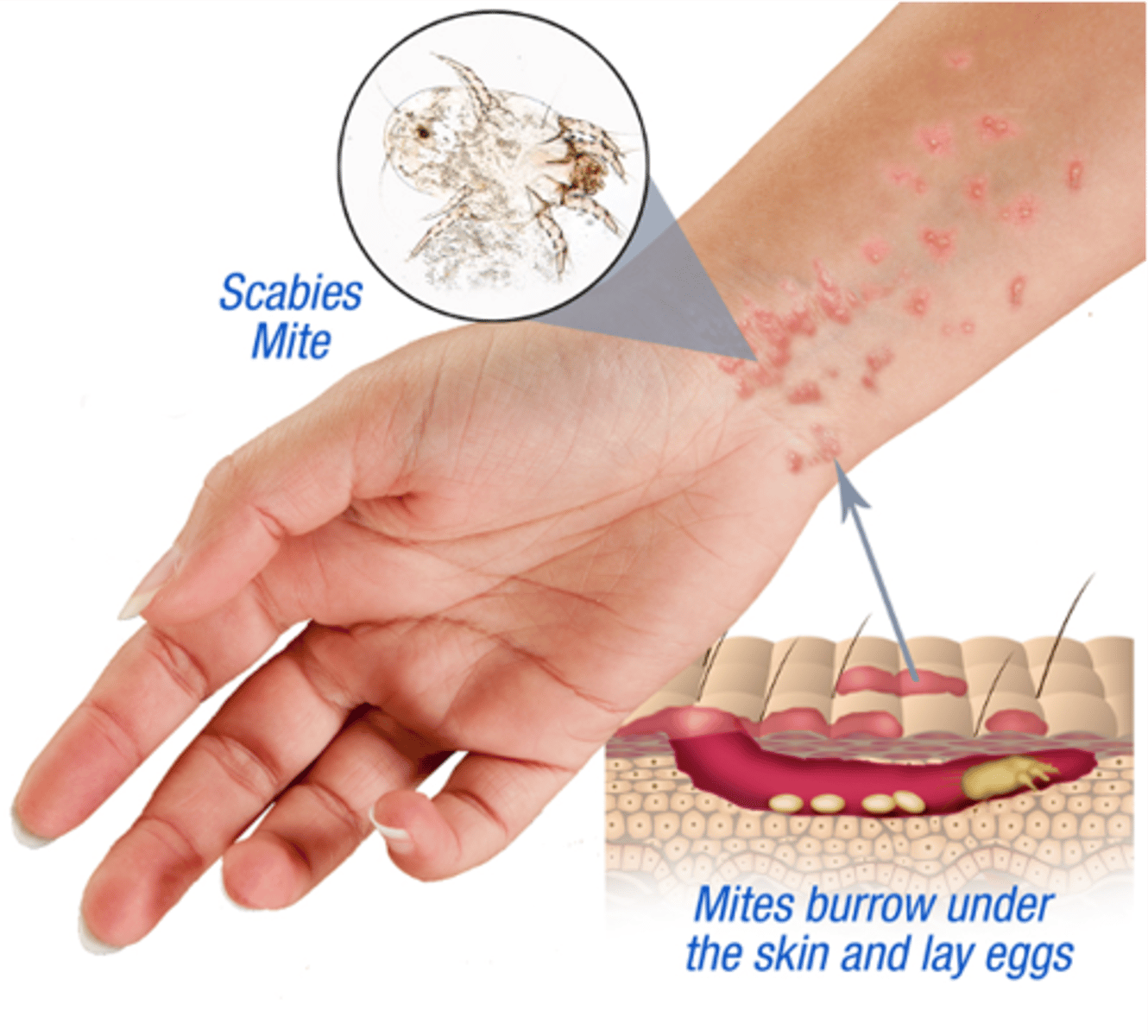
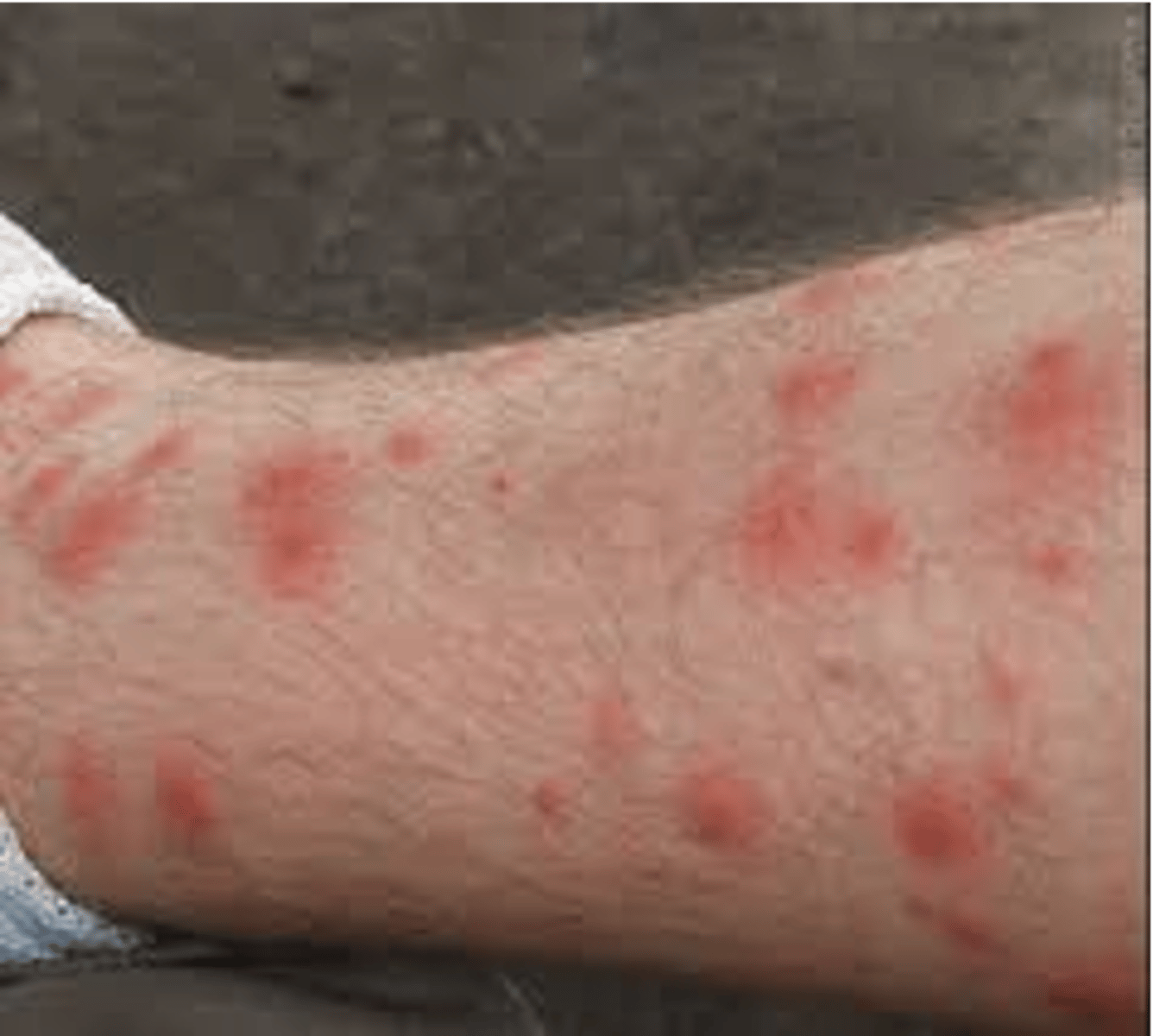
what are the distinguishing characteristics of Sacrocoptes scabiei?
burrows into skin, and causes itching
what are the distinguishing features of Eutrombicula alfreddugesi (chigger)?
