Microbiology Lab Midterm Moore
1/182
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
183 Terms
Disinfection
involves the destruction of vegetative microorganisms but not endospores, on inanimate surfaces or objects
the disinfectant in class is a
10% sodium hypochlorite solution (bleach)
Sterilization
complete destruction of all living material including endospores
Autoclave
instrument used to sterilize objects which utilizes high temperature and pressure
Dead week
time in which the lab final will be taken
Asepsis
the state of being free from disease-causing contaminants or, preventing contact with microorganisms
What to do in the event of an accident or spill (in order)
a. Notify fellow students so they may leave immediately
b. Cover spill with paper towel and disinfectant for at least 20 minutes
c. Thoroughly clean area with disinfectant to avoid widespread contamination
d. Place used paper towels in disinfectant reservoir and wash hands thoroughly afterwards
Transient flora
colonize the superficial layers of the skin and are more amenable to removal by routine hand washing
Resident flora
Part of an individual's normal flora, more anchored to deeper layers of the skin and are more resistant to removal
Nosocomial Infection
health-care associated (acquired) infections
opportunistic infections
infections that occur in individuals who do not have healthy immune systems
Universal precautions
CDC issued guidelines to reduce the risk of disease transmission
Fastidious organisms
organisms that have complex nutritional requirements
Tryptic Soy Agar (TSA)
Type: a common, nutrient-rich growth medium used for growing and maintaining bacterial cultures
Purpose: Cultivation of non-fastidious bacteria
Mannitol Salt Agar (MSA)
NaCl - 7.5%. Media is selective for salt tolerant bacteria and inhibits the growth of most microorganisms
Mannitol (a fermented alcohol)- when fermented, the pH drops and the pH indicator in the medium causes colonies to turn yellow.
Compare and contrast Semmeweis and Lister
Semmelweis was a Hungarian physician who observed the spread of disease in 1847. During this time, it was common for physicians to go directly from the autopsy room directly to their OB-GYN duty without washing or scrubbing their hands. This practice led to the development of childbed fever. Semmelweis noticed that infant mortality decreased when doctors left the hospital on vacations or extended leaves. Since nurses were not allowed into the autopsy room, women cared for by nurses had a lower mortality rate. Semmelweis hypothesized that "cadaverous particles" were responsible and implemented a policy requiring physicians to wash their hands with chorine of lime prior to patient contact. He was made fun of for his idea and was sent to an asylum after suffering a nervous breakdown. He died in 1865, the same year Lister implemented aseptic practices. Lister eventually received the Order of Merit award for his work.
Which agent used for hand washing is most efficacious for reducing the number of bacteria on hands?
alcohol based gels
List 3 commonly used agents for handwashing
non-antimicrobial soap, 2% chlorhexidine antiseptic soap, and alcohol-based hand gels (containing 60-95% ethanol or isopropanol)
Describe the proper method of hand washing
Wash hands thoroughly for 30 seconds using soap and warm water. Rinse hands thoroughly and dry using a paper towel. Turn off faucet using hand covered with paper towel. Follow with alcohol base gel and rub in until dry.
List the 6 universal precautions
i. Wash hands before and after patient contact. Wash hands after removal of gloves. Change gloves between patients. Do not keep gloves on for an extended period of time
ii. Wear gloves and gowns if there is a high possibility of soiling hands, skin, or clothing with body fluids.
iii. Wear mask and face shield if body fluids are likely to be splashing.
iv. Use disposable mouthpiece/ airway during CPR
v. Discard used needles and other sharp articles into a puncture proof container. Cannot bend, clip or recap needles
vi. Clean spills of blood or body fluids by:
-Putting on gloves or other protective equipment needed
-Wiping with disposable towels
-Washing with soap and water
-Disinfecting with a 1:10 solution of bleach and water allowing to stand for at least 20 minutes
-Do not make bleach solution more than 24 hours beforehand
Why are the CDC universal precautions important?
keeps transmission of pathogenic bacterial organisms to a minimum which protects hospital personnel and patients
One what body fluids does the universal precautions apply?
blood
List two advantages of hand washing over gloves
removing transient flora and less clumsy
List two advantages of gloves over hand washing
provide barrier against a pathogen, protect patient from normal flora
Brightfield microscope
- microscope that allows visible light rays to pass directly through to the eye without being deflected by intervening filters in the condenser
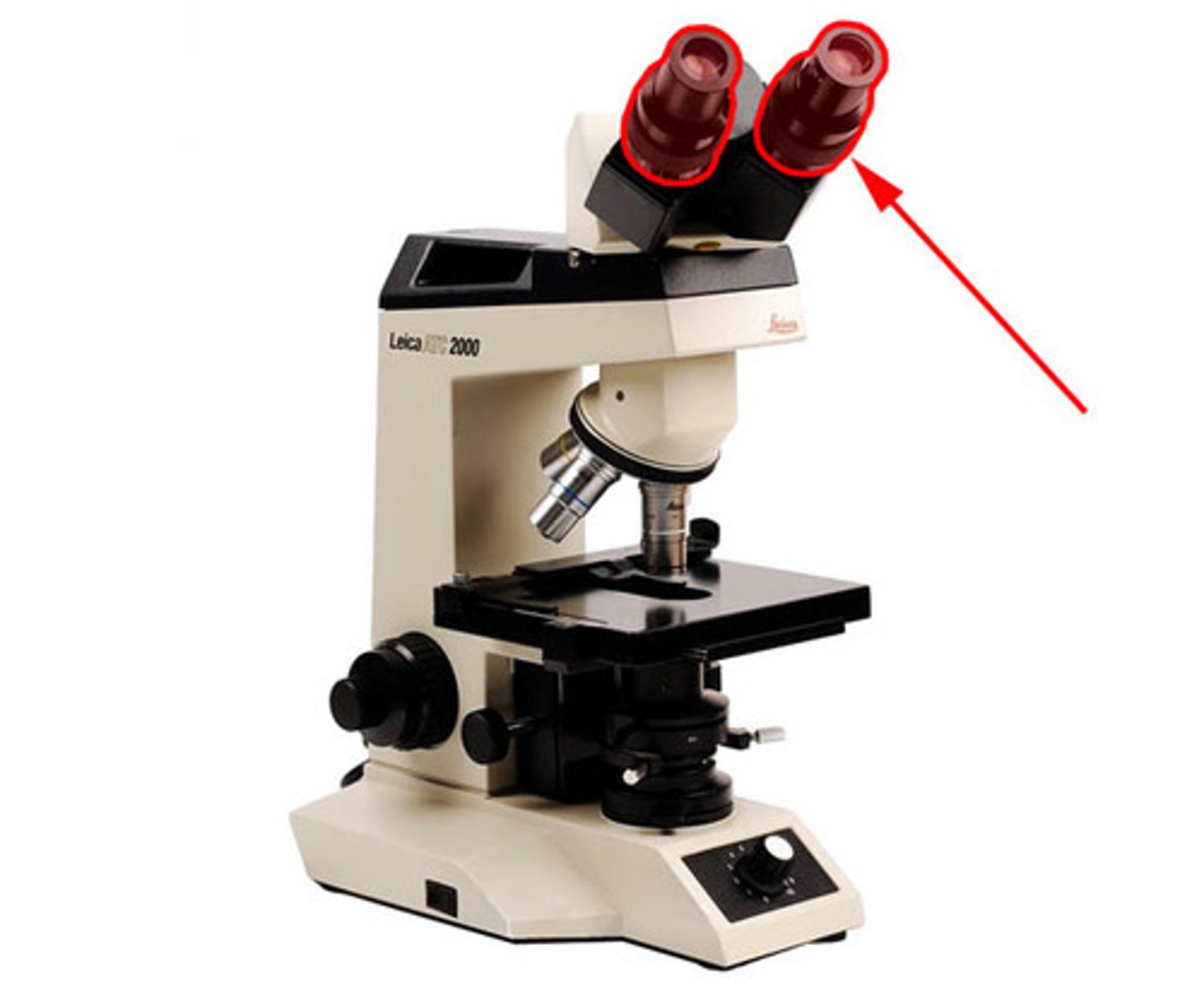
Ocular lens
remagnifies the image formed by the objective lens
Objective lenses
primary lenses that magnify the specimen
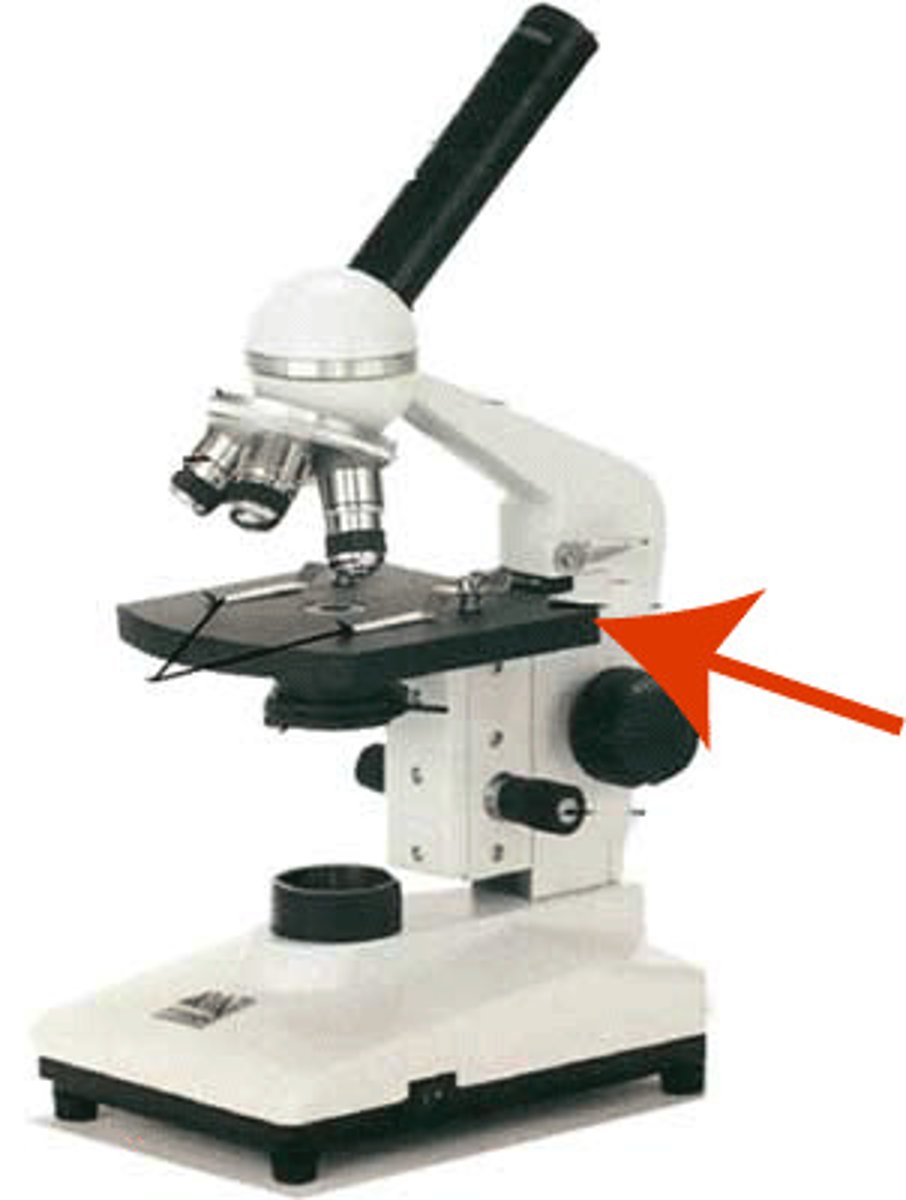
Stage
holds the microscope slide in position
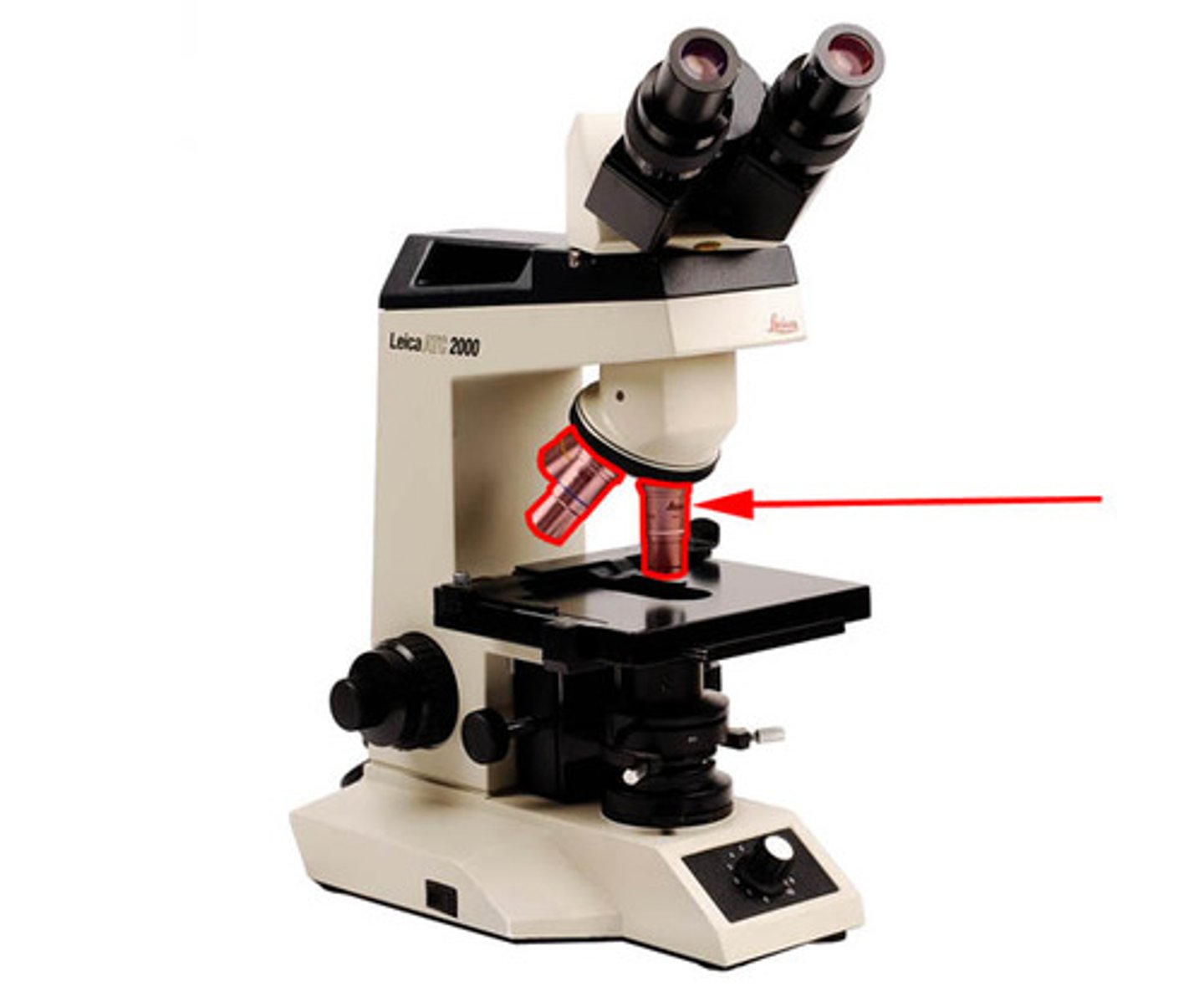
Condenser
focuses the light through the specimen
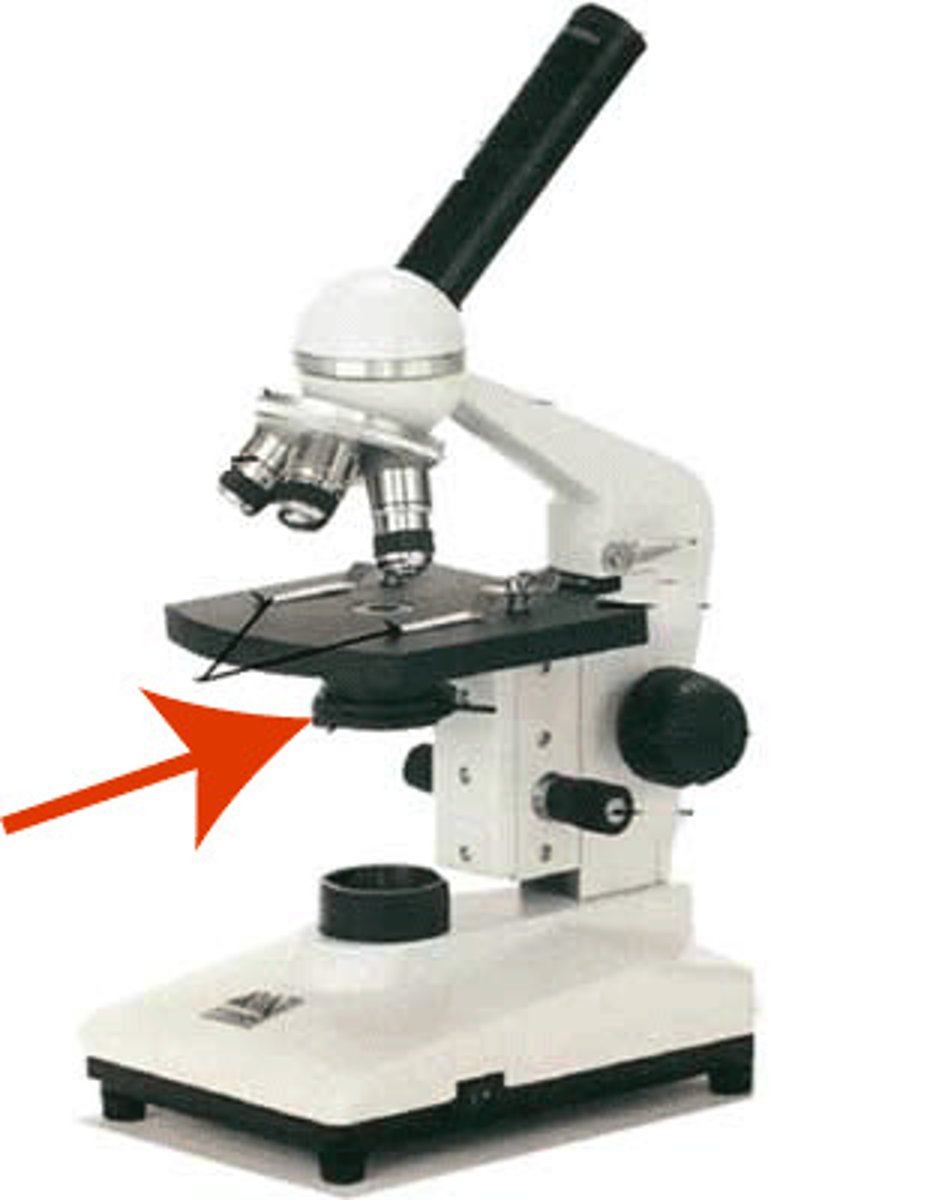
Diaphragm
- controls the amount of light entering the condenser
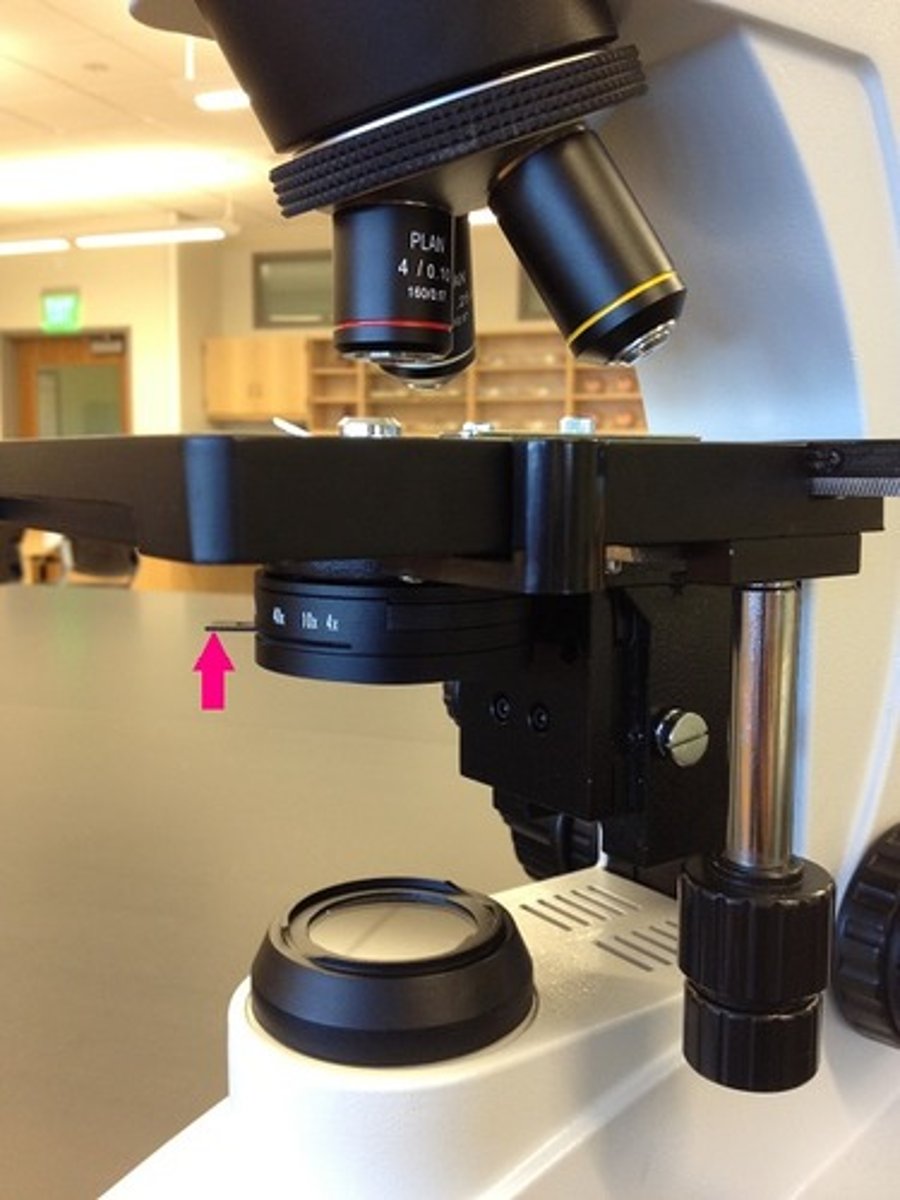

Illuminator
light source
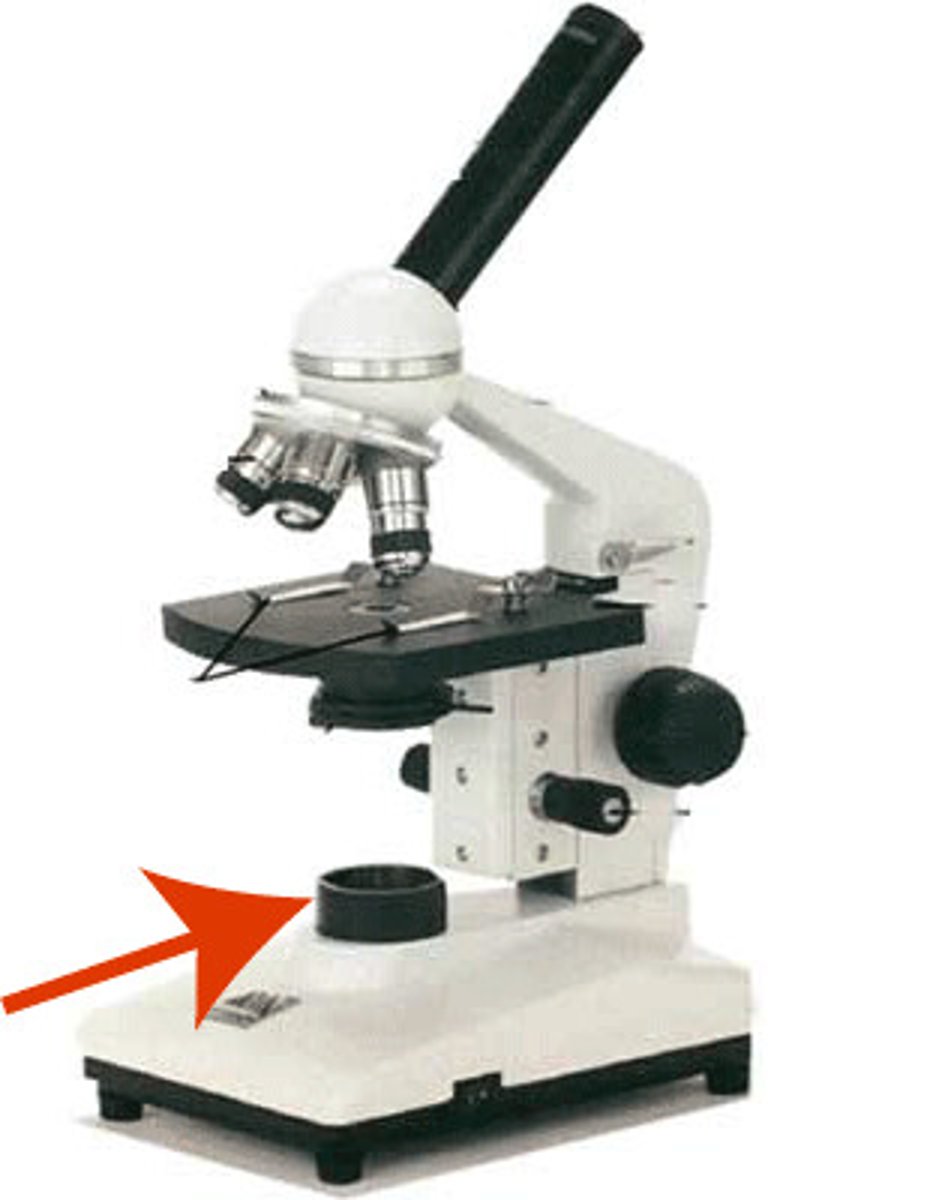

Total magnification