red in coloration, bite and feed on humans and other mammals, love Bermuda grass, active late spring to fall, eat and then leave
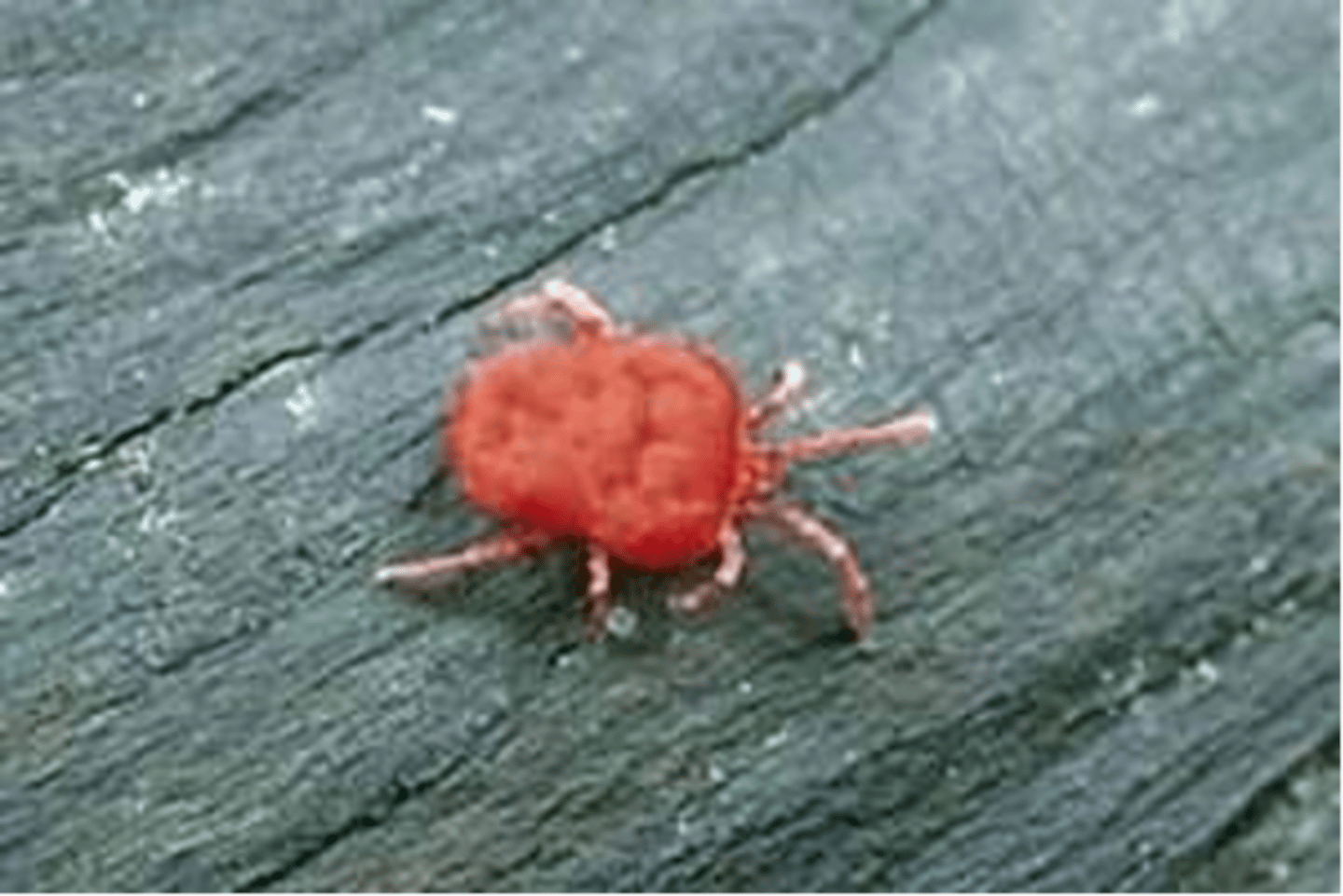

what is the clinical significance of eutrombicula alfreddugesi or chiggers?
feed on blood
what are the biological vectors on the practical?
1. moquito
2. flea
3. tick
what do fleas transmit?
plague

what are the mechanical vectors on the practical?
roaches

what is the difference between a mechanical and biological vector?
mechanical = on (crawl)
biological = microbe multiplies in vector (bite)
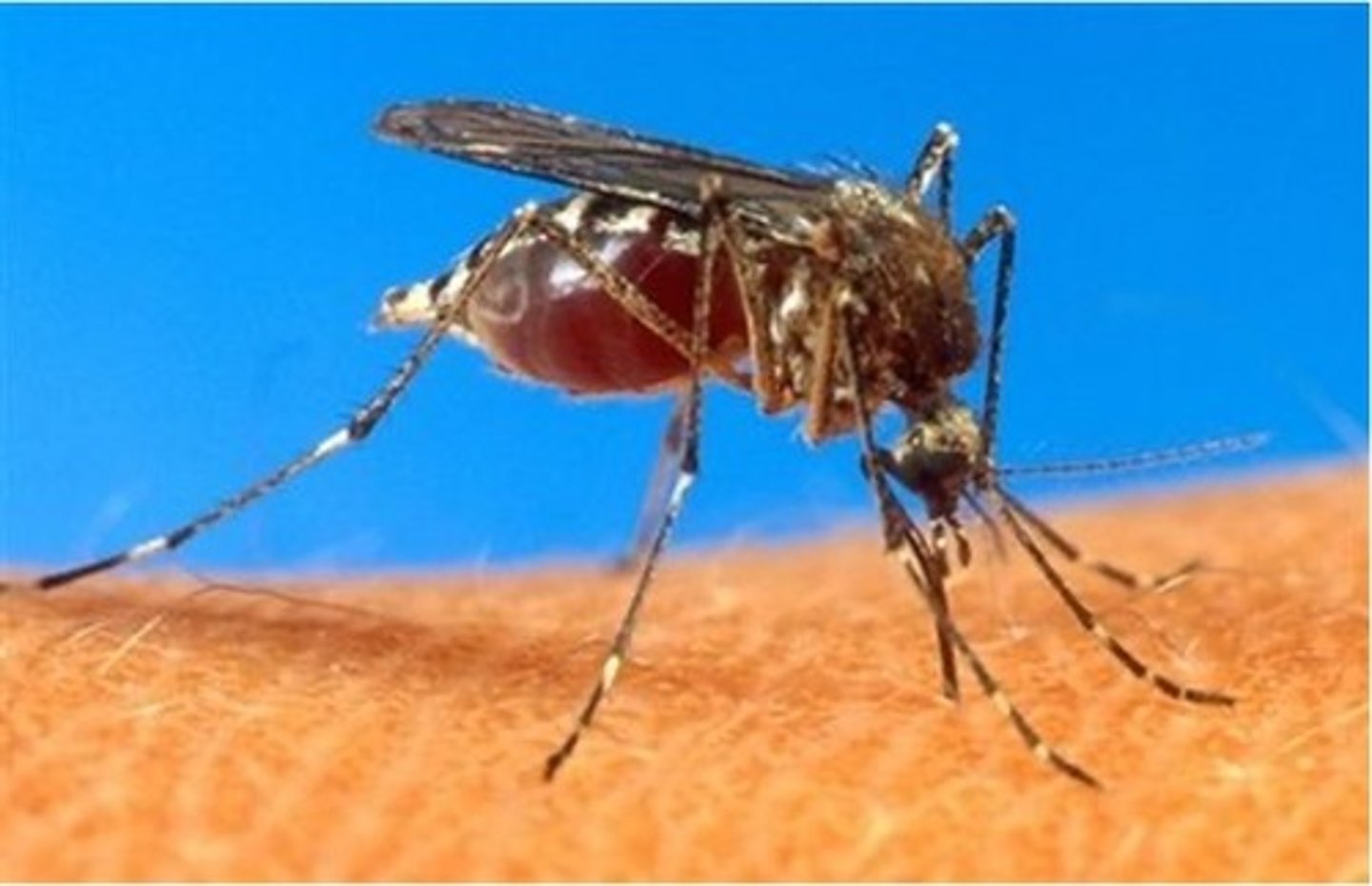
what are the distinguishing features of Aedes aegypti?