product of ocular magnification and objective magnification
resolving power (resolution)
ability to distinguish between two very small or closely spaced objects
Limit of resolution
minimum distance by which two small ofjects can be separated and still be perceived as separate objects
Numerical aperture
is a mathematical constant the describes the relative efficiency of a lens in bending light rays
Parfocal
lenses are adjusted so that the specimen remains almost in focus after the microscopist rotates the nosepiece to utilize a different objective lens
Wet mount
observation of particulate objects or living organisms in an aqueous solution
Buds
new fungal cells formed from parent cells
Pseudohyphae
short chains formed by the detachment of buds
Dimorphic
fungi that may be yeasts at 37°C but have a mold-like appearance at 25°C
Deuteromycetes
reproduce solely by asexual means
Superficial mycoses
cause infections of the skin and hair (ringworm & athletes foot)
Cutaneous mycoses
involve nails and deeper layers of the skin
Subcutaneous mycoses
involve nails and deeper layers of the skin
Systemic mycoses
cause infections of the subcutaneous and deeper tissues such as the nervous system, lungs and genital area
molds
- multicellular filamentous fungi
Thallus
macroscopic mold colony
Mycelia
a mat of strands that compose the thallus
Hyphae
individual filaments within the mycelia
Vegetative hyphae
hyphae that grow on the surface of the growth medium
Aerial hyphae
rise from the surface of the growth medium
Spores
produced by the aerial hyphae
Reproductive hyphae
aerial hyphae that give rise to spores
Septum
cross walls that separate individual cells in hyphal strands
Septae
hyphae that are composed of individual cells separated by septum
Nonseptate hyphae (coenocytic)
- fungi which lack a cross walls and as such are a contiuous mass of cytoplasm containing multiple nuclei
Potato Dextrose agar
medium that is selective for fungal growth that are simple in composition but have a low pH that inhibit the growth of bacteria
Sabourand agar
medium that is selective for fungal growth that are simple in composition but have a low pH that inhibit the growth of bacteria
Sabourand dextrose agar (Sab-Dex)
- medium that is selective for fungal growth that are simple in composition but have a low pH (4.5-6.5) that inhibit the growth of bacteria
Lacto-phenol cotton blue
stain used to help visualize the hyphal and reproductive structures of molds
Guidelines for how to put away the microscope
a) Both hands should be used to transport microscope with one hand securing the base
b) Review the parts of the microscope and their function
c) Turn the fine adjustment knob no more than one turn forward or backward
d) Never touch the ocular lens or objective lens with anything but lens paper
e) Never use immersion oil with any objective but the oil immersion lense (100X)
f) Never remove a slide while the immersion objective lens in in the light path as this may scratch the lens
g) Never decrease the distance between the slide and the 40x or 100x objective while looking through the eyepiece. Start as close to the object as possible and move slowly away until the object comes into focus
h) Never force any part of the microscope
i) If the slide is put upside down on the stage, the specimen cannot be seen using the 100x objective
Before putting away microscope, always:
j) Lower stage or offset the objective to remove the slide
k) Plays low power objective in the light path
l) Remove all traces of oil from 100x
m) Remove oil from other parts of the microscope center the moveable part of the mechanical stage
n) Grip the microscope with both hands when you return it to the cabinet
o) Place the microscope far enough back in the cabinet to prevent contact with the cabinet door
Microscope parts
Light source
Substage condenser
Iris diaphragm
Objective lens
Ocular lens
Ocular lens setting
Mechanical stage
Coarse adjustment knob
Fine adjustment knob
Light source
may be directly connected to the microscope or separate. If separate, the light must be reflected using a mirror underneath the condenser. Blue filter may be placed over the light source because the short wavelength provides maximum resolution
Substage condenser
collects and directs the light through the slide into the objective lens. Should always be kept just beneath the stage and never used for adjusting light intensity. Must be kept close to the stage when visualizing bacteria
Iris diaphragm
controls the amount of light entering the objectives. Higher magnification requires a higher light intensity than lower power. Closing the diaphragm increases image contrast and decreases resolution
Objective lens
magnifies and resolves the specimen. 4 objectives. 4x, 10x, 40x (high-dry), 100x (oil immersion)
ocular lens (eyepiece)
(10x-20x) to magnify the image formed by the objective. These can be moved to adjust for individual interpupillary distance.