strips on legs, agressive
what are the distinguishing features of anopheles psorophora?
big

what are the distinguishing features of culex?
small

what is aedes the vector for?
yellow fever, dengue and zika
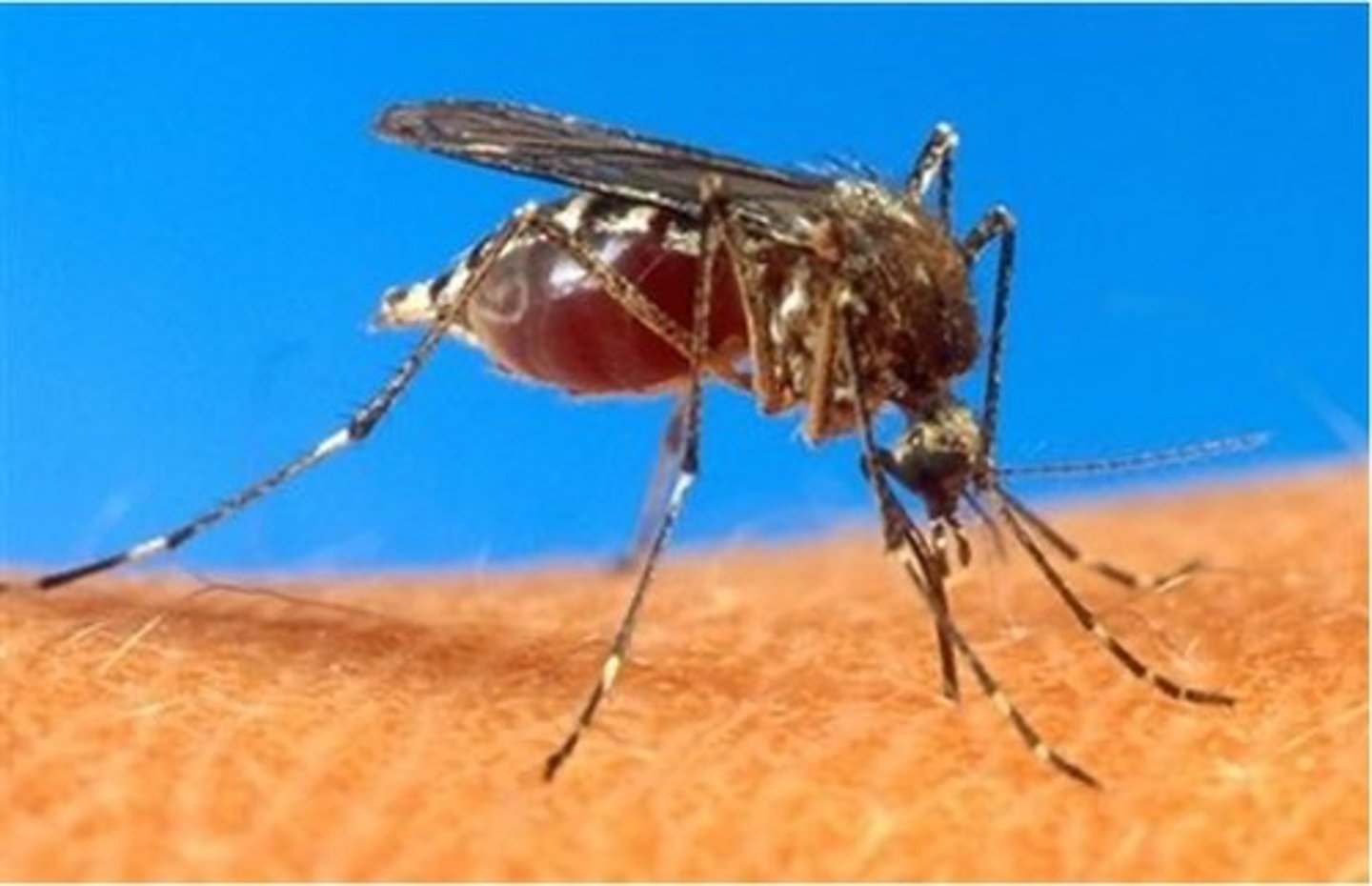
what is anopheles the vector for?
malaria, plasmodium vivax

what is culex the vector for?
encephalitis and west nile virus

what are characteristics of Trematoda?
1. flat worms known as flukes
2. are mostly monoecious (hermaphrodites)
what are characteristics of Cestoda?
1. flat worms known as tape worms
2. have scolex, that can have suckers or hooks and suckers
3. have segment (proglottids) can produce and fertilize own ova
what are characteristics of nematoda?
1. true worms, are round worm
2. have grooves (some) for movement
3. are dioecious (two sexes)
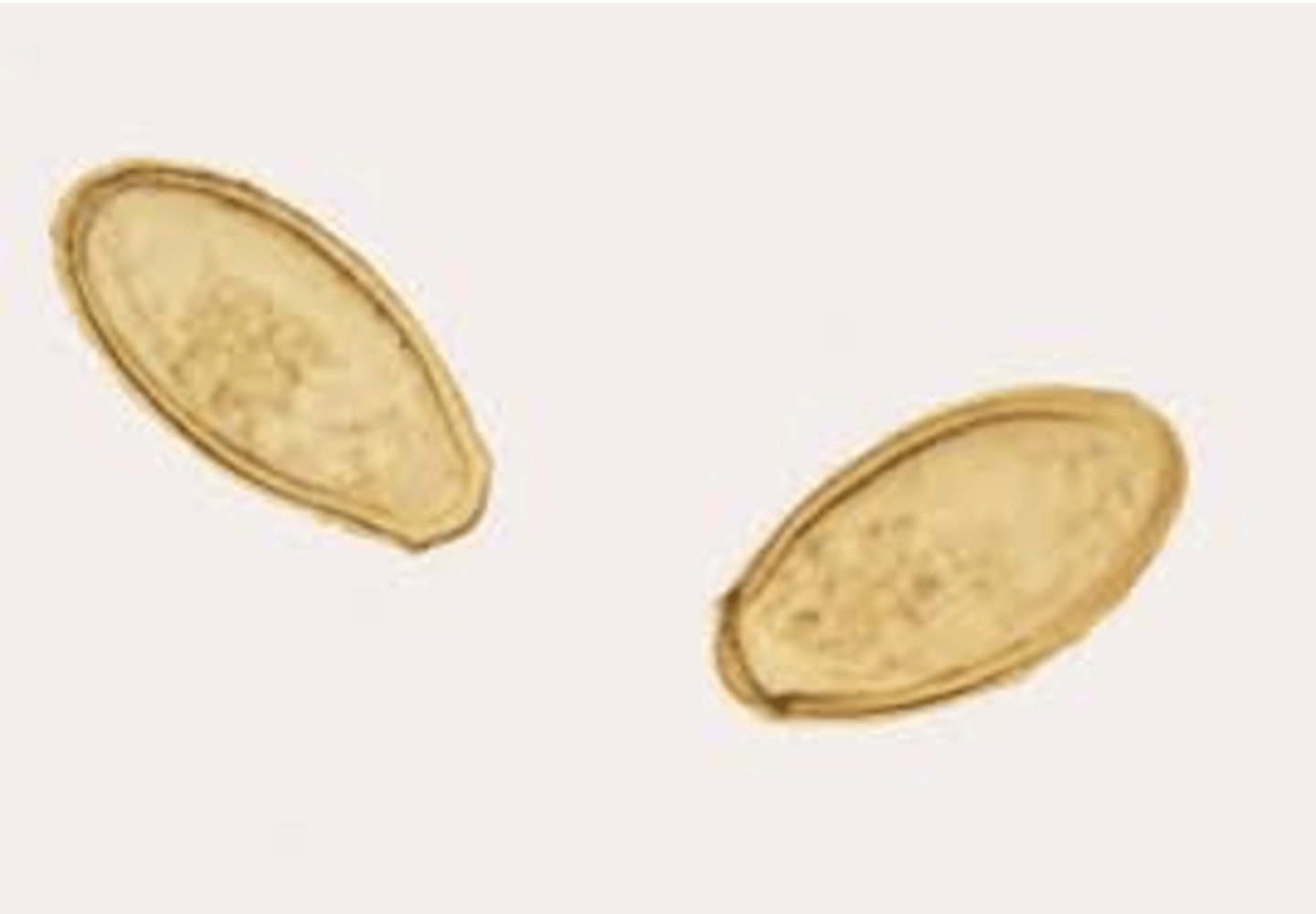
what are the distinguishing characteristics of clonorchis sinesis (cyst)?
looks like pumpkin seed, has apex

what are the distinguishing characteristics of clonorchis sinesis (adult)?
can be seen with human eye, is large
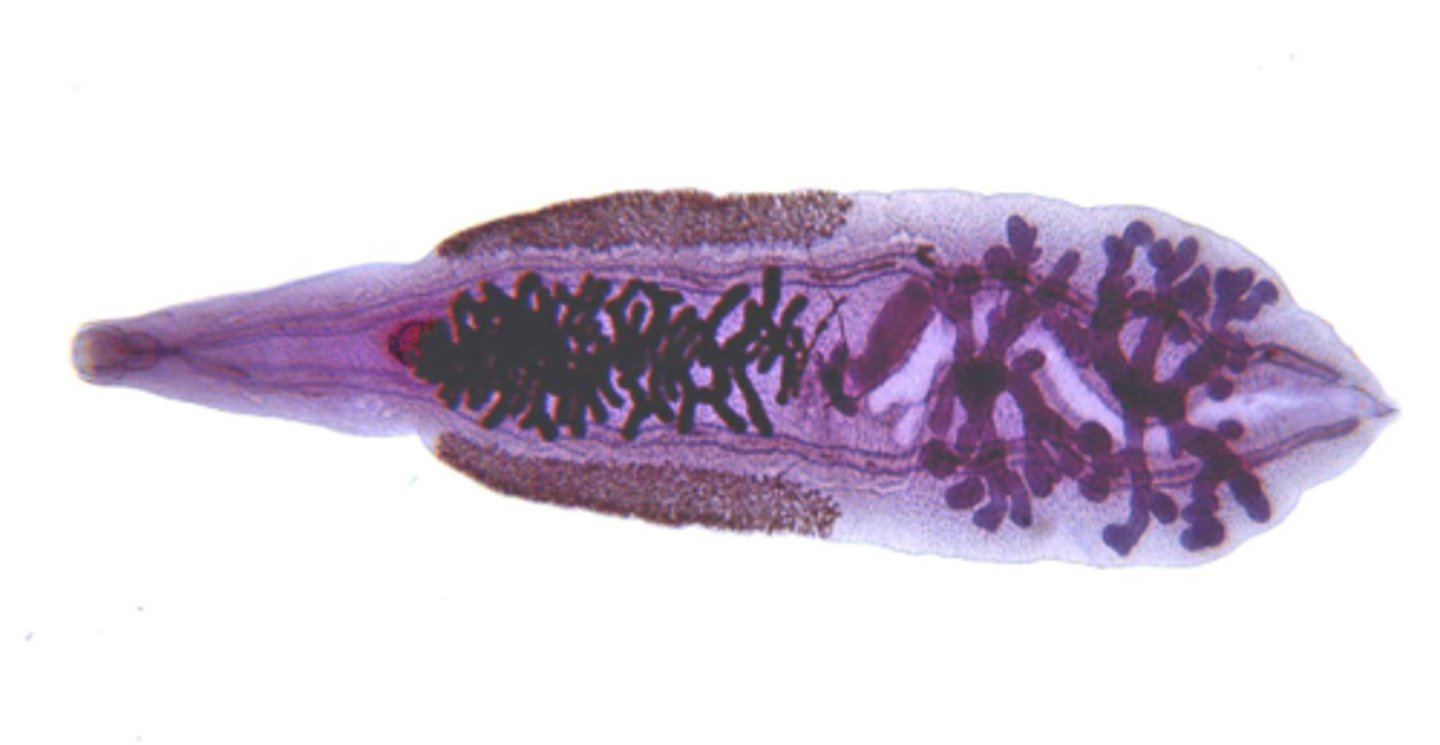
what is the clinical significance of clonorchis sinesis?
causes hepatic portal disease and hepatitis
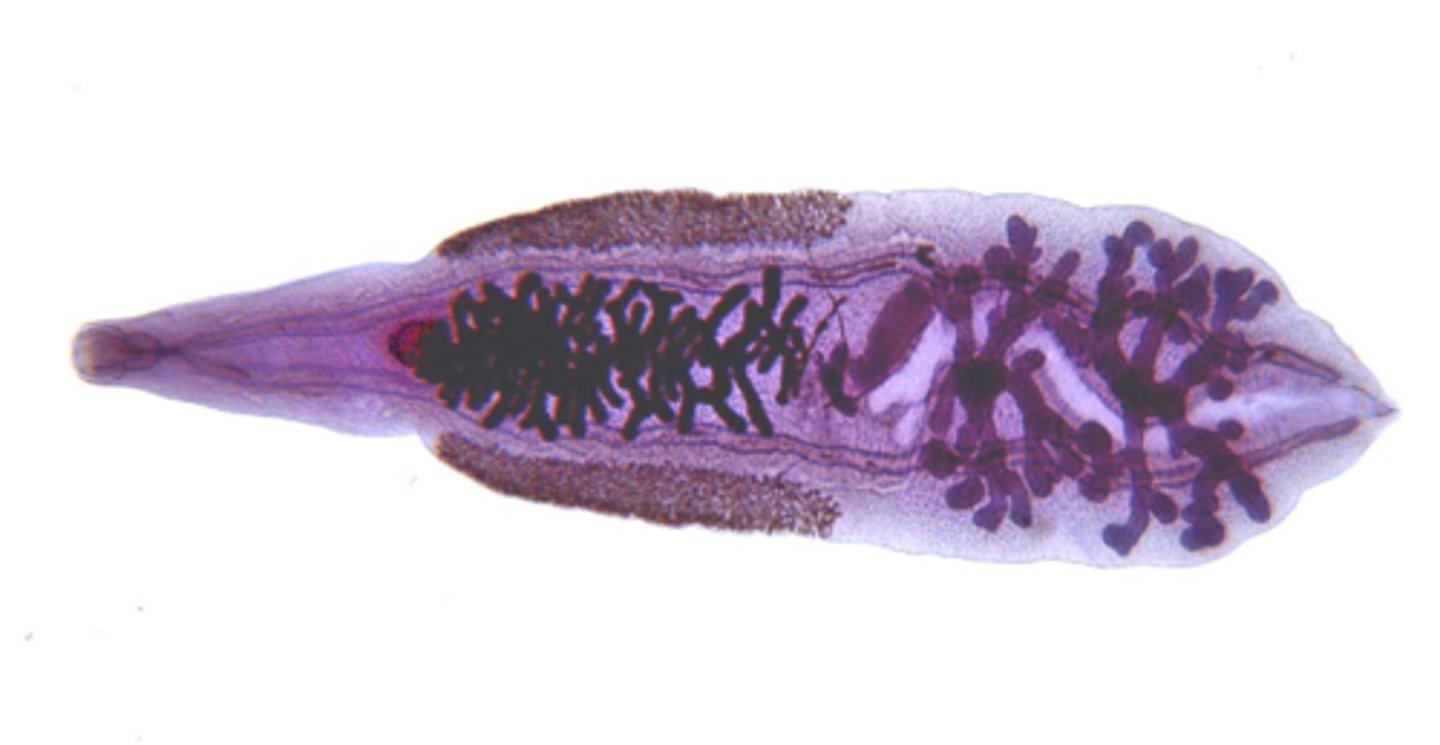
what are the distinguishing characteristics of fasciola hepatica (OVA)?