Ocular lens setting
turn slowly or physically separate and align with interpupillary distance
Mechanical stage
holds slide in position
Coarse adjustment knob
quick, approximate focusing. used to bring objects into focus
Fine adjustment knob
slow ultimate focusing of the specimen. DO NOT USE FOR GENERAL FOCUSING.
Limit of resolution equation
Limit of resolution=(Wavelength of light (λ))/(2 x numerical aperture)
Total magnification equation
Total magnification= (ocular magnification)x(objective magnification)
An average wavelength of visible light is 550nm and the high power objective lens on many microscopes have a numerical aperture of 0.65. What is the smallest object that can theoretically be seen?
423 nm
How does the inclusion of a blue light filter change resolution?
The short wavelength blue light provides maximum resolution.
What is Brownian movement?
The random movement of microscopic particles suspended in a liquid or gas, caused by collisions with molecules of the surrounding medium. False movement
Why is immersion oil important for on the oil immersion lens?
the small working distance does not allow enough light to enter the lens. the oil directs more light into the lens by limiting the loss of light
List the three categories of eukaryotic microbes
a) Fungi
b) Parasitic Protozoa
c) Parasitic Helminths
Bergey's Manual of Determinative Bacteriology
- manual published in 1923 that taxonomically classifies and documents bacterial species
The 4 major groups recognized by Bergey's Manual
Gracilicutes, Firmicutes, Tenericutes, and Mendosicutes
Gracilicutes
Thin skinned (gram negative)
Firmicutes
Thick skinned (gram positive)
Tenericutes
Soft skin (no cell wall)
Mendosicutes
archaea, primitive prokaryotes with unusual cell walls and metabolism
Genus
part of the scientific name (along with the species name)
Specific epithet (species)
second half of the scientific name
Strains/types/vars.
differences within a bacterial species
biotypes (biovars)
A biotype is a strain of bacteria distinguished from other strains of the same species by its physiological properties
morphotypes (morphovars)
a strain of bacteria distinguished from other strains of the same species by its morphology (shape)
serotypes (serovars)
Serotype bacteria distinguish different strains of the same species by their surface antigen.
Biosafety level (BSL)
categorization of microbes into classes based on their pathogenicity. Used to determine the precautions necessary to protect the public, and safety equipment needed when handling these organisms
Rules for writing names of organisms
Genus and species name is written and underlined or typed and italicized
BSL Class 1
biological agent that is unlikely to cause human disease
BSL Class 2
biological agent that can cause human disease and might be a hazard to workers; it is unlikely to spread to the community; there is usually effective prophylaxis or treatment available
BSL Class 3
biological agent hat can cause severe human disease and presents a serious hazard to workers; it may present a risk of spreading to the community, but there is usually effective prophylaxis or treatment available
BSL Class 4
biological agent that causes severe human disease and is a serious hazard to workers; it may present a high risk of spreaing to the community and there is usually no effective prophylaxis or treatment available
Class 1 example
Bacillus subtilus
Class 2 example
Staphylococcus aureus
Class 3 example
Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Yersinia pestis