larger then C. sinensis, is oval and has small lid on top (operculum)
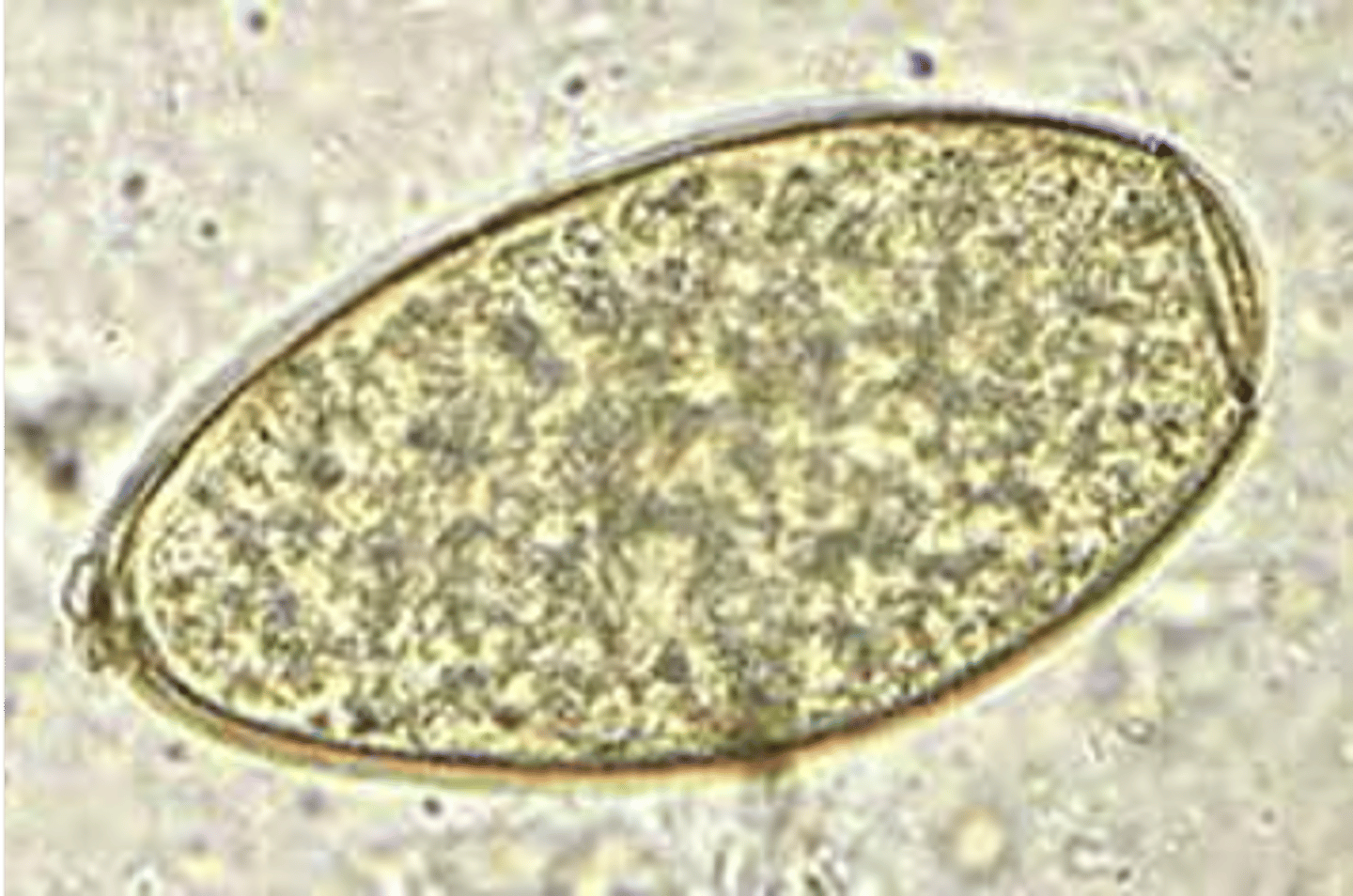
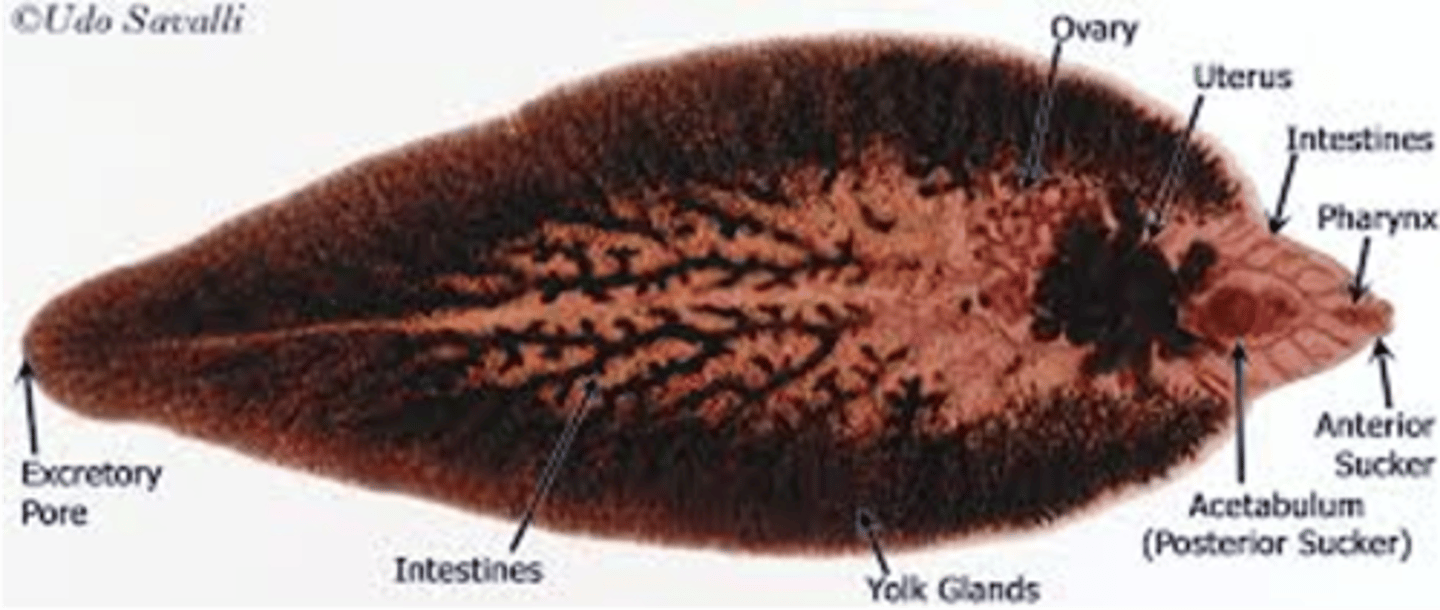
what are the distinguishing characteristics of fasciola hepatica (adult)?
very large, fits in palm of hand
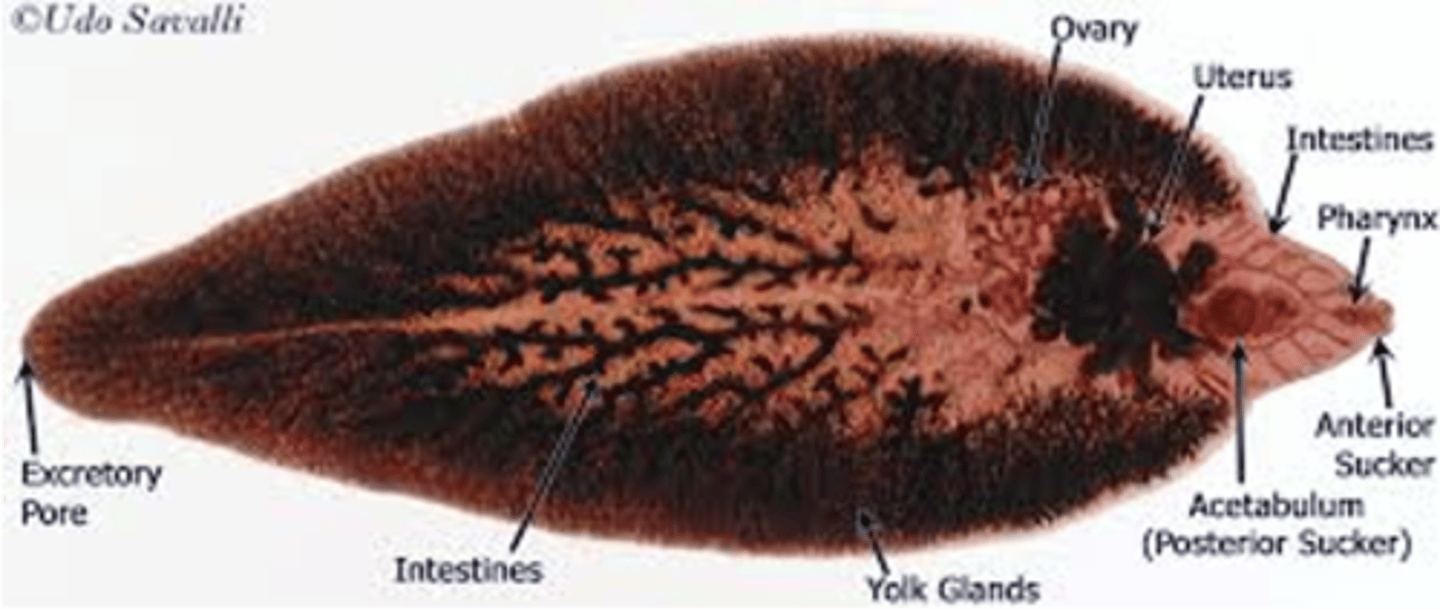

what is the clinical significance of fasciola hepatica?
infects the liver and bile ducts

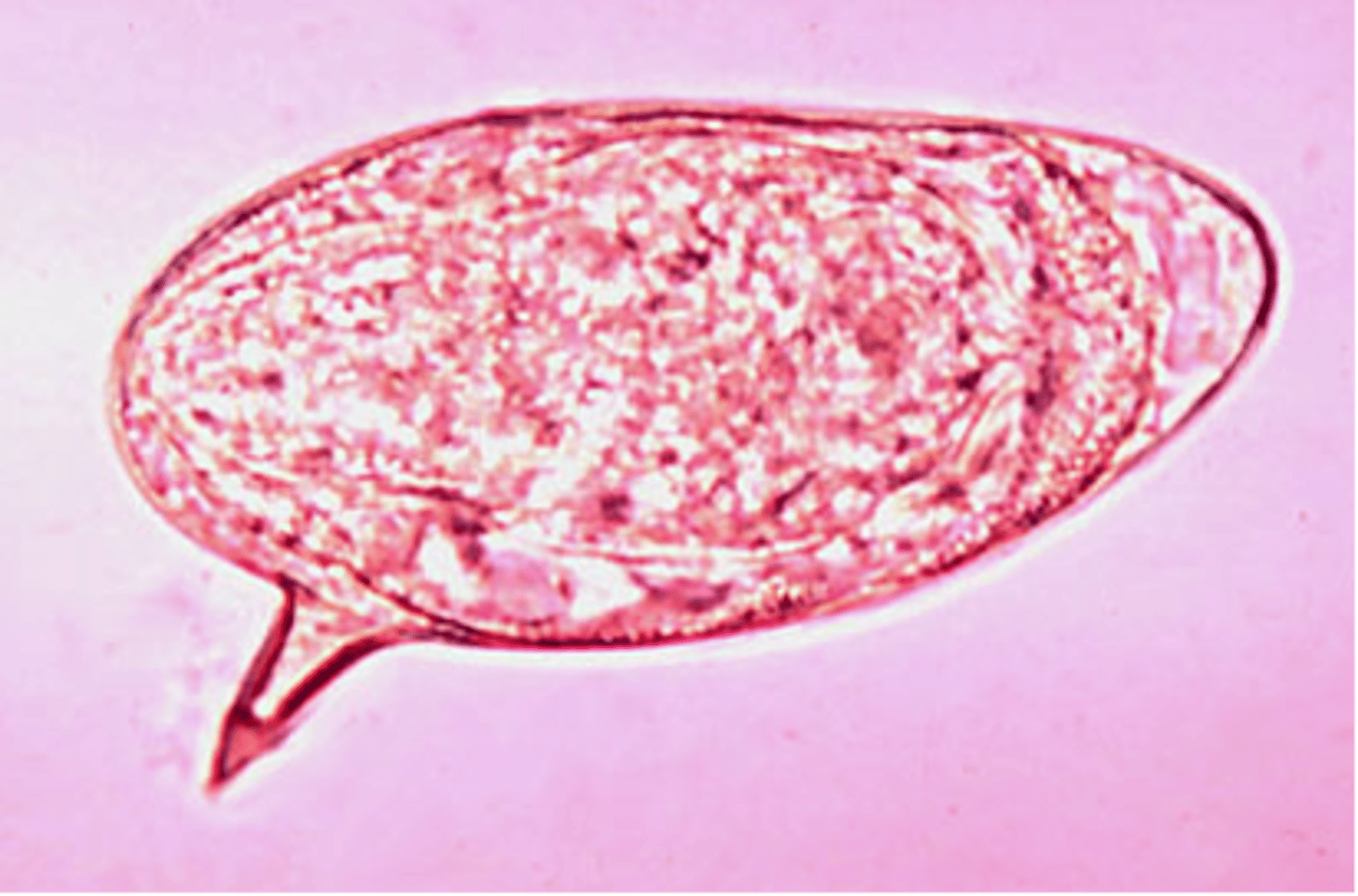
what are the distinguishing characteristics of schistosoma mansoni (OVA)?
ova has spike or fin, looks like speech bubble
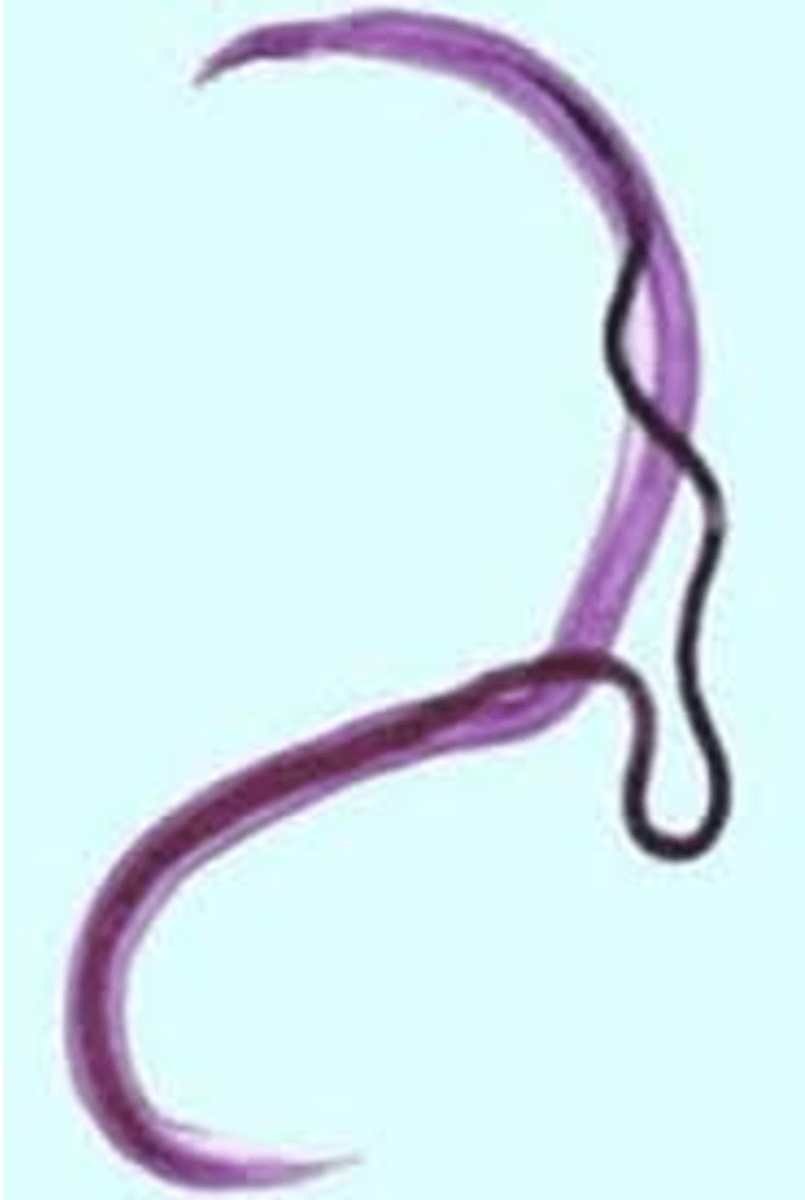
what are the distinguishing characteristics of schistosoma mansoni? (adult)
male is larger than female, female crawls into mate
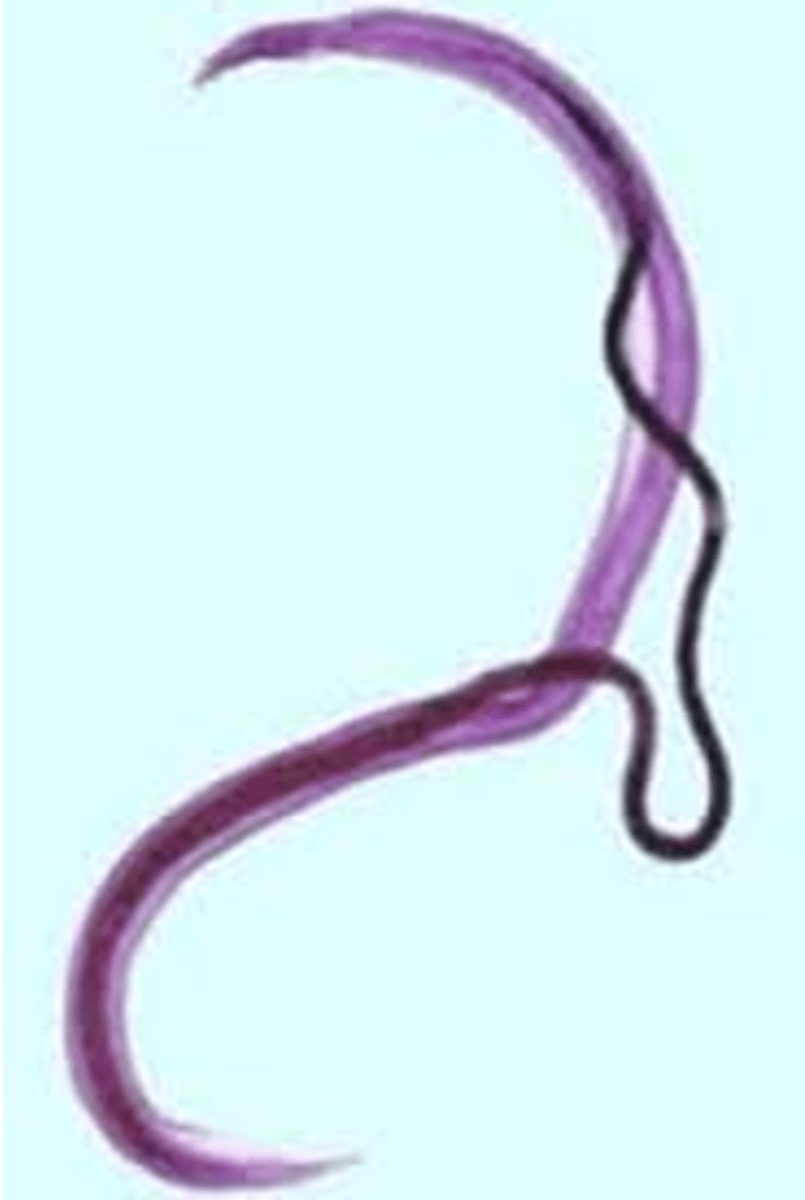
what is the clinical significance of schistosoma mansoni? (adult)
causes blood infections and hepatitis
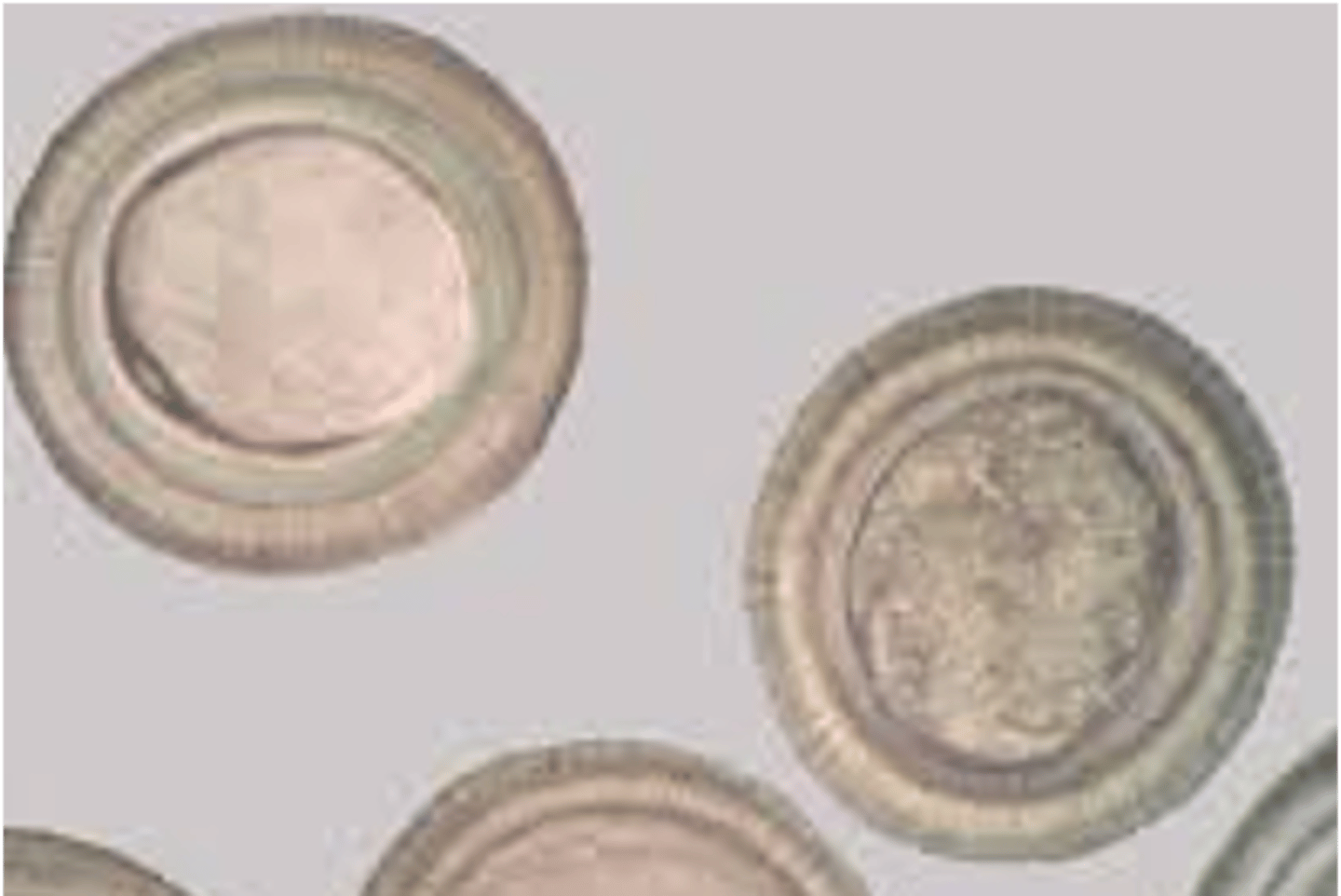
what are the distinguishing characteristics of Taenia saginatta (OVA)?
round, corticated, has segments, non distinguishing
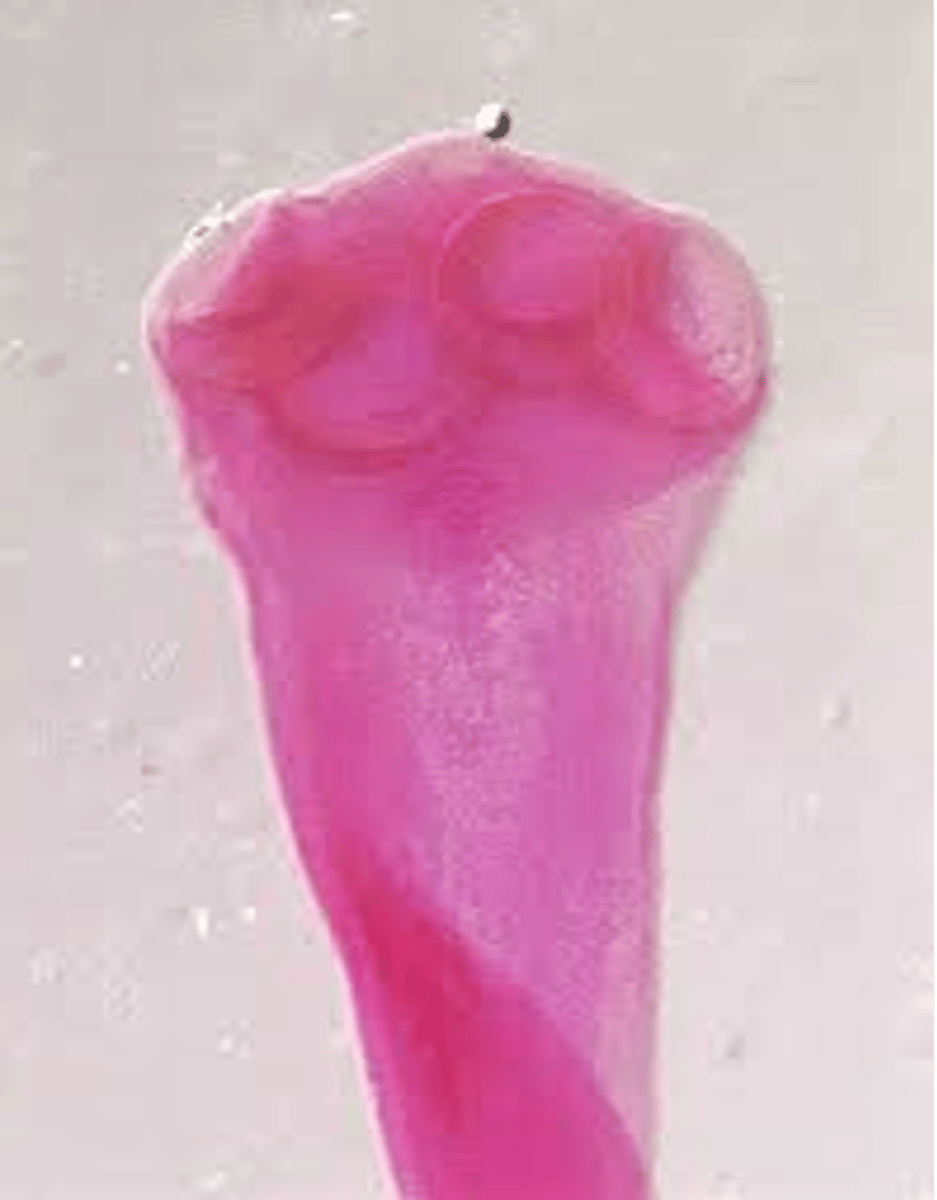
what are the distinguishing characteristics of Taenia saginatta (adult)?
adults are long, scolex only has suckers
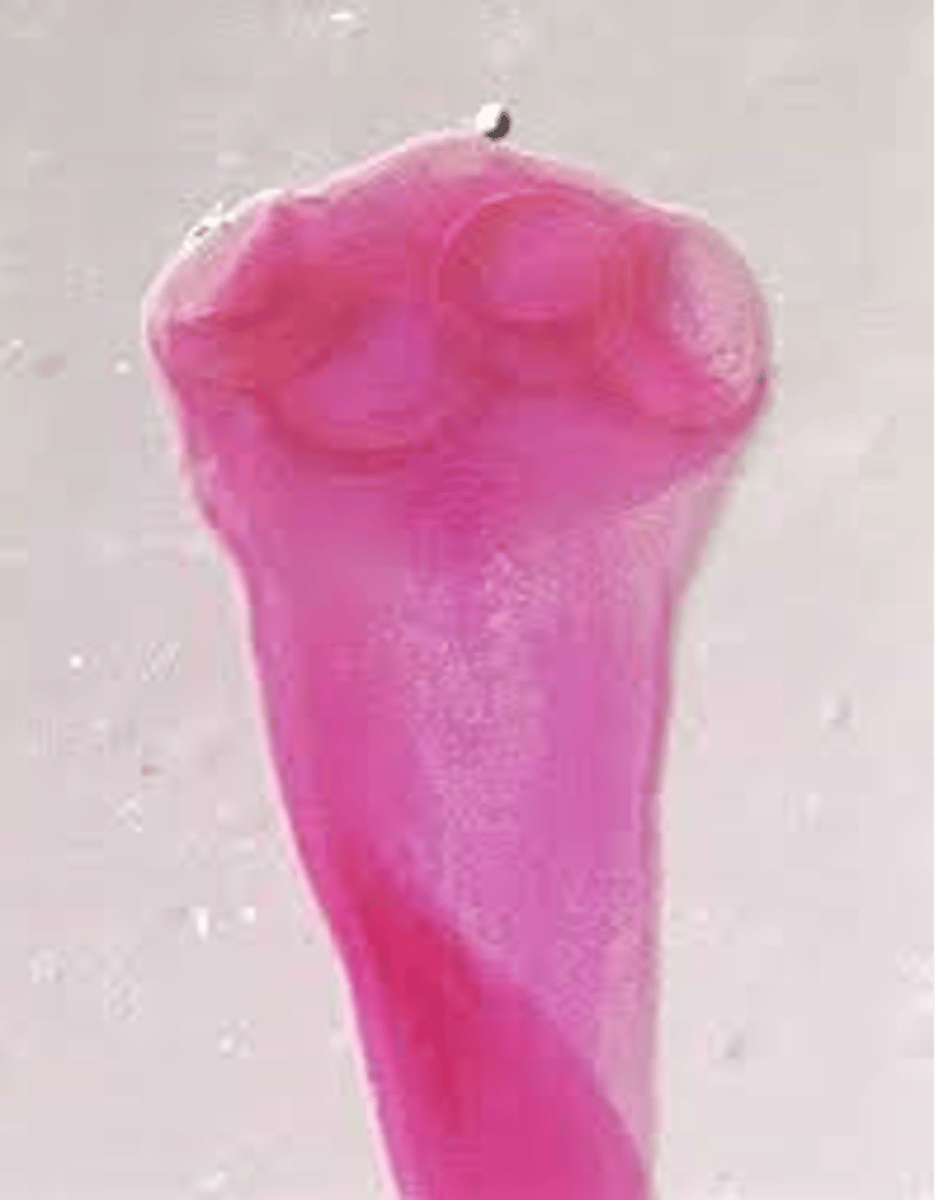
what is the clinical significance of Taenia saginatta (adult)?
attaches in small intestine and takes nutrients, can lead to anemia
what are the distinguishing characteristics of taenia solium (ova)?
round, corticated, has segments, non distinguishing